Meiosis And Mitosis Chart
Meiosis And Mitosis Chart - Knowing the differences between these fundamental cell processes is an important foundation in your understanding of genetics for the rest of the course. In meiosis i, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other and are bound together with the synaptonemal complex. In contrast to mitosis, molecular mechanisms and regulation of meiosis are much less understood. Facts explained through comparison chart with differences & similarities between their stages, along with venn diagram & picture Updated on may 12, 2024. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei, usually partitioned into two new cells. Web mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. An overview of key differences from mitosis. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division. Meiosis is the specialized cell division that generates gametes. An overview of key differences from mitosis. Web recognize the function and products of mitosis and meiosis. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent. Knowing the differences between these fundamental cell processes is an important foundation in your understanding of genetics for the rest of the course. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Predict dna content of cells in different phases of mitosis and meiosis. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. Web mitosis and meiosis, which. An overview of key differences from mitosis. It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Mitosis is how new body cells are produced, whereas meiosis is used to produce gametes (i.e. Difference between mitosis and meiosis. Knowing the differences between these fundamental cell processes is an important foundation in your understanding of genetics for the rest of the course. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase,. Web both mitosis and meiosis start out with dna replication, but with different ultimate goals. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. The key events that happen in each of the stages of meiosis are summarized. Organisms grow and reproduce through cell division. Web the main differences between mitosis and meiosis occur in meiosis i. Web recognize the function and products of mitosis and meiosis. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Meiosis occurs in the testes of men and ovaries of women. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Most cells in the body regularly go through mitosis, but some do so more often than others. Facts explained through comparison. Web both mitosis and meiosis involve: Dna replication produces identical sister chromatids. In eukaryotic cells, the production of new cells occurs as a result of mitosis and meiosis. Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Mitosis is how new body cells are produced, whereas meiosis is used to produce gametes (i.e. Web mitosis and meiosis, which are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to their very different outcomes. Web mitosis has the diploid number of chromosomes and produces two identical daughter cells with 46 chromosomes, on the contrary in meiosis four genetically distinct daughter cells with each. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei, usually partitioned into two new cells. Meiosis involves two divisions, so it’s typically broken down into meiosis i and meiosis ii. Dna replication produces identical sister chromatids. In multiple organisms, mitosis is the method of asexual reproduction. Mitosis is how new body cells are produced, whereas meiosis is used. In eukaryotic cells, the production of new cells occurs as a result of mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei, usually partitioned into two new cells. It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. The diploid number results from the fact that each cell includes one copy of each chromosome (numbered one through 22 in humans, plus one sex chromosome) from the organism's mother and one from the father. Meiosis is the specialized cell division that generates gametes. Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. In multiple organisms, mitosis is the method of asexual reproduction. Web both mitosis and meiosis involve: Web here, we outline the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46). Web both mitosis and meiosis start out with dna replication, but with different ultimate goals. Meiosis occurs in the testes of men and ovaries of women. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. Mitosis is the process by which body cells divide and create copies of themselves for growth and repair. In meiosis i, the homologous chromosome pairs become associated with each other and are bound together with the synaptonemal complex. Chiasmata develop and crossover occurs between homologous chromosomes, which then line up along the metaphase plate in tetrads with. Both mitosis and meiosis start with a diploid parent cell that splits into daughter cells.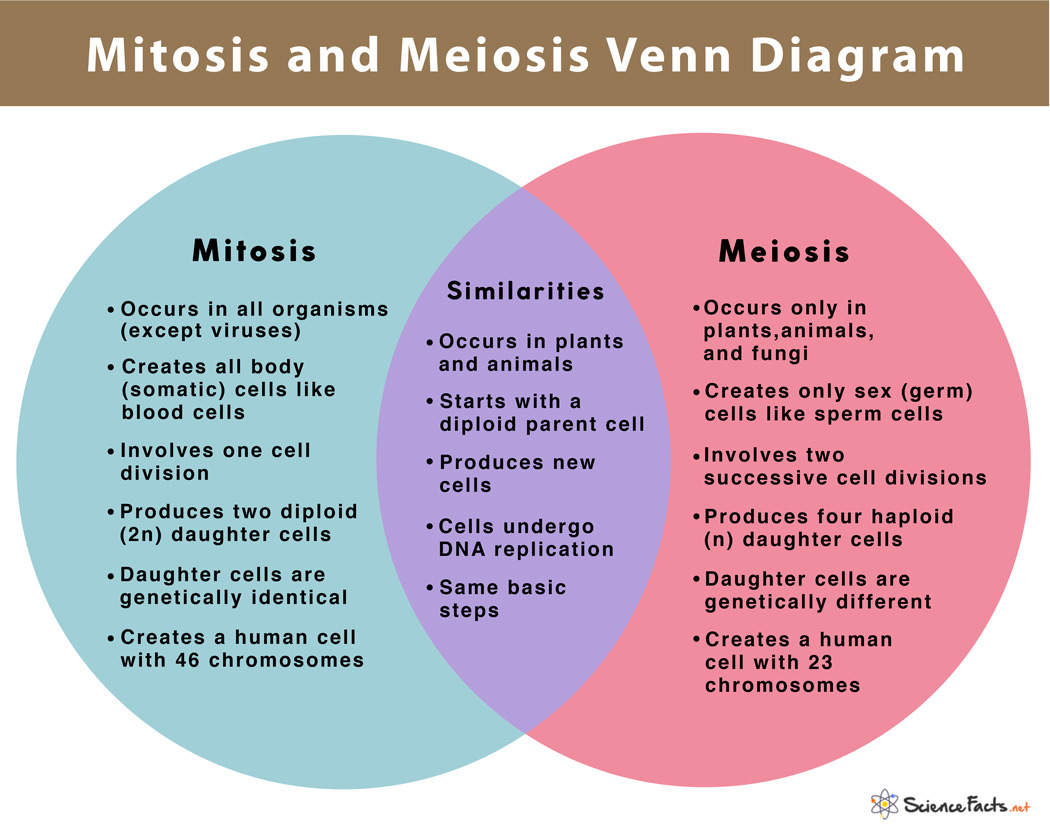
Mitosis vs Meiosis 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis Online Science Notes
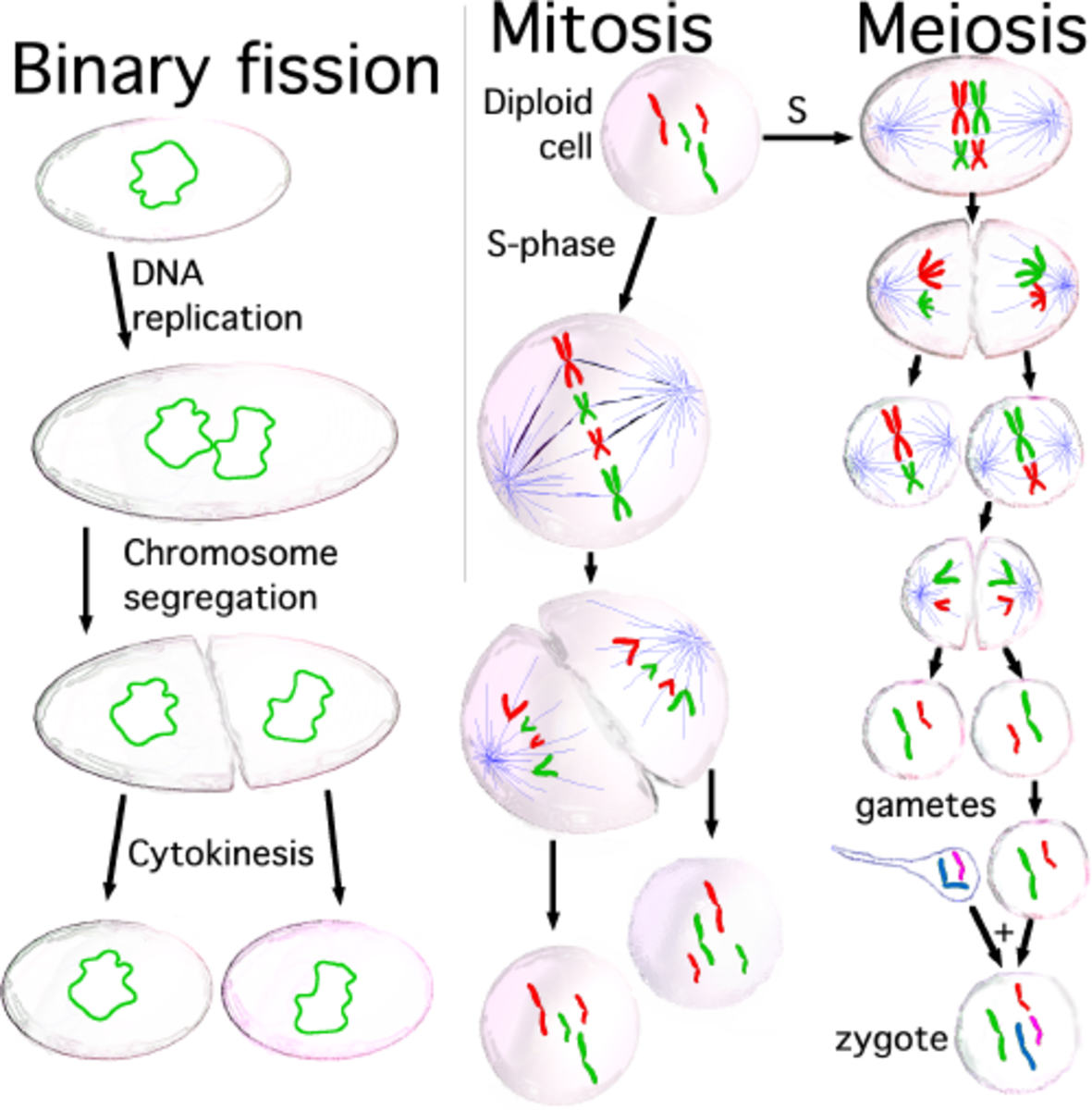
Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Owlcation
Meiosis And Mitosis
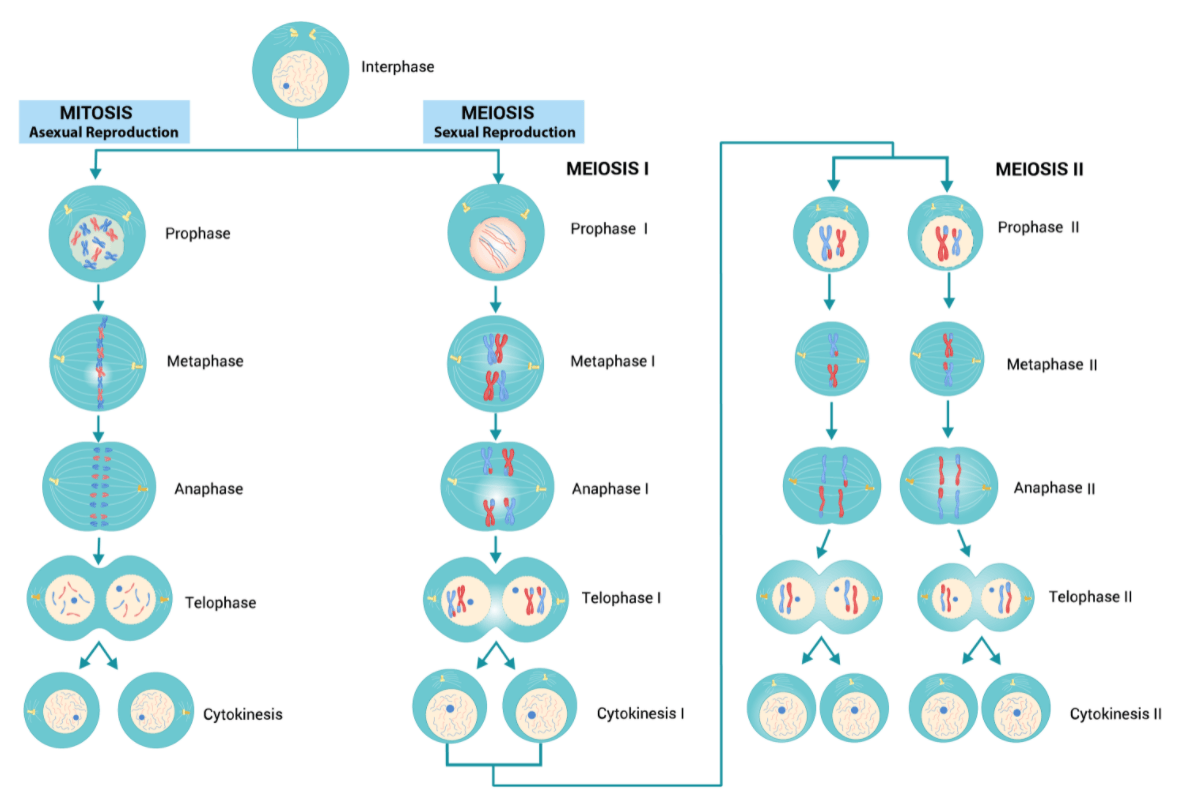
Cellular Division Mitosis and Meiosis (Video & Fact Sheet)
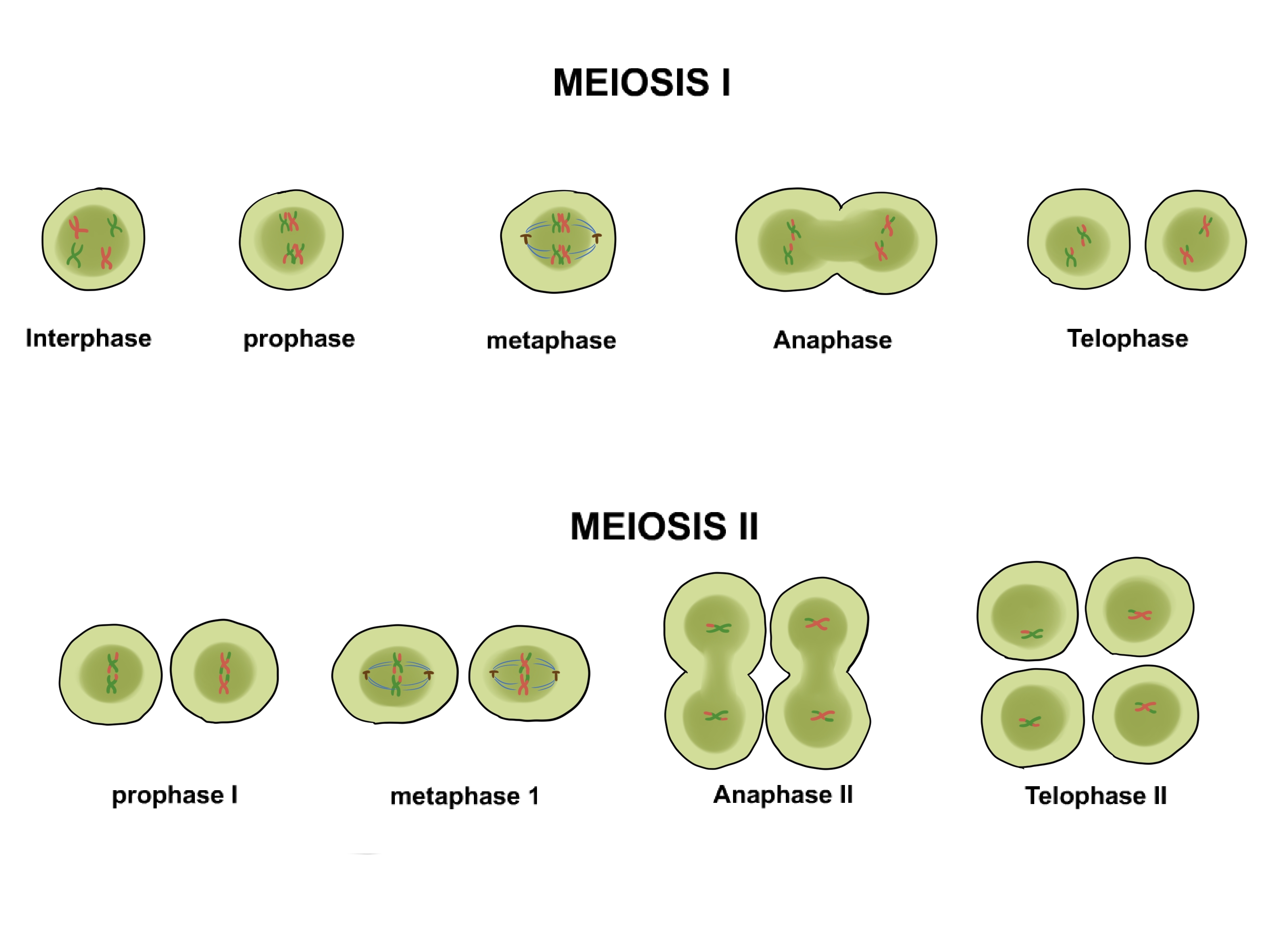
Meiosis Vs Mitosis Cells

COMPARE AND CONTRAST the phases of mitosis and meiosis with this
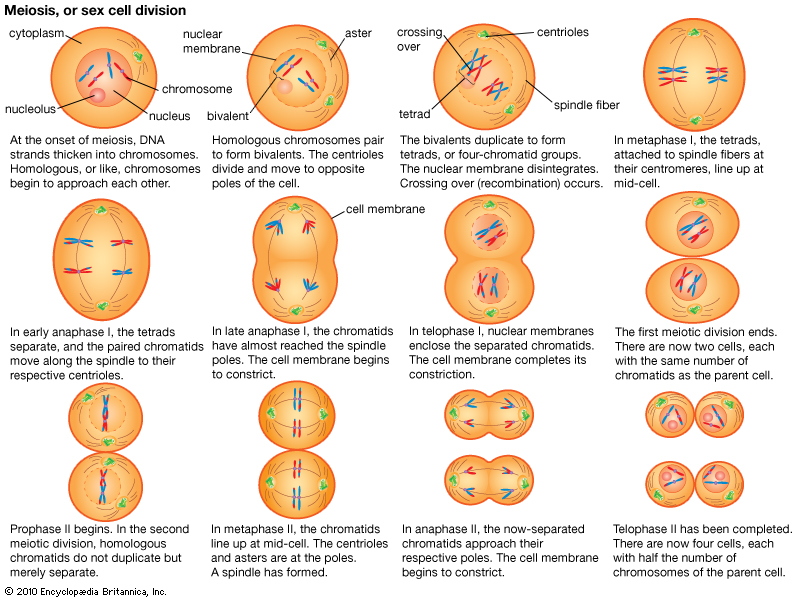
Cell Division part 3 Grade 9 Understanding of Meiosis for IGCSE 3.30

Meiosis vs Mitosis Difference and Comparison Diffen

Meiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison SchoolWorkHelper
In Contrast To Mitosis, Molecular Mechanisms And Regulation Of Meiosis Are Much Less Understood.
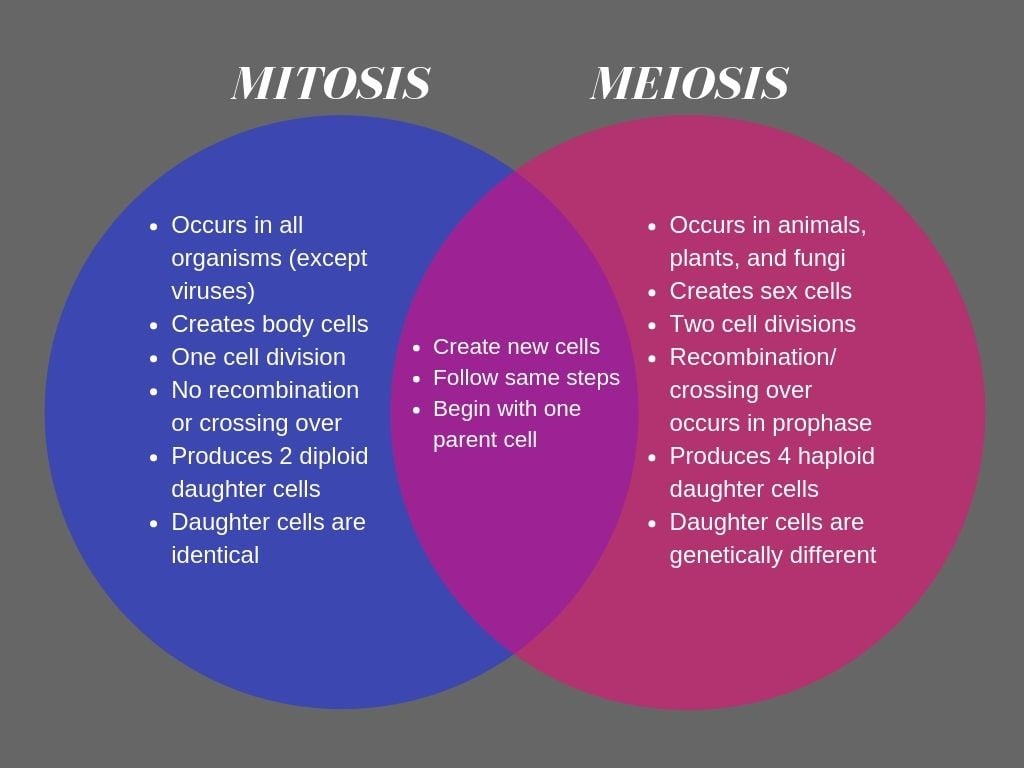
On The Left Side Of The Diagram, You Can See The Key Features Of Mitosis, On The Right Are The Key Features Of Meiosis, And Where The Two Circles Overlap Is Where Their Similarities Are Listed.
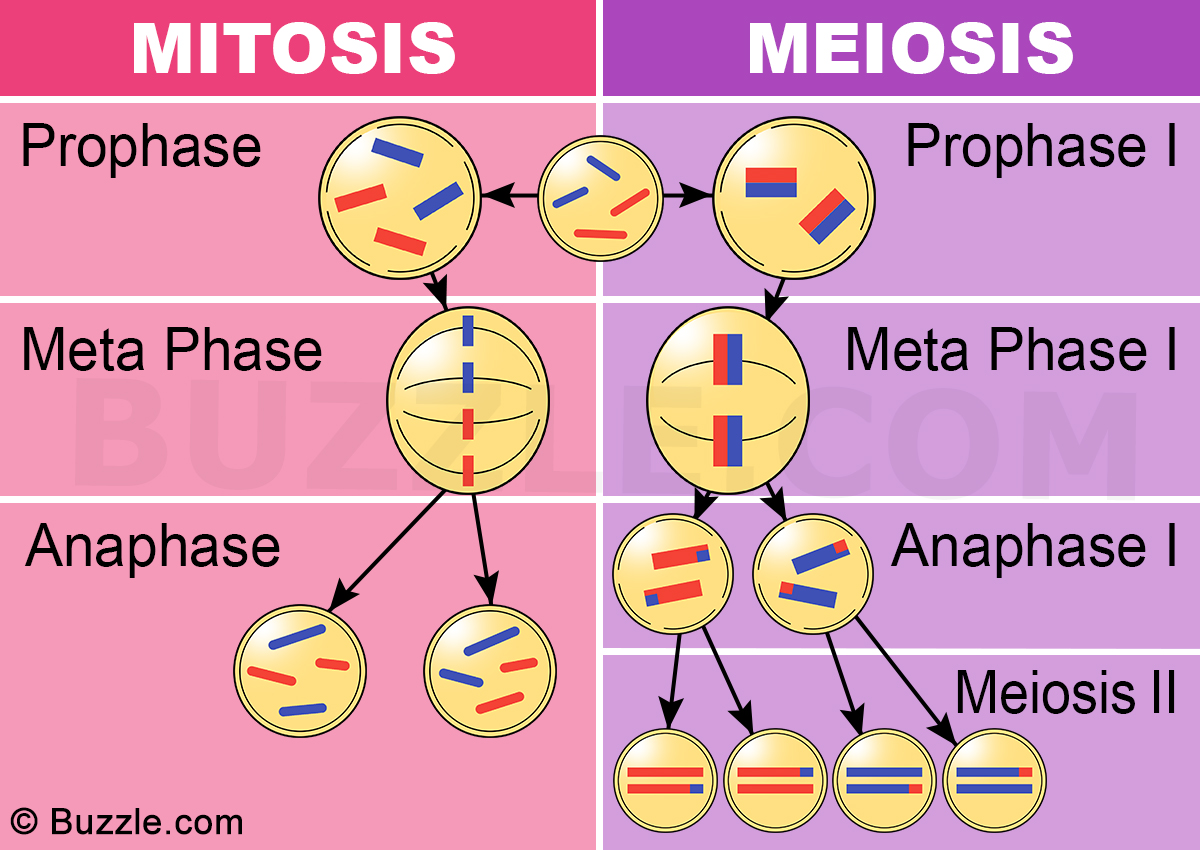
Compare And Contrast The Behaviors Of Chromosomes In Mitosis And Meiosis.
Knowing The Differences Between These Fundamental Cell Processes Is An Important Foundation In Your Understanding Of Genetics For The Rest Of The Course.
Related Post: