Organic Macromolecules Chart
Organic Macromolecules Chart - How are these molecules formed? Typically they are constructed from small, repeating units linked together to form this long chain. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or. Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). In this chapter, these questions will be explored. Web an introduction to the biological macromolecules. Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Web biological macromolecules are organic, meaning they contain carbon and are bound to hydrogen, and may contain oxygen, nitrogen, and additional minor elements. The polymer is more than the sum of. Students will identify and differentiate carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins/amino acids. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Click the card to flip 👆. Read chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. Web our main classes of organic compounds are essential to the life processes of all living things: All living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Organic macromolecule (polymer), monomer is saccharide (monosaccharide) (sugar molecule) (one saccharide can be considered a carbohydrate), made of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen (in a fixed ratio of 1:2:1) They can have very different shapes,. Web introduces main organic macromolecules found in living organisms. The polymer is more than the sum of. Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. A single cell can contain thousands of proteins, each with a unique function. This unit is part of the biology library. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as a whole. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Within all. Typically they are constructed from small, repeating units linked together to form this long chain. You will see that although these compounds are built primarily from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, these atoms occur in different ratios in each class of compound. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? They usually also contain hydrogen and oxygen, as well. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Define the term “macromolecule” distinguish between the 4 classes of macromolecules. They usually also contain hydrogen and oxygen, as well as nitrogen and additional minor elements. Students will identify and differentiate carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins/amino acids. Web biological macromolecules are organic, meaning they contain carbon and are bound to. They are small, simple compounds that play important roles in the cell, although they do not form cell structures. Organic macromolecule (polymer), monomer is saccharide (monosaccharide) (sugar molecule) (one saccharide can be considered a carbohydrate), made of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen (in a fixed ratio of 1:2:1) Web organic macromolecules graphic organizer. Web glycerol is a small organic molecule with. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? They are small, simple compounds that play important roles in the cell, although they do not form cell structures. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Read chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. Students will identify and differentiate carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins/amino acids. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web our main classes of organic compounds are essential to the life processes of all living things: What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? They usually also contain hydrogen and oxygen,. You will use this when you do your macromolecule flapbook. How are these molecules formed? All living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or. What functions do they serve? This small difference is enough for enzymes to tell glucose and galactose apart, picking just one of the sugars to take part in chemical reactions 1. They usually also contain hydrogen and oxygen, as well as nitrogen and additional minor elements. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web biological macromolecules are organic, meaning they contain carbon and are bound to hydrogen, and may contain oxygen, nitrogen, and additional minor elements. Web an introduction to the biological macromolecules. The polymer is more than the sum of. Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Organic macromolecule (polymer), monomer is saccharide (monosaccharide) (sugar molecule) (one saccharide can be considered a carbohydrate), made of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen (in a fixed ratio of 1:2:1) Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web macromolecules are very large molecules.
Worksheets On Macromolecules
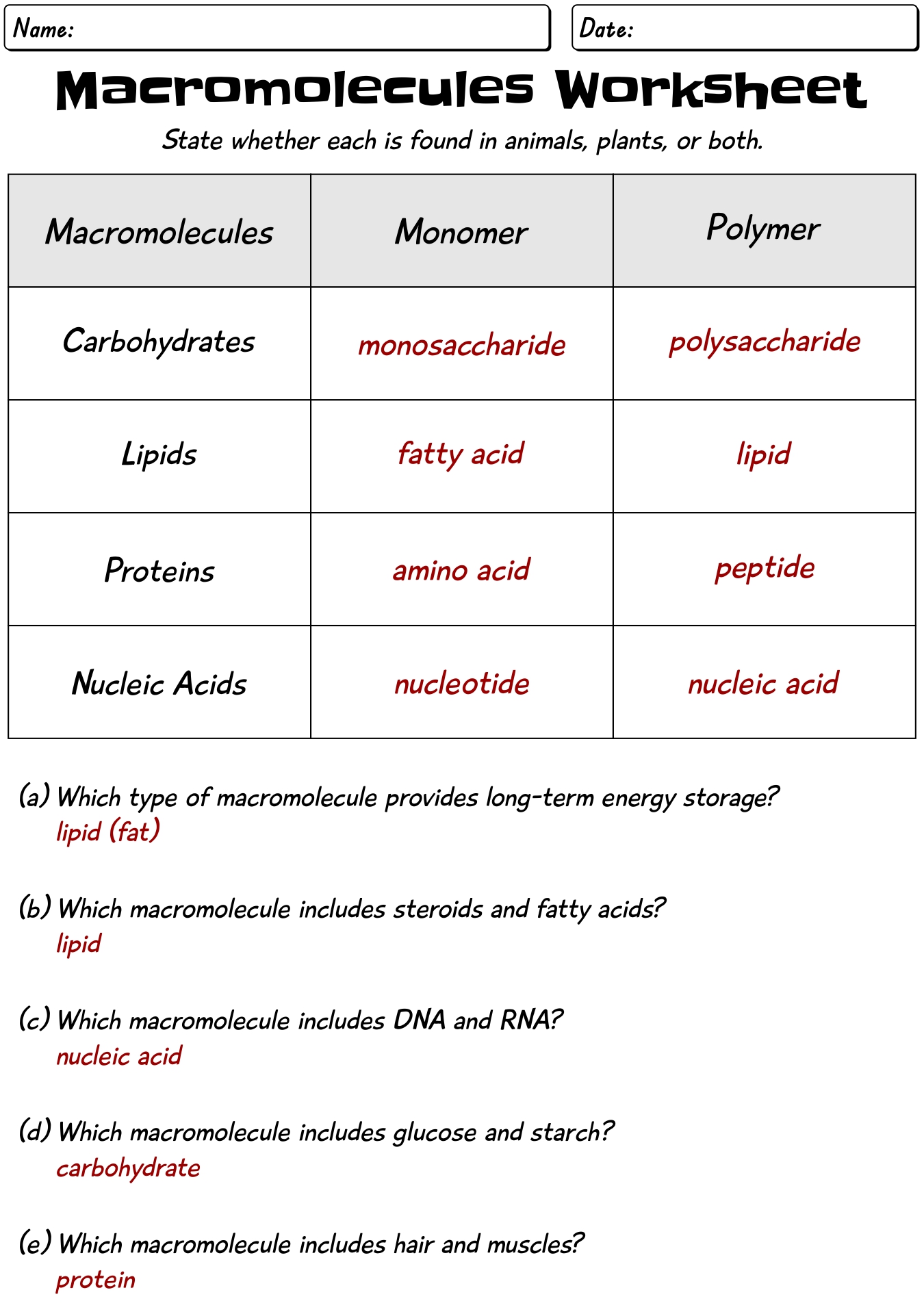
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /
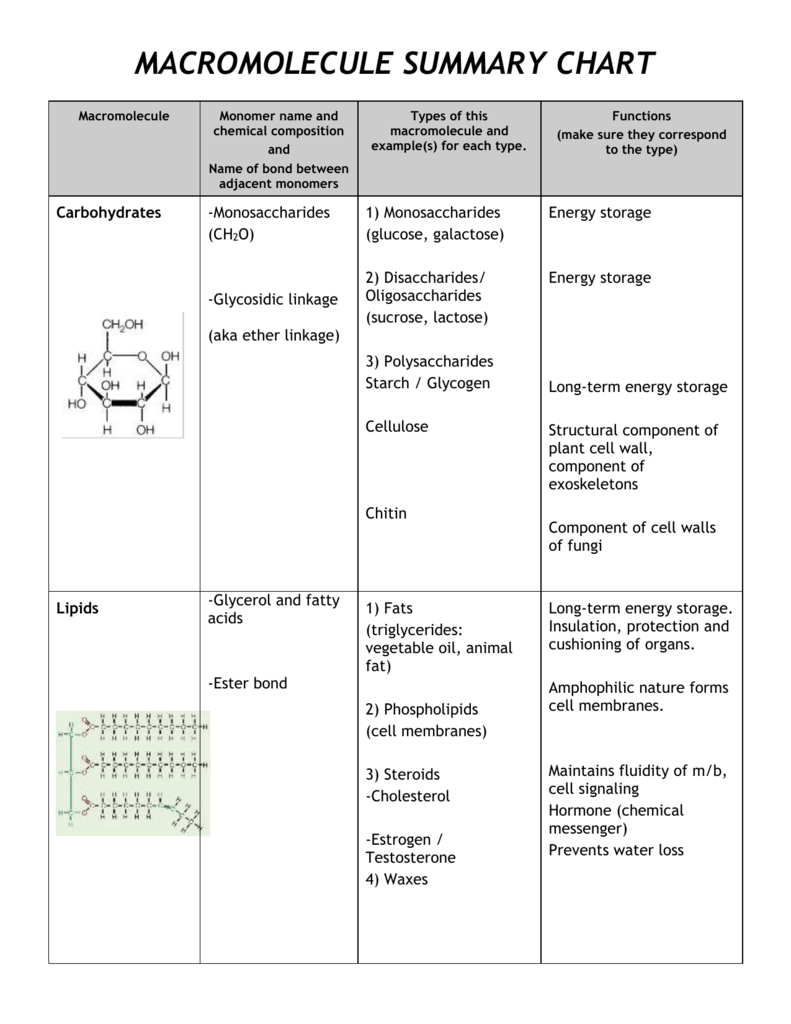
Four Macromolecules Chart
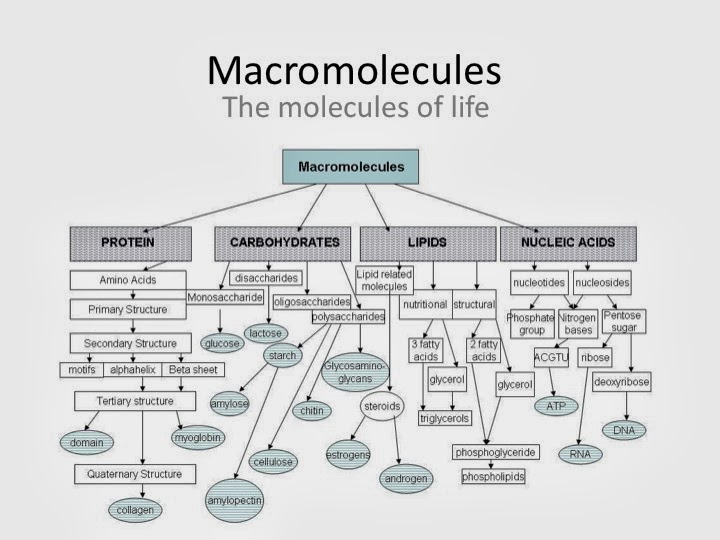
403 Forbidden

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
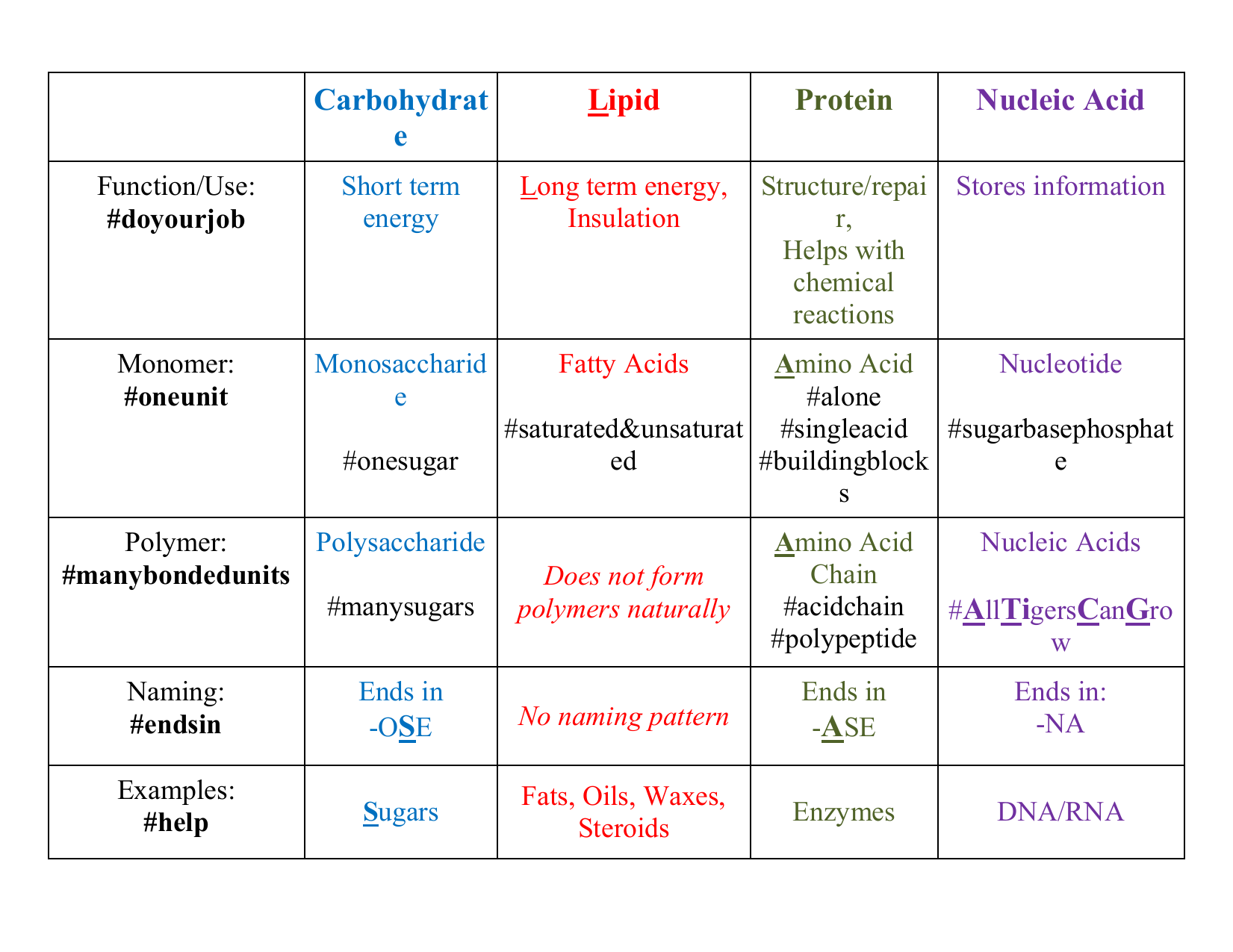
Organic Molecule Chart
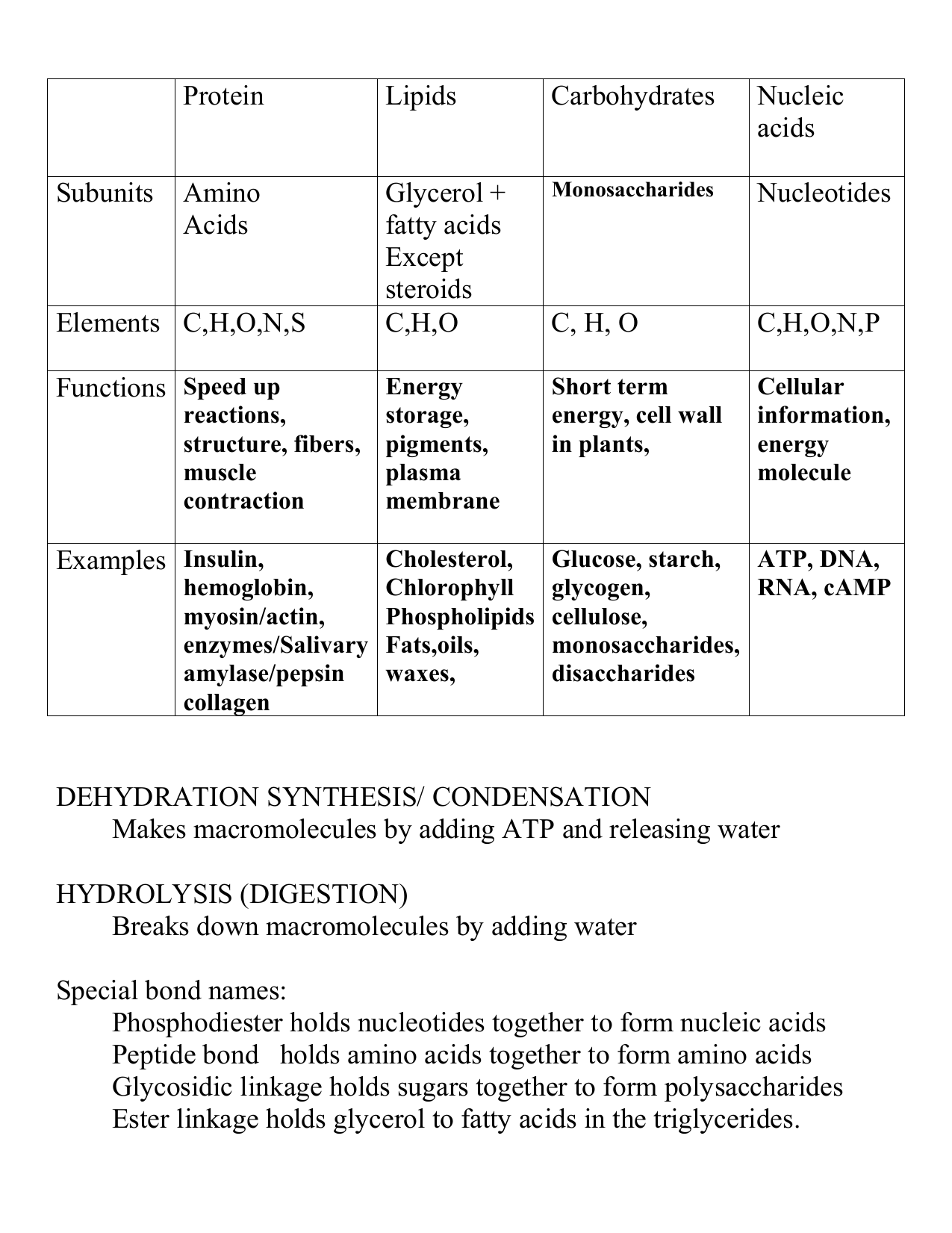
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

macromolecules comparison table
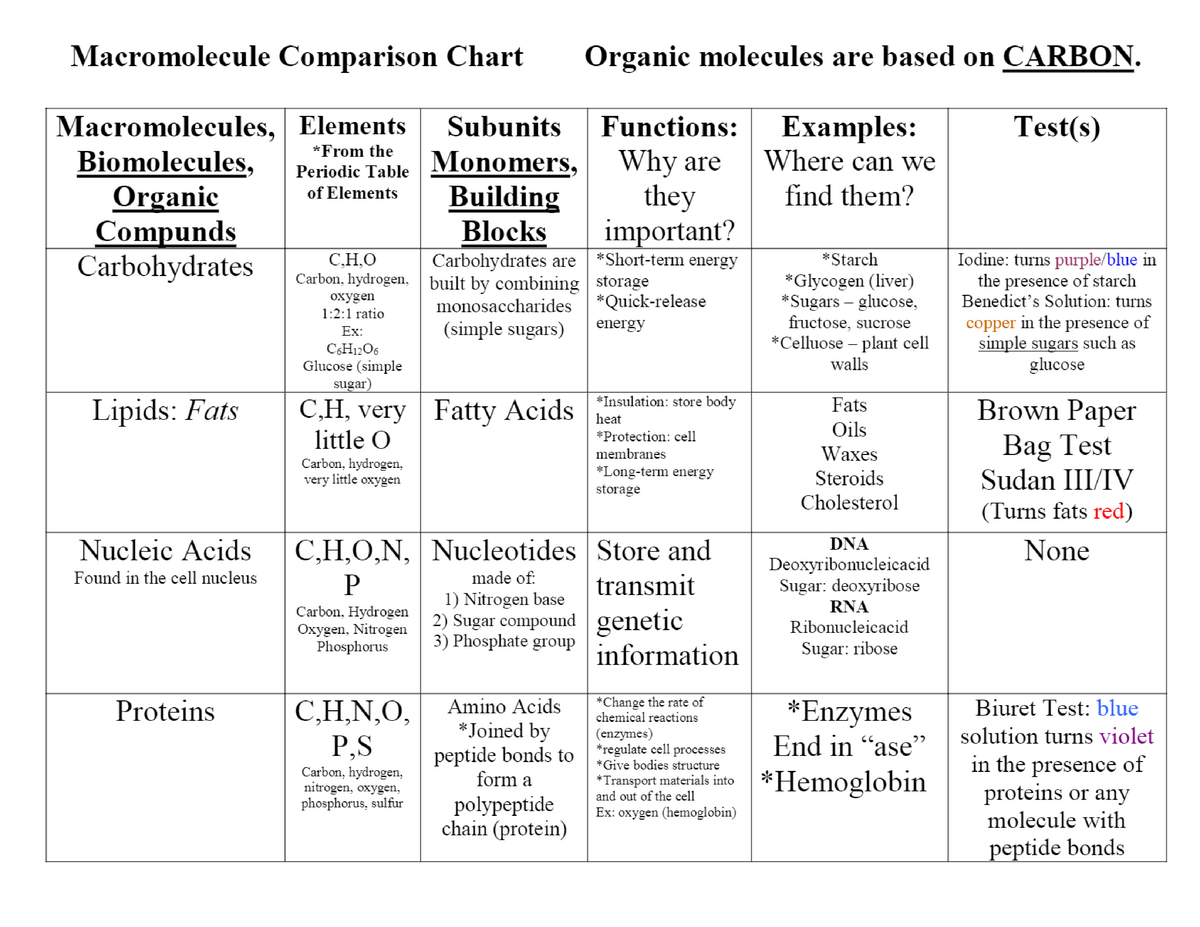
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu

Organic Molecules Chart Organic Molecules Contrast Chart
What Specific Types Of Biological Macromolecules Do Living Things Require?
Web You Can See This In The Diagram As A Switch In The Orientation Of The Hydroxyl ( Oh ) Group, Marked In Red.
Click The Card To Flip 👆.
Macromolecules Are Made Up Of Single Units Known As Monomers That Are Joined By Covalent Bonds To Form Larger Polymers.
Related Post: