Lymphatic System Chart
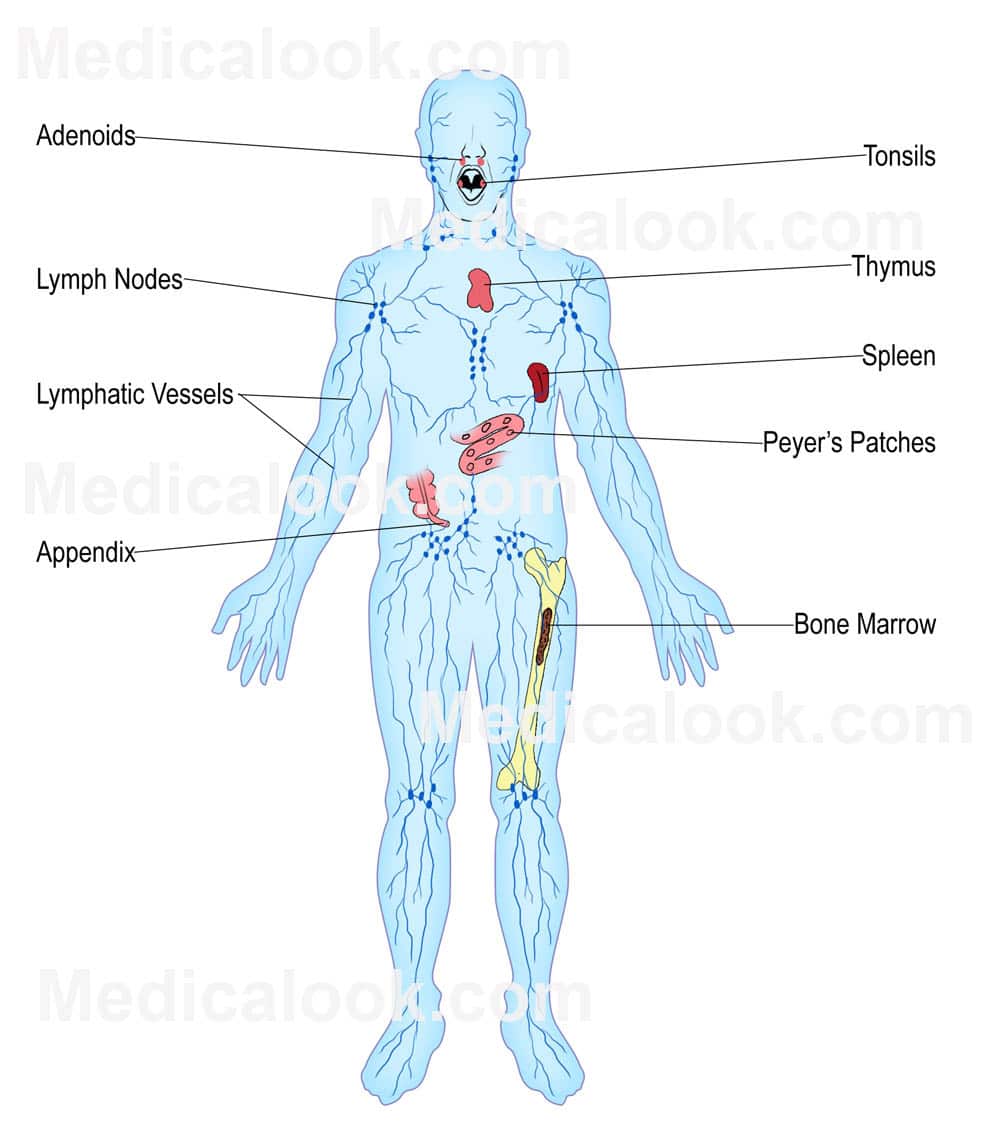
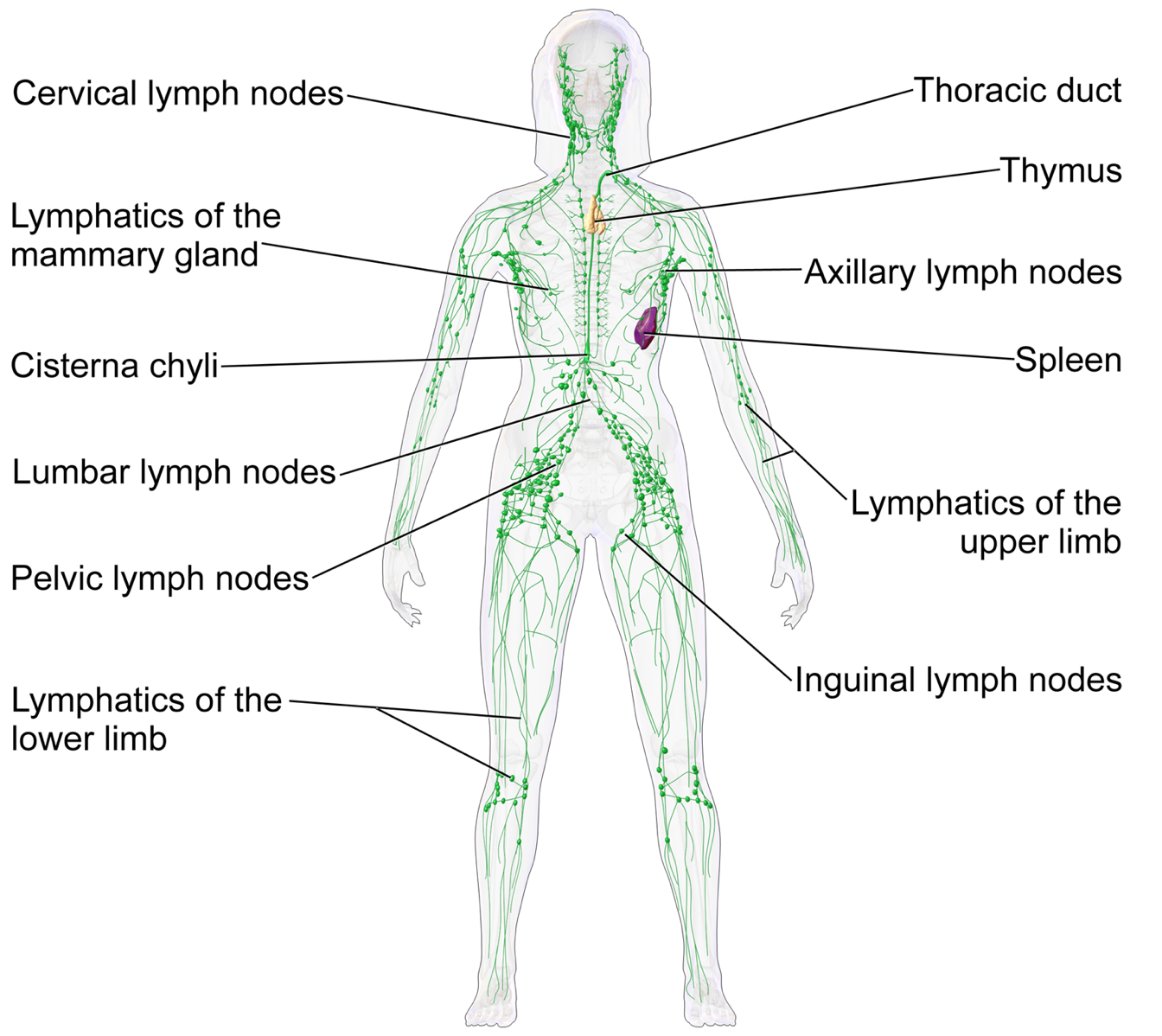
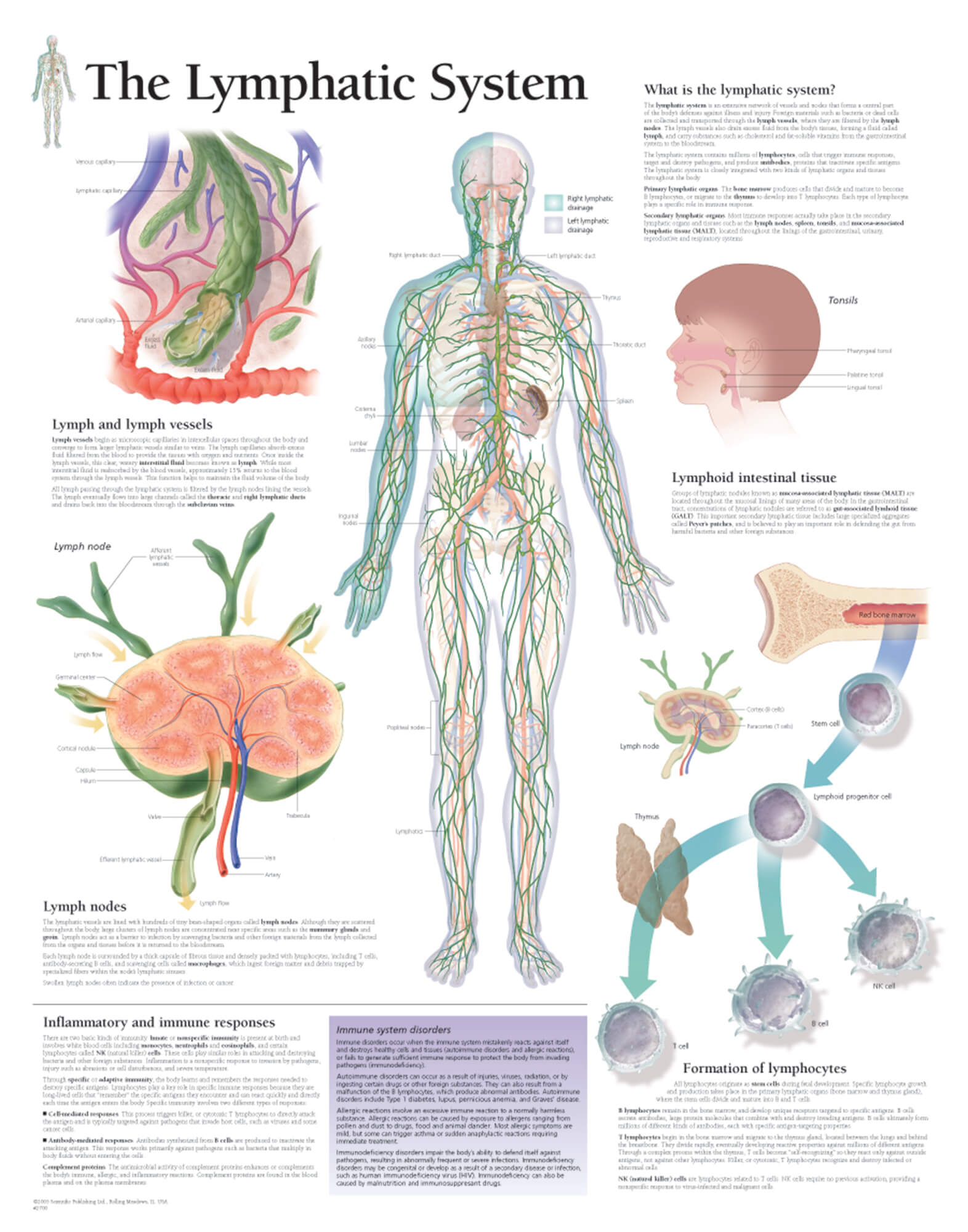
Lymphatic System Chart - It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. The lymph from the rest of the body enters the bloodstream through the thoracic duct via all the remaining lymphatic trunks. Lymphatic tissues and organs lymphoid tissue is found in many organs including the lymph nodes, as well as in the lymphoid follicles in the pharynx such as the tonsils. These vessels carry a fluid called lymph away from body tissues and capillary beds to be filtered by nodes and organs, then returned to the bloodstream. Lymphatic capillaries originate in tissues as tiny blind ended sacs. Some rush to attack any harmful microbes that invade the body. Web how does the body destroy harmful pathogens? Single layer of endothelial cells like blood capillaries. Web the lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. It forms a vital part of the body’s immune defence. Unlike the blood vascular system, lymphatic circulation is not a closed loop. Web lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood.. Web the lymphatic system, for most people, is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable. The right lymphatic duct receives lymph from only the upper right side of the body. Web how does the body destroy harmful pathogens? It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs,. These cells look for and destroy invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and. The lymphatic system is part of the. Web explore the lymphatic system with innerbody's interactive guide. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. ), the spleen, and the. Lymphatic capillaries originate in tissues as tiny blind ended sacs. Some rush to attack any harmful microbes that invade the body. Components of the lymphatic system include lymph, lymphatic vessels and plexuses, lymph nodes, lymphatic cells, and a variety. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens. Web explore the lymphatic system with innerbody's interactive guide. Single layer of endothelial cells like blood capillaries. The vessel network and the nodes and organs. Lymph reenters the cardiovascular system at subclavian veins situated near. Web the lymphatic system is a series of vessels and nodes that collects and filters excess tissue fluid (lymph), before returning it to the venous. Unlike the blood vascular system, lymphatic circulation is not a closed loop. The swelling of lymph nodes during an infection and the transport of lymphocytes via the lymphatic vessels are but two examples of the many connections between these critical organ systems. Single layer of endothelial cells like blood capillaries. Web the lymphatic system is a series of vessels and. Lymphatic vessels, located throughout the body, are larger than capillaries (the smallest blood vessels, which connect arteries and veins), and most are smaller than the smallest veins. Web the lymphatic system, for most people, is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable. View detailed illustrations of lymph nodes, vessels, and other. Immunity is the body’s defense system against infection and disease. Components of the lymphatic system include lymph, lymphatic vessels and plexuses, lymph nodes, lymphatic cells, and a variety. Lymphatic vessels, located throughout the body, are larger than capillaries (the smallest blood vessels, which connect arteries and veins), and most are smaller than the smallest veins. Web your lymphatic system is. Lie side by side with blood capillaries. Web the lymphatic system, for most people, is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable. Web explore the lymphatic system with innerbody's interactive guide. The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is one of the components of the circulatory system, and it serves a critical. Single layer of endothelial cells like blood capillaries. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymphatic tissues and organs lymphoid tissue is found in many organs including the lymph nodes, as well as in the lymphoid follicles in the pharynx such as the tonsils. Lymphatic vessels and ducts provide the. Web how does the body destroy harmful pathogens? Web the lymphatic system, for most people, is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable. These cells look for and destroy invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and. Web the overall drainage system of the body is asymmetrical (see figure 18.1.3 18.1. White blood cells play a key role. As well as the circulatory system and comprises the. The lymphatic system involves many organs, including the tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus. Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. Web lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. First is the maintenance of fluid balance, second is the facilitation of the absorption of dietary fats from the gastrointestinal tract to the bloodstream for metabolism or storage, and third is the enhancement and facilitation of the immune system. Web there are three primary functions of the lymphatic system: Network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and ducts that carries lymph from the tissues and back to the bloodstream. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. Web the lymphatic system is a series of vessels and nodes that collects and filters excess tissue fluid (lymph), before returning it to the venous circulation. Unlike the blood vascular system, lymphatic circulation is not a closed loop.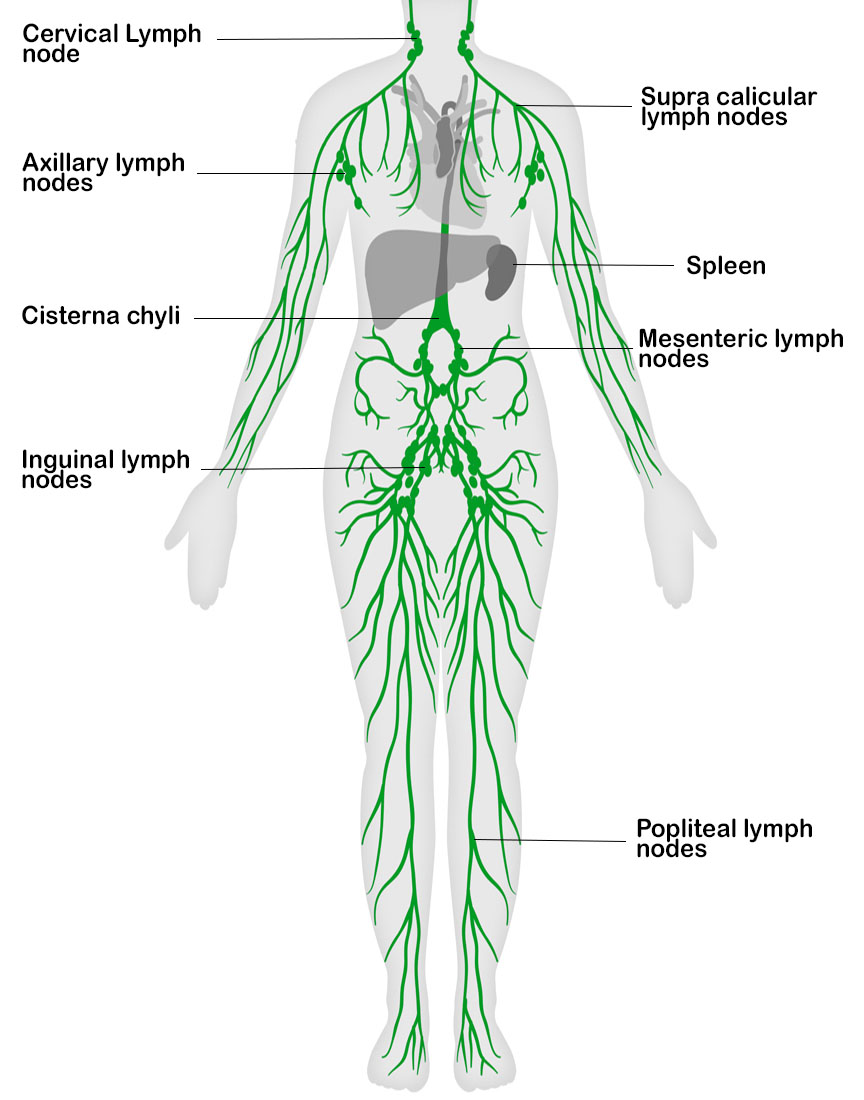
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Lab Medica Healthcare

Anatomy and Physiology The Lymphatic System Sarah Wayt
Lymphatic System Functional Medicine Coast Chiropractic Clinic Hove
20.3 Lymphatic System Biology LibreTexts
/lymphatic_system_2-58110f0c5f9b58564c6e31cb.jpg)
Lymphatic System Components Spleen, Thymus, Nodes
The Lymphatic System Scientific Publishing
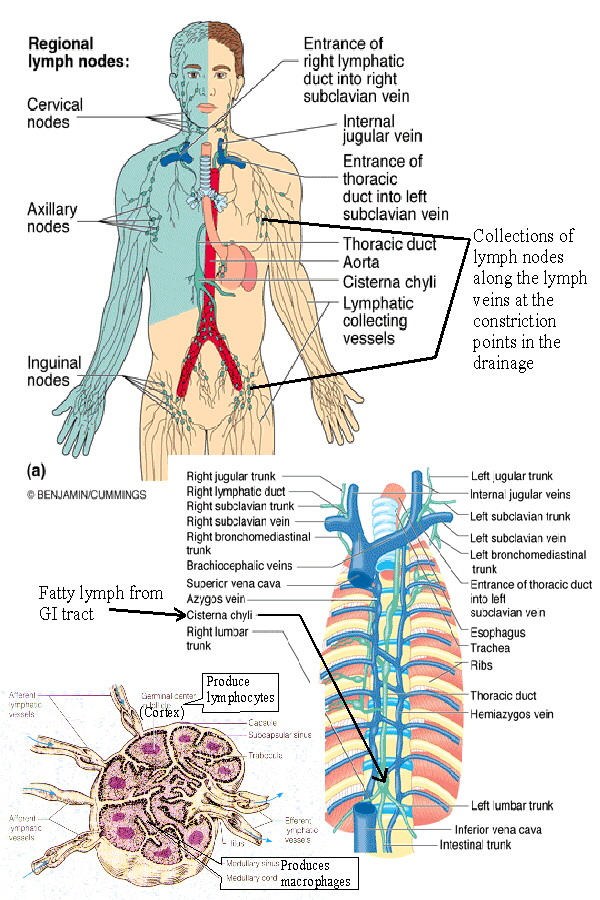
Understanding the Lymphatic System

Human Body Lymphatic System Carolina Biological Supply
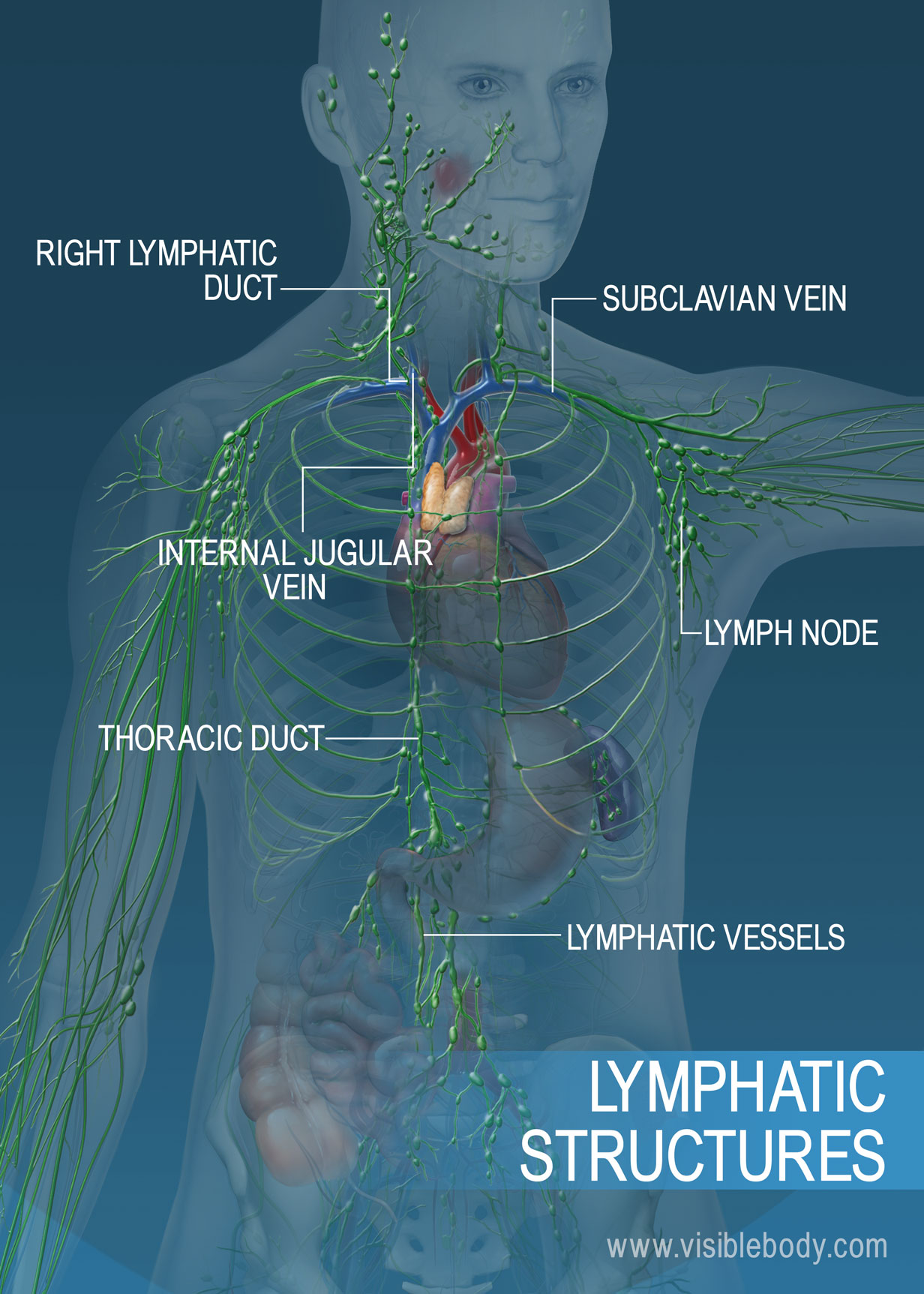
Lymphatic System
![What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute](http://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/7367-Lymphatic-System-Infographic.png)
What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute
Immunity Is The Body’s Defense System Against Infection And Disease.
Lymphatic Tissues And Organs Lymphoid Tissue Is Found In Many Organs Including The Lymph Nodes, As Well As In The Lymphoid Follicles In The Pharynx Such As The Tonsils.
), The Spleen, And The.
The Lymphatic System Consists Of Two Main Parts:
Related Post: