X Bar And R Chart
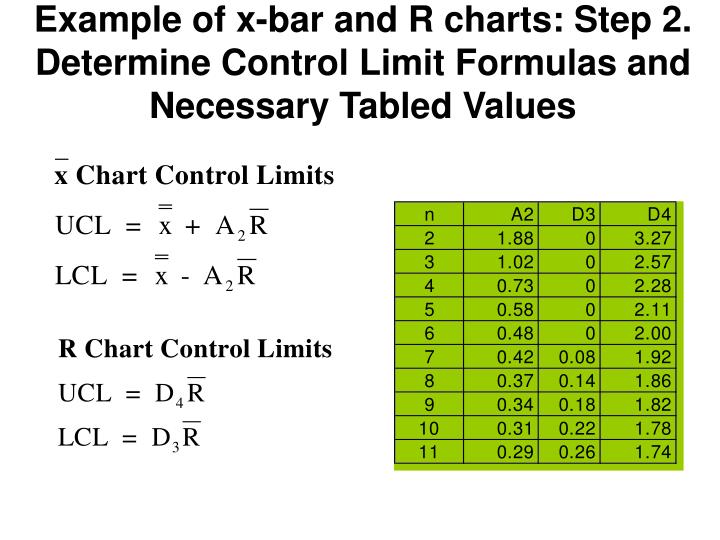
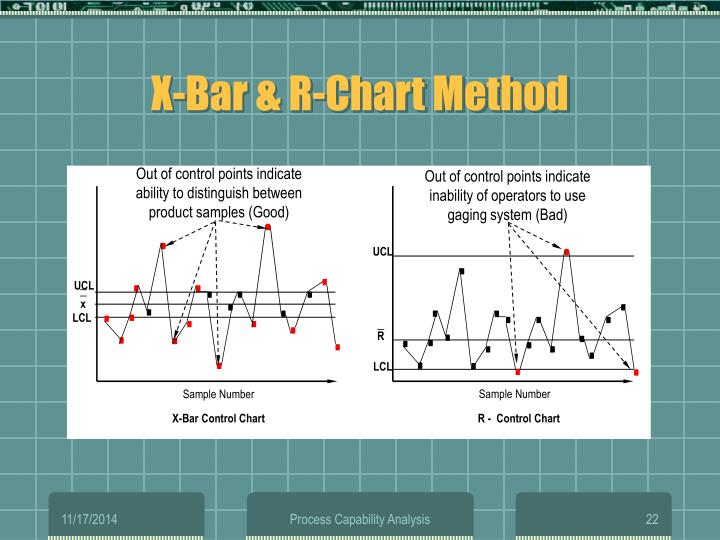
X Bar And R Chart - Web the ¯ and r chart plots the mean value for the quality characteristic across all units in the sample, ¯, plus the range of the quality characteristic across all units in the sample as follows: Are they complementing each other like peanut butter and jelly, or are they contrasting like night and day? Web xbar r charts are often used collectively to plot the process mean (xbar) and process range (r) over time for continuous data. Process that is in statistical control is predictable, and characterized by points that fall between the lower and upper control limits. Control charts typically contain the following elements: Web an xbar chart is a graphical representation of the average value of a data set over a period of time. But is there a difference between them? Web if the r chart validates that the process variation is in statistical control, the xbar chart is constructed. Like most other variables control charts, it is actually two charts. Examine the r chart to determine whether the process variation is in control. Web mordukhovich’s generalized differentiation theory lies at the heart of modern variational analysis, which has been a very active and fruitful field of mathematics in the past few decades; Web the simplest way to describe the limits is to define the factor a 2 = 3 / ( d 2 n) and the construction of the x ¯ becomes u. We refer the readers to [8,9,10, 21] and references therein for extensive expositions of the theory and its applications.as variants/generalizations of lipschitzian. Web an xbar chart is a graphical representation of the average value of a data set over a period of time. Key output includes the xbar chart, r chart, and test results. Like most other variables control charts,. Process that is in statistical control is predictable, and characterized by points that fall between the lower and upper control limits. Web the ¯ and r chart plots the mean value for the quality characteristic across all units in the sample, ¯, plus the range of the quality characteristic across all units in the sample as follows: Examine the r. Web the simplest way to describe the limits is to define the factor a 2 = 3 / ( d 2 n) and the construction of the x ¯ becomes u c l = x ¯ ¯ + a 2 r ¯ center line = x ¯ ¯ l c l = x ¯ ¯ − a 2 r ¯.. Open the sample data, camshaftlength.mtw. Web mordukhovich’s generalized differentiation theory lies at the heart of modern variational analysis, which has been a very active and fruitful field of mathematics in the past few decades; Please let me know if you find it helpful! Examine the r chart to determine whether the process variation is in control. Typically n is between. Key output includes the xbar chart, r chart, and test results. Web the ¯ and r chart plots the mean value for the quality characteristic across all units in the sample, ¯, plus the range of the quality characteristic across all units in the sample as follows: Web if the r chart validates that the process variation is in statistical. The factor a 2 depends only on n , and is tabled below. Control charts typically contain the following elements: Open the sample data, camshaftlength.mtw. Data points representing process outcomes. They provide continuous data to determine how well a process functions and stays within acceptable levels of variation. Web the simplest way to describe the limits is to define the factor a 2 = 3 / ( d 2 n) and the construction of the x ¯ becomes u c l = x ¯ ¯ + a 2 r ¯ center line = x ¯ ¯ l c l = x ¯ ¯ − a 2 r ¯.. Data points representing process outcomes. Control charts typically contain the following elements: Use this control chart to monitor process stability over time so that you can identify and correct instabilities in a process. But is there a difference between them? Are they complementing each other like peanut butter and jelly, or are they contrasting like night and day? Control charts typically contain the following elements: An r chart is a type of statistical chart. The factor a 2 depends only on n , and is tabled below. Like most other variables control charts, it is actually two charts. Examine the xbar chart to determine whether the process mean is in control. Steps in constructing an r chart. We refer the readers to [8,9,10, 21] and references therein for extensive expositions of the theory and its applications.as variants/generalizations of lipschitzian. Please let me know if you find it helpful! Are they complementing each other like peanut butter and jelly, or are they contrasting like night and day? Like most other variables control charts, it is actually two charts. Control limits depict the range of normal process variability. The other chart is for subgroup ranges (r). Use this control chart to monitor process stability over time so that you can identify and correct instabilities in a process. One chart is for subgroup averages ( x ). They provide continuous data to determine how well a process functions and stays within acceptable levels of variation. The range (r) chart shows the variation within each variable (called subgroups). The factor a 2 depends only on n , and is tabled below. Process that is in statistical control is predictable, and characterized by points that fall between the lower and upper control limits. An r chart is a type of statistical chart. Web the control chart basics, including the 2 types of variation and how we distinguish between common and special cause variation, along with how to create a ra. Web mordukhovich’s generalized differentiation theory lies at the heart of modern variational analysis, which has been a very active and fruitful field of mathematics in the past few decades;
Xbar and R Chart Formula and Constants The Definitive Guide

When to use an Xbar R Chart versus Xbar S Chart
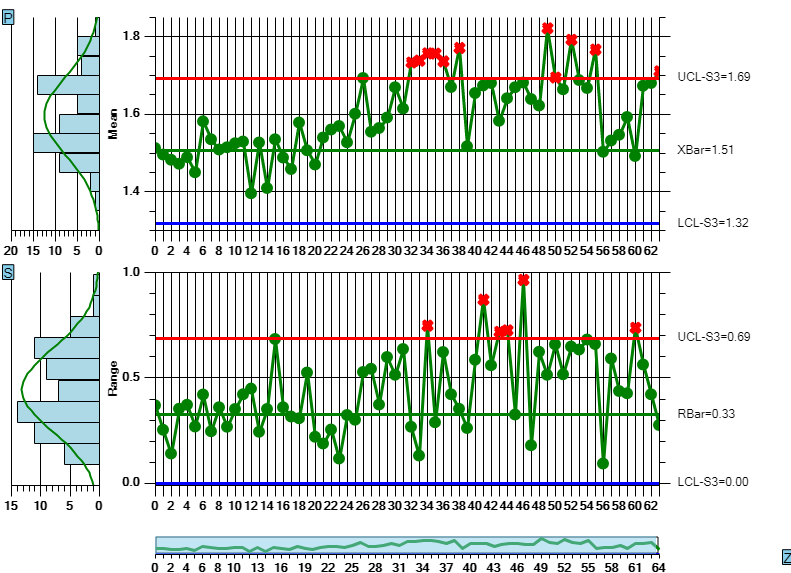
XBarR Chart SPC Charts Online
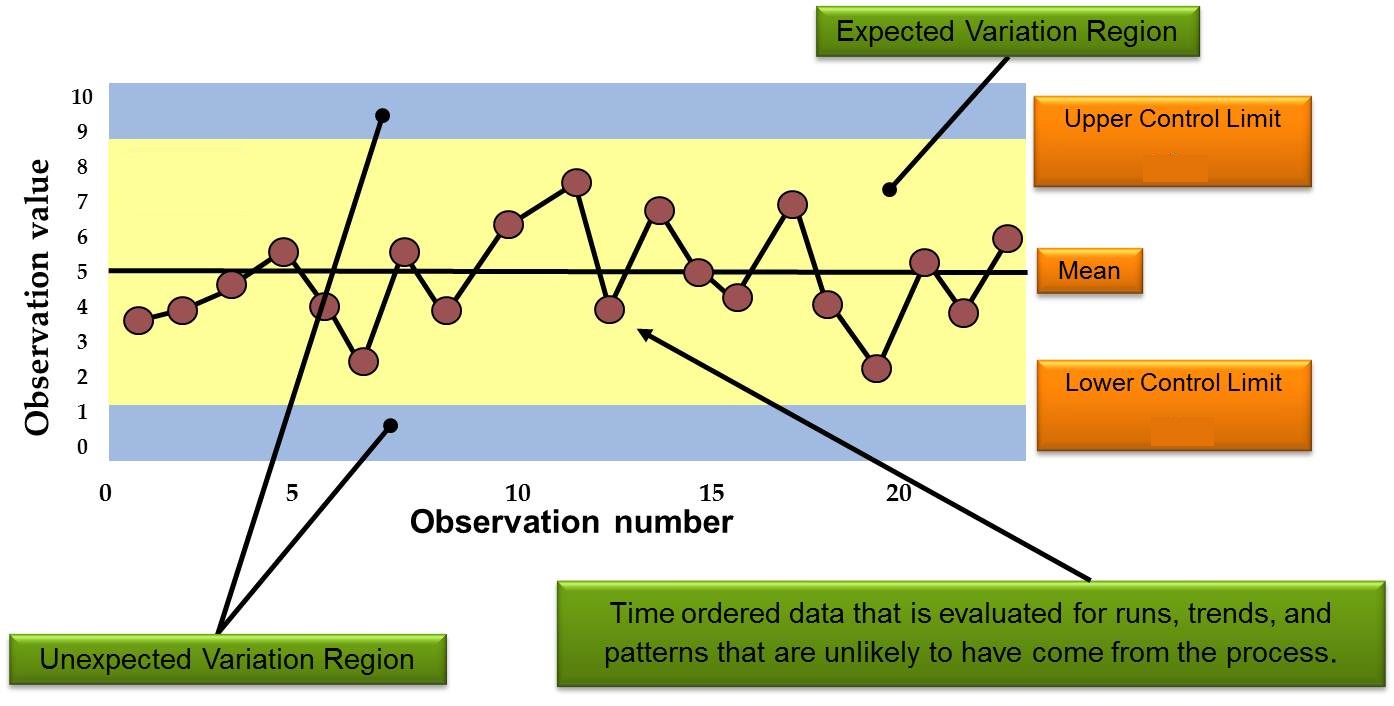
After discussing the several aspects and uses ofXbar and R Charts, we
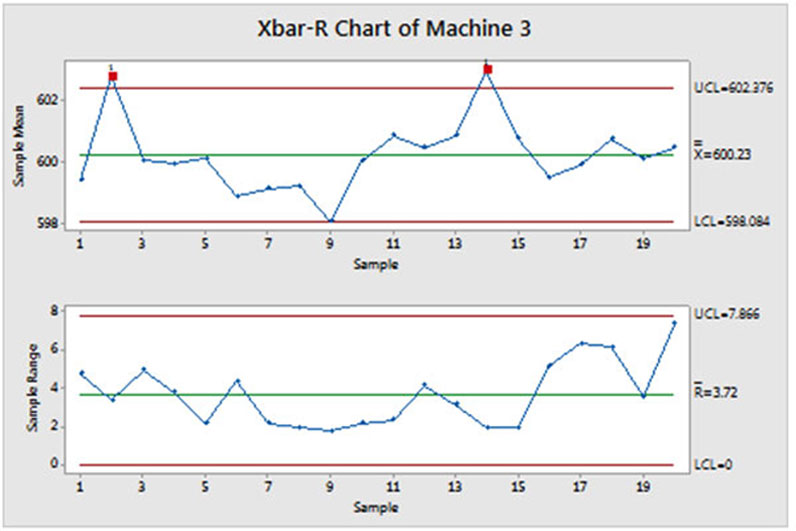
How To Analyze Xbar And R Charts Chart Walls

How To Create an XBar R Chart Six Sigma Daily
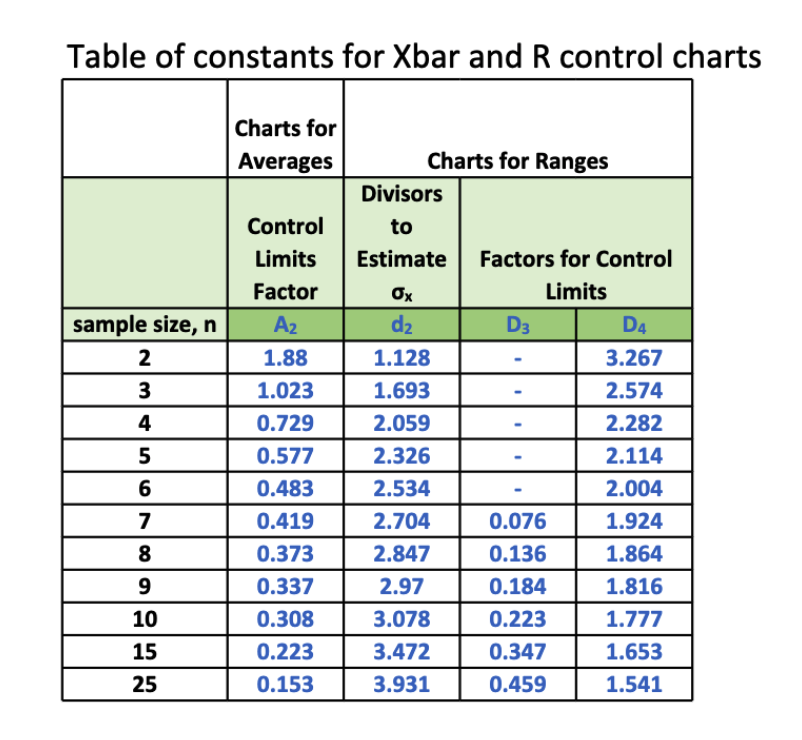
Solved Table of constants for Xbar and R control charts

Control Limits for xbar r chart show out of control conditions
nibhtpb Blog
X Bar And R Chart
Web The Simplest Way To Describe The Limits Is To Define The Factor A 2 = 3 / ( D 2 N) And The Construction Of The X ¯ Becomes U C L = X ¯ ¯ + A 2 R ¯ Center Line = X ¯ ¯ L C L = X ¯ ¯ − A 2 R ¯.
Examine The Xbar Chart To Determine Whether The Process Mean Is In Control.
3, 4, Or 5 Measurements Per Subgroup Is Quite Common.
Web Xbar R Charts Are Often Used Collectively To Plot The Process Mean (Xbar) And Process Range (R) Over Time For Continuous Data.
Related Post: