Sediment Grain Size Chart
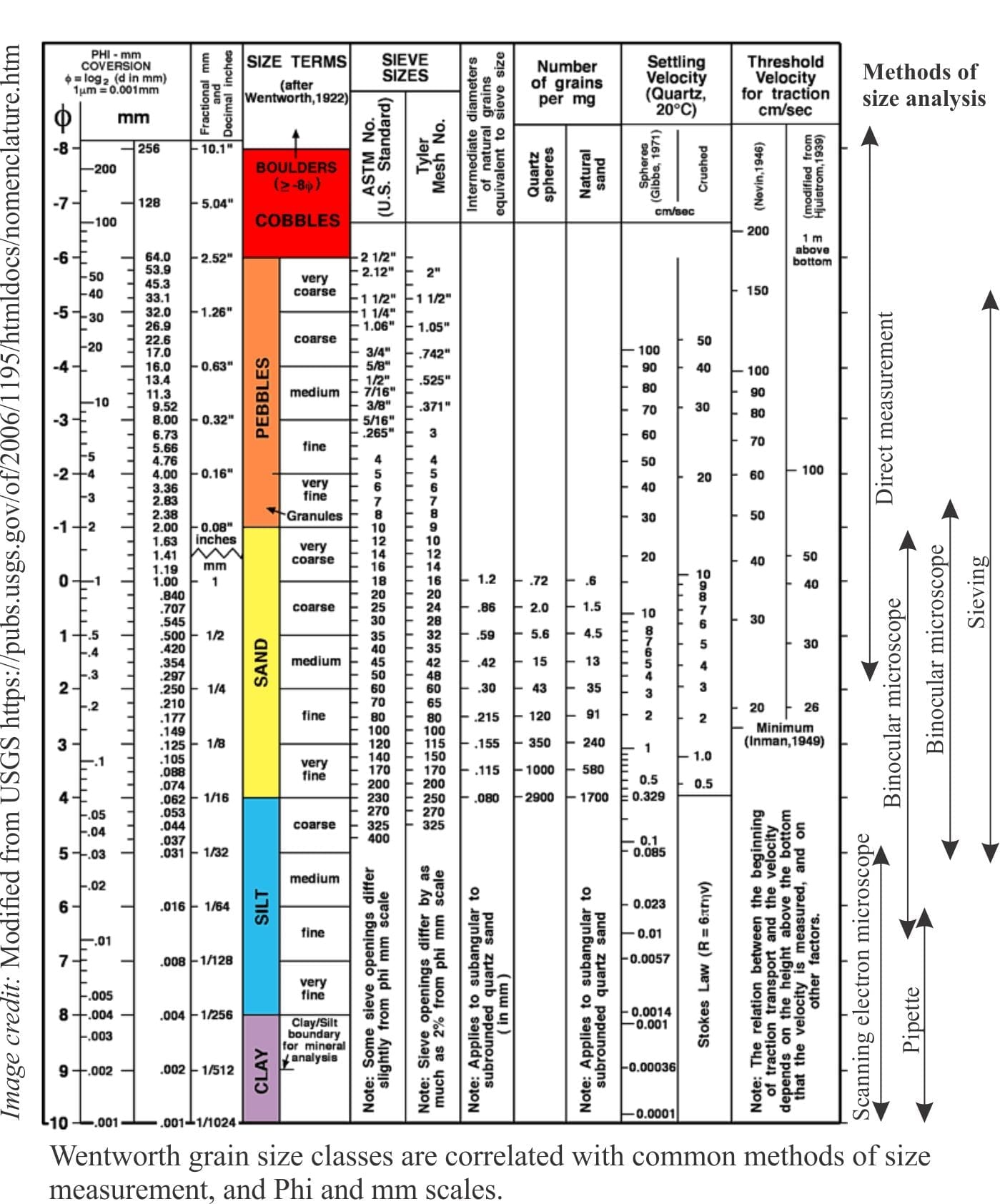
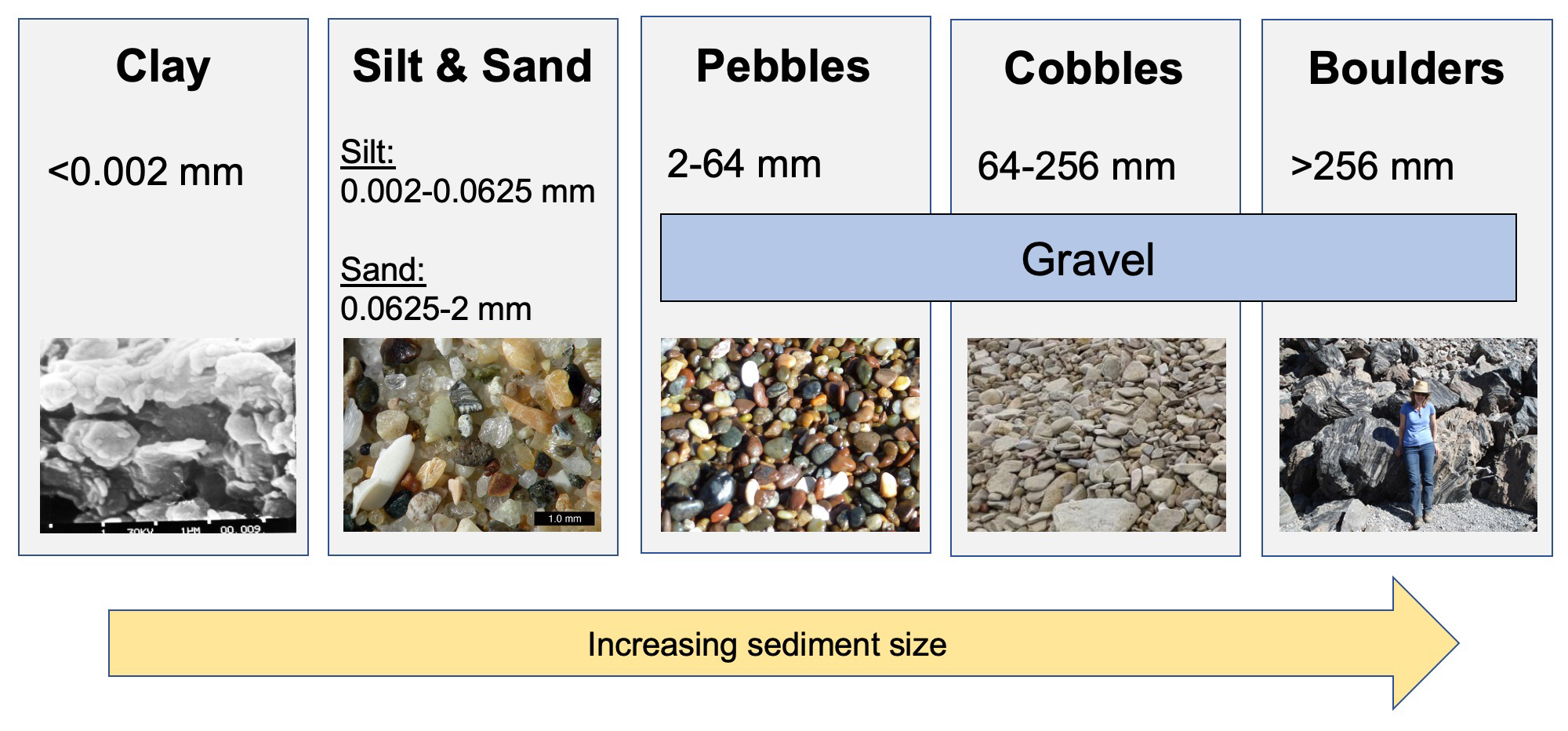
Sediment Grain Size Chart - Any categorization of grains larger than 100mm will be conducted. Web the first is grain size. Find out why grain size is important and how to estimate it in the field. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Web learn the canonical definition of sediment grain sizes by geologist chester k. Use these grain size cards in your observations of sedimentary rocks. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Convert between millimeters and phi units. A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Web mean grain size of loose sediments is measured by size analysis using sieves. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. See also related sediment classification schemes by folk and shepard. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Web sediments by grain size. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Sediments are classified by particle size, ranging from the finest clays (diameter <0.004 mm) to the largest boulders (> 256 mm) (figure 12.1.2). Web sieve grain size analysis is capable of determining the particles’ size ranging from 0.075 mm to 100 mm. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter. Sediments are classified by particle size, ranging from the finest clays (diameter <0.004 mm) to the largest boulders (> 256 mm) (figure 12.1.2). > coarse grain size (granules<pebble<cobbles<boulders) 0.06 to 2mm medium grain. Web grain size is the average size of the grains in a sediment sample. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to. Web mean grain size of loose sediments is measured by size analysis using sieves. Grain size is the average diameter of individual grains (particles) of clastic sediments and rocks. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a. Use these grain size cards in your observations of sedimentary rocks. You can use them for hand specimens at home or in the classroom, or on rock outcrops. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment,. D_x is defined as the sediment particle. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Web sieve grain size analysis is capable of determining the particles’ size ranging from 0.075 mm to 100 mm. Use these grain size cards in your observations of sedimentary rocks. This is different. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Any categorization of grains larger than 100mm will be conducted. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). You can use them for hand specimens at home or in the classroom, or on rock outcrops. Web two important parameters for sediment. A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Granular material can range from very small colloidal particles, through clay, silt, sand, gravel, and cobbles, to boulders. Grain size is the average diameter of individual grains (particles) of clastic sediments and rocks. Find out why grain size is important and how to estimate it in the field. Web learn the. You can use them for hand specimens at home or in the classroom, or on rock outcrops. Web the science of grain size distributions developed in concert with rapidly evolving concepts of sedimentary facies and a more sophisticated approach to. > coarse grain size (granules<pebble<cobbles<boulders) 0.06 to 2mm medium grain. Web grain size is the average size of the grains. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Convert between millimeters and phi units. Web grain size is the average size of the grains in a sediment sample. Web mean grain size of loose sediments is measured by size analysis using sieves. Sand consists of grains of particle. It is also known as the particle size. Wentworth in 1922, with a simple and a detailed chart. See also related sediment classification schemes by folk and shepard. Grain size is the average diameter of individual grains (particles) of clastic sediments and rocks. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Web two important parameters for sediment transport are the median particle diameter d_ {50} and the grading, for example, d_ {90}/d_ {10}. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Web the first is grain size. Web learn the canonical definition of sediment grain sizes by geologist chester k. Any categorization of grains larger than 100mm will be conducted. Sediments are classified by particle size, ranging from the finest clays (diameter <0.004 mm) to the largest boulders (> 256 mm) (figure 12.1.2). A visual reference for descriptions of sorting (top) and roundness (bottom) of sediments and grains in clastic sedimentary rocks. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. Web sediments by grain size. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). Convert between millimeters and phi units.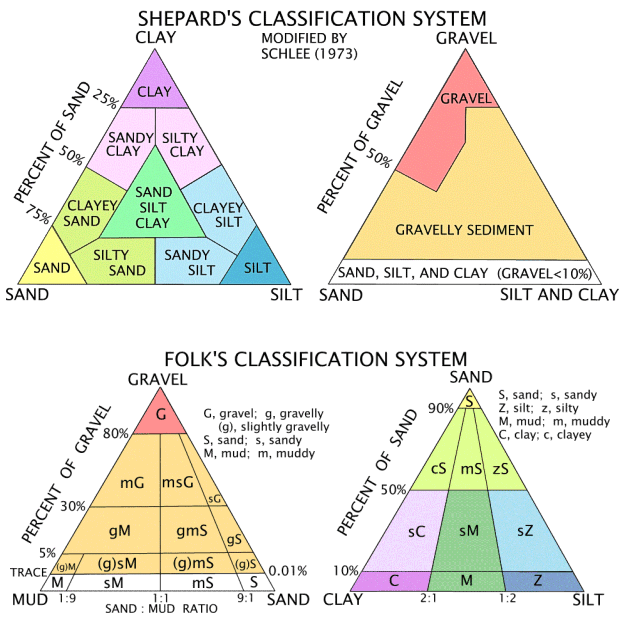
Wentworth (1922) grain size classification The Society

Sedimentary grain size and sorting cheat sheet. Geology, Sedimentary
Grain size of clastic rocks and sediments Geological Digressions

Grain size Geology is the Way

Sediment grainsize scale Download Table
Sediment Grain Size Chart

Sediment classification based on grain size Download Table

Sedimentary rock Grain Size, Stratification, Deposition Britannica

Comparison of grain sizes to soils and loess sediment classification

Grain Size Chart Geology A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Find Out Why Grain Size Is Important And How To Estimate It In The Field.
Particle Size, Also Called Grain Size, Refers To The Diameter Of Individual Grains Of Sediment, Or The Lithified Particles In Clastic Rocks.
You Can Use Them For Hand Specimens At Home Or In The Classroom, Or On Rock Outcrops.
> Coarse Grain Size (Granules<Pebble<Cobbles<Boulders) 0.06 To 2Mm Medium Grain.
Related Post: