Shock Hemodynamics Chart
Shock Hemodynamics Chart - Or, in other words, it's the decreased delivery of oxygen to different organs of the body, and perfusion, this delivery of oxygen to the body, is essentially equal to the amount of flow, so the amount of blood flow that gets to the organs, over the amount of tissue that is being. Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume, decreased cardiac output, and vasodilation, sometimes with shunting of blood to bypass capillary exchange beds. Web hemodynamics is how your blood flows through your arteries and veins and the forces that affect your blood flow. Web shock is a common condition in critical care, affecting about one third of patients in the intensive care unit (icu). Web shock can be categorized according to the underlying cause, including septic shock, cardiogenic shock, anaphylactic shock and shock associated with burns, trauma and hemorrhage. It flows fastest in the middle of a blood vessel,. Classify the type of shock (see “overview of types of shock”). 1 a diagnosis of shock is based on clinical, hemodynamic, and biochemical. Web hemodynamic monitoring enables (1) characterization of the type of cardiac dysfunction and the degree of its severity, (2) very early detection of associated vasoplegia, (3) detection and monitoring of organ dysfunction and tissue oxygenation, and (4) guidance of the introduction and optimization of inotropes and vasopressors as well. In vivo, receptor effects are often mixed. 1 a diagnosis of shock is based on clinical, hemodynamic, and biochemical. Shock is defined as inadequate organ and peripheral tissue perfusion and is categorized on the basis of its etiology as being either hypovolemic, cardiogenic, or restrictive (vasodilatory/distributive). Or, in other words, it's the decreased delivery of oxygen to different organs of the body, and perfusion, this delivery of. Web hemodynamics is how your blood flows through your arteries and veins and the forces that affect your blood flow. Cardiogenic shock, hemodynamic monitoring, echocardiography, pulmonary artery catheterization. Untreated hs usually leads to death. Critically assess the pressure waveforms for proper fidelity. Web shock can be categorized according to the underlying cause, including septic shock, cardiogenic shock, anaphylactic shock and. Critically assess the pressure waveforms for proper fidelity. (1) what are the epidemiologic and pathophysiologic features of shock in the icu? Classify the type of shock (see “overview of types of shock”). Four types of hemodynamic shock are recognized [ 5 ]. Shock is defined as inadequate organ and peripheral tissue perfusion and is categorized on the basis of its. Topics addressed were as follows: This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics of children with kd and develop. Symptoms include altered mental status, tachycardia, hypotension, and oliguria. Classification of shock and general principles of treating shock. Collect hemodynamics in a systematic method using established protocols. Shock is defined as inadequate organ and peripheral tissue perfusion and is categorized on the basis of its etiology as being either hypovolemic, cardiogenic, or restrictive (vasodilatory/distributive). In recent years, a logistic regression prediction model has been widely used to predict the occurrence probability of various diseases. Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume, decreased cardiac output, and vasodilation, sometimes with. Web cardiogenic shock (cs) remains a deadly disease entity challenging patients, caregivers, and communities across the globe. Prompt recognition and intervention are the cornerstones of mitigating the dire consequences of hs. However, septic shock can occur with an elevated cardiac output due to micro vascular dysfunction at the tissue level (blood shunts through some vessels, while ignoring others). The goal. Collect hemodynamics in a systematic method using established protocols. 1 a diagnosis of shock is based on clinical, hemodynamic, and biochemical. Web a total of 17 recommendations were developed to provide guidance to intensive care physicians monitoring and caring for the patient with shock. Or, in other words, it's the decreased delivery of oxygen to different organs of the body,. Web the study of forces involved in blood circulation. Classification of shock and general principles of treating shock. Four types of hemodynamic shock are recognized [ 5 ]. Shock is the final manifestation of a complex list of etiologies and could be fatal without timely management. A systematic approach to hemodynamic interpretation. Web shock can occur following either hypoperfusion or inadequate perfusion of end organs leading to the loss of the physiological balance between oxygen delivery (do2) and oxygen consumption (vo2) as well as being associated with elevated blood lactate values. Web hemodynamic shock (hs) is a clinical syndrome that is commonly observed in hospitalized patients. Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume,. This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics of children with kd and develop. Classification of shock and general principles of treating shock. Shock is defined as inadequate organ and peripheral tissue perfusion and is categorized on the basis of its etiology as being either hypovolemic, cardiogenic, or restrictive (vasodilatory/distributive). Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume, decreased cardiac output, and. (2) should we monitor preload and fluid responsiveness in shock?. Cardiogenic shock, hemodynamic monitoring, echocardiography, pulmonary artery catheterization. A systematic approach to hemodynamic interpretation. Shock is defined as inadequate organ and peripheral tissue perfusion and is categorized on the basis of its etiology as being either hypovolemic, cardiogenic, or restrictive (vasodilatory/distributive). Mechanisms may involve decreased circulating volume, decreased cardiac output, and vasodilation, sometimes with shunting of blood to bypass capillary exchange beds. Topics addressed were as follows: Or, in other words, it's the decreased delivery of oxygen to different organs of the body, and perfusion, this delivery of oxygen to the body, is essentially equal to the amount of flow, so the amount of blood flow that gets to the organs, over the amount of tissue that is being. Web shock can be categorized according to the underlying cause, including septic shock, cardiogenic shock, anaphylactic shock and shock associated with burns, trauma and hemorrhage. Web shock is a state of organ hypoperfusion with resultant cellular dysfunction and death. Confirm the scale of the recording. The goal of using hemodynamics is to evaluate cardiac and circulatory function as well as evaluate response to interventions. Web consider invasive monitoring for severe shock (e.g., central venous pressure, arterial line). Web hemodynamic shock (hs) is a clinical syndrome that is commonly observed in hospitalized patients. Collect hemodynamics in a systematic method using established protocols. Web shock is a common condition in critical care, affecting about one third of patients in the intensive care unit (icu). Web the most simple physiology of shock is cardiogenic shock, with low cardiac output to the entire body.
Typical Hemodynamics in Various Shock States and Their Differential
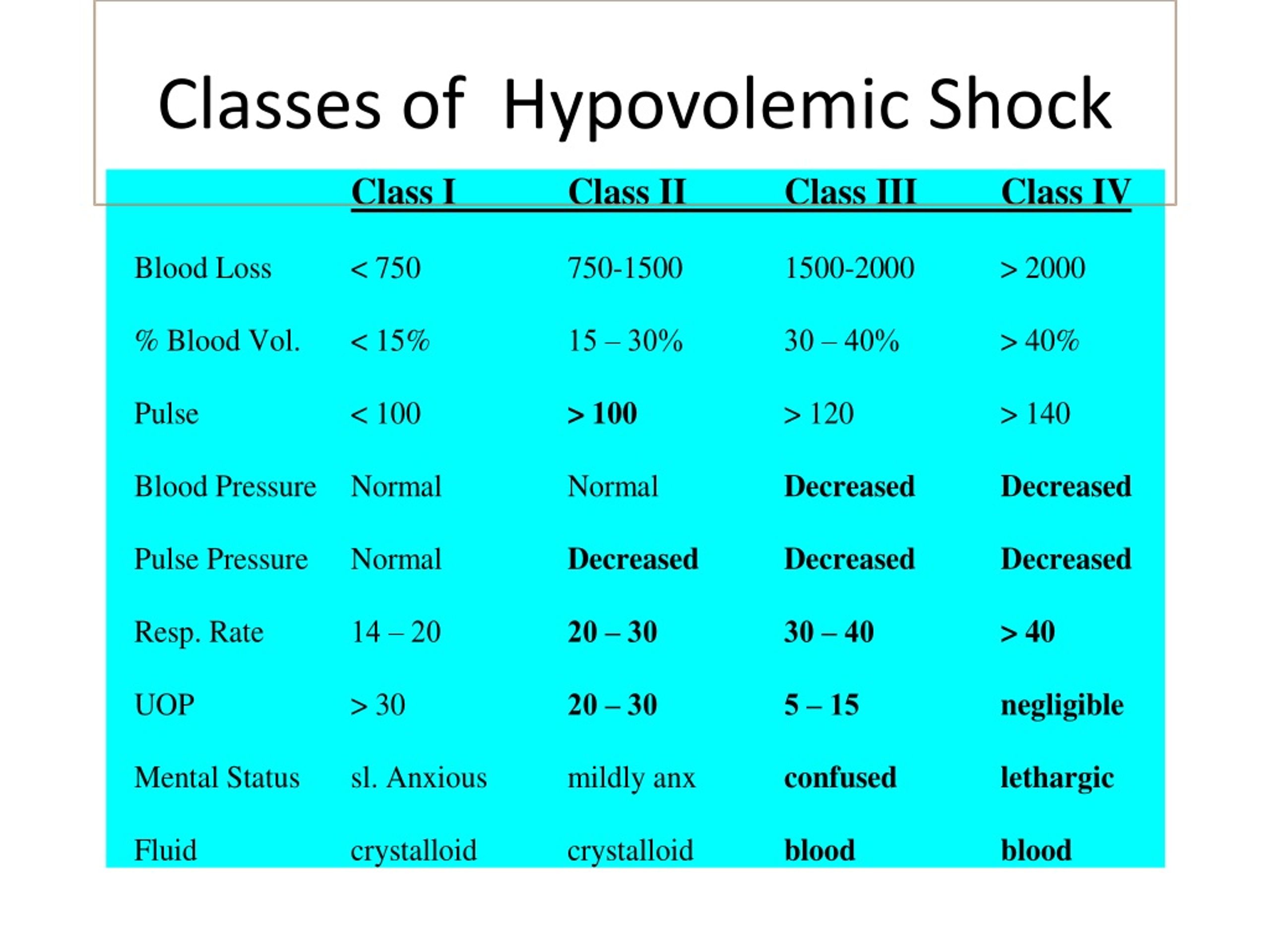
PPT shock PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID250122
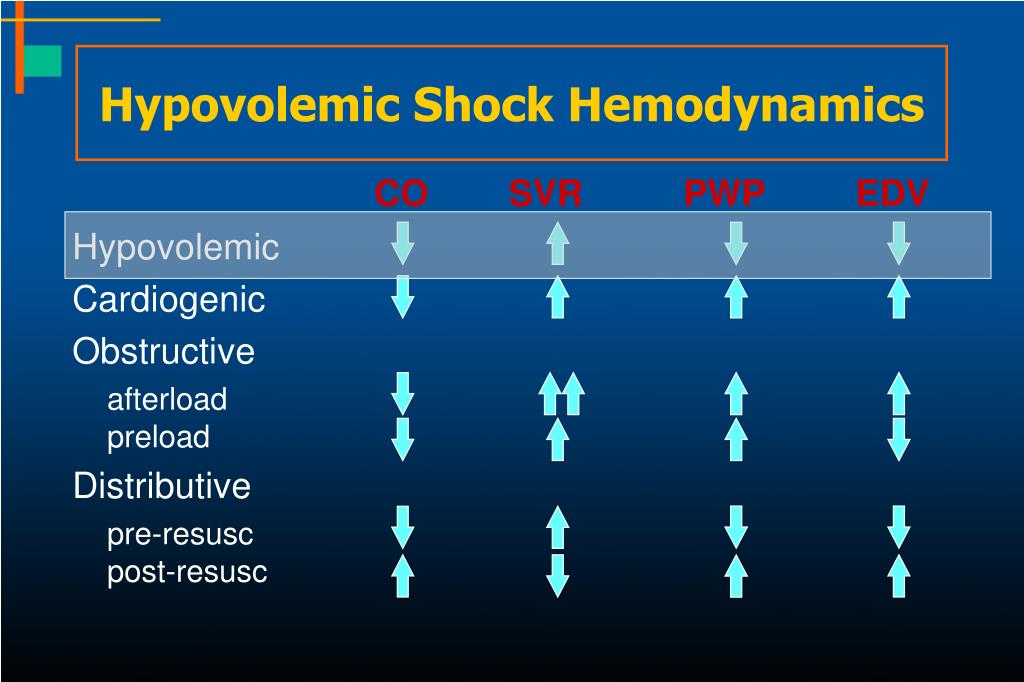
PPT Approach and Hemodynamic Evaluation of Shocks PowerPoint
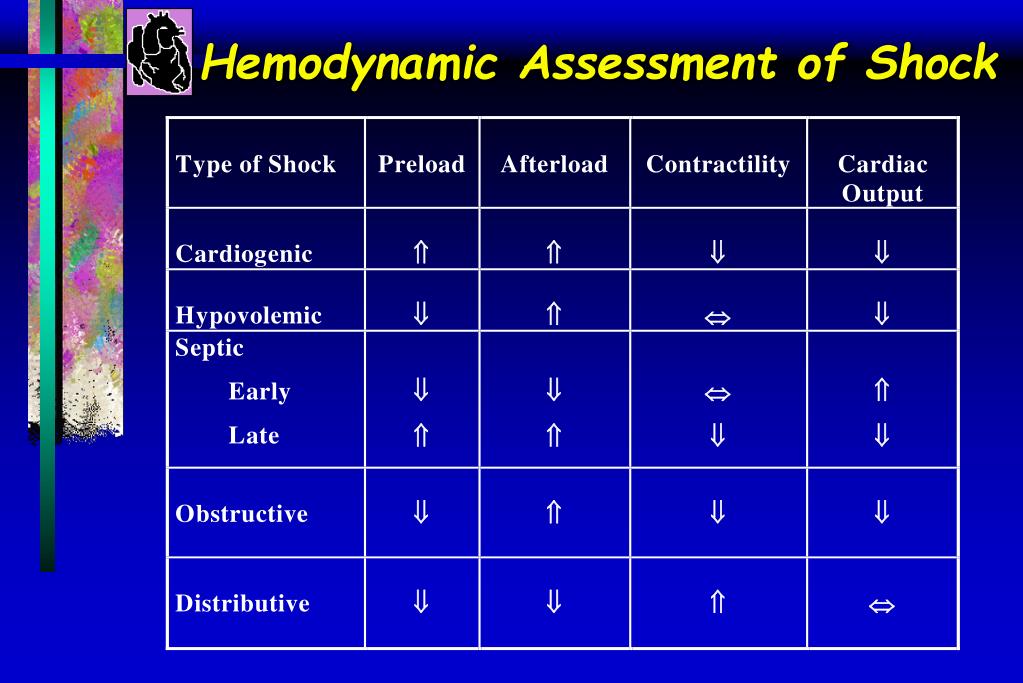
PPT Shock in the Pediatric Patient or Oxygen Don’t Go Where the
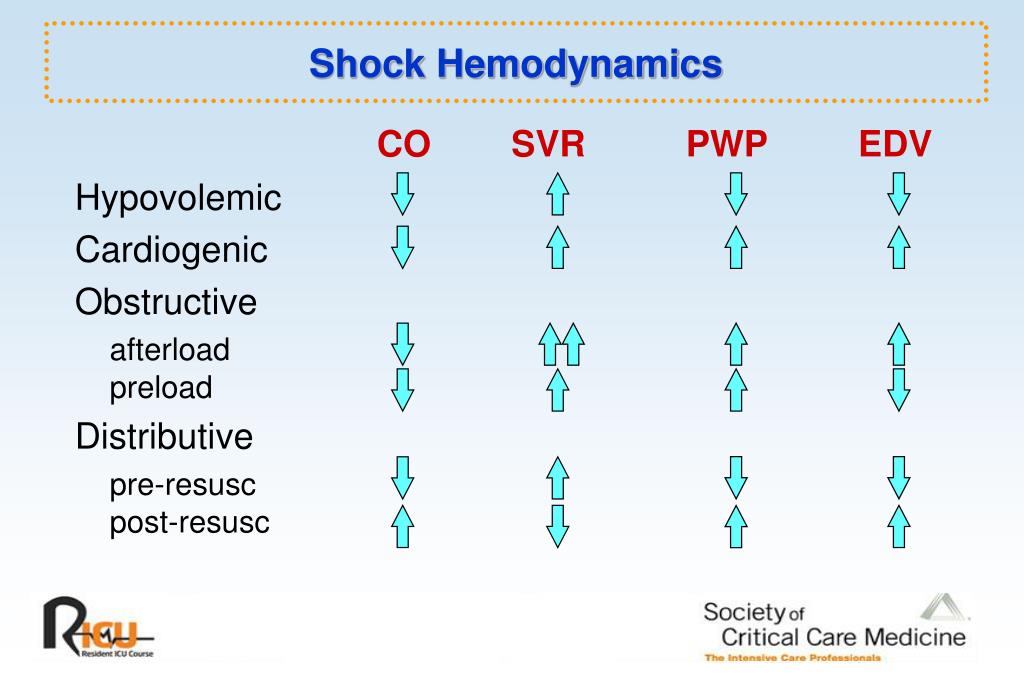
PPT Shock Pathophysiology, Classification, and Approach to Management
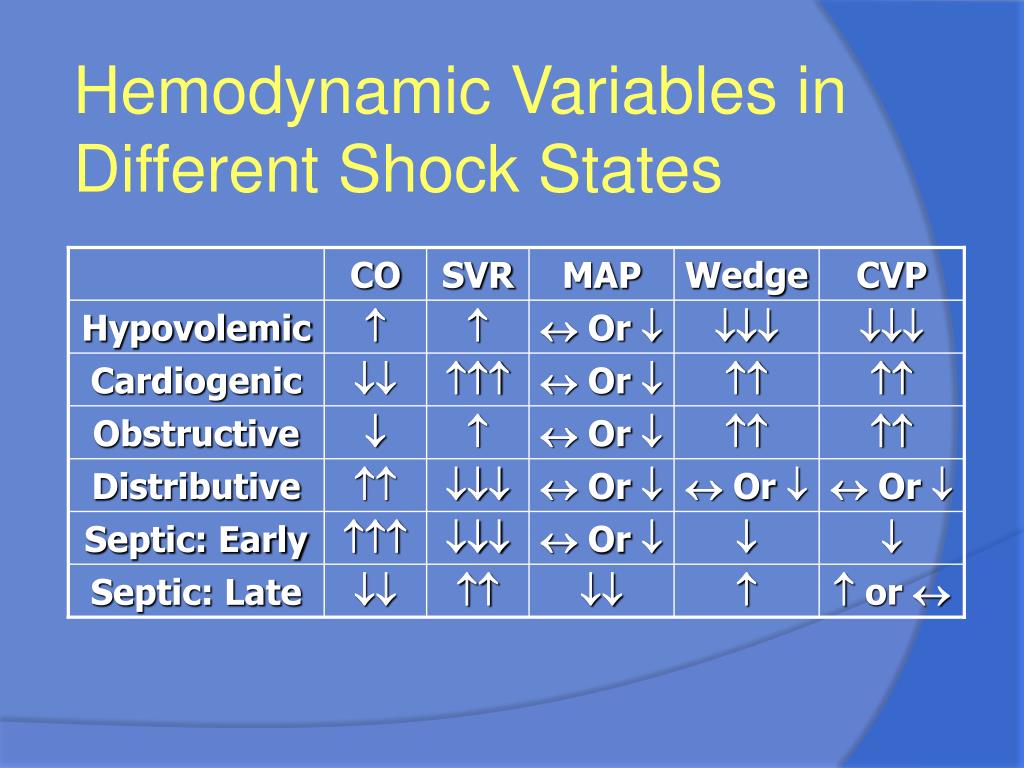
PPT Pediatric Shock PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID601587

Shock Types and Classification DISTRIBUTIVE 66 GrepMed
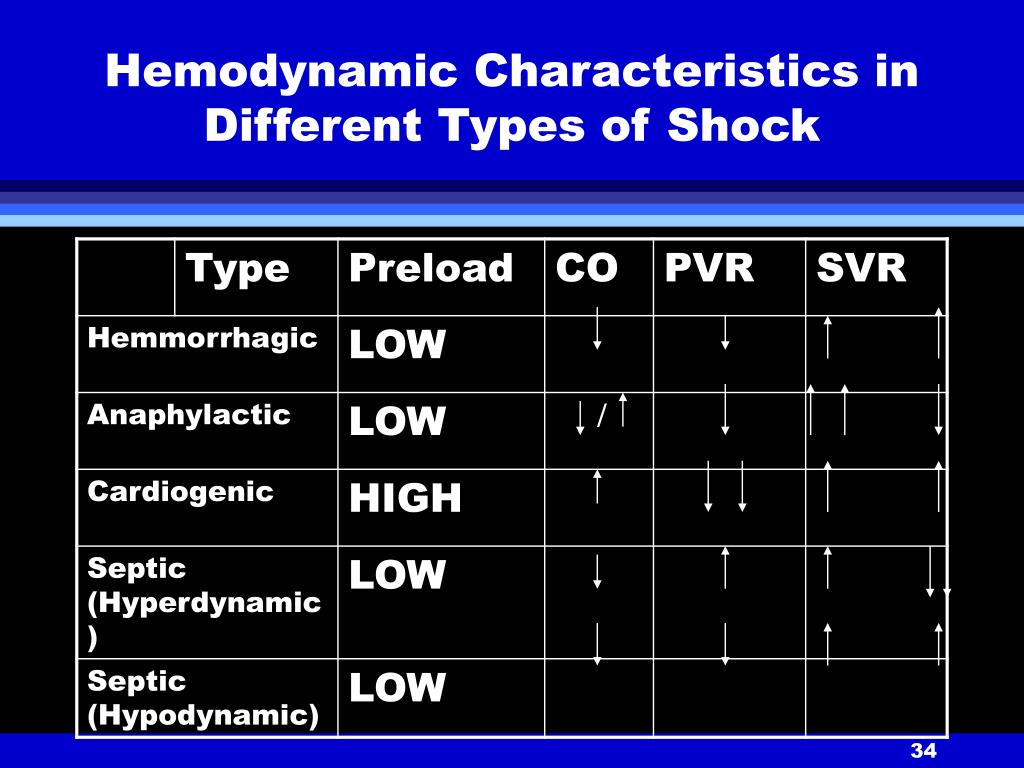
PPT SHOCK PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6206310
Shock With Hemodynamic Changes

Understanding Hemodynamics in Different Types of Shock
In Vivo, Receptor Effects Are Often Mixed.
Web A Total Of 17 Recommendations Were Developed To Provide Guidance To Intensive Care Physicians Monitoring And Caring For The Patient With Shock.
Establish The Zero Level And Balance Transducer.
Critically Assess The Pressure Waveforms For Proper Fidelity.
Related Post:
