Pie Chart Of The Cell Cycle
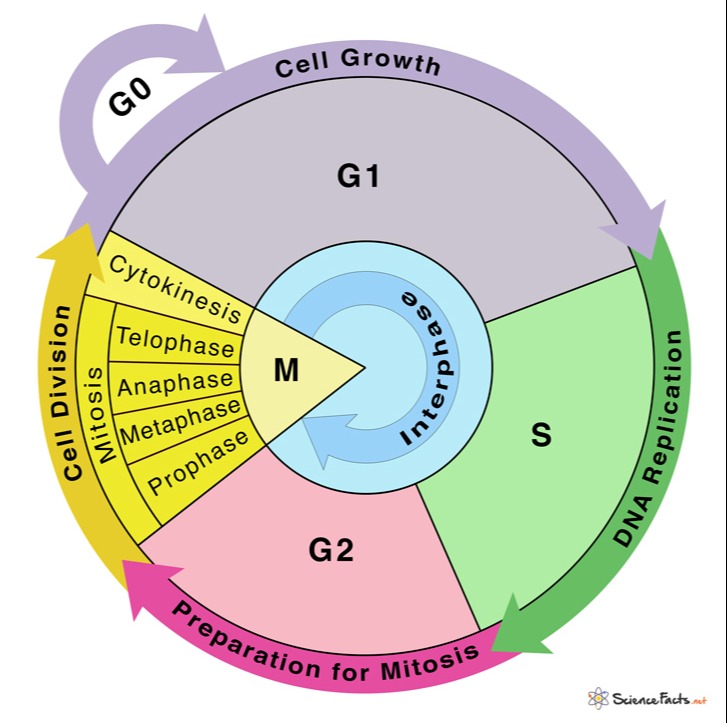
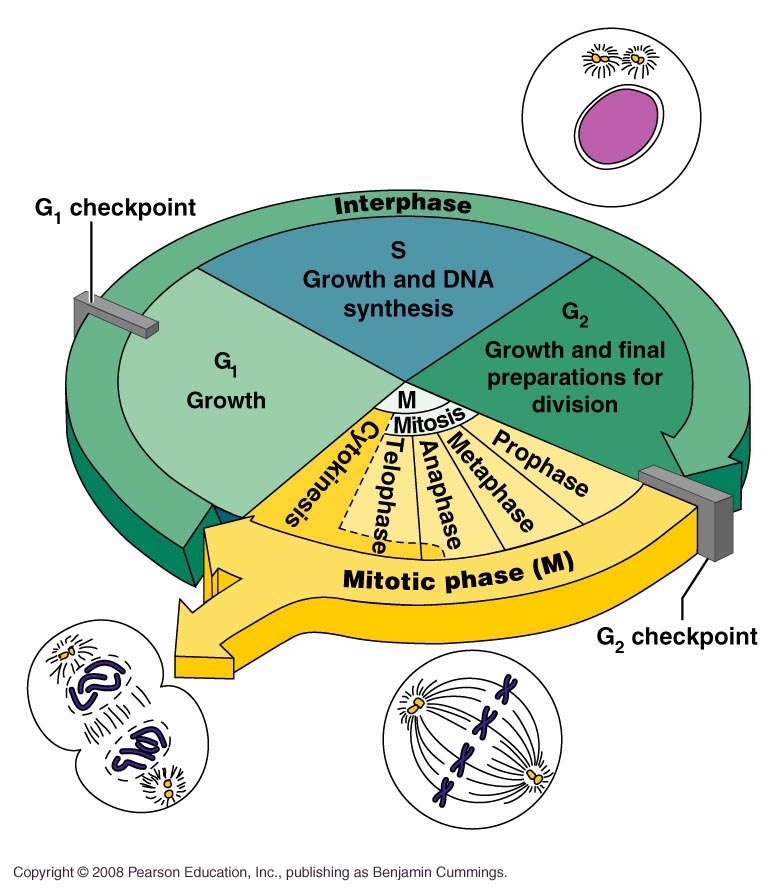
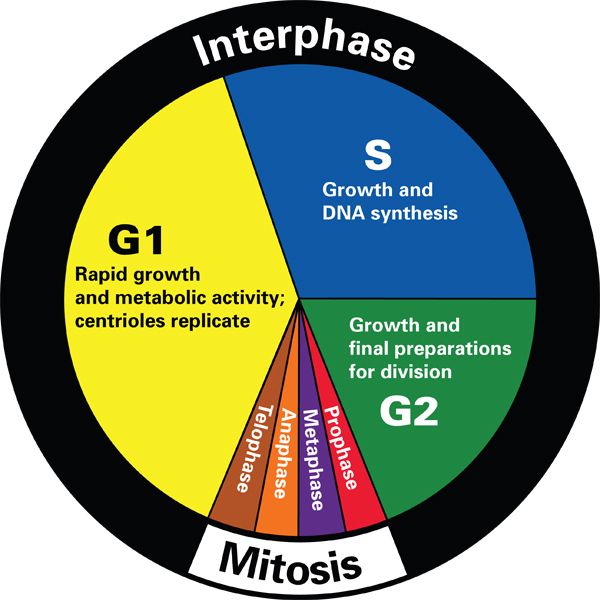
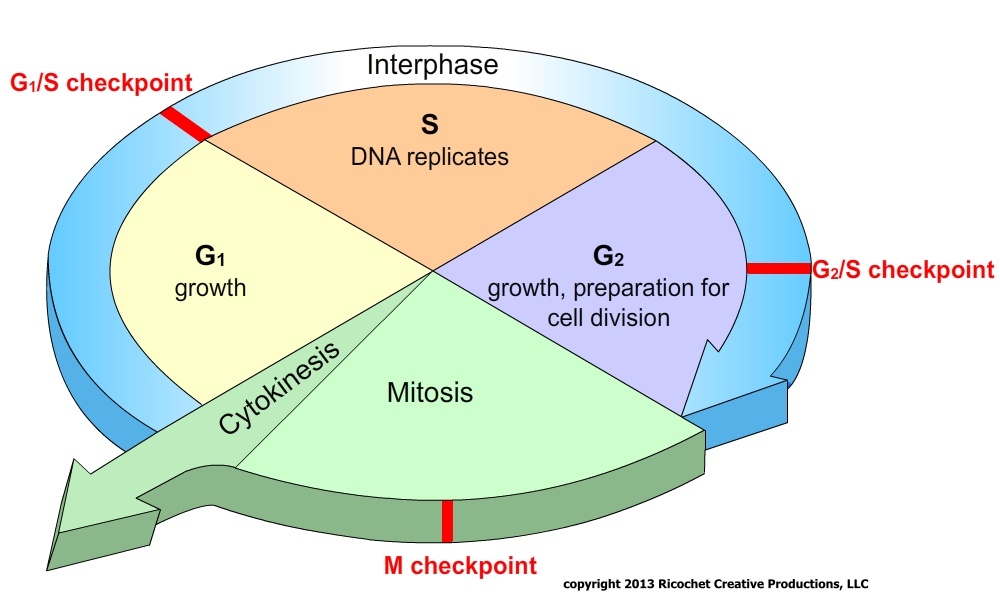
Pie Chart Of The Cell Cycle - Cellular growth and the preparation of cells for division between two successive cell divisions is called the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Web the cell cycle is the repeating pattern of cell growth (increase in size), followed by nuclear and then cytoplasmic division (splitting of one cell to produce identical daughter cells in mitosis, or to produce unique gametes in meiosis). Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Web the cell cycle has three phases: To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is. Milks if you need a quick. What are the two major steps of cell division in a eukaryotic cell? This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. The two broad phases of the cell cycle are interphase and mitosis. The first is marked a, the second. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Which phases of the cell cycle will have cells with twice the amount of dna? The products formed in each round replicate the process in the next round. Web the cell. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. Control of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is divided into several phases; Web what is the cell cycle? The length of these particular cell cycle phases is an. During interphase, cells grow, replicate their dna and organelles, and prepare for division. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. The cell cycle is divided into several phases; Web the figure shows the pie chart of the cell. Web the cell cycle is defined as the events that enable cells to proceed from one cell division event to the next. Cell cycle durations reflect minimal doubling times under ideal conditions. Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. Web stages of the cell cycle. The stages g1, s, and. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. Web the cell cycle is a repeating series of events that include growth, dna synthesis, and cell division. Interphase is divided into three phases: Prokaryotic cells such as bacteria use a process called. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by mitosis and cytokinesis. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cell. Interphase is divided into three phases: Milks if you need a quick. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by mitosis and cytokinesis. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows. The cell grows, its dna replicates, and the cell divides. Gap 1 (g 1), dna synthesis (s), and gap 2 (g 2). Cell division itself consists of the overlapping processes of mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm). Web draw and label a pie chart of the onion root tip cell cycle using the data from your table.. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Web your pie chart should start interphase at 24 hours (like how our clock starts at 12). Web the cell cycle is a repeating series of events that include growth, dna synthesis, and cell division. Web draw and label a pie chart of the onion root tip cell cycle using the. Web why do cells divide? The stages g1, s, and g2 make up interphase, which accounts for the span between cell divisions. The cell cycle is divided into several phases; Cell division itself consists of the overlapping processes of mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm). The length of these particular cell cycle phases is an. Web the cell cycle is the repeating pattern of cell growth (increase in size), followed by nuclear and then cytoplasmic division (splitting of one cell to produce identical daughter cells in mitosis, or to produce unique gametes in meiosis). Web your pie chart should start interphase at 24 hours (like how our clock starts at 12). To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Web draw and label a pie chart of the onion root tip cell cycle using the data from your table. The cell grows, its dna replicates, and the cell divides. Cells divide into new (daughter) cells through a series of events that take place in steps. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. Web the cell cycle has three phases: Milks if you need a quick. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase.
Cell Cycle Graph
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
CSIR LIFE SCIENCE PREPARATION Fundamental Processes Overview of the

cell cycle pie chart Diagram Quizlet
Teaching the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division
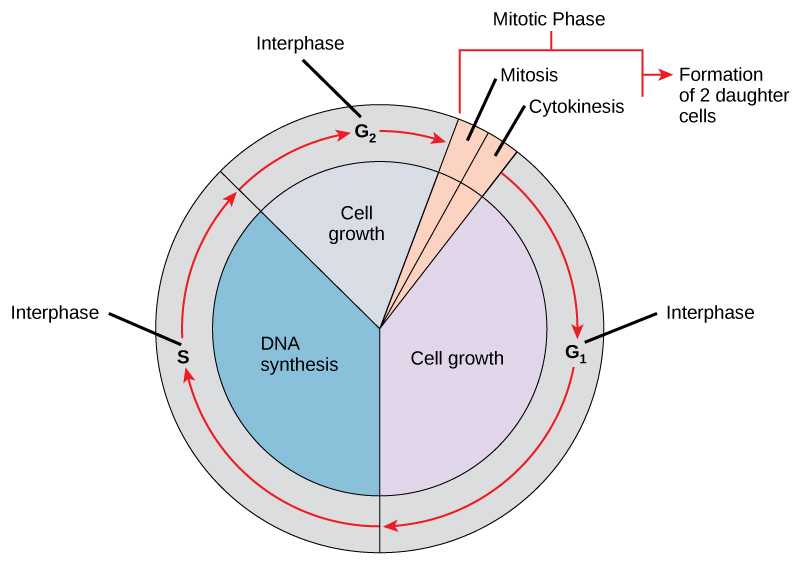
6.2 The Cell Cycle Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Cell cycle pie chart

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
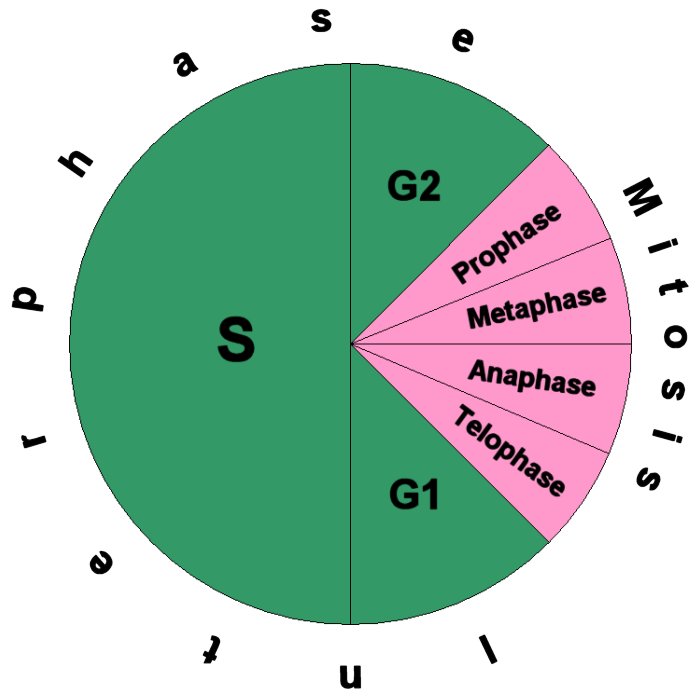
Cell Cycle Diagram ClipArt Best
Web Most Of The Cell Cycle Is The Period During Which The Cell Is Not Dividing, Which Is Called Interphase.
The G 1, S, And G 2 Phases.
Web Each Pie Chart Shows The Fraction Of The Cell Cycle Devoted To Each Of The Primary Stages Of The Cell Cycle.
Cells Divide During Mitosis (M).
Related Post: