Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart
Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart - As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Web there are four basic kinds of biological macromolecules: How are these molecules formed? A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. These polymers are composed of different monomers and serve different functions. They are necessary for energy storage. The four families of molecules. Web go to the main menu for your course. Web many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. How are these molecules formed? Web carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically important carbohydrates belong to three categories: Click the card to flip 👆. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Web go to the main menu for your course. Click the card to flip 👆. Today millions of different organic compounds are known. Carbon atoms attaching to each other can form straight or branched chains and ringed structures of organic compounds. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: The small molecular units are called monomers (mono means one, or single), and they are linked together into long chains called polymers (poly means many, or multiple. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids. Therefore, polymer nomenclature is generally based upon a type of a monomer residue comprising a polymer. Click the card to flip 👆. Polymers are made of many small molecules linked together. Web many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. Web the monomer is a small molecule, which can undergo polymerization, thereby contributing constitutional units to the essential structure. The four families of molecules. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? Molecules composed of sugar monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Web discuss biological macromolecules and the differences between the four classes. Polymers are made of many small molecules linked together. These macromolecules are also called polymers. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? Web go to the main menu for your course. Molecules composed of sugar monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are built from small molecular units that are connected to each other by strong covalent bonds. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Web monomers and. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. The four families of molecules. Click the card to flip 👆. Polymers are made of many small molecules linked together. Web basic functional groups of biological macromolecules. In this article, we’ll learn more about each type of carbohydrates, as well as the essential energetic and structural roles they play in humans and other organisms. This unit is part of the biology library. The four families of biological molecules. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? How are these molecules formed? Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. These macromolecules are also called polymers. In doing so, monomers release water. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Therefore, polymer nomenclature is generally based upon a type of a monomer residue comprising a polymer. What functions do they serve? Web these macromolecules (polymers) are built from different combinations of smaller organic molecules (monomers). Web carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically important carbohydrates belong to three categories: In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. Web many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration. What functions do they serve? In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web discuss biological macromolecules and the differences between the four classes.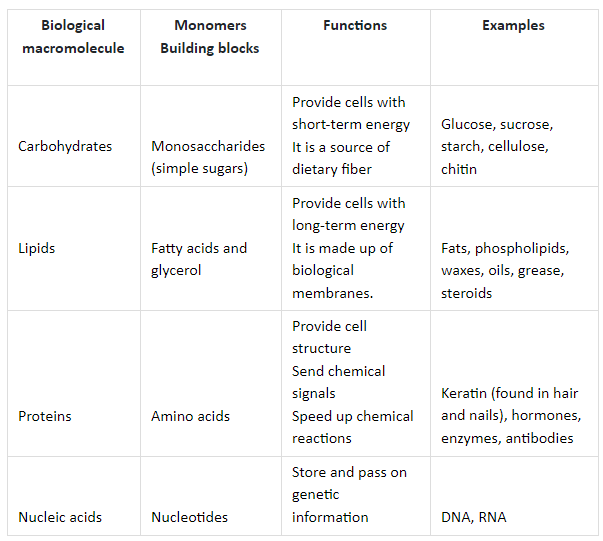
Structure and Function of Biological Macromolecules Study Guide

BIO101 Biological Macromolecule Monomers & Polymers Diagram Quizlet

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
15 Best Images of Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet Macromolecule

LabXchange
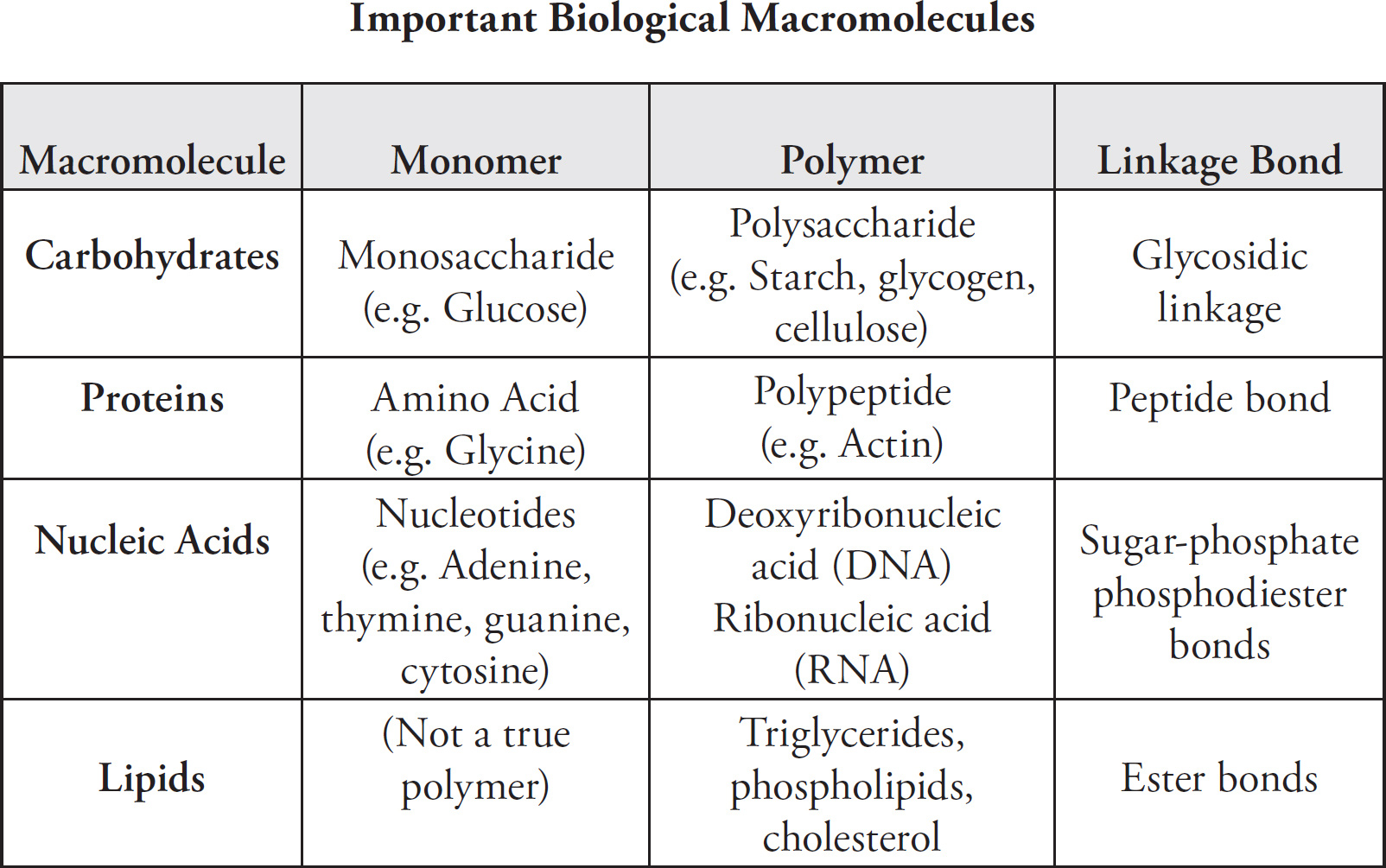
Biological macromolecules

simple diagram of macromolecules, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and

Polymers And Monomers Chart
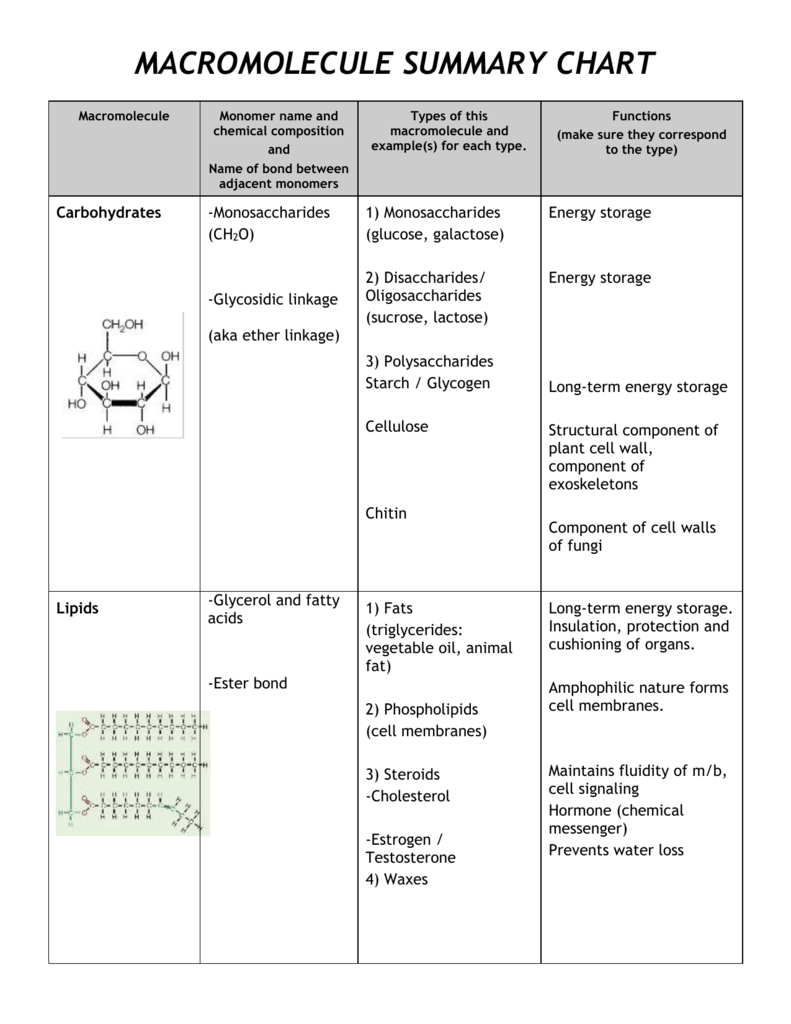
macromolecule summary chart

Image Gallery Monomers Chart
Polymers Are Made Of Many Small Molecules Linked Together.
Carbon Atoms Attaching To Each Other Can Form Straight Or Branched Chains And Ringed Structures Of Organic Compounds.
Web Most Large Biological Molecules Are Polymers, Long Chains Made Up Of Repeating Molecular Subunits, Or Building Blocks, Called Monomers.
Molecules Composed Of Sugar Monomers.
Related Post: