Cattle Teeth Age Chart
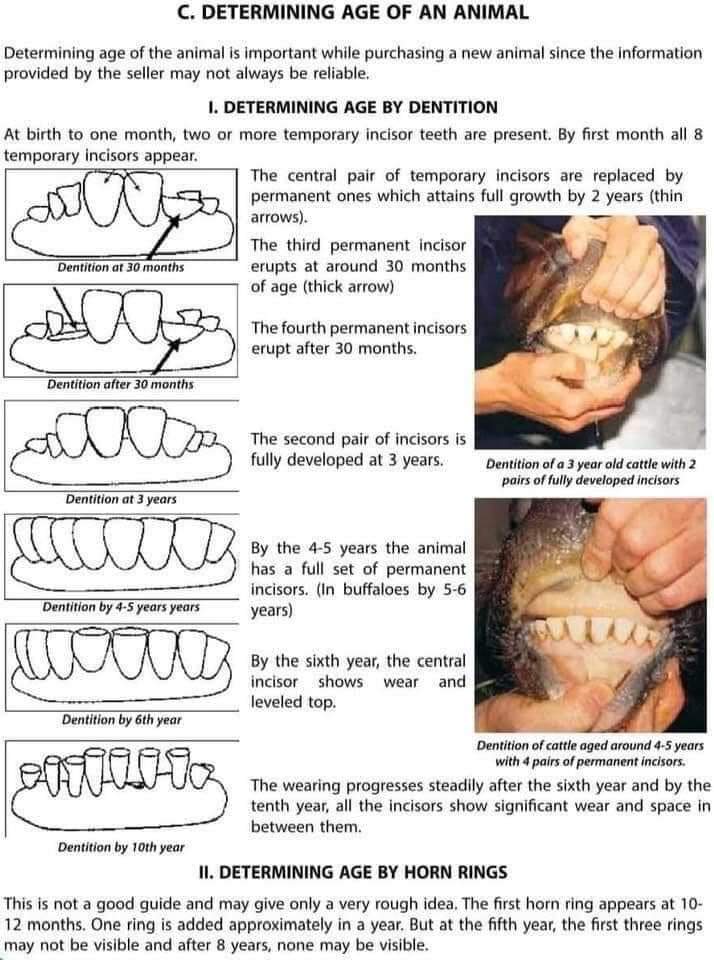
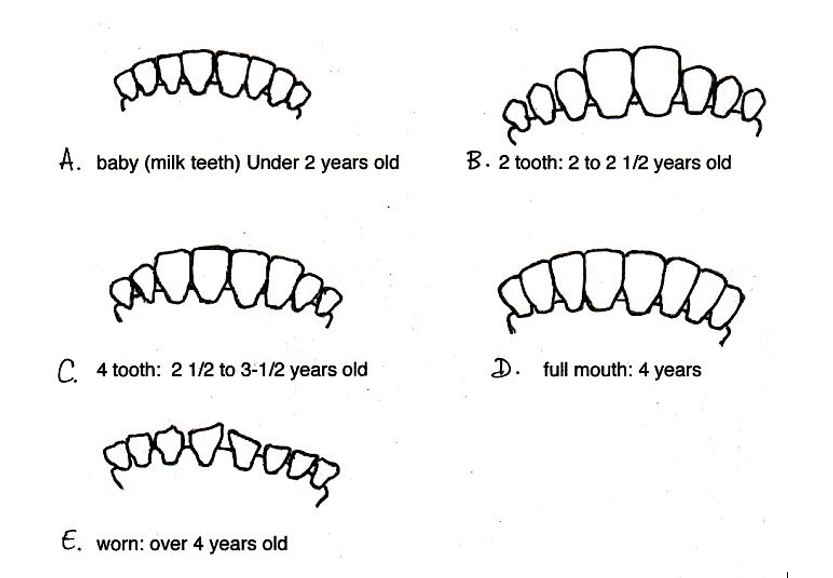
Cattle Teeth Age Chart - Beef cattle depend on forages as their major source of nutrients. It is very difficult to determine age of cattle by examination of teeth when they are more than eight years old. In the last phase of the site, half of. The front of the upper jaw is a hard dental pad without teeth. In general, a heifer younger than 18 months will only have her temporary milk or “baby” teeth. The age of a cow is not always important provided she is physically sound and productive. Web under rough feed conditions, accuracy of aging cattle is reduced, particularly in animals over five years of age where tooth wear is the only indicator. Web rather than the number of permanent incisors that have erupted, tooth wear and degree of separation between teeth is the indicator of age in older cows. Sheep have no teeth in the front part of the upper jaw which consists of a dense, hard, fibrous pad. The incisors appear toward the front of the mouth and only on the bottom jaw of cattle. Web what happens to teeth in cattle varies between breeds, individual animals, properties and seasons. In general, a heifer younger than 18 months will only have her temporary milk or “baby” teeth. Did you know that cattle don’t get all their permanent teeth until they’re 5 years old? Web cattle were butchered at different ages throughout the site's history, which. Cattle first develop 20 temporary teeth, known also as deciduous, milk, or baby teeth ( figure 3 ). Copyrighted graphics used by permission from anatomy of domestic animals, sudz publishing (email:[email protected]) Web under rough feed conditions, accuracy of aging cattle is reduced, particularly in animals over five years of age where tooth wear is the only indicator. Web the center. Web a guide to ageing cattle by their teeth, including a table of average age and the range of ages that teeth erupt for different breeds, photos and diagrams. And, if you are prepared to give her your. Did you know that cattle don’t get all their permanent teeth until they’re 5 years old? In this diagram, all the incisors. Web the center pair show wear at five, second pair at six, third pair at seven and the corners at eight years of age. In this diagram, all the incisors are permanent teeth. Web this document will discuss and demonstrate: Sheep have no teeth in the front part of the upper jaw which consists of a dense, hard, fibrous pad.. This article will offer an introduction to the basics of how age is estimated in cattle two years of age and older. The incisors appear toward the front of the mouth and only on the bottom jaw of cattle. Adjusting the accompanying chart to match feed conditions is essential to accurately determine the age of cattle. In this diagram, all. Types of teeth and their location in bovine jaws, deciduous incisors versus permanent incisors, eruption times for deciduous and permanent teeth and using eruption times of permanent incisors to age cattle. Further reference data were obtained from study of the literature (42 data points) (jones and. Web determining the age of cows up to 5 years of age is simple. The front of the upper jaw is a hard dental pad without teeth. Locations and types of teeth in a bovine skull. Web this is a diagram of the incisors associated with the lower jaw. Sheep have no teeth in the front part of the upper jaw which consists of a dense, hard, fibrous pad. Web a guide to ageing. Web he meantime, the teeth gradually become riangular in shape, distinctly separated, and how progressive wearing to stubs. The incisors appear toward the front of the mouth and only on the bottom jaw of cattle. Web the center pair show wear at five, second pair at six, third pair at seven and the corners at eight years of age. In. In general, a heifer younger than 18 months will only have her temporary milk or “baby” teeth. It is very difficult to determine age of cattle by examination of teeth when they are more than eight years old. Web what happens to teeth in cattle varies between breeds, individual animals, properties and seasons. Web rather than the number of permanent. Sheep have no teeth in the front part of the upper jaw which consists of a dense, hard, fibrous pad. Web per the letter, “most (> 95 percent) u.s. The premolars appear adjacent to the incisors on the sides and further towards the rear of the mouth. Web this document will discuss and demonstrate: Adjusting the accompanying chart to match. Evidence of wear becomes more distinct and the teeth obtain a triangular shape with continued wear. Web what happens to teeth in cattle varies between breeds, individual animals, properties and seasons. The stockman's handbook by ensminger, 2nd ed. In this diagram, all the incisors are permanent teeth. It is very difficult to determine age of cattle by examination of teeth when they are more than eight years old. Web this is a diagram of the incisors associated with the lower jaw. Adjusting the accompanying chart to match feed conditions is essential to accurately determine the age of cattle. The animal has two permanent incisors at 2 years of age, four at 3 years of age, six at 4 years of age and a full. Web the age of cattle is determined chiefly by examination of the teeth, and less perfectly by the horn rings or the length of the tail brush; Sheep have no teeth in the front part of the upper jaw which consists of a dense, hard, fibrous pad. Web rather than the number of permanent incisors that have erupted, tooth wear and degree of separation between teeth is the indicator of age in older cows. Types of teeth and their location in bovine jaws, deciduous incisors versus permanent incisors, eruption times for deciduous and permanent teeth and using eruption times of permanent incisors to age cattle. This article will offer an introduction to the basics of how age is estimated in cattle two years of age and older. These conditions become more marked with increasing age source: The incisors appear toward the front of the mouth and only on the bottom jaw of cattle. Web estimating cattle age by their teeth involves noting how many incisor teeth there are, what type of teeth they are (baby or milk teeth, or permanent teeth), their degree of wear, and overall appearance.
Cattle Teeth Aging Chart
Cow Teeth Diagram

The parameter estimates from Model 5 Download Table
Teeth Examination Enables Age Determination in Cows

Revised edition. "This publication shows how to determine, by the size

Amass Farming Tips & Info Age determination cattle, sheep and goats

Estimating Cattle Age by Dentition YouTube
Determining the Age of Cattle by the Teeth UNT Digital Library

Farmer's Creek TEETH VS AGE
Determining the Age of Cattle by the Teeth Page 1 UNT Digital Library
The Lower Front Teeth, Known As Incisors, Come In Over A Period Of Years, 2 Pair At A Time, Starting With The Two Center Teeth.
Locations And Types Of Teeth In A Bovine Skull.
This Means That You Can Tell The Age Of Your Animals By How Many Of The Front Incisors They Have.
Cattle First Develop 20 Temporary Teeth, Known Also As Deciduous, Milk, Or Baby Teeth ( Figure 3 ).
Related Post: