Lung Volume Chart Labeled
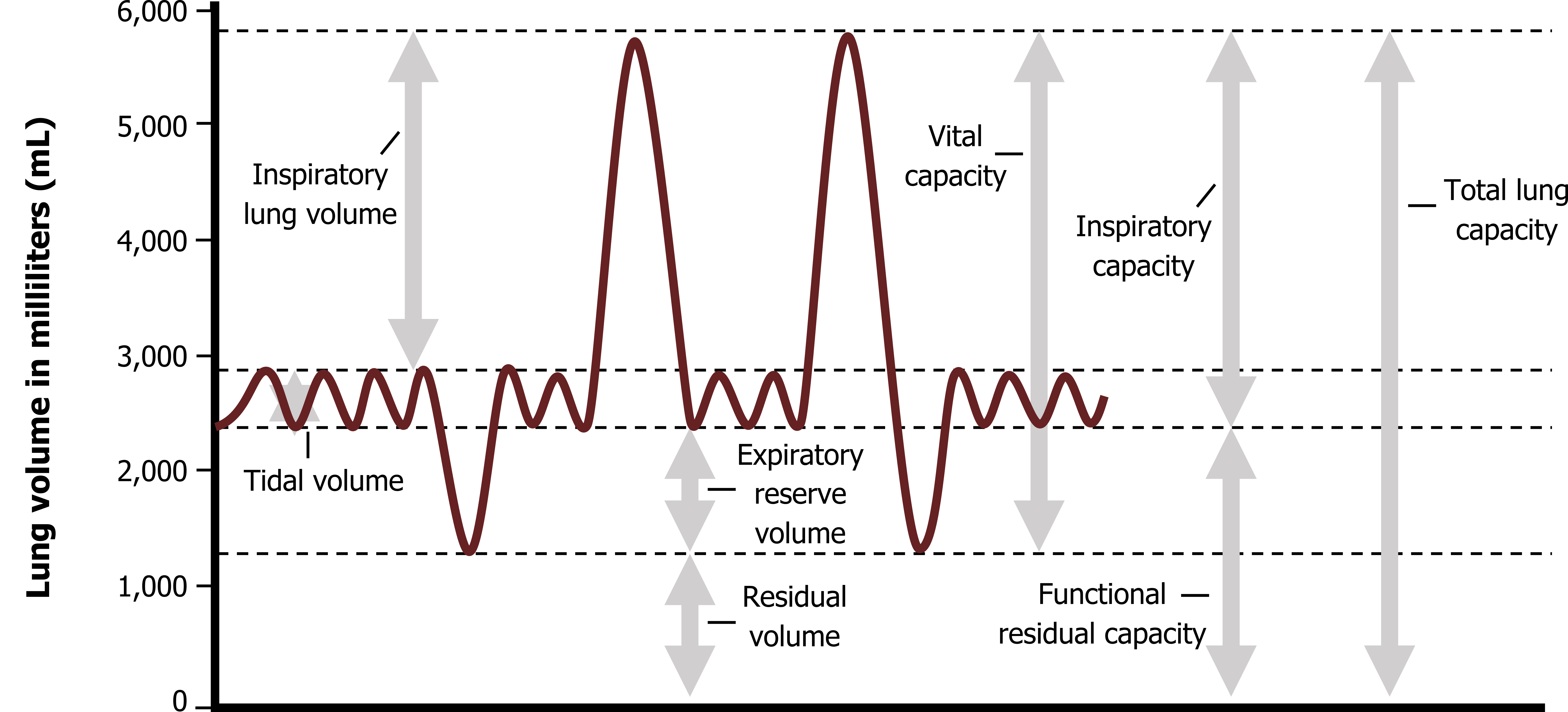
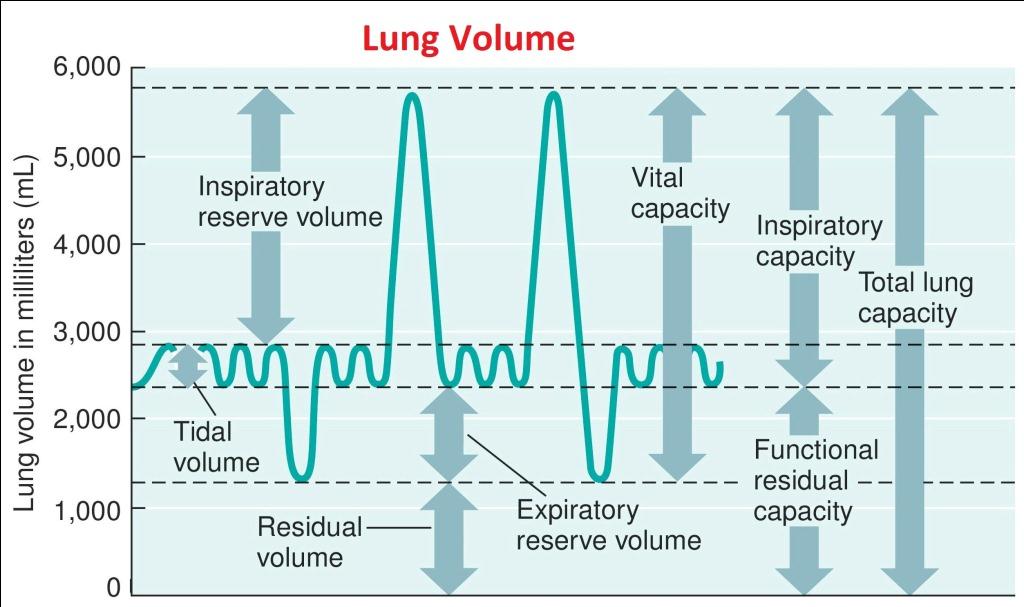
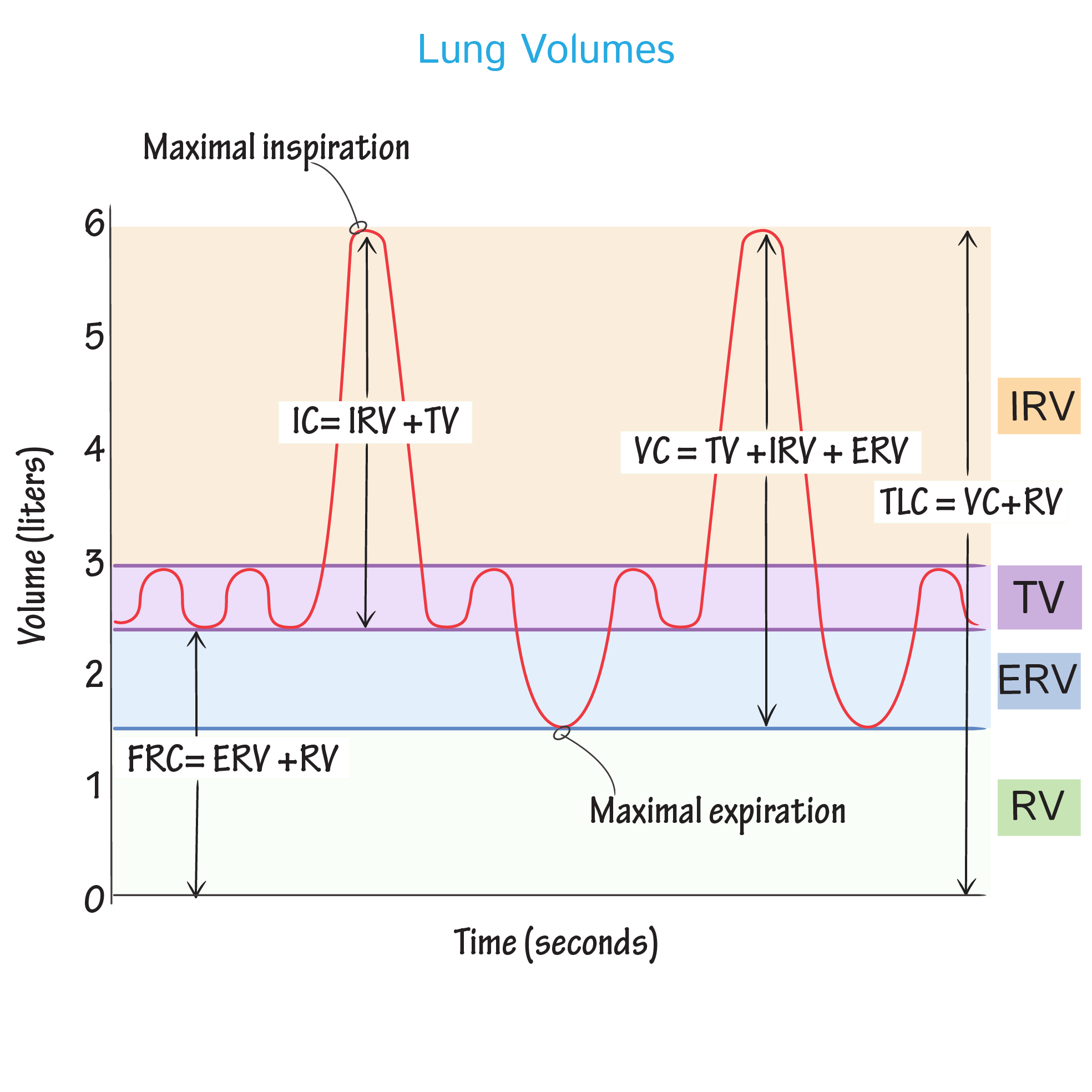
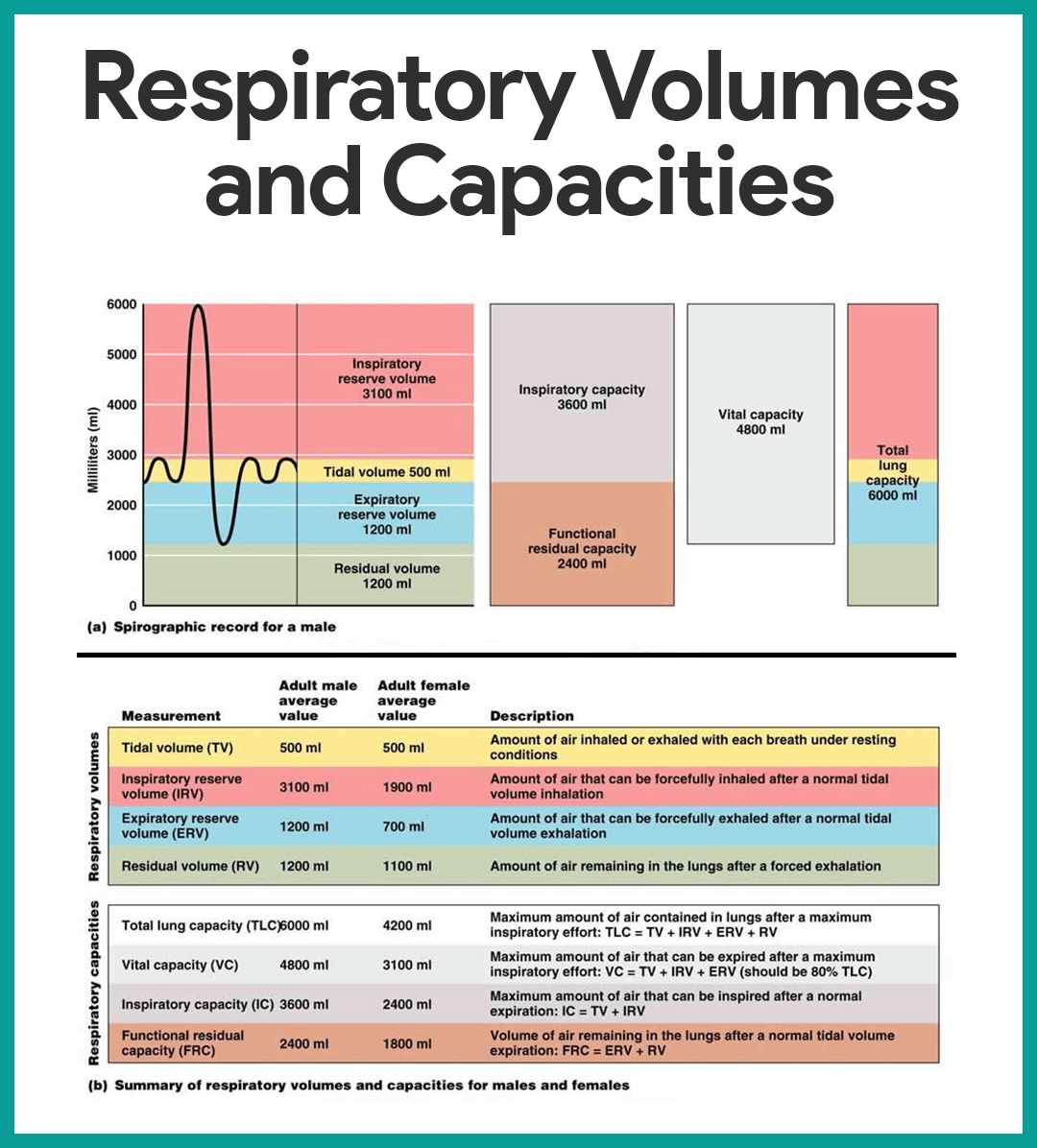
Lung Volume Chart Labeled - Major lung volumes include the tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume , expiratory reserve volume , and the residual volume. Web lung volumes are measured by determining functional residual capacity (frc). Web illustrated in figure 1, panel a, the lung capacities can be further divided into the following lung volumes: Web in this article we will look at the lung volumes and capacities, how they are measured and how they are affected by pathology. Frc is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after normal exhalation. The vital capacity is the total volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inhalation or maximum air that a person can breathe in after forced expiration. Web in this section we’ll look at some of the nomenclature for a variety of lung volumes and how these are clinically pertinent and can change in disease. Vital capacity is used to diagnose restrictive diseases, while the fev1/fvc ratio is used to diagnose obstructive diseases. There is residual air leftover in the lungs during normal breathing. Web there are four major types of respiratory volumes: Web the below lung volumes and capacities chart provides the average and normal lung volumes and capacities for men and women. The vital capacity is the total volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inhalation or maximum air that a person can breathe in after forced expiration. The total lung capacity (tlc) is the volume of gas. Vital capacity is used to diagnose restrictive diseases, while the fev1/fvc ratio is used to diagnose obstructive diseases. Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathing; Spirometry is used to measure lung volumes and air flow. Attached to the wall of the thoracic cavity, the parietal pleura forms the outer layer of the membrane. Web lung capacity is a measure of lung. Tidal volume (tv) is the amount of air that normally enters the lungs during quiet breathing, which is about 500 milliliters. Web the below lung volumes and capacities chart provides the average and normal lung volumes and capacities for men and women. Web in this section we’ll look at some of the nomenclature for a variety of lung volumes and. We’ll also begin to look at the work. In this section we’ll look at some of the nomenclature for a variety of lung volumes and how these are clinically pertinent and can change in disease. Web lung volumes refer to the volume of air in the lungs, measured at various phases of the respiratory cycle. Web the volume in the. The air pressure within the alveoli, called alveolar pressure ( palv ); Web lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle. Frc is the amount of air remaining in the lungs after normal exhalation. Alongside clinical assessment, it is an essential tool used in the diagnosis, assessment. The amount of air in the lungs can be subdivided into four (4) lung volumes: Tidal volume (tv), inspiratory reserve volume (irv), expiratory reserve volume (erv), and the residual volume (rv). Measurement of lung volumes is an integral part of complete pulmonary function testing. Web the volume in the lung can be divided into four units: Tidal volume, expiratory reserve. Tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. Web normal lung volumes erv = expiratory reserve volume; The visceral pleura forms the inner layer of the membrane covering the outside surface of the lungs. Irv = inspiratory reserve volume; The air pressure within the alveoli, called alveolar pressure ( palv ); The total lung capacity (tlc) is the volume of gas that is contained in the lungs at the end of maximal inspiration. Some lung volumes can be measured during spirometry; Irv = inspiratory reserve volume; The air pressure within the alveoli, called alveolar pressure ( palv ); Tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. These volumes tend to vary, depending on the depth of respiration, ethnicity, gender, age, body composition [1] and in certain respiratory diseases. Tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. Vital capacity is used to diagnose restrictive diseases, while the fev1/fvc ratio is used to diagnose obstructive diseases. Measurement of lung volumes is an integral part of. It is an important measure of a person’s respiratory health. Web spirometry · part one. It measures the volume of air exhaled at specific time points during complete exhalation by force, which is preceded by a maximal inhalation. Web lung capacity is a measure of lung volume inferred from the exhaled during the various cycles of breathing. Frc is the. Tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. Web the volume in the lung can be divided into four units: Lung volumes measurement is an integral part of pulmonary function test. Describe the measurement and interpretation of pulmonary function tests, including diffusion capacity. Web illustrated in figure 1, panel a, the lung capacities can be further divided into the following lung volumes: Web the average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air. Alongside clinical assessment, it is an essential tool used in the diagnosis, assessment and monitoring of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd)1, may contribute to the diagnosis of asthma and detect restrictive respiratory conditions.2. The tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such. The visceral pleura forms the inner layer of the membrane covering the outside surface of the lungs. The amount of air in the lungs can be subdivided into four (4) lung volumes: Web there are four major types of respiratory volumes: In this section we’ll look at some of the nomenclature for a variety of lung volumes and how these are clinically pertinent and can change in disease. Web the major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure ( patm ); Attached to the wall of the thoracic cavity, the parietal pleura forms the outer layer of the membrane. Tidal volume (tv) measures the amount of air that is inspired and expired during a normal breath. Web lung volumes refer to the volume of air in the lungs, measured at various phases of the respiratory cycle.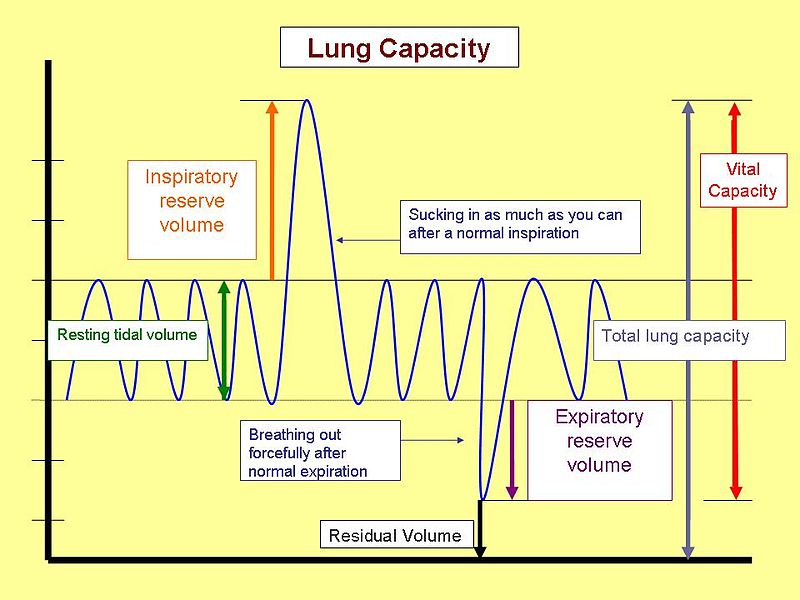
Respiratory Physiology Airways, Lung Volume, Pulmonary Gas Exchange
Lung Volumes and Compliance Pulmonary Physiology for PreClinical
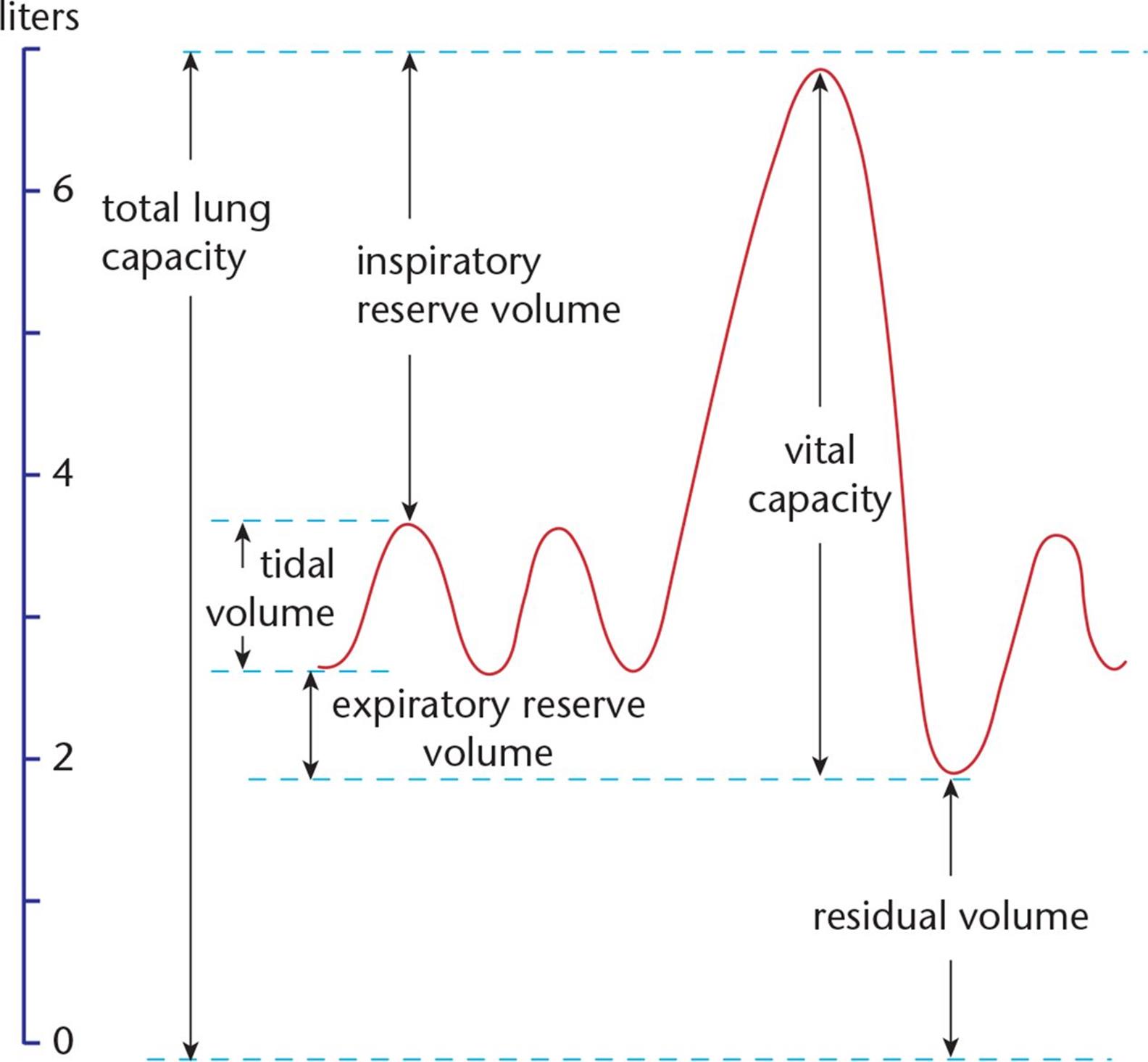
Figure 6.4. Lung Volumes

Respiratory System Lung Volume and Capacity ditki medical

The Process of Breathing · Anatomy and Physiology

Normal spirogram and subdivisions of lung volume.Volume describes the
Lung Volumes and Capacities PDF Exhalation Breathing
Lungs Volume Karuna YogaBest Yoga Teacher Training Course. Bangalore
Physiology Glossary Lung Volumes & Capacities Draw It to Know It
Respiratory System Anatomy and Physiology Nurseslabs
Tlc = Total Lung Capacity;
However, Measurement Of The Residual Volume (Rv), Functional Residual Capacity (Frc), And Total Lung Capacity (Tlc) Requires Special Techniques.
Web The Below Lung Volumes And Capacities Chart Provides The Average And Normal Lung Volumes And Capacities For Men And Women.
Irv = Inspiratory Reserve Volume;
Related Post:
