Liquid Liquid Extraction Flow Chart
Liquid Liquid Extraction Flow Chart - \text{ml}\) of diethyl ether (an exact amount is not necessary), as described previously, making sure to appropriately label each layer (e.g. Web a very typical extraction flow diagram is shown below, where a reaction mixture is quenched with water, extracted (several times), washed with brine, dried, filtered and finally evaporated to yield a crude product or a pure product. Determining number of stages when (1) feed rate; Perform a single extraction using approximately \(25 \: The two phases are put into a device called a separatory funnel, and compounds in the system will distribute between the two phases. Web ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and their mixtures are among the preferred extraction solvents for phenylureas, triazoles, amides, carbamates, benzimidazoles, and chlorotriazines. Usually one of the solvents is water. Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. The other solvent is a liquid that does not dissolve very well in water, such as diethyl ether (this is the most common type of ether, and it. The preparation of a cup of coffee or tea involves the extraction of flavor and odor components from dried vegetable matter with hot water. Determining number of stages \(n\) when (1) feed rate; Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. Usually one of the solvents is water. The other solvent is a liquid that does not dissolve very well in water, such as diethyl ether (this is the most common type of ether, and it. Web ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and their mixtures are among the preferred. When you select new problem, a new phase envelope is shown and a new feed composition and feed flow rates are set. After these two phases have been separated, they must be purified of the solvent they contain. Determining number of stages when (1) feed rate; The extraction efficiency is modified by adjustment of ph and ionic strength in the. The two phases are put into a device called a separatory funnel, and compounds in the system will distribute between the two phases. Web liquid/liquid extraction is the most common technique used to separate a desired organic product from a reaction mixture or to isolate an organic substance from its natural source. In its simplest form, this involves the extraction. In its simplest form, this involves the extraction of a solute from a binary solution by bringing it into contact with a second immiscible solvent in which the solute is soluble. The extraction efficiency is modified by adjustment of ph and ionic strength in the aqueous phase. Web liquid/liquid extraction is the most common technique used to separate a desired. Web a very typical extraction flow diagram is shown below, where a reaction mixture is quenched with water, extracted (several times), washed with brine, dried, filtered and finally evaporated to yield a crude product or a pure product. Determining number of stages when (1) feed rate; The technique works well if your target compound is more soluble in. The two. When you select new problem, a new phase envelope is shown and a new feed composition and feed flow rates are set. Web solvent partitioning requires two solvents that are not miscible in each other. The extraction efficiency is modified by adjustment of ph and ionic strength in the aqueous phase. Top organic layer and bottom aqueous layer). This article. Return the aqueous layer to the separatory funnel. The technique works well if your target compound is more soluble in. Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. Usually one of the solvents is water. The preparation of a cup of coffee or tea involves the extraction of flavor and odor components from dried vegetable matter with hot water. Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. The other solvent is a liquid that does not dissolve very well in water, such as diethyl ether (this is the most common type of ether, and it. Usually one of the solvents is water. Background extraction is one of humankind’s oldest chemical operations. The extraction efficiency is modified by adjustment of ph and ionic. Determining number of stages \(n\) when (1) feed rate; Background extraction is one of humankind’s oldest chemical operations. Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. Web a very typical extraction flow diagram is shown below, where a reaction mixture is quenched with water, extracted (several times), washed with brine, dried, filtered and finally evaporated to yield a crude product or a pure. Perform a single extraction using approximately \(25 \: Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. Web ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and their mixtures are among the preferred extraction solvents for phenylureas, triazoles, amides, carbamates, benzimidazoles, and chlorotriazines. In its simplest form, this involves the extraction of a solute from a binary solution by bringing it into contact with a second immiscible solvent in. Return the aqueous layer to the separatory funnel. And (5) outgoing raffinate composition have been specified/selected. The technique works well if your target compound is more soluble in. Dissolving the mixture in the first solvent and then adding a second immiscible solvent that will selectively dissolve one. The other solvent is a liquid that does not dissolve very well in water, such as diethyl ether (this is the most common type of ether, and it. After these two phases have been separated, they must be purified of the solvent they contain. The preparation of a cup of coffee or tea involves the extraction of flavor and odor components from dried vegetable matter with hot water. Web chem 344 extraction flowchart. Web ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, and their mixtures are among the preferred extraction solvents for phenylureas, triazoles, amides, carbamates, benzimidazoles, and chlorotriazines. Web liquid/liquid extraction is the most common technique used to separate a desired organic product from a reaction mixture or to isolate an organic substance from its natural source. \text{ml}\) of diethyl ether (an exact amount is not necessary), as described previously, making sure to appropriately label each layer (e.g. Of acid rco 2 h rco 2 h acid rnh 2 base n neutral extract with 5% naoh organic phase aqueous phase extract with 10% hcl evap. In its simplest form, this involves the extraction of a solute from a binary solution by bringing it into contact with a second immiscible solvent in which the solute is soluble. The two phases are put into a device called a separatory funnel, and compounds in the system will distribute between the two phases. Background extraction is one of humankind’s oldest chemical operations. Determining number of stages when (1) feed rate;
Schematic flow diagram for the solvent extraction process. Download
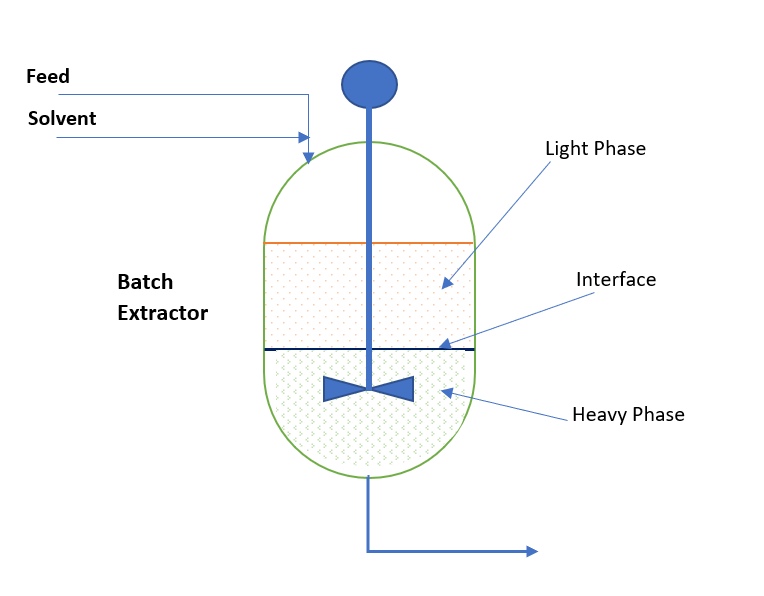
Liquid Liquid Extraction System Process Calculation ChemEnggHelp

Liquid Liquid Extraction Lab Report Uitm A Flowchart Of The My XXX
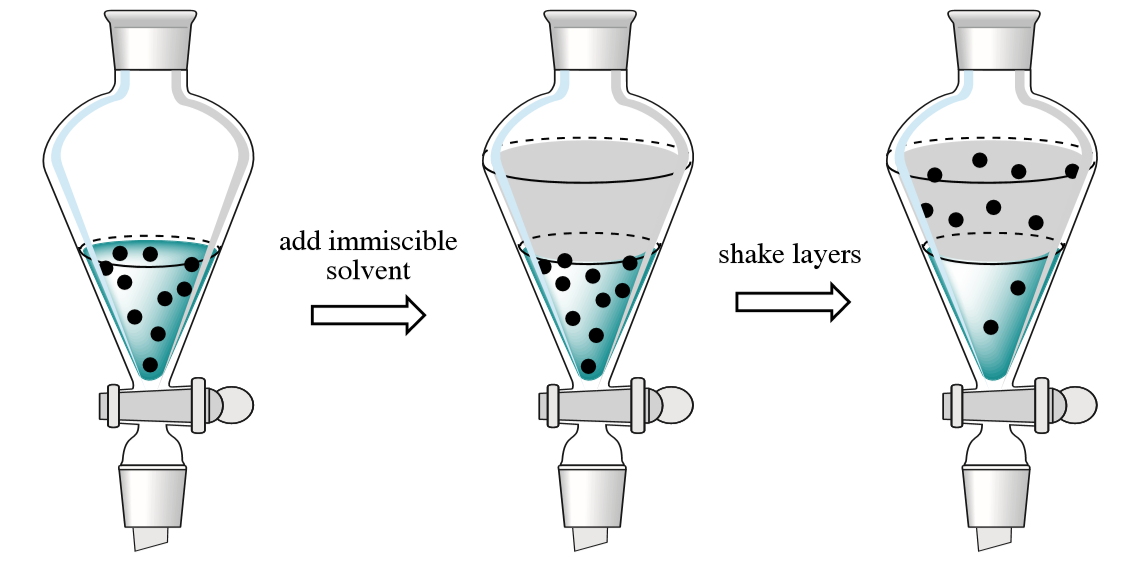
liquid liquid extraction experiment Ryan Baker
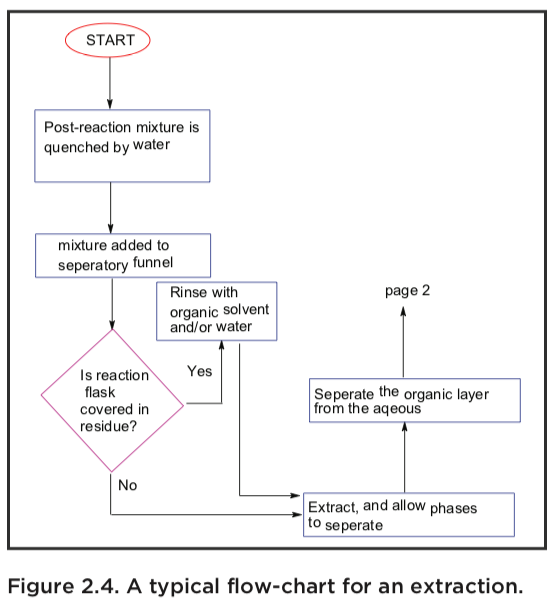
Liquid Liquid Extraction Flow Chart

DNA Extraction Flow Chart

Diagrammatic illustration of liquidliquid extraction (adapted from

Diagrammatic illustration of liquidliquid extraction (adapted from

Liquid Liquid Extraction Flow Chart

Liquid Liquid Extraction Flow Chart A Visual Reference of Charts
Web Solvent Partitioning Requires Two Solvents That Are Not Miscible In Each Other.
Top Organic Layer And Bottom Aqueous Layer).
Web A Very Typical Extraction Flow Diagram Is Shown Below, Where A Reaction Mixture Is Quenched With Water, Extracted (Several Times), Washed With Brine, Dried, Filtered And Finally Evaporated To Yield A Crude Product Or A Pure Product.
When You Select New Problem, A New Phase Envelope Is Shown And A New Feed Composition And Feed Flow Rates Are Set.
Related Post: