Tarlov Cyst Size Chart
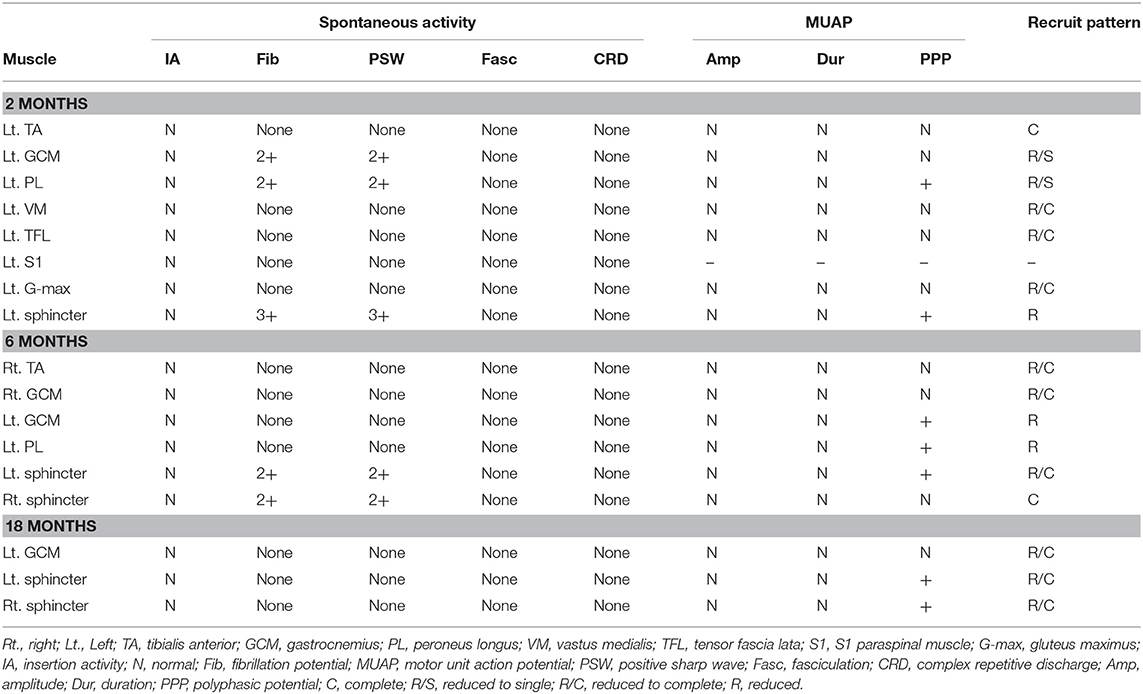
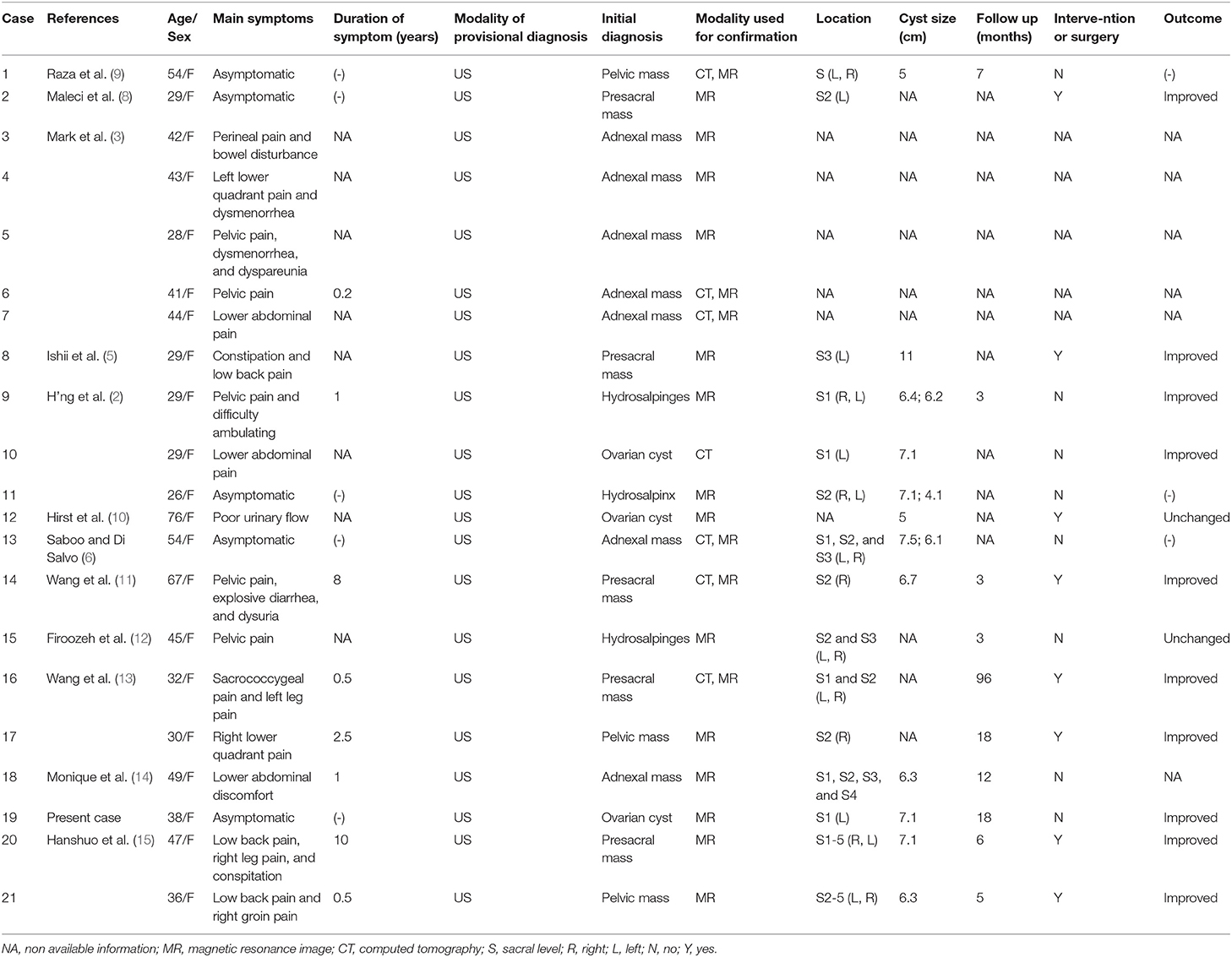
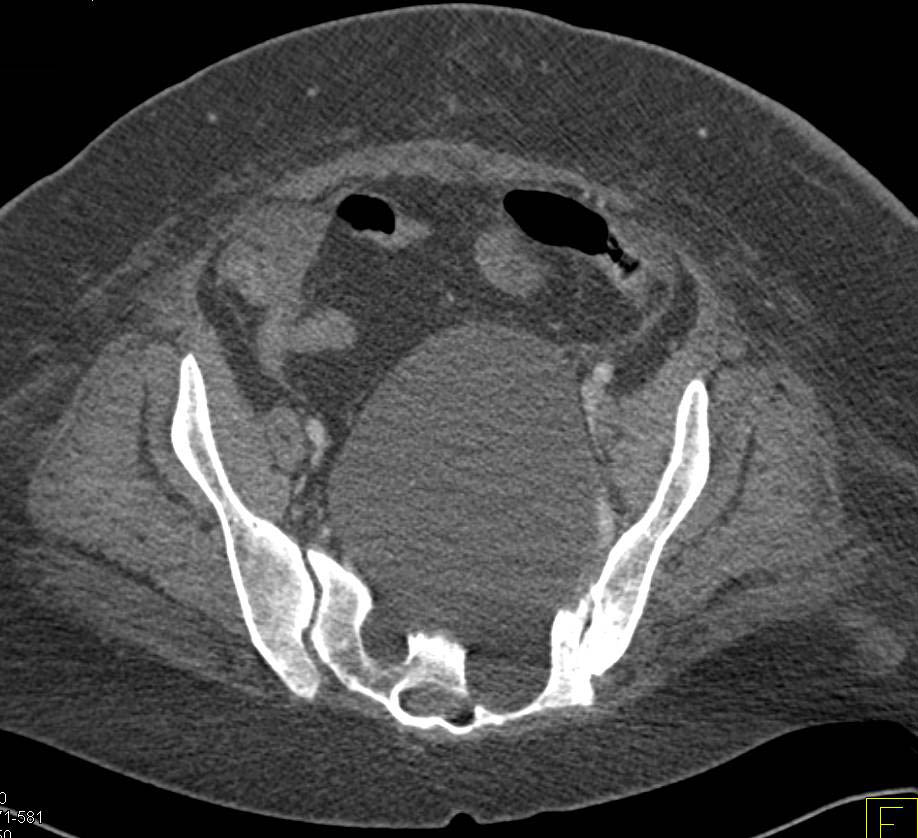
Tarlov Cyst Size Chart - Signal characteristics of typical tarlov cyst are those of csf on all sequences. The main feature that distinguishes tarlov cysts from other spinal lesions is the presence of spinal nerve. They can occur anywhere in the spine but most frequently around the sacral nerve roots, with s2 being the most common level. Tarlov cysts (hereafter referred to as tcs) are also known as perineural/perineurial, or sacral nerve root cysts. Web tarlov cysts are perineural cysts between the perineurium and endoneurium, arising near the dorsal root ganglion. They are dilations of the nerve root sheaths and are abnormal sacs filled with cerebrospinal fluid (hereafter referred to as csf) that can cause a progressively painful radiculopathy (nerve pain). Web tarlov cysts were most commonly located from s2 to s3 (73%), and ranged in size from 1 to 2 cm (55%). Tarlov cysts are a condition where you develop cysts on the nerves of your spine. Cysts can be valved or nonvalved. Web tarlov cysts are perineural cysts between the perineurium and endoneurium, arising near the dorsal root ganglion. Web tarlov cysts were most commonly located from s2 to s3 (73%), and ranged in size from 1 to 2 cm (55%). Tarlov cysts are a condition where you develop cysts on the nerves of your spine. Cerebral spinal fluid gets trapped inside the sheath and forms a cyst. The cysts appear in the roots of the nerves that grow. Small, asymptomatic cysts can slowly increase in size eventually causing symptoms. They can occur anywhere in the spine but most frequently around the sacral nerve roots, with s2 being the most common level. The main feature that distinguishes tarlov cysts from other spinal lesions is the presence of spinal nerve. Signal characteristics of typical tarlov cyst are those of csf. Web symptoms sometimes caused by tarlov cysts include pain in the area served by the affected nerves, numbness and altered sensation, an inability to control bladder and bowel movements (incontinence), impotence, and, rarely, weakness in the legs. Web tarlov cyst disease is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid between the endoneurium and perineurium of spinal, usually sacral, nerve roots. These cysts. Cysts can be valved or nonvalved. Web tarlov cysts vary in size. On mr the perineural cysts predominantly originating near the sacral nerves adjacent to the dorsal root ganglion. Web tarlov cysts (also known as meningeal or perineurial cysts) occur on weakened areas of spinal nerve roots. Cerebral spinal fluid gets trapped inside the sheath and forms a cyst. Web tarlov cysts are perineural cysts between the perineurium and endoneurium, arising near the dorsal root ganglion. Tarlov cysts (hereafter referred to as tcs) are also known as perineural/perineurial, or sacral nerve root cysts. What can i do to improve or control my symptoms, while i am waiting for an appointment with a knowledgeable doctor who will assist me with. The pressure of a growing cyst on the spinal nerves can cause pain and a number of debilitating symptoms. Web tarlov cysts vary in size. How are tarlov cysts most often diagnosed? Web tarlov cysts are perineural cysts between the perineurium and endoneurium, arising near the dorsal root ganglion. The cysts appear in the roots of the nerves that grow. These cysts can become symptomatic in 20% of patients, causing lower back pain, radiculopathy, bladder and bowel dysfunction necessitating medical or surgical intervention. Cerebral spinal fluid gets trapped inside the sheath and forms a cyst. Signal characteristics of typical tarlov cyst are those of csf on all sequences. What is a tarlov cyst? They are dilations of the nerve root. Small, asymptomatic cysts can slowly increase in size eventually causing symptoms. They can occur anywhere in the spine but most frequently around the sacral nerve roots, with s2 being the most common level. Web 3 min read. Welch recommends asking your physician or neurosurgeon. Web symptoms sometimes caused by tarlov cysts include pain in the area served by the affected. On mr the perineural cysts predominantly originating near the sacral nerves adjacent to the dorsal root ganglion. A tarlov cyst is a dilation of the nerve root sheath or outer covering of the nerve. Web tarlov cysts are perineural cysts between the perineurium and endoneurium, arising near the dorsal root ganglion. Web tarlov cysts (also known as meningeal or perineurial. Web tarlov cyst disease is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid between the endoneurium and perineurium of spinal, usually sacral, nerve roots. Web there is no consensus on the management of these cysts, and based on these findings and experience with over 1000 patient referrals, a treatment decision algorithm for symptomatic tarlov cysts was constructed to provide guidance for appropriate management. Web tarlov cyst disease is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid between the endoneurium and perineurium of spinal, usually sacral, nerve roots. A tarlov cyst is a dilation of the nerve root sheath or outer covering of the nerve. What can i do to improve or control my symptoms, while i am waiting for an appointment with a knowledgeable doctor who will assist me with treatment? Welch recommends asking your physician or neurosurgeon. They are dilations of the nerve root sheaths and are abnormal sacs filled with cerebrospinal fluid (hereafter referred to as csf) that can cause a progressively painful radiculopathy (nerve pain). The cysts appear in the roots of the nerves that grow out of the spinal cord. Web faqs | tarlov cyst disease foundation. If you’ve been diagnosed with a tarlov cyst or suspect you may be experiencing symptoms, check out the 4 questions dr. How are tarlov cysts most often diagnosed? The main feature that distinguishes tarlov cysts from other spinal lesions is the presence of spinal nerve. Small, asymptomatic cysts can slowly increase in size eventually causing symptoms. Is a tarlov cyst causing my symptoms? Web tarlov cysts (also known as meningeal or perineurial cysts) occur on weakened areas of spinal nerve roots. Web 3 min read. Web the website provides information about symptomatic tarlov cysts, which may cause such symptoms as sciatica, difficulty sitting or standing for more than short periods of time, coccyx (tailbone) pain, pain in buttocks and legs, leg cramps, paresthesias (strange sensations in legs and feet), bladder and bowel dysfunction,chronic pelvic, abdominal,. Web a statistical analysis comparing cyst size and location to clinical findings was significant for a correlation between an s2 location and cns symptoms (p=0.02), larger cyst size and urinary dysfunction (p=0.05), and smaller cyst size and an early sensation of.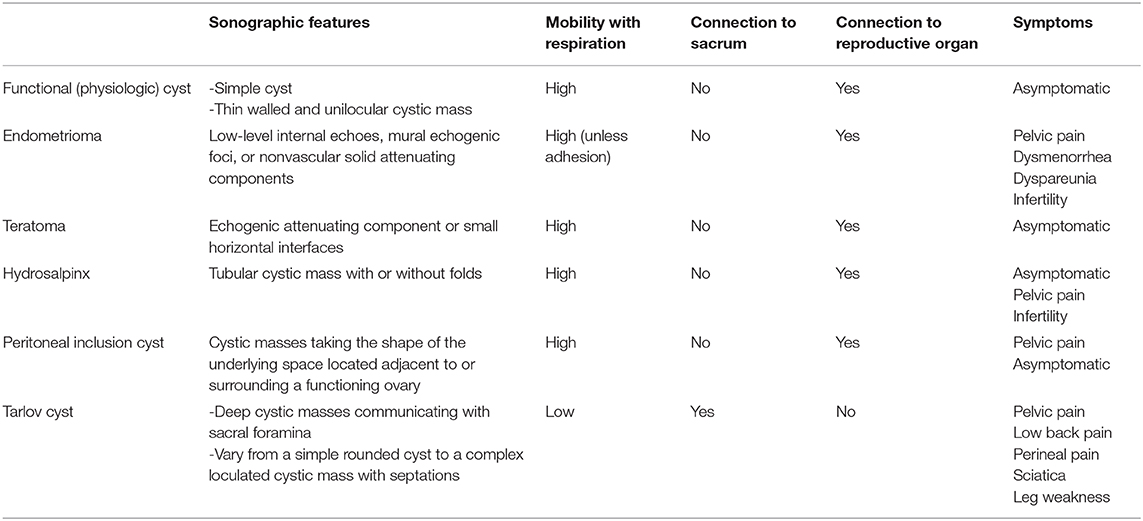
Tarlov Cyst Size Chart
Tarlov Cyst Size Chart

Tarlov Cyst Size Chart

Tarlov Cyst Size Chart
Tarlov Cyst Size Chart
Tarlov Cyst Size Chart

Treatment of 213 Patients with Symptomatic Tarlov Cysts by CTGuided
.png)
Tarlov Cysts AIMIS Healthcare Group

Tarlov Cyst Excel Spine

Tarlov Cyst Size Chart
What Is A Tarlov Cyst?
Cerebral Spinal Fluid Gets Trapped Inside The Sheath And Forms A Cyst.
Web Four Questions To Ask.
They Can Occur Anywhere In The Spine But Most Frequently Around The Sacral Nerve Roots, With S2 Being The Most Common Level.
Related Post: