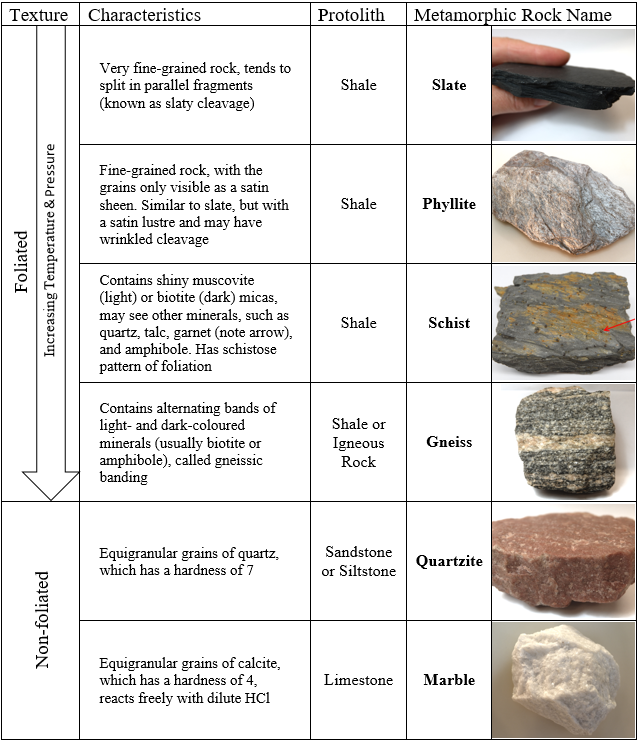
Metamorphic Rock Identification Chart
Metamorphic Rock Identification Chart - Web 9 metamorphic rock identification match the name to the rock: Dense, microscopic grains, may exhibit slight sheen (or dull luster). Simply put, metamorphism occurs when a previously existing rock, the parent rock, is buried in the earth under. Describe what a contact aureole is and how contact metamorphism affects surrounding rock. Web 12.001 introduction to geology, blank chart for metamorphic rocks. Web metamorphic buried hills are characterized as fractured reservoirs with immense potential for hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation. Web metamorphic rocks form by subjecting a rock (protolith) to pressure, temperature, and chemically active fluids. If foliation is present, noting the type of foliation will allow you to identify the rock. A rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Limestone / calcite original rock will fizz when an acid (vinegar) is dropped on the surface. Drag the rock name to the correct rock. Sedimentary rocks originate when particles settle out of water or air, or by precipitation of minerals from water. Dense, microscopic grains, may exhibit slight sheen (or dull luster). Rocks fall into one of these categories depending. These rocks start out as igneous or sedimentary rocks (or metamorphic) and are altered or rearranged by a combination of heat and pressure. A rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. Mostly white from pure quartz mineral, may have some small amount of other minerals (does not fizz) marble. If the rock is. Generalized rock identi cation chart for common metamorphic rocks. Explain how metamorphic facies relate to plate tectonic processes. There is no evidence of foliation. Mostly white from pure quartz mineral, may have some small amount of other minerals (does not fizz) marble. A rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. There are two basic types of metamorphic rocks. Web metamorphic rocks form by subjecting a rock (protolith) to pressure, temperature, and chemically active fluids. In this study, we established a new. Generalized rock identi cation chart for common metamorphic rocks. Indicate in the name (s) of the probable parent rock (s) in the last column of the metamorphic rock identification. Identifying their effective reservoirs is crucial for prioritizing exploration and development efforts. Please note that you can expand this image to fill the screen by clicking on the blue arrows on the right side of the diagram. A very hard rock with a granular appearance and a glassy lustre. There are two basic types of metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks originate. Explain what foliation is and how it results from directed pressure and recrystallization. Use mineral id skills to help distinguish among some of these! Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Simply put, metamorphism occurs when a previously existing rock, the parent rock, is buried in the. Web 9 metamorphic rock identification match the name to the rock: Simply put, metamorphism occurs when a previously existing rock, the parent rock, is buried in the earth under. Light / white, pink, yellow,tan, green. Identify and describe the three principal metamorphic agents. Identify the properties and the names of the 8 unknown metamorphic rocks. In this study, we established a new. The classification of metamorphic rocks is based on the minerals that are present and the temperature and pressure at which these minerals form. A rock with visible crystals of mica and with small crystals of andalusite. Describe what a contact aureole is and how contact metamorphism affects surrounding rock. Identify the properties and. Metamorphic rocks have been modified by heat, pressure, and chemical processes, usually while buried deep below earth's surface. A rock is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals or mineraloids. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. Light / white, pink, yellow,tan,. Here are some tips for distinguishing them from igneous or sedimentary rocks, as well as for identifying specific types of metamorphic rocks: Explain how metamorphic facies relate to plate tectonic processes. When identifying metamorphic rocks, it is common for geologists to focus on specific ‘indicator minerals’ that serve as clues about the degree of metamorphism a rock has undergone. If. Explain how metamorphic facies relate to plate tectonic processes. Limestone / calcite original rock will fizz when an acid (vinegar) is dropped on the surface. Rocks undergoing metamorphism will experience changes in both composition and texture. Describe what a contact aureole is and how contact metamorphism affects surrounding rock. Finally, compare the properties of your rock to those of known rock types while looking for other identifying characteristics. The classification of metamorphic rocks is based on the minerals that are present and the temperature and pressure at which these minerals form. However, current methods are inadequate for such reservoirs. Describe the role of hydrothermal metamorphism in. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Here are some tips for distinguishing them from igneous or sedimentary rocks, as well as for identifying specific types of metamorphic rocks: Drag the rock name to the correct rock. Web metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone a change from their original form due to changes in temperature, pressure or chemical alteration. Web metamorphic rocks form by subjecting a rock (protolith) to pressure, temperature, and chemically active fluids. Use mineral id skills to help distinguish among some of these! In this study, we established a new.
Metamorphic Parent Rock Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Metamorphic Rocks Examples With Names

Metamorphic Rocks Definition, Formation, Types, & Examples

Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Rock Chart
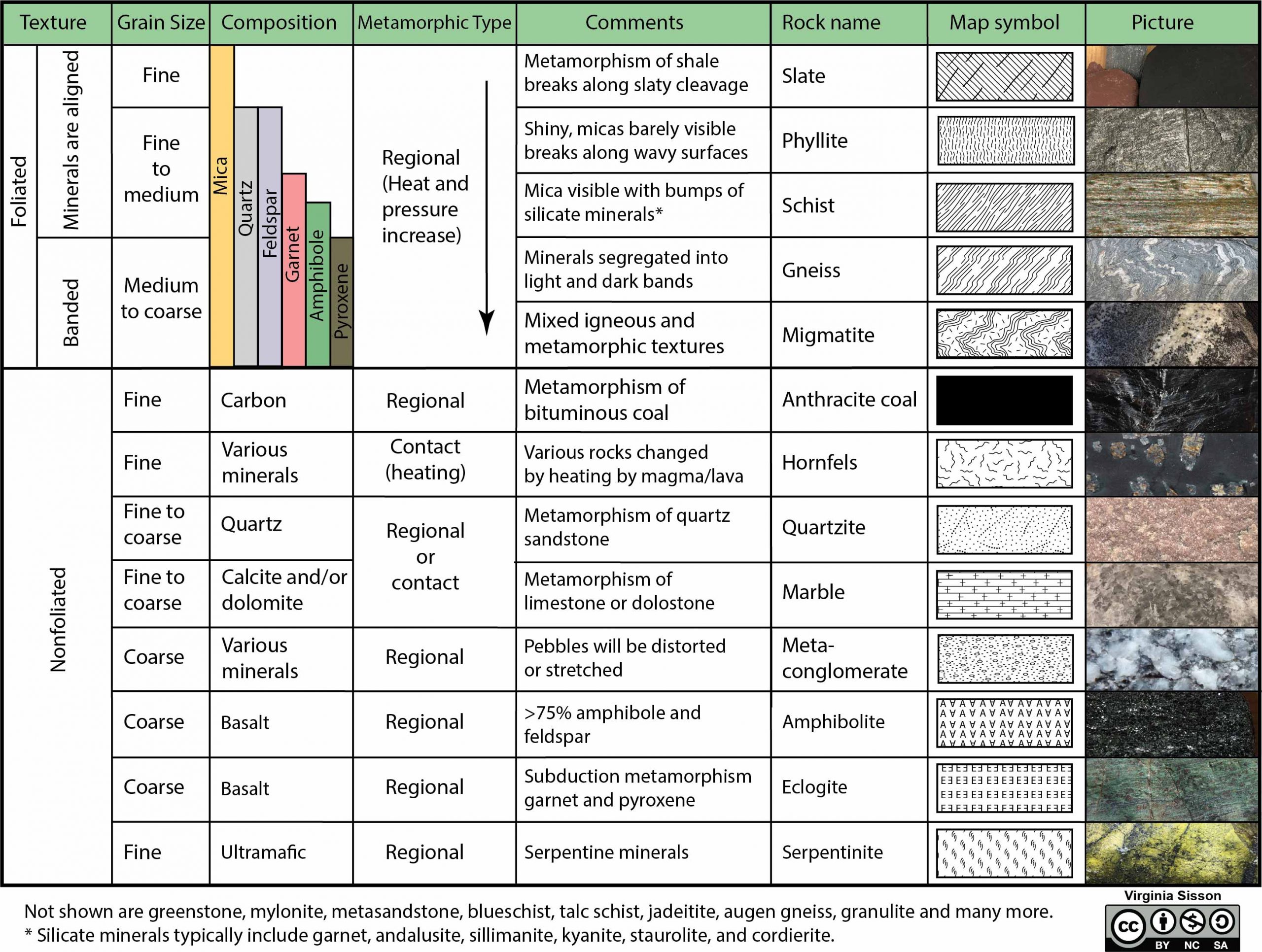
Chapter 2 Earth Materials The Story of Earth An Observational Guide

MR15PM Collection of 15 Metamorphic Rocks PM.jpg (1778×1357) Rock

Metamorphic Rock Identification Chart
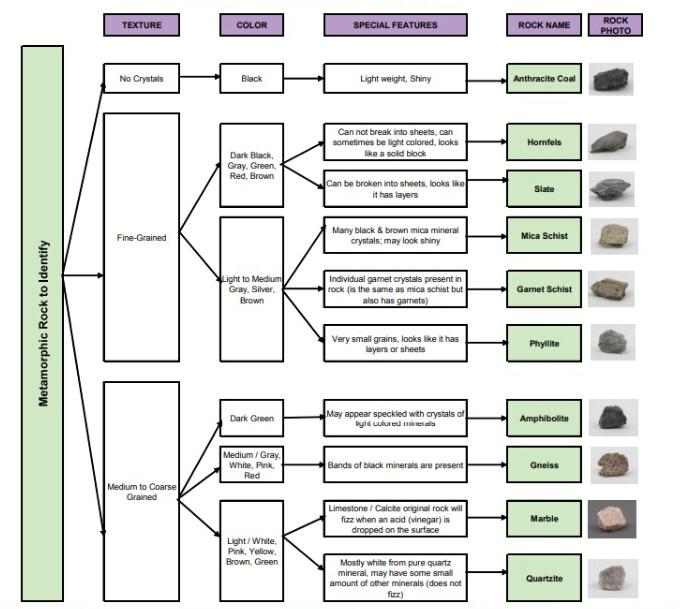
Metamorphic Rock Identification Chart Labb by AG

Overview of Metamorphic Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science

American Educational Identifying Metamorphic Rock Chart
If Foliation Is Present, Noting The Type Of Foliation Will Allow You To Identify The Rock.
Web Read The Descriptions In Your Lab Manual Or Textbook For The Source Rock Of Each Of The Metamorphic Rocks That You Identify.
Web To Identify Your Rock, First Take Note Of Its Physical Properties Like Color, Luster, Banding, Layering, And Grain Size.
In Order To Name Metamorphic Rocks, A Logical First Step Is To Examine The Rock For Evidence Of Any Pattern Or Foliation.
Related Post: