Nutrition Density Chart
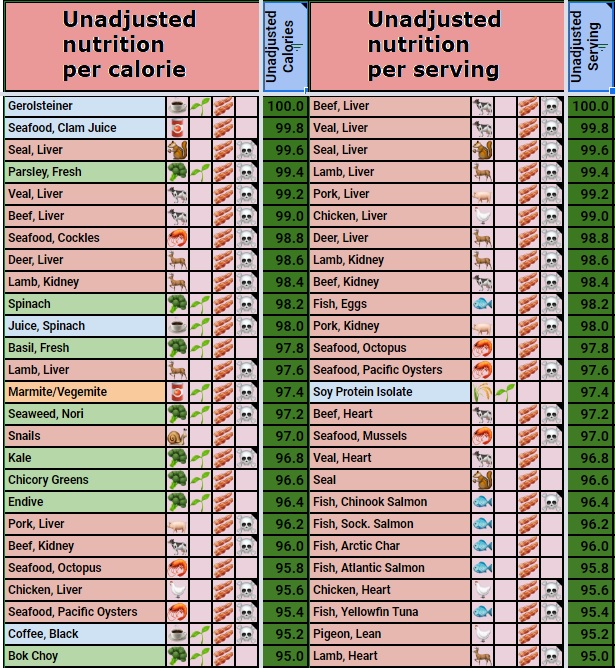
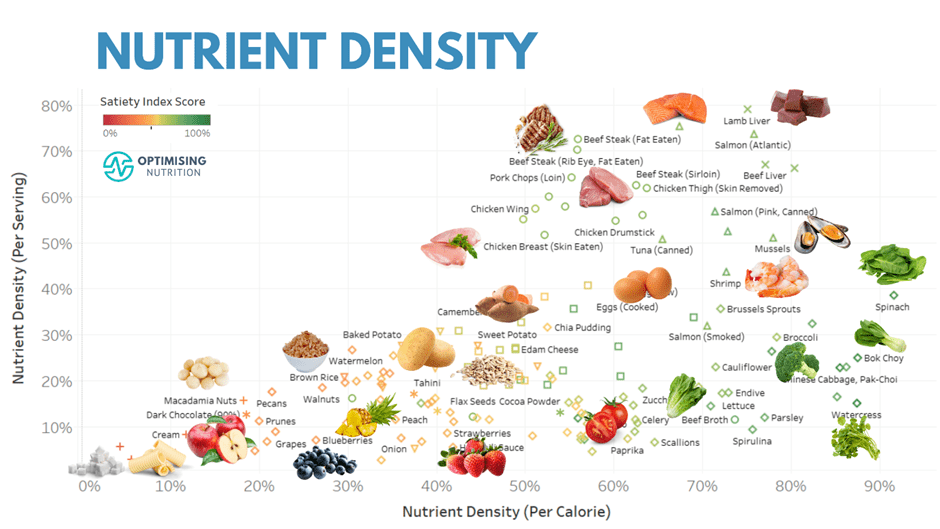
Nutrition Density Chart - Web we find that the top sources of priority micronutrients are organs, small fish, dark green leafy vegetables, bivalves, crustaceans, goat, beef, eggs, milk, canned fish with bones, mutton, and lamb. What are the methods used to measure nutrients per 100 grams of food? What is nutrient density and why is it important? Web what food composition data compilation method does your company use? Why does bioavailability matter in the context of nutrition from real foods? The nutrient adequacy of a diet is typically assessed by comparing estimated nutrient intakes with established average nutrient requirements. This comprehensive chart amalgamates three potent nutritional scoring systems to provide a clear, intuitive roadmap to making food choices that resonate with your unique dietary goals and preferences. Why do different food databases show different measurements for the same food? Why is thiamin important for the body? What is the difference between energy density and nutrient density? How many different nutrients does the human body require? Web what are nutrient dense foods? Does thiamin convert to other nutrients within the body? Why do different food databases show different measurements for the same food? Web click to read the nutrient density chart’s substack, by the nutrient density chart ®️, a substack publication. Because recommended intakes for micronutrients for any given age, sex, or physiological group do not vary by energy requirements, the total energy consumed is not taken into. Web what are nutrient dense foods? What are the essential bodily functions that thiamin supports? Why does bioavailability matter in the context of nutrition from real foods? Fuhrman created the andi (aggregate nutrient. Vitamins a, c, and e; Web nutrient profile models calculate the content of key nutrients per 100 g, 100 kcal, or per serving size of food. Web this extensive guide elucidates nutrient density, unveils a meticulous nutrient density chart, and offers insightful tactics to harness the full spectrum of essential nutrients. How is thiamin absorbed and metabolized in the body?. Web the nutrient density chart® (digital chart) provides a comprehensive and accessible way to engage with nutritional data. What are examples of high nutrient dense foods? Are there any specific prerequisites for the effective utilization of thiamin in the body? Rating the nutrient density of foods. Web nutrient profile models calculate the content of key nutrients per 100 g, 100. Web click to read the nutrient density chart’s substack, by the nutrient density chart ®️, a substack publication. To find out more about how the nutrients were scored to create the above chart, please visit: What is nutrient density and why is it important? The nutrient density chart’s substack. What is the difference between energy density and nutrient density? Why is thiamin important for the body? The nourished by science nutrient density scores are a measure of the amounts of the most important micronutrients in a food, relative to the calorie content of that food. How do you account for the bioavailability of nutrients in real foods? How many different nutrients does the human body require? Web click to. Why do different food databases show different measurements for the same food? To find out more about how the nutrients were scored to create the above chart, please visit: Does thiamin convert to other nutrients within the body? Web the final nrf9.3 index was based on 9 beneficial nutrients (protein; Web we find that the top sources of priority micronutrients. Web what are nutrient dense foods? Web we find that the top sources of priority micronutrients are organs, small fish, dark green leafy vegetables, bivalves, crustaceans, goat, beef, eggs, milk, canned fish with bones, mutton, and lamb. How is thiamin absorbed and metabolized in the body? Vitamins a, c, and e; Web what food composition data compilation method does your. And magnesium) and on 3 nutrients to limit (saturated fat, added sugar, and sodium). Web what food composition data compilation method does your company use? What are the essential bodily functions that thiamin supports? What is nutrient density and why is it important? Does thiamin convert to other nutrients within the body? Because recommended intakes for micronutrients for any given age, sex, or physiological group do not vary by energy requirements, the total energy consumed is not taken into. Does thiamin convert to other nutrients within the body? Vitamins a, c, and e; Soy is exalted as a health food by some, with claims of taming hot flashes, warding off osteoporosis, and. Soy is exalted as a health food by some, with claims of taming hot flashes, warding off osteoporosis, and protecting. Why do different food databases show different measurements for the same food? How many different nutrients does the human body require? In a nutshell, the higher the nutrient density score of a food, the higher its content of critical micronutrients per calorie. Web nutrient profile models calculate the content of key nutrients per 100 g, 100 kcal, or per serving size of food. This comprehensive chart amalgamates three potent nutritional scoring systems to provide a clear, intuitive roadmap to making food choices that resonate with your unique dietary goals and preferences. Nutrient content of foods, expressed per reference amount, typically 100 kcal, 100 g, or per serving. Web what food composition data compilation method does your company use? Why does bioavailability matter in the context of nutrition from real foods? The nutrient density chart’s substack. The nutrient adequacy of a diet is typically assessed by comparing estimated nutrient intakes with established average nutrient requirements. Rating the nutrient density of foods. The nourished by science nutrient density scores are a measure of the amounts of the most important micronutrients in a food, relative to the calorie content of that food. Are there any specific prerequisites for the effective utilization of thiamin in the body? Web what are nutrient dense foods? Fuhrman created the andi (aggregate nutrient density index) to show how popular foods stack up in terms of micronutrient density per calorie.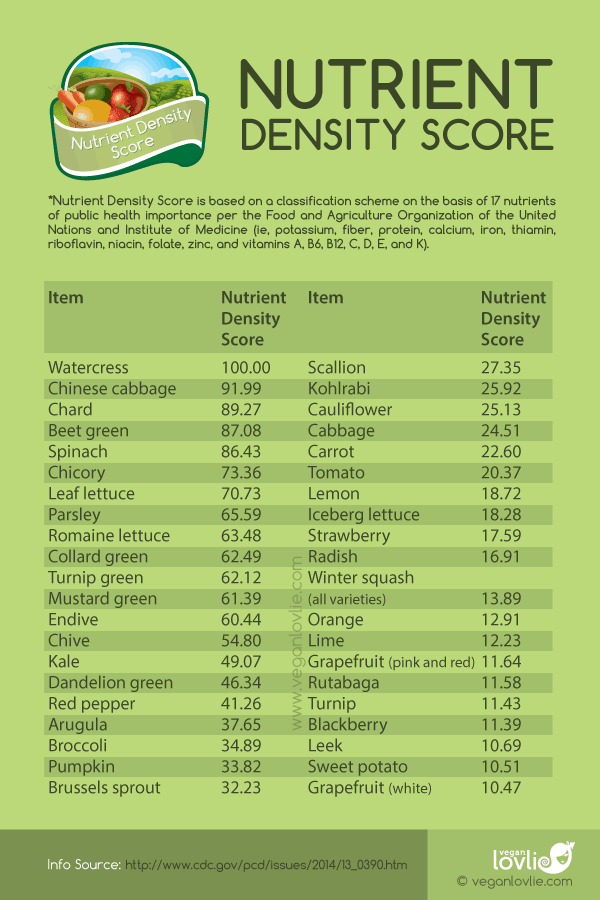
Nutrient Density Food Chart

Aggregate Nutrient Density Index or ANDI Score The Guide
Nutrient Density Food Chart

Nutrient and Caloric Density Cracking the nutrition code for good

Nutrient Density Part 2 Incorporating Nutrient Density into your Diet

A handy chart ranking foods by nutrient density. How does your plate

Why Nutrient Density Is a Mustfollow Thing Useful Tips on What Foods
Unlock Nutrient Density for a Healthier You A Comprehensive Guide

nutrient density chart Nutrient Density Dr. Fuhrman’s ANDI (Nutrient

Calorie Density Chart. Healthy Eating Concept. Editable Vector
High In Omega 3S And Minerals.
What Are The Methods Used To Measure Nutrients Per 100 Grams Of Food?
Web We Find That The Top Sources Of Priority Micronutrients Are Organs, Small Fish, Dark Green Leafy Vegetables, Bivalves, Crustaceans, Goat, Beef, Eggs, Milk, Canned Fish With Bones, Mutton, And Lamb.
Does Thiamin Convert To Other Nutrients Within The Body?
Related Post: