Sacrum Diagnosis Chart
Sacrum Diagnosis Chart - Web what is the sacrum. Web plain radiographs, although limited in evaluation of the sacrum, should be carefully examined when abnormalities of the sacrum are suspected. The oblique axis will occur on the side opposite. Web pie chart showing the relative incidence of various types of sacral masses. During the physical exam, some tests may be performed, like a. Sacral tumours and their mimics: Web sacroiliitis can be hard to diagnose. With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. They frequently are accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as low back pain and pelvic pressure. Web in a case series of 34 patients with sacral metastases , 61% of patients had distal organ involvement, whereas 41% demonstrated widespread spinal metastases. Web the sacrum is a fusion of five vertebrae that holds the pelvis and spinal column together. Seated flexion test step two: Web sif is most frequently found in patients with sacroiliac joint pathology in the setting of a sacrum compromised due to conditions such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid. Depending on the type of sacral injury or nerve damage, its location. Pictorial review and diagnostic strategy. Depending on the type of sacral injury or nerve damage, its location affects the nerves in that area and leads to lack of control and pain: Web types of sacral spine injury. It's been linked to a group of diseases that cause inflammatory arthritis of. Web sif is most frequently found in patients with sacroiliac. They frequently are accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as low back pain and pelvic pressure. This seated flexion test is modified from traditional. It's been linked to a group of diseases that cause inflammatory arthritis of. Depending on the type of sacral injury or nerve damage, its location affects the nerves in that area and leads to lack of control. Web sacral torsions encompass anterior (l on l / r on r) or posterior (l on r / r on l) torsion dysfunctions of the sacrum. Web how do we decide what diagnosis is? Web the sacrum, as a site of hematopoietic or red marrow in the adult, is a common site for metastatic disease as well as hematologic malignancies.. This seated flexion test is modified from traditional. The oblique axis will occur on the side opposite. A complete history and physical examination are critical. Web how do we decide what diagnosis is? Web when diagnosing the sacrum using the still technique you diagnose with two things: They frequently are accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as low back pain and pelvic pressure. Web diagnosing the sacrum includes three important steps: Seated flexion test step two: It can be mistaken for other causes of low back pain. Web plain radiographs, although limited in evaluation of the sacrum, should be carefully examined when abnormalities of the sacrum are suspected. The oblique axis will occur on the side opposite. Web when diagnosing the sacrum using the still technique you diagnose with two things: Web sacral torsions are commonly diagnosed by a review of medical history and a physical examination. Web in a case series of 34 patients with sacral metastases , 61% of patients had distal organ involvement, whereas 41%. Web sacral torsions encompass anterior (l on l / r on r) or posterior (l on r / r on l) torsion dysfunctions of the sacrum. A complete history and physical examination are critical. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction is a common cause of low back pain and accurate diagnosis can be challenging. Web the sacrum, as a site of. Web diagnosing the sacrum includes three important steps: We go from 8 diagnosis to 4. Depending on the type of sacral injury or nerve damage, its location affects the nerves in that area and leads to lack of control and pain: They frequently are accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as low back pain and pelvic pressure. It is important for. Web the sacrum is a fusion of five vertebrae that holds the pelvis and spinal column together. Web sacral torsions are commonly diagnosed by a review of medical history and a physical examination. Web sif is most frequently found in patients with sacroiliac joint pathology in the setting of a sacrum compromised due to conditions such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid. Web. Spring test or sphinx test step three: Web types of sacral spine injury. Web what is the sacrum. It can be mistaken for other causes of low back pain. They frequently are accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as low back pain and pelvic pressure. Web sif is most frequently found in patients with sacroiliac joint pathology in the setting of a sacrum compromised due to conditions such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid. Seated flexion test step two: With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ila will be on the opposite side. This seated flexion test is modified from traditional. It is important for motion, strength, and balance. Web in a case series of 34 patients with sacral metastases , 61% of patients had distal organ involvement, whereas 41% demonstrated widespread spinal metastases. Web to make a sacral diagnosis you will need to know the following: The oblique axis will occur on the side opposite. Sacral tumours and their mimics: A complete history and physical examination are critical. Web the sacrum, as a site of hematopoietic or red marrow in the adult, is a common site for metastatic disease as well as hematologic malignancies.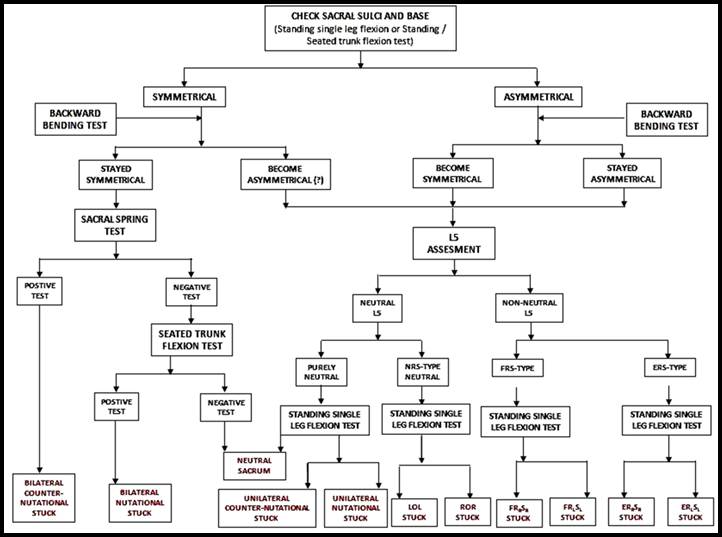
Soccer Syndrome 3 Common Sacral Malalignments and Its Manual

Osteopathic diagnosis of the sacrum. Diagnosis, Positivity, Negativity

Sacral Torsion What Is It, Causes, Treatment, and More Osmosis

Sacral fractures An updated and comprehensive review Injury

SacrumT8 Anatomical Model Clinical Charts and Supplies

Inferior Lateral Angle Of Sacrum Palpation
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sacroiliac-joint-pain-189250-V1-5d9c0b81b3294cb69347d22ef581d05d.jpg)
Una panoramica del dolore articolare sacroiliaco Consiglio Medico

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Schematic illustration demonstrating GCT of the sacrum. Midline tumor
During The Physical Exam, Some Tests May Be Performed, Like A.
Web Sacral Torsions Are Commonly Diagnosed By A Review Of Medical History And A Physical Examination.
Web Diagnosing The Sacrum Includes Three Important Steps:
Pictorial Review And Diagnostic Strategy.
Related Post: