Kingdoms And Domains Chart
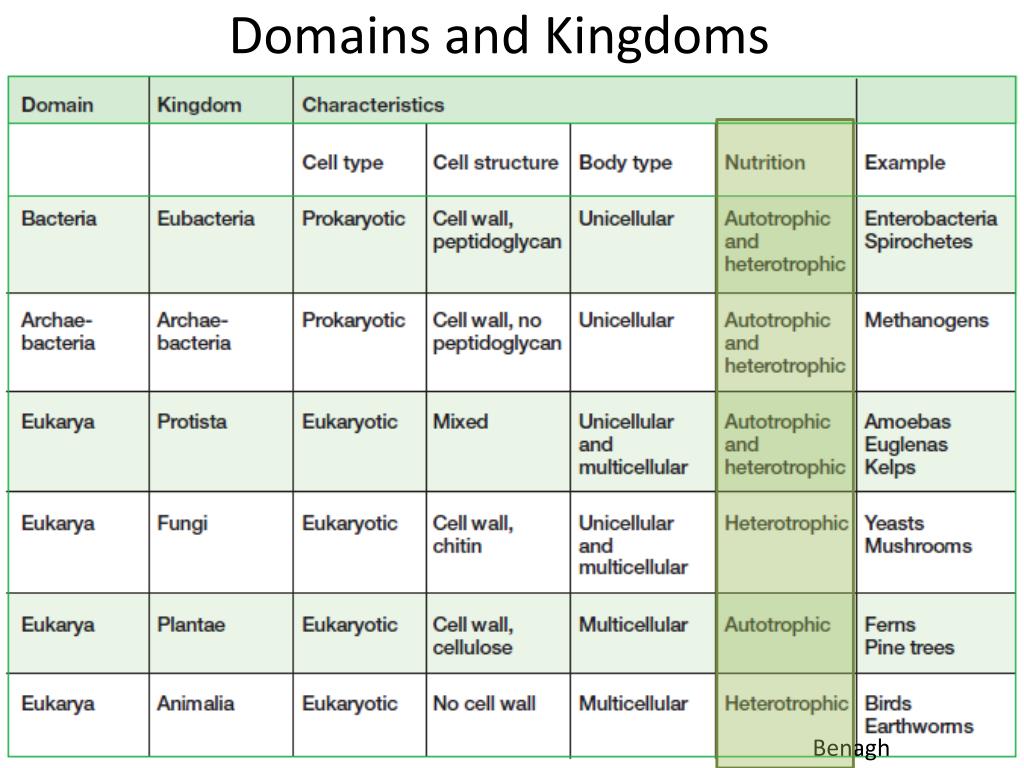
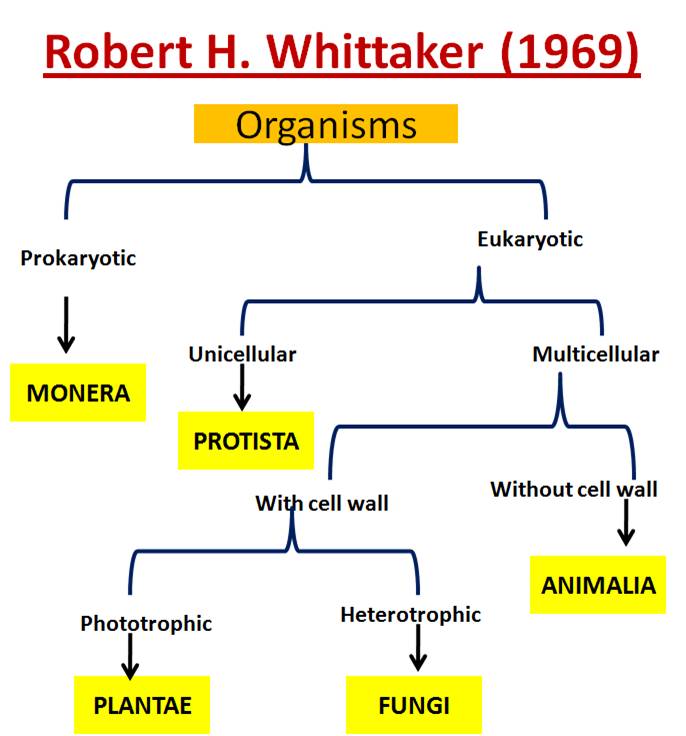
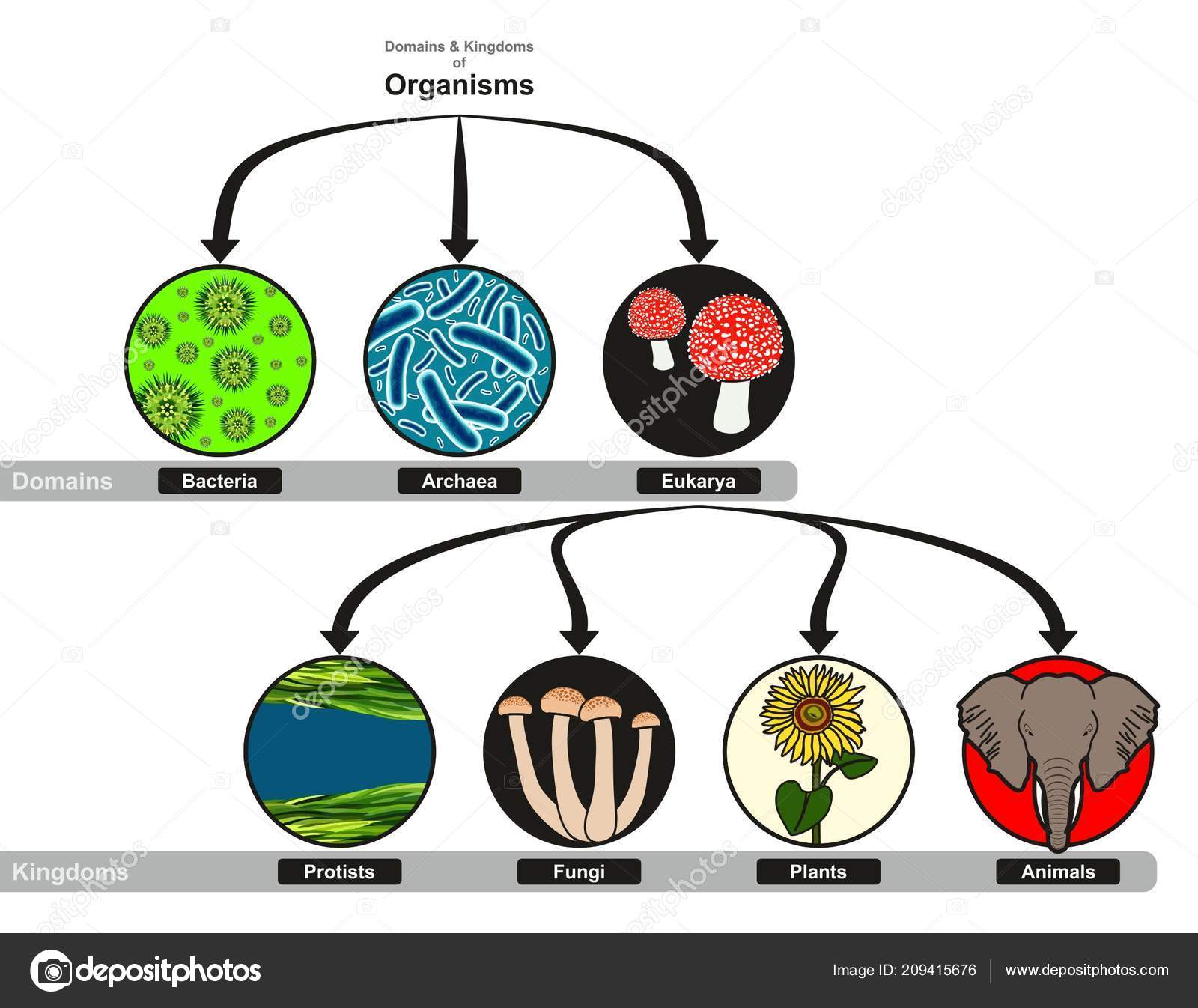
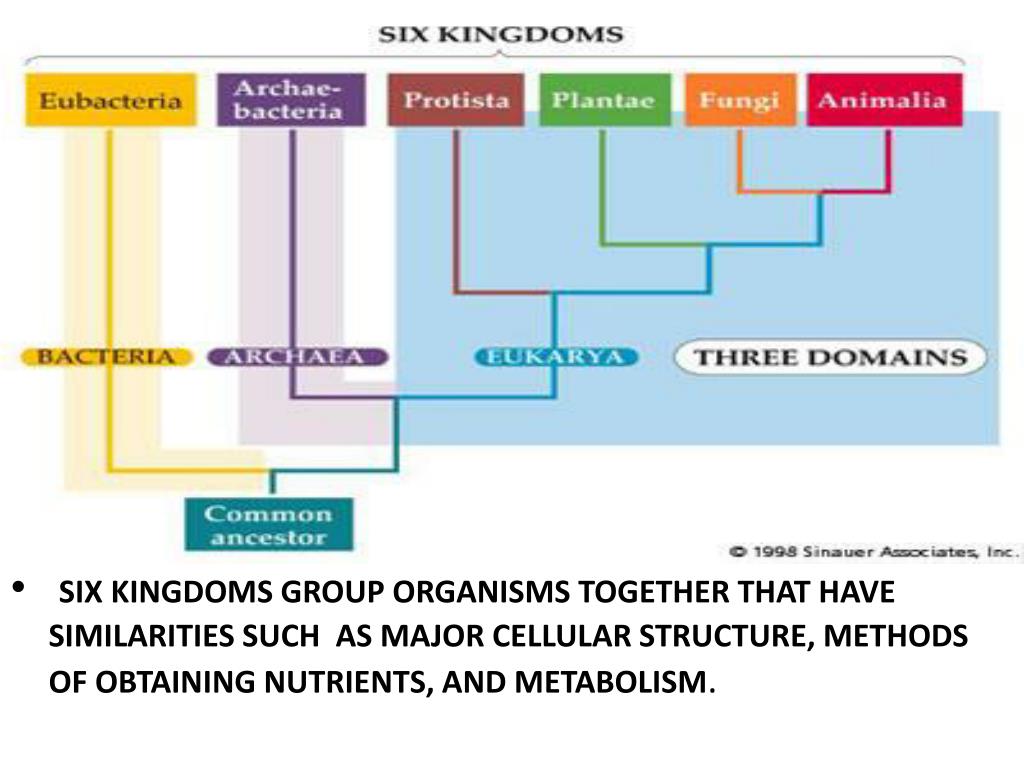
Kingdoms And Domains Chart - Organisms can be classified and placed into domains by their characteristics. Table 1 identifies the scientists who introduced the kingdoms and the dates the kingdoms were introduced. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: It accesses the full range of life forms that still inhabit our planet and logically and explicitly. 3 three domains and six kingdoms. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. 1 classification of living things and naming of organisms. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. Unicellular, cell wall (w/peptidoglycan), prokaryote, autotroph & heterotroph, mobile characteristics of archaeabacteria Web which two domains have only unicellular organisms? Web the three domain system, developed by carl woese in 1990, is a system for classifying biological organisms. 6 classification of living things practice questions. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. 3 three domains and six kingdoms. Before woese's discovery of archaea as distinct from bacteria in 1977, scientists believed there were only two types of life: •prokaryotic (— only a circle of dna) •cell walls contain no peptidoglycan. Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Web the narrative follows zoophytes and other transgressive beings through subsequent philosophical and religious traditions, myths, travellers’ tales, the occult literature, alchemy, scholasticism, the consolidation of vernacular languages, and the rise of scientific botany and zoology. Their existence was not discovered until the 1980s. — how is cell structure used. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: Web cell structure is used to classify organisms into domains and kingdoms. Web the narrative follows zoophytes and other transgressive beings through subsequent philosophical and religious traditions, myths, travellers’ tales, the occult literature, alchemy, scholasticism, the consolidation of vernacular languages,. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. It accesses the full range of life forms that still inhabit our planet and logically and explicitly. Web the three domain system, developed by carl woese in 1990, is a system for classifying biological organisms. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Web cell structure. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. •live in most extreme environments possible: Web the three domains of life (archaea, eubacteria and eukarya) quickly supplanted the older division of living things into five kingdoms, the monera (prokaryotes),. Web generously illustrated, now in full color, kingdoms and domains is remarkably easy to read. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: In a final surprise, the sequences of archaebacterial genes clearly indicate a common ancestry of archaea and eukarya.. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Before woese's discovery of archaea as distinct from bacteria in 1977, scientists believed there were only two types of life: — how is cell structure used to classify organisms into taxonomic groups? Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Organisms can be classified and placed into. Web identify the six kingdoms of life. •cell division by binary fission. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. Web generously illustrated, now in full color, kingdoms and domains is remarkably easy to read. Organisms can be classified and placed into domains by their characteristics. Volcanic hot springs, brine pools, black organic mud… •many can survive only in the absence of oxygen. Web in biological taxonomy, a domain (/ d ə ˈ m eɪ n / or / d oʊ ˈ m eɪ n /) (latin: 3 three domains and six kingdoms. However, archaebacteria. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). — how is cell structure used to classify organisms into taxonomic groups? Web a domain contains one or more kingdoms. Table 1 identifies the scientists who introduced the kingdoms and the dates the kingdoms were introduced. Regio), also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. •live in most extreme environments possible: Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: 6 classification of living things practice questions. 3 three domains and six kingdoms. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. •cell division by binary fission. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Volcanic hot springs, brine pools, black organic mud… •many can survive only in the absence of oxygen. 5 phylogeny, cladistics, and cladograms. However, archaebacteria are the oldest known living organisms.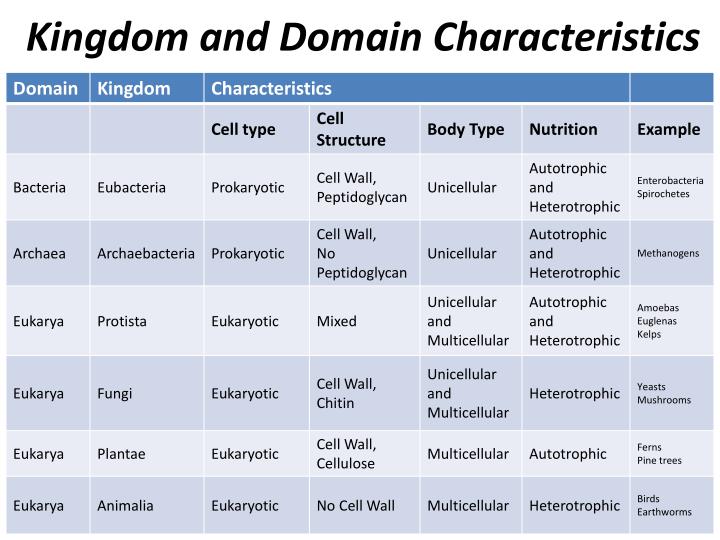
PPT Kingdoms and Domains PowerPoint Presentation ID5353746
PPT Kingdoms, Classification, and Plants PowerPoint Presentation

What are the 3 domains of life and their characteristics? Three Domain
a. Biological classification BIOLOGY4ISC
Domain Kingdoms Organisms Classification Chart Infographic Diagram
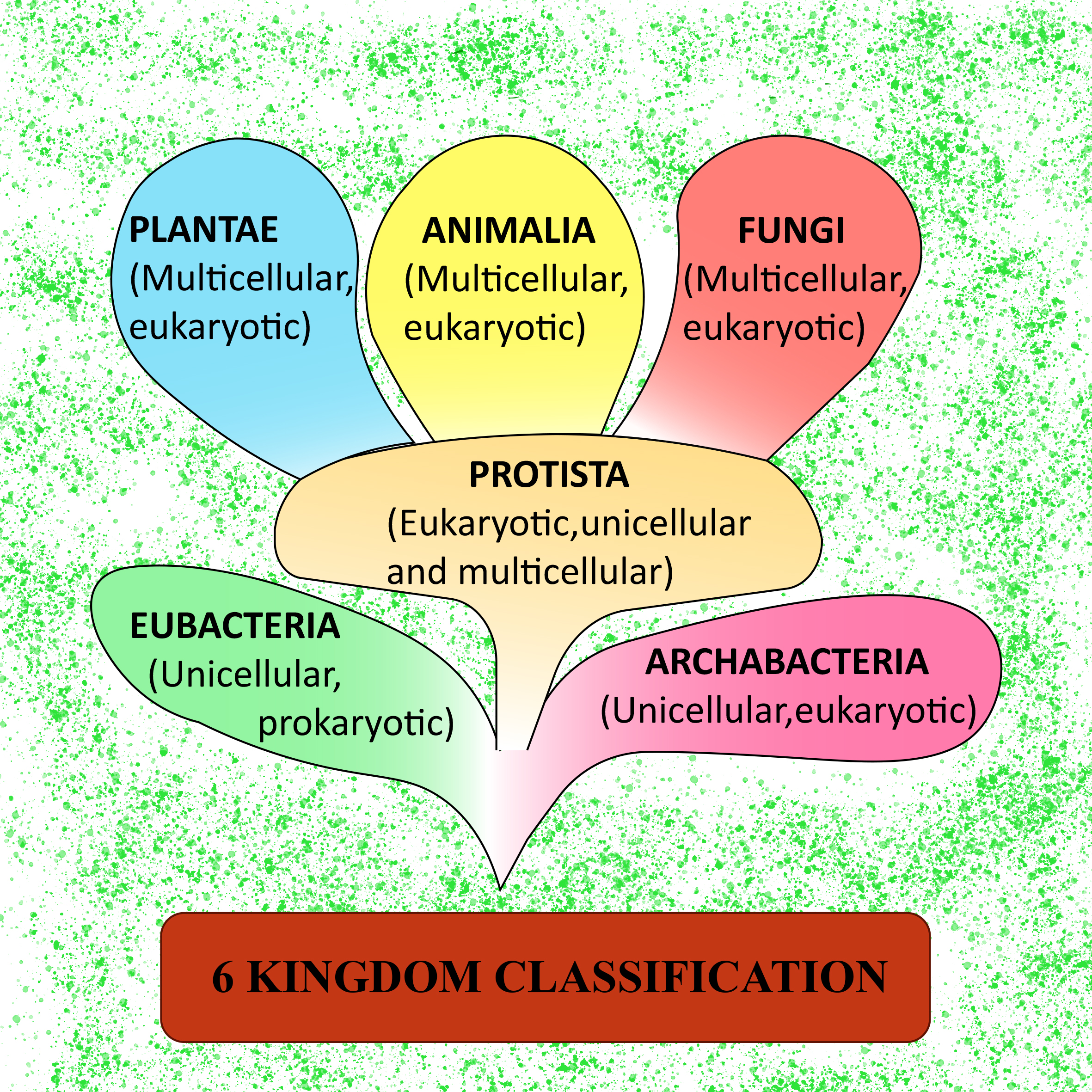
6 Kingdoms Chart
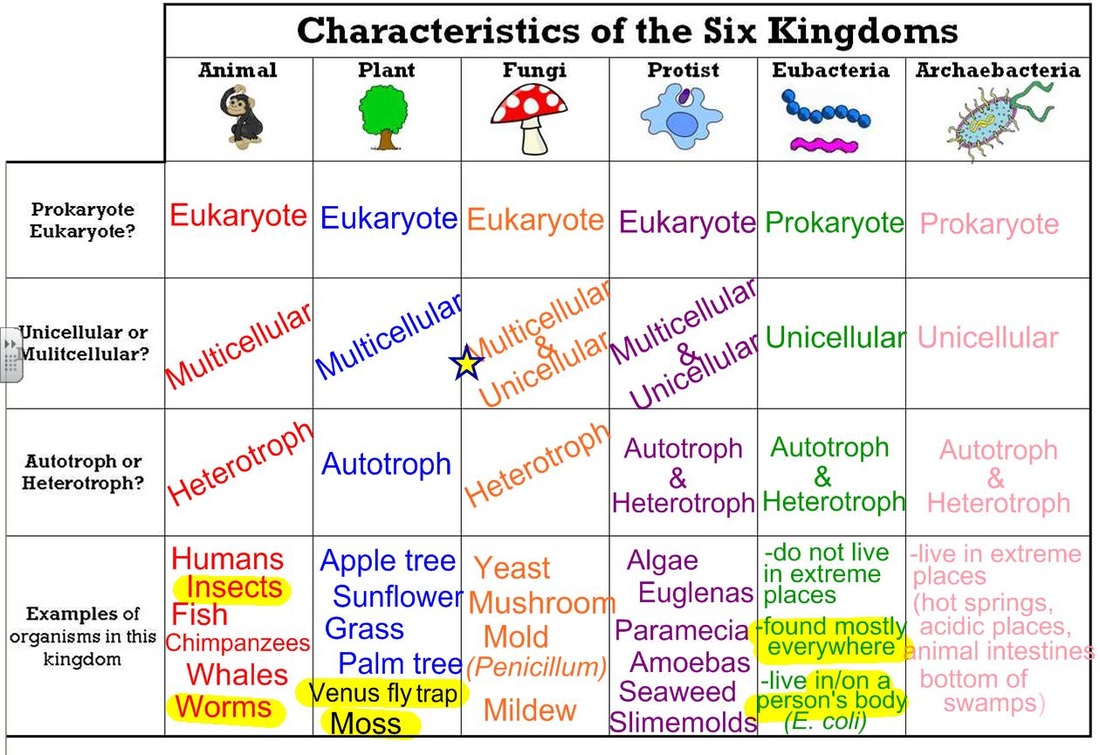
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
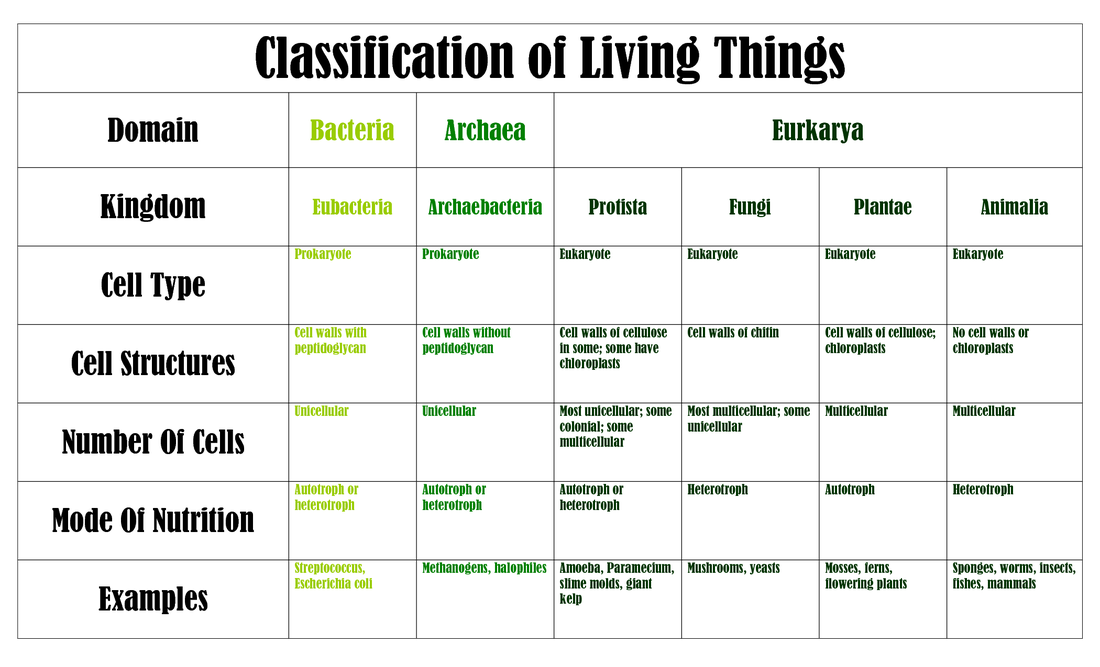
Classification of Living Things michelleburden
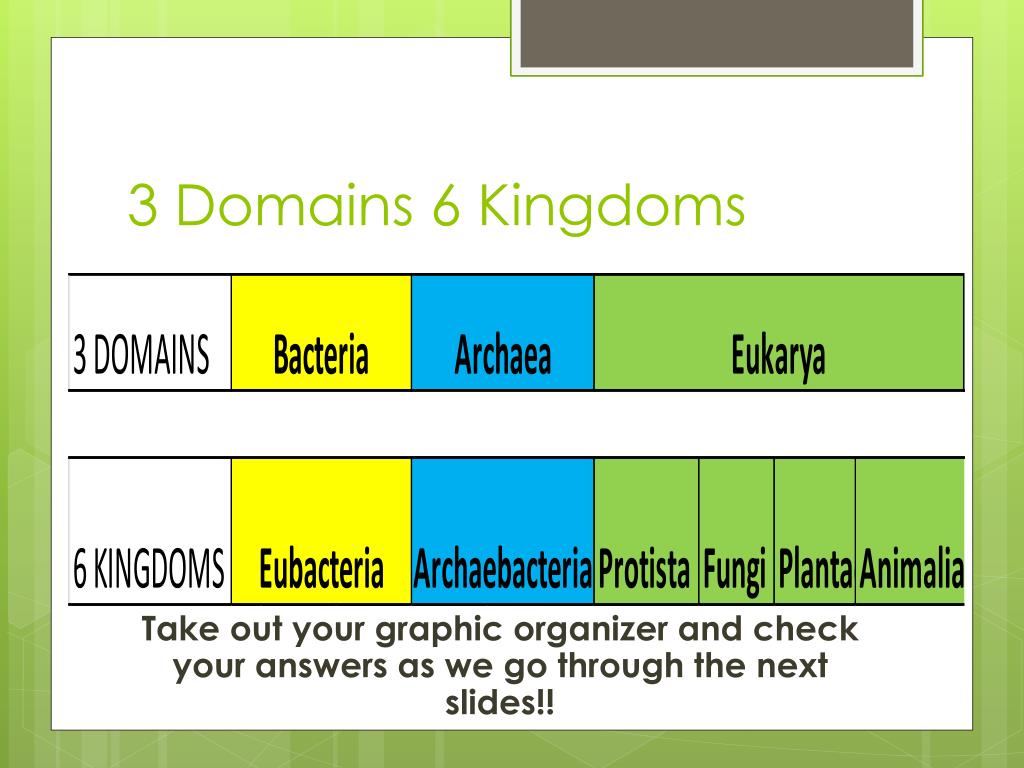
PPT Domains and Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT Classification Chapter 17 Taxonomy 6 Kingdoms Dissection notes
Describe Characteristics Of The Kingdom Fungi.
Web The Narrative Follows Zoophytes And Other Transgressive Beings Through Subsequent Philosophical And Religious Traditions, Myths, Travellers’ Tales, The Occult Literature, Alchemy, Scholasticism, The Consolidation Of Vernacular Languages, And The Rise Of Scientific Botany And Zoology.
Web In Biological Taxonomy, A Domain (/ D Ə ˈ M Eɪ N / Or / D Oʊ ˈ M Eɪ N /) (Latin:
Kingdom, Phylum Or Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, And Species.
Related Post: