Ionization Energy Chart
Ionization Energy Chart - Group 18 noble gas es have an octet of electrons, which causes them to be chemically inert and nonreactive. The ionization energy differs for each atom. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. Web ionization is the process of removing an electron from a neutral atom (or compound). Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: According to the octet rule, atoms strive to have a complete set of 8 valence electrons. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. Web ionization energy (ie) is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or cation in its gaseous phase. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. An element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. Web ionization energy is the energy needed to ionize an atom in the gas phase. Ie is also known as ionization potential. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web ionization energy chart of. Web ionization energy (ie) is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or cation in its gaseous phase. Web the ionization energy is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of gaseous atoms or ions. An+(g) a(n+1)+ (g) +e− ie = δu a ( g) n + a ( g). The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Ionization energy chart of all elements of periodic table. 1st in a periodic table cityscape style. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): Group 18 noble gas es have an octet of electrons, which causes them to be chemically inert and nonreactive. Across a period, ionization energy tends to increase. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. According to the octet rule, atoms strive to have a complete set of 8 valence electrons. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction Web ionization energy (the energy associated with forming a cation) decreases down a group and mostly increases across a period because it is. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Click on any element's name for further information on chemical properties, environmental data or health effects. The size of that attraction will be governed by: The ionization energy of the elements. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web the ionization energy is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole. Web ionization energy (ie) is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or cation in its gaseous phase. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. The ionization energy of the elements within a period.. Web ionization energy is the energy needed to ionize an atom in the gas phase. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Click on any element's name for further information on chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.. Web ionization energy, once called the ionization potential, is the amount of energy a neutral, gas phase atom in its ground electronic state must absorb in order to remove the outermost valence electron; Web ionization energy is the energy needed to ionize an atom in the gas phase. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as. Web the elements of the periodic table sorted by ionization energy. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): Ionization energy is always positive. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Web ionization energy (ie) is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or cation in its gaseous phase. It is a measure of. H(g) → h+(g) +e− (1) (1) h ( g) → h + ( g) + e −. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Ie is also known as ionization potential. An element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element.
Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
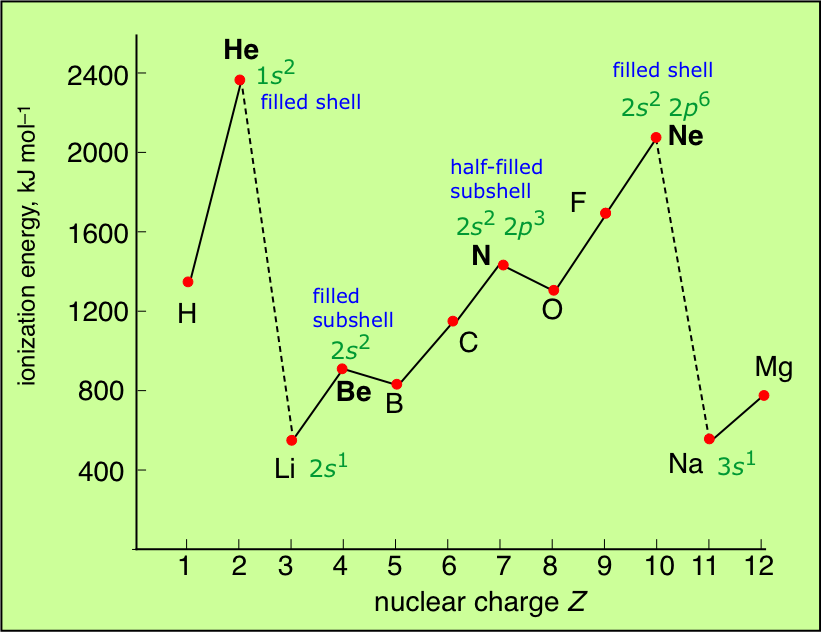
Which element has the highest first ionization energy? Socratic
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
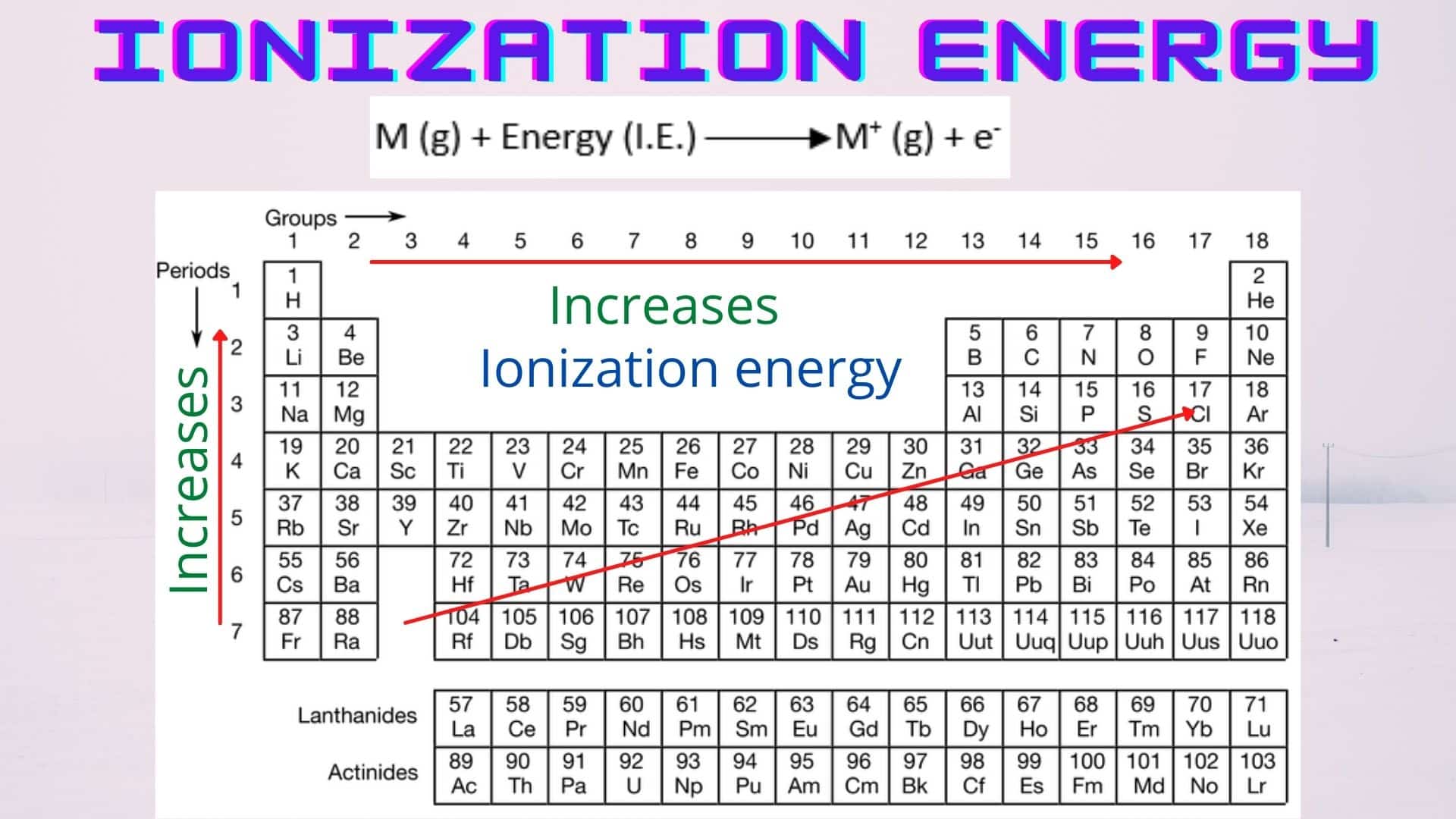
Ionization energy and ionization potential Chemistry Notes
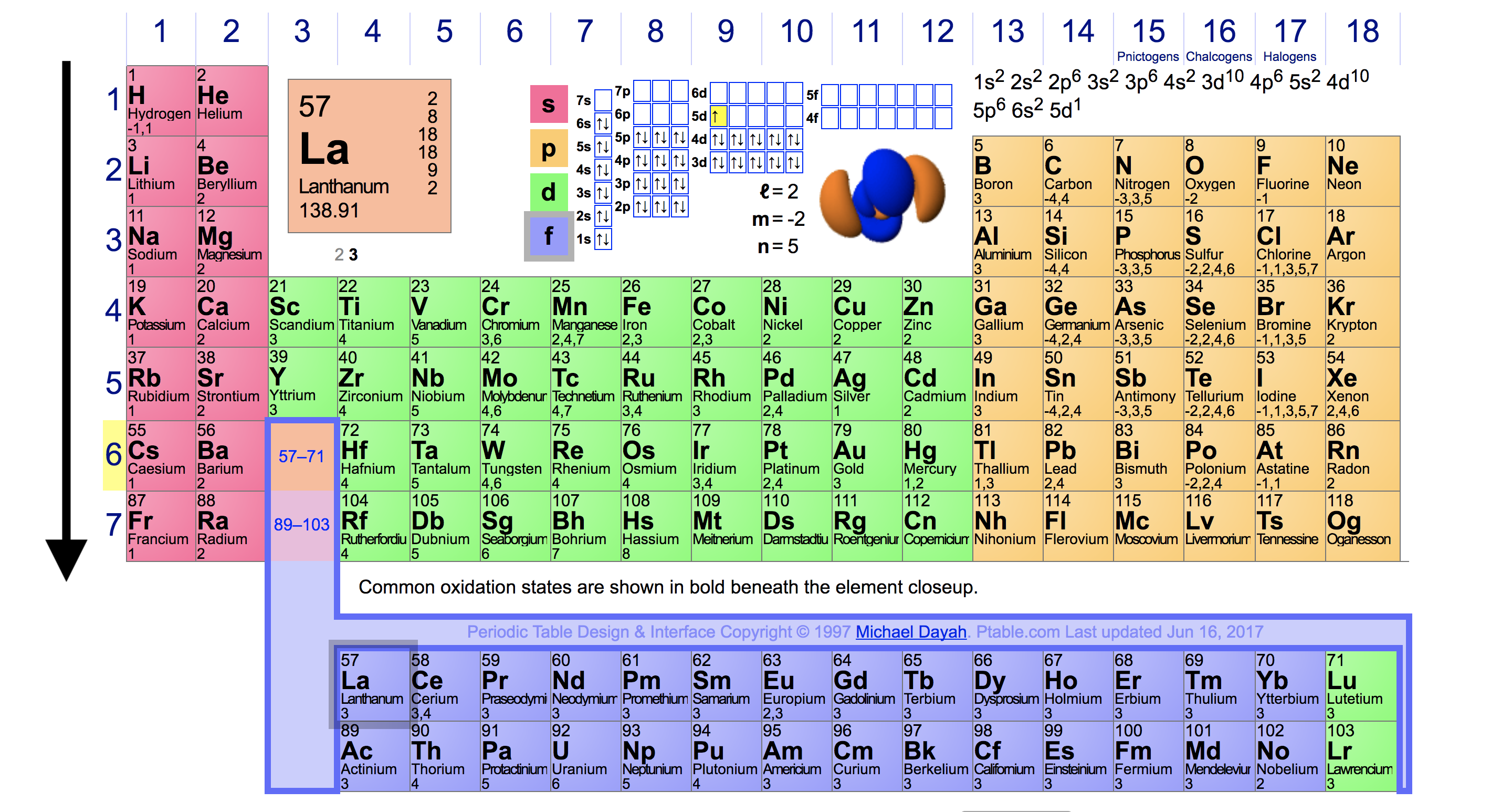
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
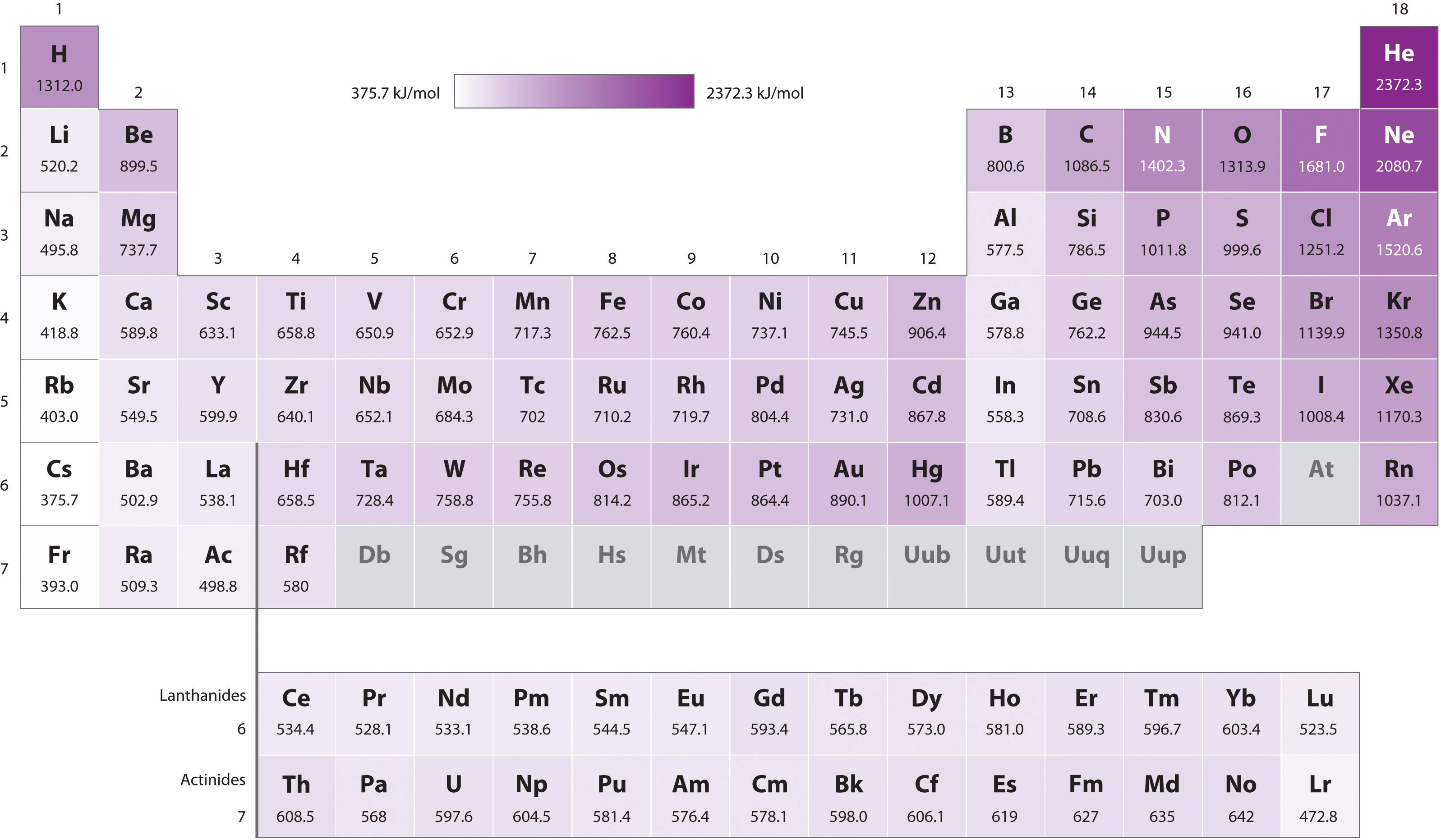
8.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
Amazing Ideas Of Ionization Energy Table Photos Darkata
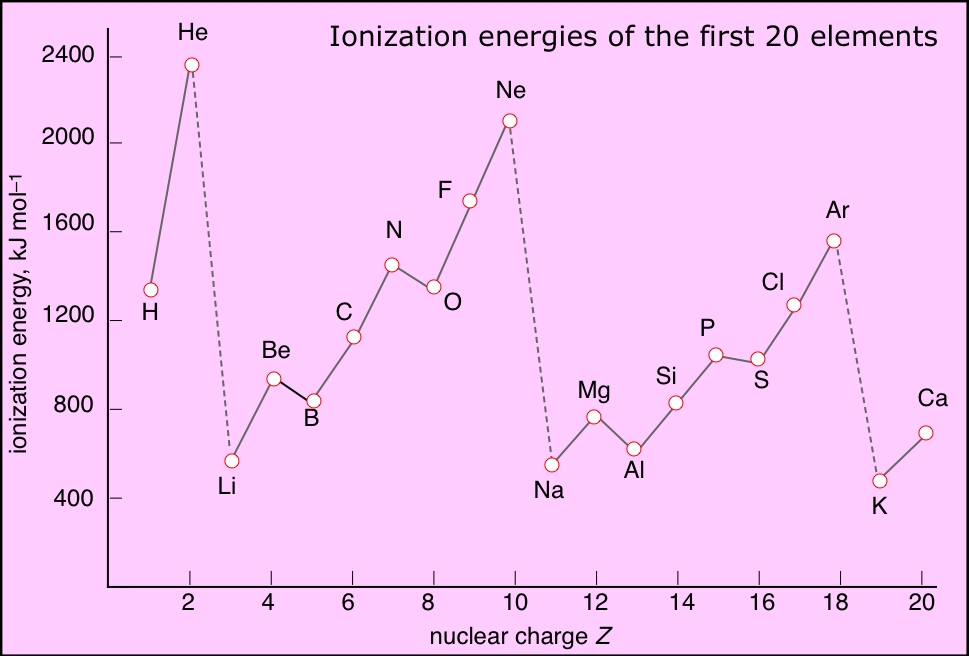
savvychemist Ionization Energy (3) Sub Shell Atomic Structure and
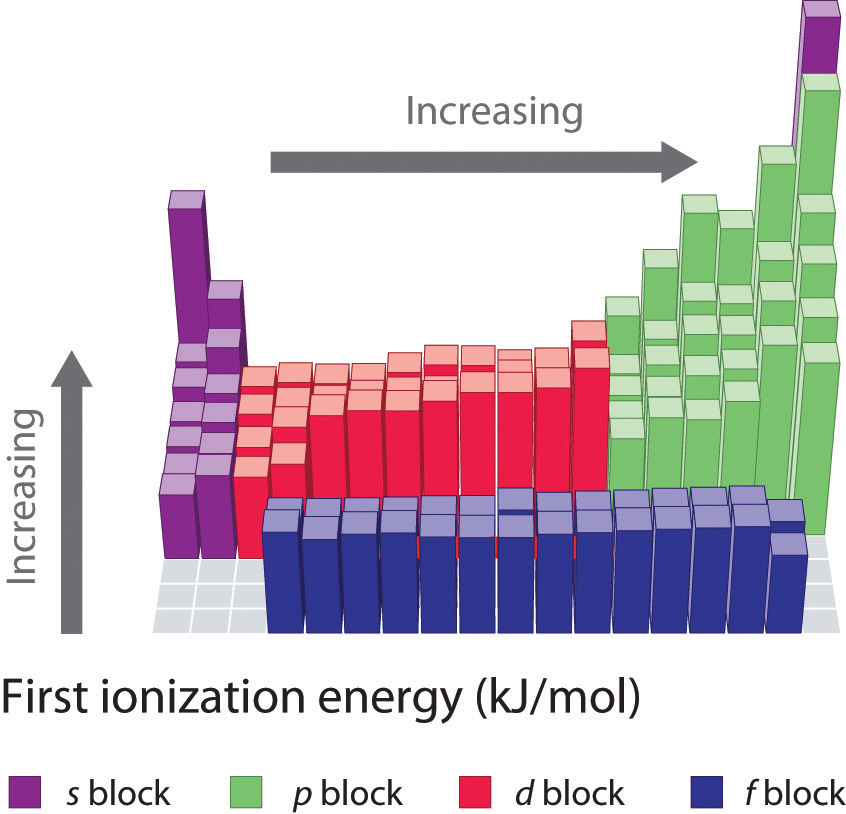
Chapter 3.3 Energetics of Ion Formation Chemistry LibreTexts

Ionization Energy Definition, Chart & Periodic Table Trend
This Is The Energy Per Mole Necessary To Remove Electrons From Gaseous Atoms Or Atomic Ions.
Web Ionization Energy Is The Energy Required To Remove An Electron From A Neutral Atom In Its Gaseous Phase.
Web The Ionization Energy Is A Measure Of The Energy Required To Remove One Electron From One Mole Of Gaseous Atoms Or Ions.
Ionization Leads To A Positive Electrical Charge.
Related Post:
