Residual Sugar In Wine Chart
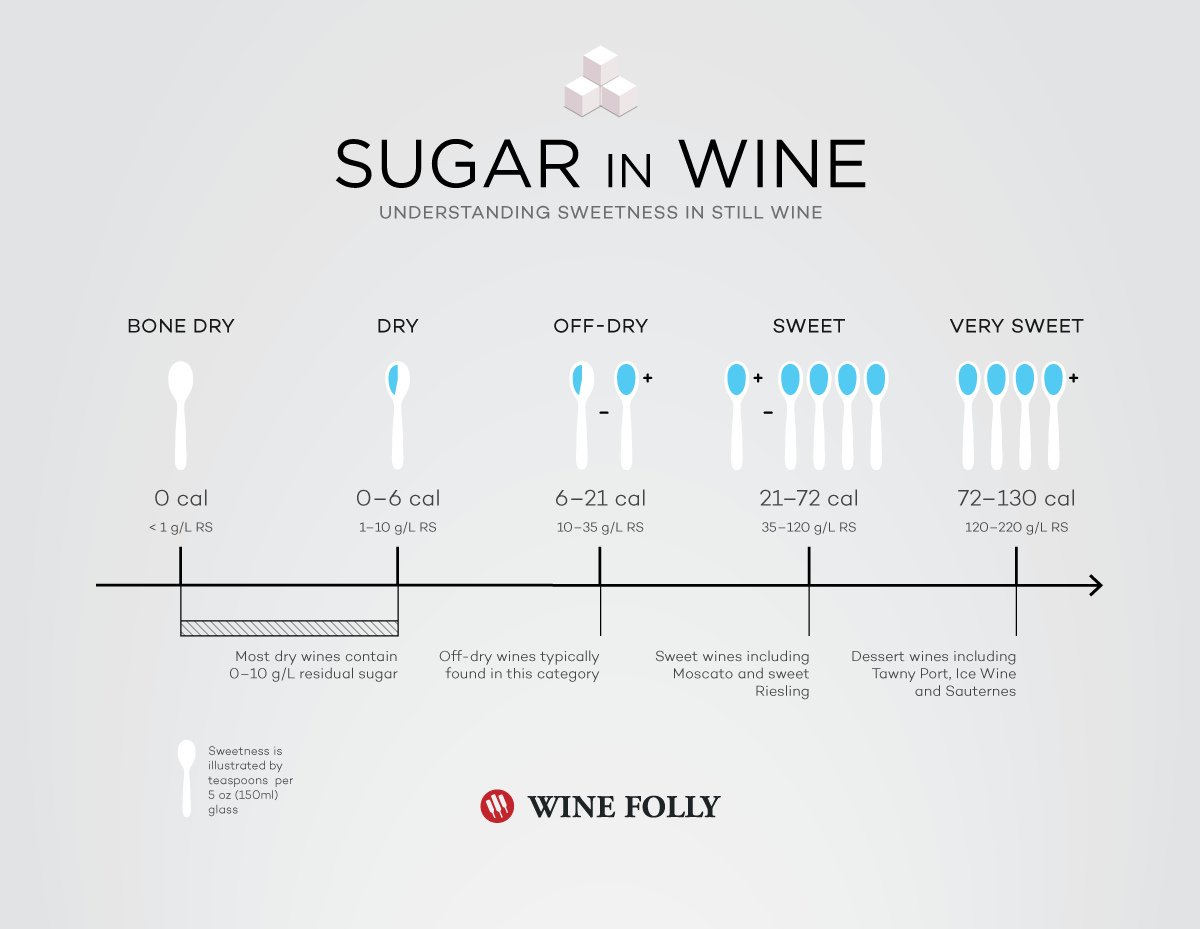
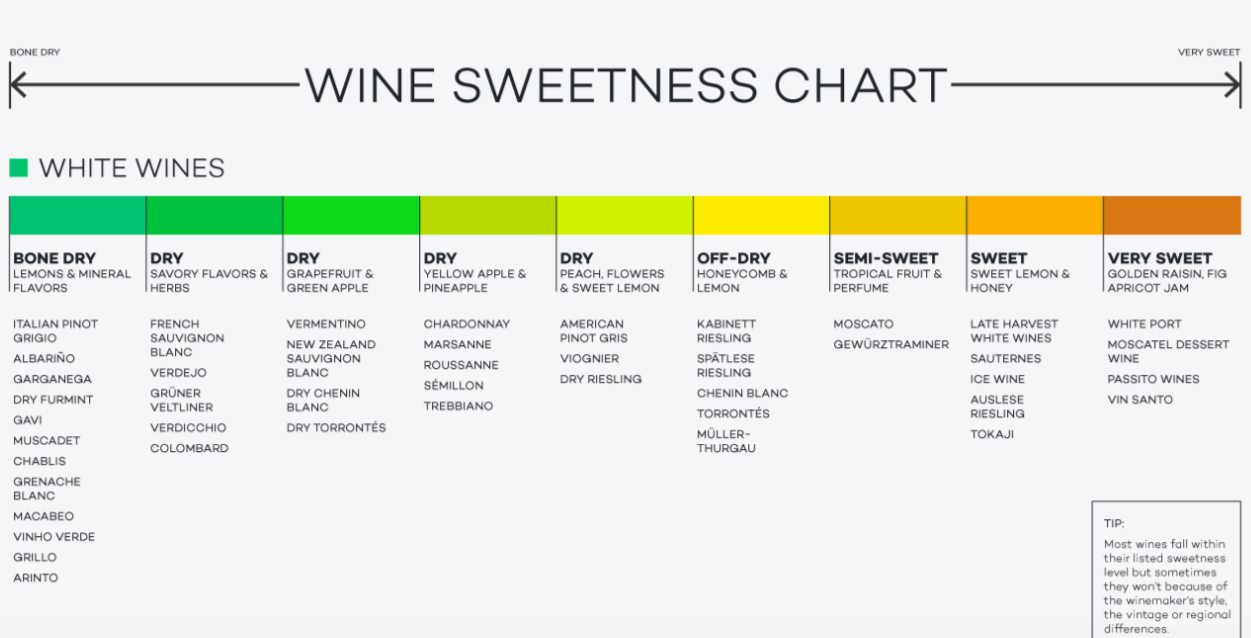
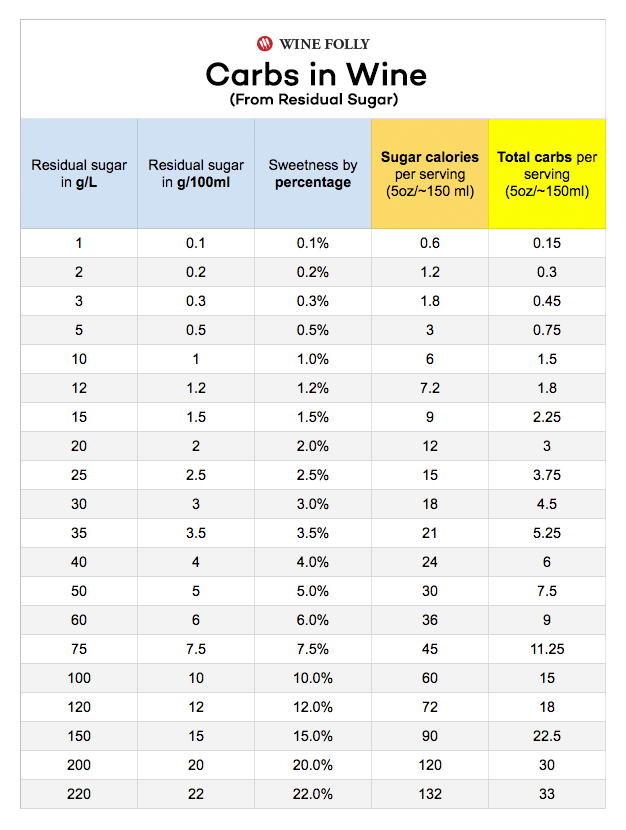
Residual Sugar In Wine Chart - Web residual sugar is usually displayed in 1 of three ways: Wines range from 0 to 220 grams per liter sugar (g/l), depending on the style. Web residual sugar refers to the level of sugar that remains in the wine after fermentation is complete. Web residual sugar is a term commonly used in the wine industry to describe the amount of sugar that remains in the wine after fermentation. Many dry wines have none at all. Web a wine must contain less than 1% residual sugar to be classified as dry. You can use wine tech sheets to find the exact number. Web residual sugars are the grape sugars left over after fermentation in winemaking. (so useful!) when reading a tech sheet: Web you can learn to identify nearly undetectable sweetness in mostly dry wines. This quantity of sugar is hardly detectable by your taste senses. Below 1% sweetness, wines are considered dry. Web they may taste light and fruity, but they are dry because they don't have any residual sugar left in the finished wine. The highlighted wine name will bring you directly to the wine description, food pairing, and much more! Web residual. It is an important factor in determining the sweetness level of a wine. Wines range from 0 to 220 grams per liter sugar (g/l), depending on the style. Just build a repertoire in your memory of wines you’ve tasted that you know to contain residual sugar. A wine sweetness chart categorizes wines based on their rs levels, giving you a. The amount of residual sugar affects a wine’s sweetness and, in the eu, the rs level is linked to specific labelling terms. The only wine chart you will ever need. Check out this chart that compares wine sweetness. It plays a crucial role in determining the taste and style of the wine. Web a regionally developed and adapted dessert apple,. The actual sugar content is measured in grams per liter or g/l: Web residual sugar refers to the level of sugar that remains in the wine after fermentation is complete. Due to the importance of yeast strain on the perceived quality of fermentation products, five commercial yeast strains, three. Web a regionally developed and adapted dessert apple, ‘wodarz’, was explored. It’s measured in grams per liter. This is a measurement of the percentage of sugar in the grape juice at harvest. This is the primary source of a wine's sugar content. Web a regionally developed and adapted dessert apple, ‘wodarz’, was explored for its potential in apple cider production because of its consistent productivity when other apple cultivars have struggled. Web residual sugar (or rs) is from natural grape sugars leftover in a wine after the alcoholic fermentation finishes. It’s measured in grams per liter. So for example, a wine with 10 grams per liter of residual sugar has 1% sweetness or a total of ~1.8 carbohydrates per serving (5 ounces / 150 ml). Web after fermentation, any fermentable sugars. The actual sugar content is measured in grams per liter or g/l: So for example, a wine with 10 grams per liter of residual sugar has 1% sweetness or a total of ~1.8 carbohydrates per serving (5 ounces / 150 ml). (so useful!) when reading a tech sheet: Web a wine must contain less than 1% residual sugar to be. (so useful!) when reading a tech sheet: Many dry wines have none at all. The amount of residual sugar affects a wine’s sweetness and, in the eu, the rs level is linked to specific labelling terms. Up to 4 g/l or up to a maximum of 9 g/l if the total acidity is not lower than 2 g/l below this. Due to the importance of yeast strain on the perceived quality of fermentation products, five commercial yeast strains, three. Typically, wines with less than 10 g/l are considered dry. The amount of residual sugar affects a wine’s sweetness and, in the eu, the rs level is linked to specific labelling terms. Conversely, sweet wine has a considerably greater residual sugar. Web you can learn to identify nearly undetectable sweetness in mostly dry wines. Web there are several different sweetness charts and coding systems on the market, but they’re not that far apart from each other in describing the residual sugar level in wine. Acidity +2 up to a maximum of 9. For example, 10 grams per liter of residual sugar. It is measured by grams of sugar per litre (g/l). Several producers of new zealand sauvignon blanc will leave a couple of grams of residual sugar in their wines because the acidity is. This is the primary source of a wine's sugar content. Typically, wines with less than 10 g/l are considered dry. So for example, a wine with 10 grams per liter of residual sugar has 1% sweetness or a total of ~1.8 carbohydrates per serving (5 ounces / 150 ml). A wine that has higher acidity will taste more ‘dry’ than a wine with less acidity. Or, expressed as a formula: Up to 4 g/l or up to a maximum of 9 g/l if the total acidity is not lower than 2 g/l below this value. Web a regionally developed and adapted dessert apple, ‘wodarz’, was explored for its potential in apple cider production because of its consistent productivity when other apple cultivars have struggled with north dakota’s climate. Web it is important to note that the sweetness of wine is not a measure of sugar content, but rather the amount of residual sugar in a wine after fermentation. Web you can learn to identify nearly undetectable sweetness in mostly dry wines. For example, almost all sparkling wine contains low, but perceptible, levels of sugar. Web the residual sugar in wine varies depending on when fermentation stops. The chart below shows the sweetness of different red and white wines. Web since wine ranges in sweetness, you have to do some research to figure out the actual residual sugar in a specific bottle. This stands for residual sugar and is the measure of sweetness in wine.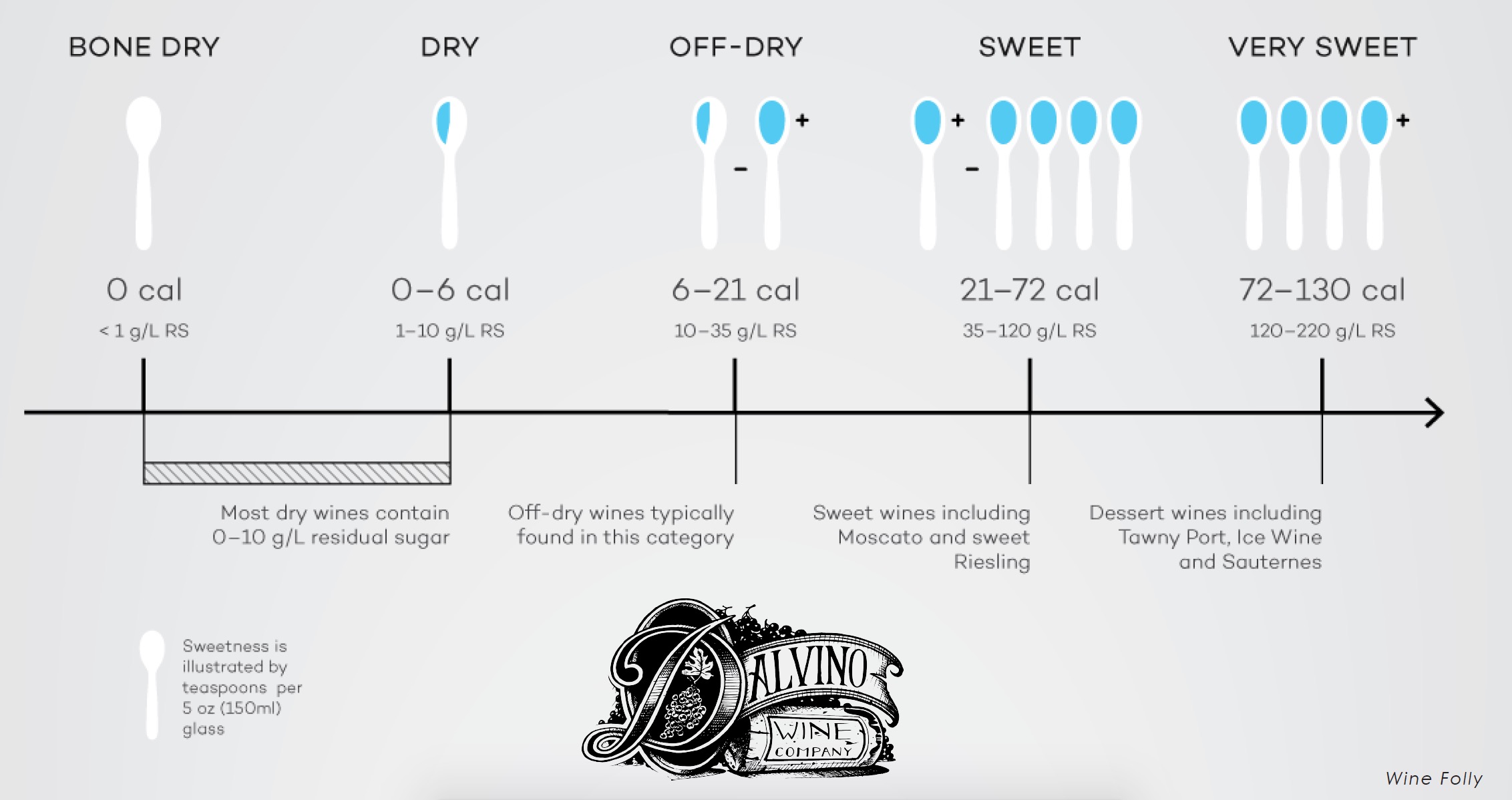
Residual Sugar in Wine and How it's Measured Dalvino Wine Company

Residual Sugar in Wine Chart
Sugar in Wine Chart (Calories and Carbs) Wine Folly
Residual Sugar and Cheap Wines

Residual Sugar In Wine Chart

What is Residual Sugar in Wine? Wine Folly in 2021 Wine folly, Wine

Sugar in Wine Grape to Glass

UNCORKED Wine's residual sugar determines sweetness, dryness
The Reality About Sugar and Carbs in Wine Wine Folly

You're So Sweet All About Residual Sugar in Wine At Home
Web Residual Sugar (Or Rs) Is From Natural Grape Sugars Leftover In A Wine After The Alcoholic Fermentation Finishes.
For Example, 10 Grams Per Liter Of Residual Sugar Is Equal To 1 Percent Sweetness.
Web Residual Sugar Is Usually Displayed In 1 Of Three Ways:
Wines Can Be Classified Based On Their Residual Sugar Content, Ranging From Bone Dry To Lusciously Sweet.
Related Post: