Nerve Innervation Chart
Nerve Innervation Chart - Web below is a chart that outlines the main functions of each of the spine nerve roots: They are the structures through which the central nervous system (cns) receives sensory information from the periphery, and through which the activity of the trunk and the limbs is regulated. Web all innervate the lower limb and the pelvic region (figure 12.4.9 12.4. Web spinal nerves are an integral part of the peripheral nervous system (pns). Also they transmit the motor commands from the cns to the muscles of the. Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. Web its sensory fibers provide cutaneous innervation to the scalp, neck, chest, and axilla, as well as proprioceptive innervation of the same area via the lesser occipital nerve (c2 to c3), the great auricular nerve (c2, c3), transverse cervical nerve (c2, c3), and the supraclavicular nerve (c3, c4). Nerves of the lower limb. Web we’ve created muscle anatomy charts for every muscle containing region of the body: Axillary, musculocutaneous, median, radial, and ulnar nerves. Web click on your choice below: Also they transmit the motor commands from the cns to the muscles of the. Web below is a chart that outlines the main functions of each of the spine nerve roots: Web explore the nervous system with innerbody's interactive guide. Web the somatic, voluntary, nervous system is responsible for providing sensory and motor innervation. While the structure of a nerve is simple, their functions, innervations and nomenclature can be complex. Nerve cells are also called neurons. Web the 30 dermatomes explained and located. This is a list of muscle innervations grouped by nerves and includes the spinal nerve roots that contribute to the innervation of each muscle. 9 and figure 12.4.10 12.4. Web the 30 dermatomes explained and located. Its small branches innervate anterior thigh muscles and receives sensory information from the anterior and medial aspects of the thigh. The cranial nerves are a set of twelve nerves that originate in the brain. There’s also a quick dermatomal map and myotomal chart for easy reference. For example, upper limb muscles are grouped. The nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses (action potentials) are generated. Web all innervate the lower limb and the pelvic region (figure 12.4.9 12.4. They include the olfactory nerve, which is. Web below is a chart that outlines the main functions of each of the spine nerve roots: In this article, we break down. Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. The central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). While the structure of a nerve is simple, their functions, innervations and nomenclature can be complex. Nerves of the pelvis & perineum. Web we’ve created muscle anatomy charts for every muscle containing. They include the olfactory nerve, which is. The sciatic nerve is a terminal branch of the sacral plexus. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. The cranial nerves are a set of twelve nerves that originate in the brain. Each chart groups the muscles of that region into its component groups, making your revision a. For example, upper limb muscles are grouped by shoulder and arm, forearm and. Web below is a chart that outlines the main functions of each of the spine nerve roots: While the structure of a nerve is simple, their functions, innervations and nomenclature can be complex. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. Web explore. 9 and figure 12.4.10 12.4. Axillary, musculocutaneous, median, radial, and ulnar nerves. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating or digesting food. Web neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. It is important to mention that after the spinal nerves exit from the spine, they join together to form four. In this article, we break down the different types of nerves, as well. Web spinal nerves are an integral part of the peripheral nervous system (pns). Web all innervate the lower limb and the pelvic region (figure 12.4.9 12.4. Web knowing muscle innervations is an important skill for medical professionals such as physical therapists, physicians, and occupational therapists. Web nerves. Web spinal nerves are an integral part of the peripheral nervous system (pns). It is important to mention that after the spinal nerves exit from the spine, they join together to form four paired clusters of. While the structure of a nerve is simple, their functions, innervations and nomenclature can be complex. Web we’ve created muscle anatomy charts for every. The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is. In other words, it carries sensations from the body (pain, touch, temperature, proprioception) and innervates skeletal muscles that are under conscious, or voluntary control. Web the nervous system has two major parts: Web nerves of the upper limb. Its small branches innervate anterior thigh muscles and receives sensory information from the anterior and medial aspects of the thigh. Clinically relevant nerves to the lower extremity. Web the somatic, voluntary, nervous system is responsible for providing sensory and motor innervation to skin, muscles and sensory organs. Each has a different function responsible for sense or movement. The cranial nerves are a set of twelve nerves that originate in the brain. Web neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. View detailed diagrams of the brain, spinal cord, and other nervous system structures. It is formed from both anterior and posterior divisions of the anterior (ventral) rami of spinal nerves l4 through s3. This is a list of muscle innervations grouped by nerves and includes the spinal nerve roots that contribute to the innervation of each muscle. A dermatome is an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve. They are the structures through which the central nervous system (cns) receives sensory information from the periphery, and through which the activity of the trunk and the limbs is regulated. Web its sensory fibers provide cutaneous innervation to the scalp, neck, chest, and axilla, as well as proprioceptive innervation of the same area via the lesser occipital nerve (c2 to c3), the great auricular nerve (c2, c3), transverse cervical nerve (c2, c3), and the supraclavicular nerve (c3, c4).
Upper Limbs Nervous System Poster Anterior Chartex

Nervous System Anatomy Posters Set of 6 Etsy Nervous system anatomy
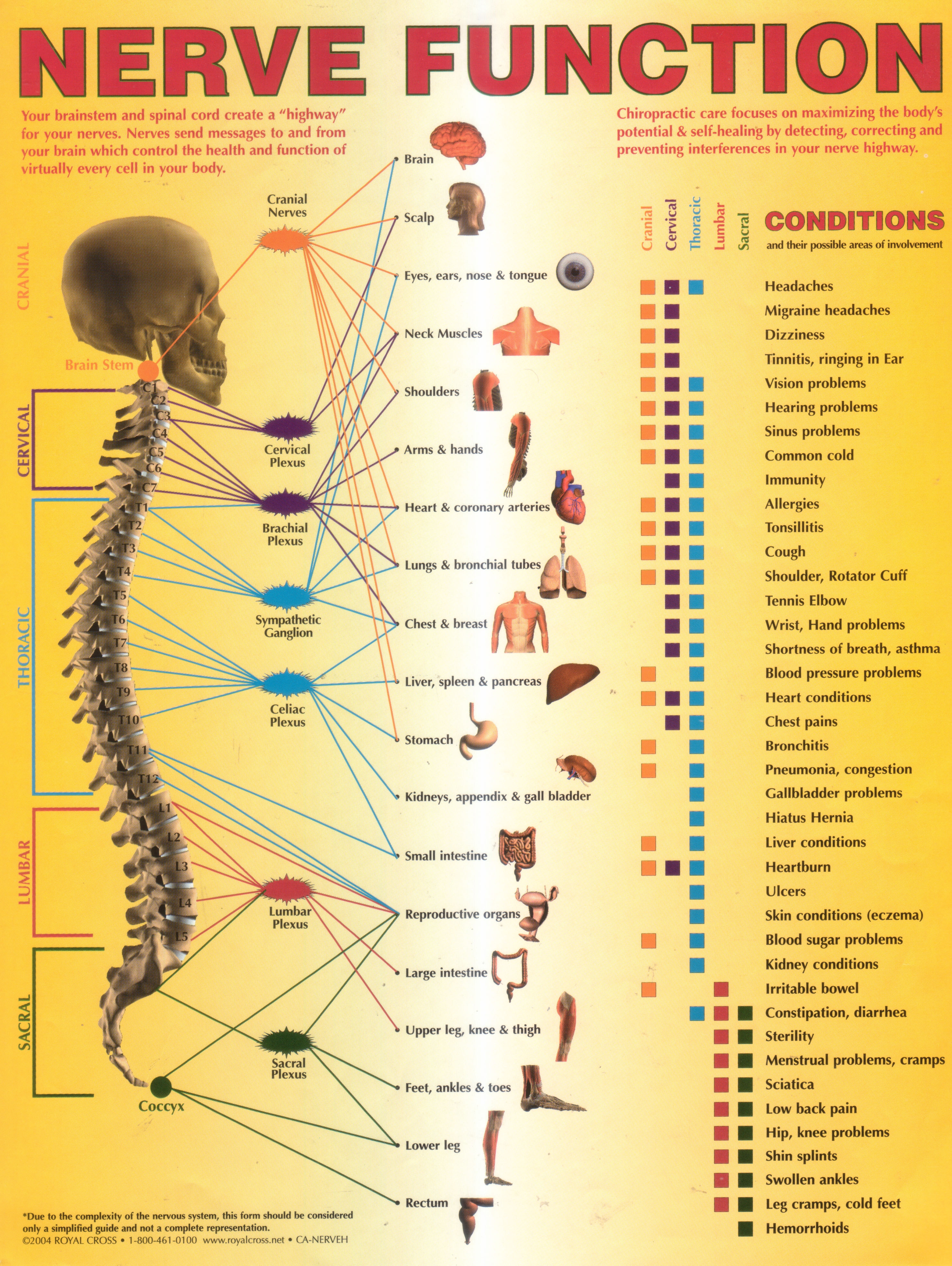
Annual World Spine Day Campaign Nerve Function Chart
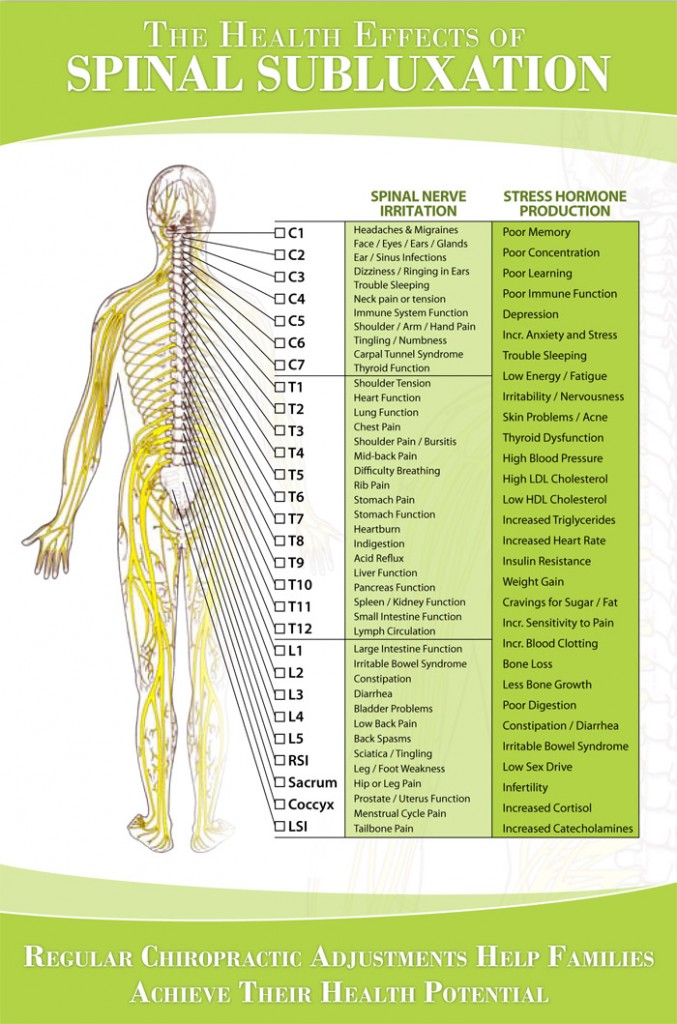
Nerve Chart Hunter Chiropractic Wellness Centre
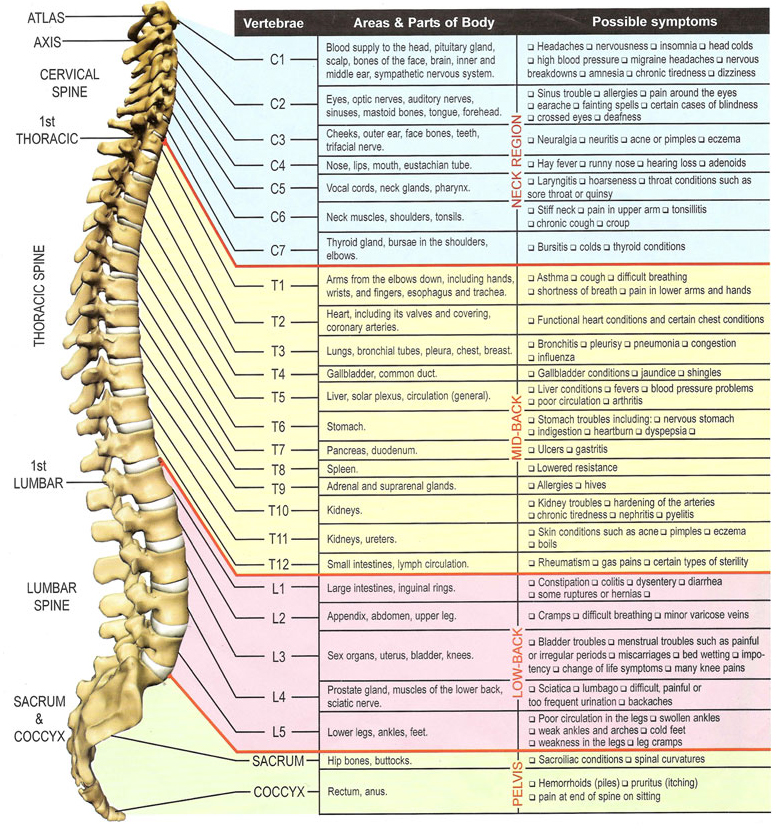
Lumbar Spinal Nerve Chart

Nerve compression causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment

Upper Extremity Nerve Innervation Chart

Anatomy Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord And Nerves Youtube vrogue.co

upper extremity peripheral nerves netter Google Search Thần kinh

Spinal Nerve Function Anatomical Chart Anatomy Models and Anatomical
For Example, Upper Limb Muscles Are Grouped By Shoulder And Arm, Forearm And.
Web Click On Your Choice Below:
It Is Important To Mention That After The Spinal Nerves Exit From The Spine, They Join Together To Form Four Paired Clusters Of.
Every Neuron Consists Of A Body (Soma) And A Number Of Processes (Neurites).
Related Post: