Reinforcement Punishment Chart
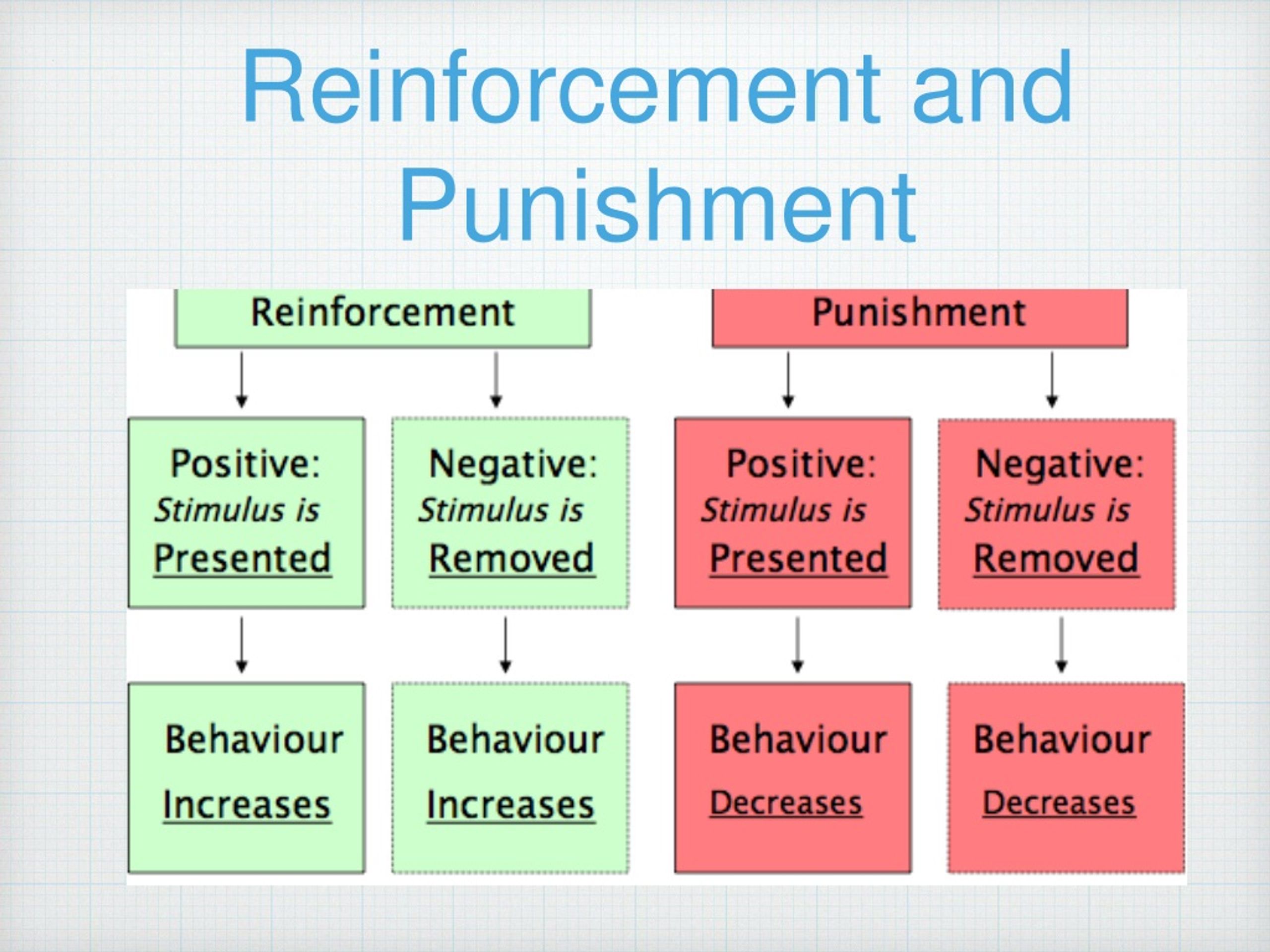
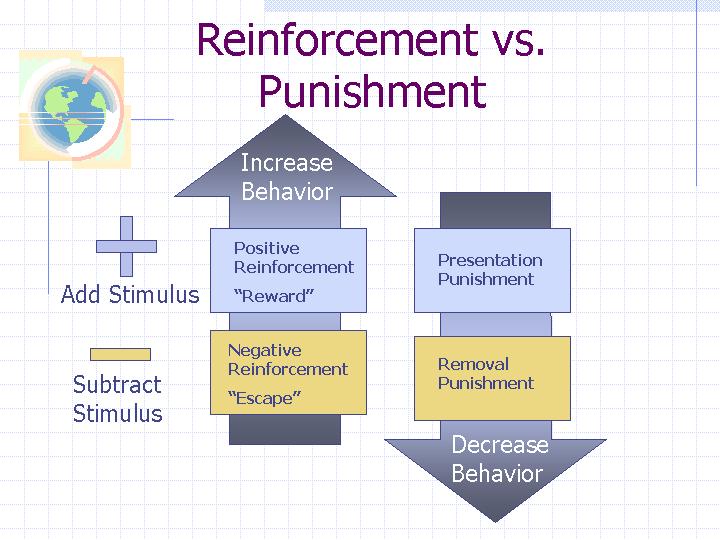
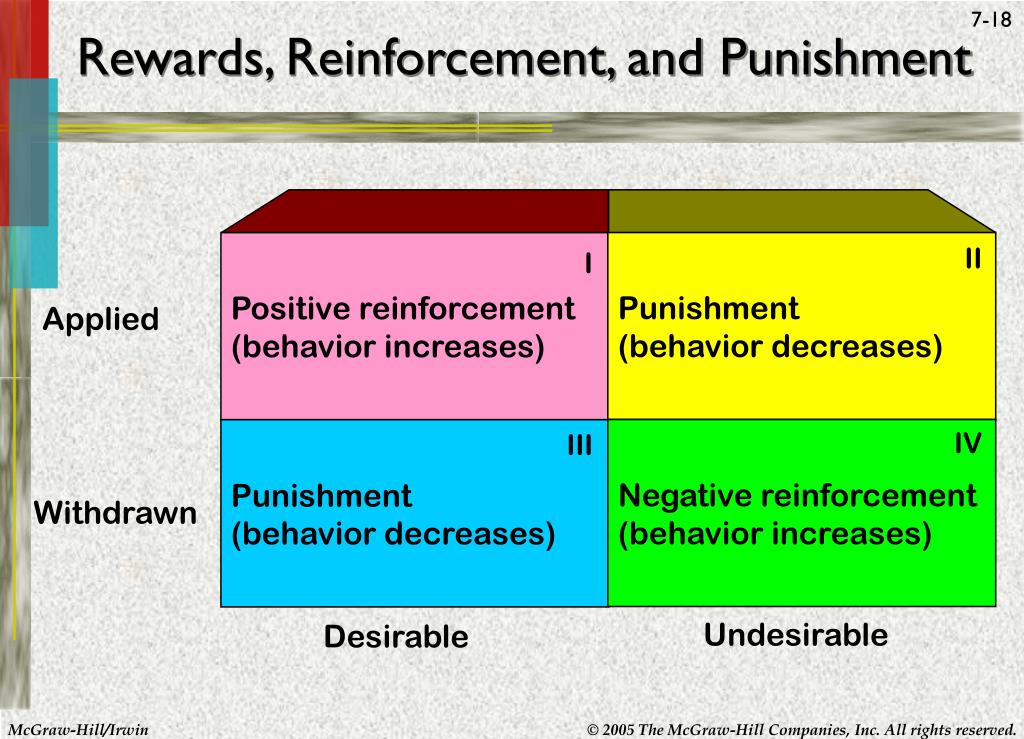
Reinforcement Punishment Chart - Reinforcement aims to encourage a behavior, whereas punishment aims to reduce a behavior. Reinforcement and punishment can also be further broken. All reinforcers (positive or negative) increase the likelihood of a behavioral response. Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. Web in reinforcement, a stimulus is either added (positive reinforcement) or removed (negative reinforcement) to encourage the behavior. Web reinforcement, either positive or negative, works by increasing the likelihood of a behavior. Web the five principles of operant conditioning are positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, positive punishment, negative punishment, and extinction. Web a reinforcement schedule is a rule stating which instances of behavior, if any, will be reinforced. The result of reinforcement will increase the frequency of. Web it's split into two key consequences: For example, spanking a child when he throws a tantrum is an example of positive punishment. Web operant conditioning flow chart what is the goal? Outline the principles of operant conditioning. Extinction occurs when a response is no longer reinforced or punished, which can lead to the fading and disappearance of the behavior. Positive reinforcement is the addition of a. Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. All reinforcers (positive or negative) increase the likelihood of a behavioral response. 8.2 changing behaviour through reinforcement and punishment: All reinforcers (positive or negative) increase the likelihood of a behavioral response. Operant conditioning, or instrumental conditioning, is a theory of learning where. Reinforcement and punishment, each with positive and negative types. The result of reinforcement will increase the frequency of. Web operant conditioning flow chart what is the goal? Outline the principles of operant conditioning. Extinction occurs when a response is no longer reinforced or punished, which can lead to the fading and disappearance of the behavior. Behavior that is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior that is punished will occur less frequently. In contrast, punishment involves adding (positive punishment) or removing (negative punishment) a stimulus to deter the behavior. Web when referring to consequences, positive and negative are used to qualify the type of reinforcement or punishment. However, let’s talk about real life examples. Web thorndike ( 1898, 1911) and skinner ( 1938) have shown that reinforcement (also known as reward) strengthens a behavior, i.e., increases its frequency, whereas punishment weakens a behavior, i.e., decreases its frequency. Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and. Web how it works. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Reinforcement schedules can be divided into two broad categories: Reinforcement and punishment, each with positive and negative types. Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. Negative reinforcement is the removal of a negative outcome to strengthen a behavior. For example, spanking a child when he throws a tantrum is an example of positive punishment. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Operant conditioning, or instrumental conditioning, is a theory of learning where behavior is influenced by. Web operant conditioning flow chart what is the goal? Reinforcement can also be distinguished as primary/secondary and intrinsic/extrinsic. Web here’s an easy chart to try to keep things straight: Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. 8.2 changing behaviour through reinforcement and punishment: Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Web when referring to consequences, positive and negative are used to qualify the type of reinforcement or punishment. Web the five principles of operant conditioning are positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, positive punishment, negative punishment, and extinction. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment. Web reinforcement theory is a framework, also known as operant conditioning, detailed in the chart below: Reinforcement aims to encourage a behavior, whereas punishment aims to reduce a behavior. Web in reinforcement, a stimulus is either added (positive reinforcement) or removed (negative reinforcement) to encourage the behavior. Reinforcement can also be distinguished as primary/secondary and intrinsic/extrinsic. However, let’s talk about. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Web reinforcement theory is a framework, also known as operant conditioning, detailed in the chart below: Positive reinforcement is the addition of a positive outcome to strengthen behavior. Your alarm goes off in the morning and you press the snooze button. 8.2 changing behaviour through reinforcement and punishment: Web when referring to consequences, positive and negative are used to qualify the type of reinforcement or punishment. Web both methods are employed to influence behavior, but positive punishment looks to remove or decrease a “bad” behavior while negative reinforcement seeks to encourage or increase a “good” behavior. For example, spanking a child when he throws a tantrum is an example of positive punishment. Web here’s an easy chart to try to keep things straight: Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Extinction occurs when a response is no longer reinforced or punished, which can lead to the fading and disappearance of the behavior. Web thorndike ( 1898, 1911) and skinner ( 1938) have shown that reinforcement (also known as reward) strengthens a behavior, i.e., increases its frequency, whereas punishment weakens a behavior, i.e., decreases its frequency. Web in reinforcement, a stimulus is either added (positive reinforcement) or removed (negative reinforcement) to encourage the behavior. Web it's split into two key consequences: Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative.
Negative Reinforcement Explained Reinforcement, Negativity, Positive
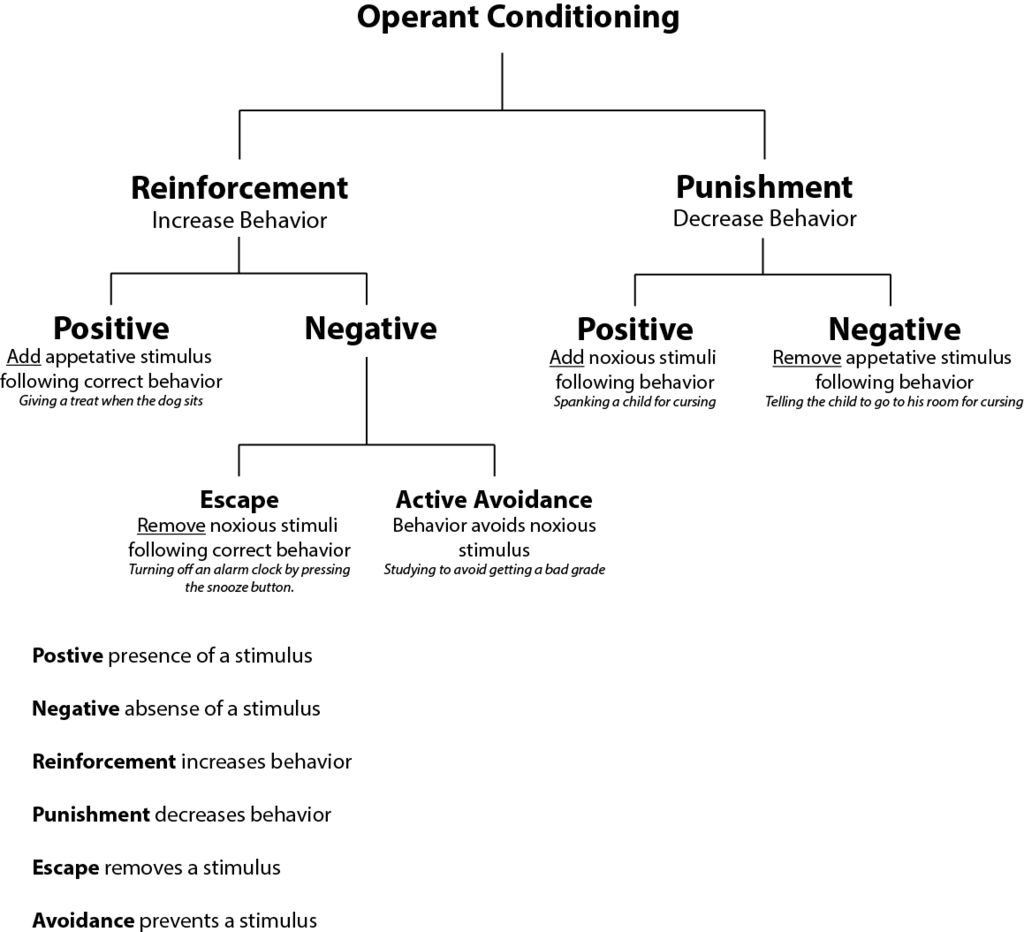
Reading Reinforcement Theory Introduction to Business
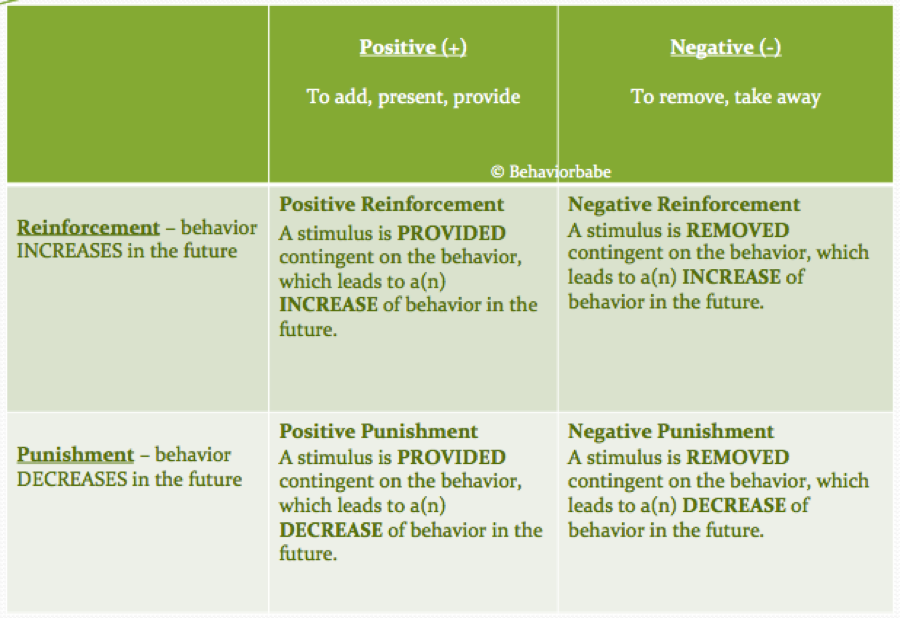
Reinforcement Theory

Reinforcement/Punishment Diagram Quizlet

Positive And Negative Reinforcement Chart
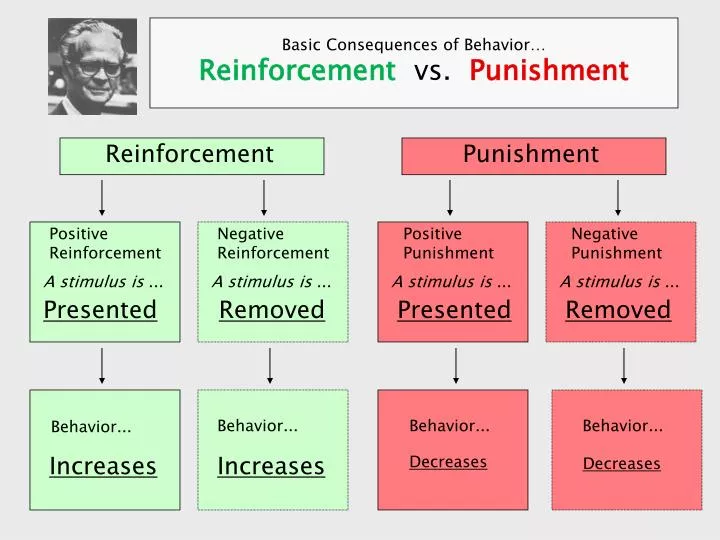
Positive And Negative Reinforcement Chart
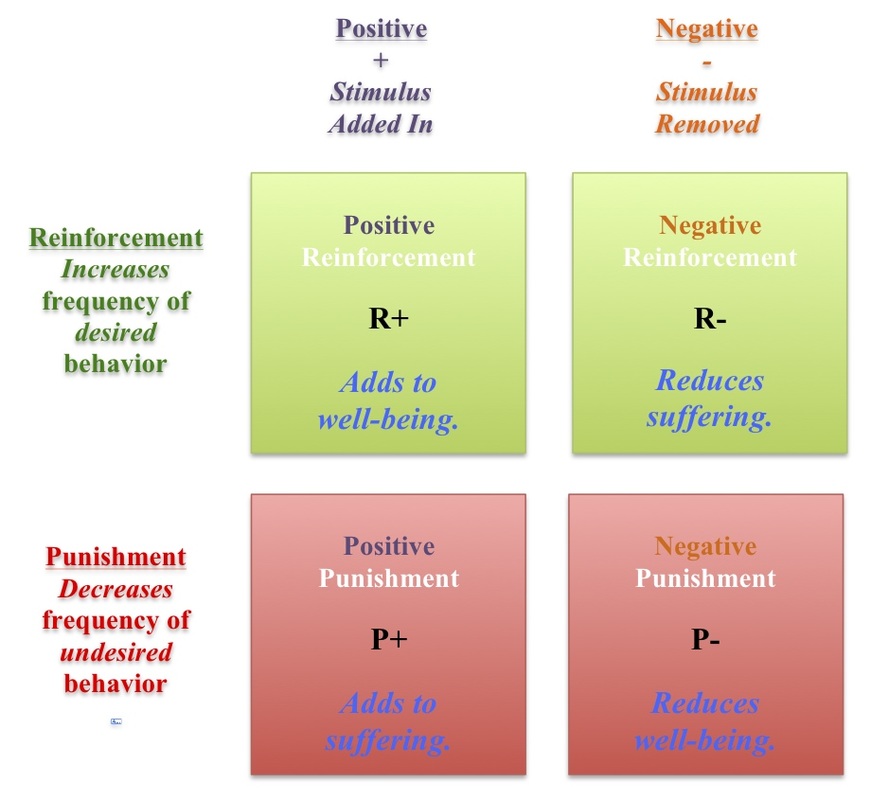
Behavior Management Jon Weinberger Impact of Special Needs
PPT Operant Conditioning PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Psychology Class Chp9.2 Operant Conditioning
PPT Evaluation, Feedback, and Rewards PowerPoint Presentation ID310544
Reinforcement Can Be Positive Or Negative, And Punishment Can Also Be Positive Or Negative.
Continuous Schedules And Partial Schedules (Also Called Intermittent Schedules).
Web Reinforcement Means You Are Increasing A Behavior, And Punishment Means You Are Decreasing A Behavior.
However, Let’s Talk About Real Life Examples (Psst, Most Parents Don’t Care About The Terminology Even If You Think They Should!).
Related Post: