Ionisation Energy Chart
Ionisation Energy Chart - Chemical elements listed by ionization energy. First ionization energies generally decrease down a column. The first of these quantities is used in atomic physics, the second in chemistry, but both refer to the same basic property of the element. The ionization energy differs for each atom. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. This is due to increasing nuclear charge, which results in the outermost electron being. The size of that attraction will be governed by: The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Want to join the conversation? Web ionization energies increase from left to right across each row, with discrepancies occurring at ns 2 np 1 (group 13), ns 2 np 4 (group 16), and ns 2 (n − 1)d 10 (group 12) electron configurations. Web ionization energy is the energy needed to ionize an atom in the gas phase. Click on any element's name for further. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web values from crc are ionization energies given in the unit ev; The ionization energy is the quantity of energy that an isolated, gaseous atom in the ground electronic state must absorb to discharge an electron, resulting in a cation. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. Unlike atomic radii, we can and do measure ionization energies in the gas phase, when the atom or ion is not interacting with anything else. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements. Unlike atomic radii, we can and do measure ionization energies in the gas phase, when the atom or ion is not interacting with anything else. For example, look at the pattern from li to ne, and then compare it with the identical pattern from na to ar. Web ionization is the process of removing an electron from a neutral atom. The size of that attraction will be governed by: There are trends that match the structure of the periodic table. Web ionization energies increase from left to right across each row, with discrepancies occurring at ns 2 np 1 (group 13), ns 2 np 4 (group 16), and ns 2 (n − 1)d 10 (group 12) electron configurations. Web values. Across a period, ionization energy tends to increase. H(g) → h+(g) +e− (1) (1) h ( g) → h + ( g) + e −. Web ionization energy is denoted by the symbols ie, ip, δh° and has units of kilojoule per mole ( (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev). Web ionization energies increase from left to right across each row,. The ionization energy differs for each atom. X + is an ion of atom x with a single positive charge. Ie is also known as ionization potential. Web the first 20 elements. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. Ie is also known as ionization potential. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. Web ionization energy (the energy associated with forming a cation) decreases down a group and mostly increases across a period because it. H(g) → h+(g) +e− (1) (1) h ( g) → h + ( g) + e −. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. That means that it varies in a repetitive way as you move through the periodic table. Web ionization is the process. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction There are exceptions to this periodic table. Web ionization is the process of removing an electron from a neutral atom (or compound). The ionization energy is the quantity of energy that an isolated, gaseous atom in the ground electronic state must absorb to discharge an electron, resulting in a cation. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction There are exceptions to this periodic table. Web describe the significance and periodic trend of ionization energy. There are trends that match the structure of the periodic table. The first of these quantities is used in atomic physics, the second in chemistry, but both refer to the same basic property of the element. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. From left to right, the atomic number of the elements increases gradually, increasing the number of protons and the nuclear charge. Ie is also known as ionization potential. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Ionization energy increases moving across a period and decreases moving down a group. Web ionization energy is denoted by the symbols ie, ip, δh° and has units of kilojoule per mole ( (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev). An+(g) a(n+1)+ (g) +e− ie = δu a ( g) n + a ( g) ( n + 1) + + e − i e = δ u. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Across a period, ionization energy tends to increase.
Ionization Energy Definition, Chart & Periodic Table Trend

Successive Ionisation Energy vigglegiggle
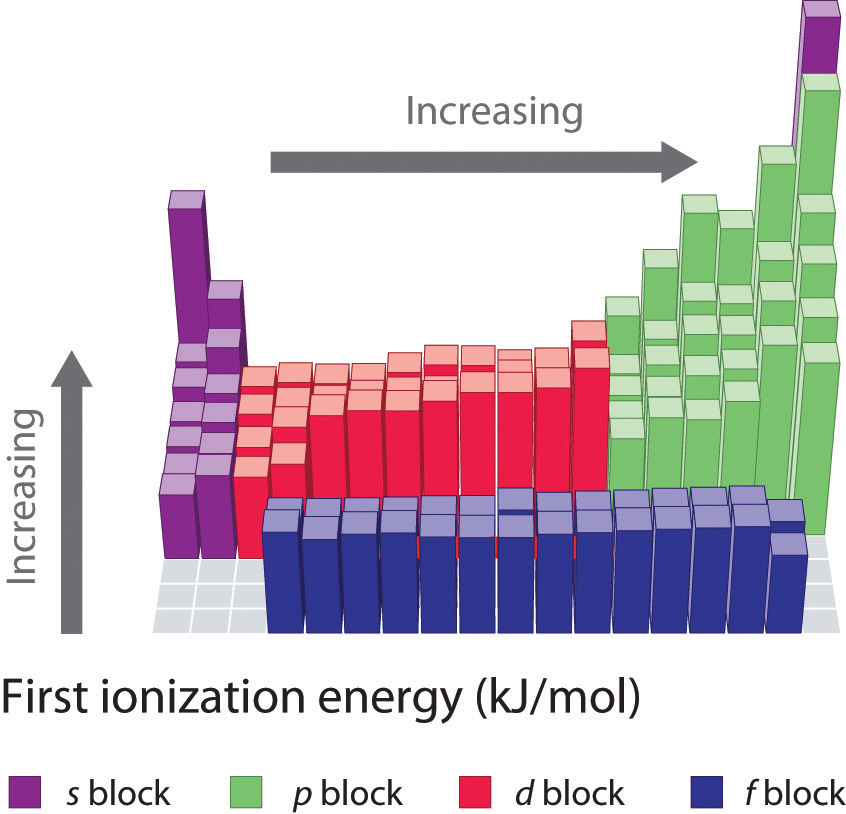
Chapter 3.3 Energetics of Ion Formation Chemistry LibreTexts
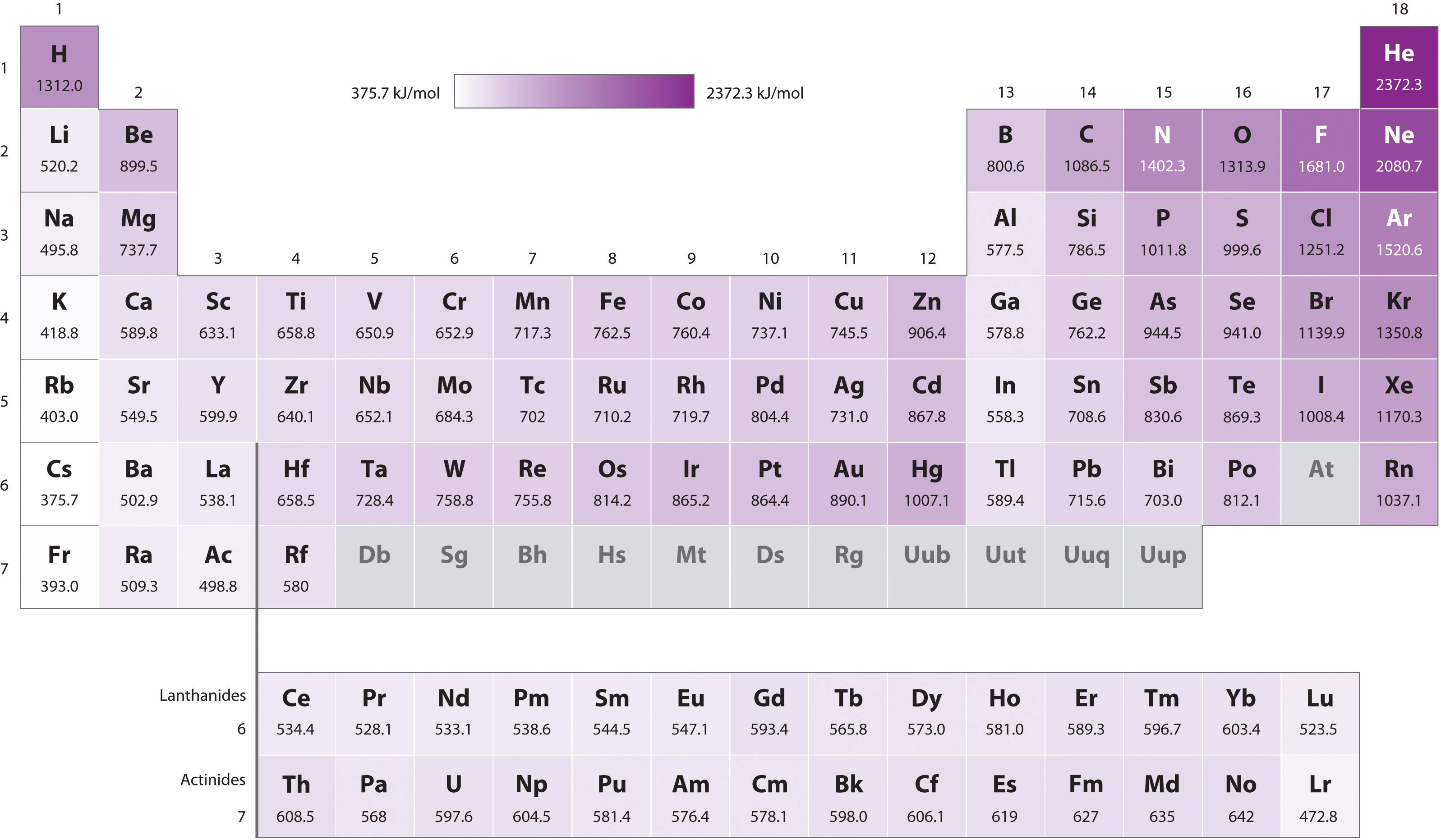
8.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts

Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemwiki
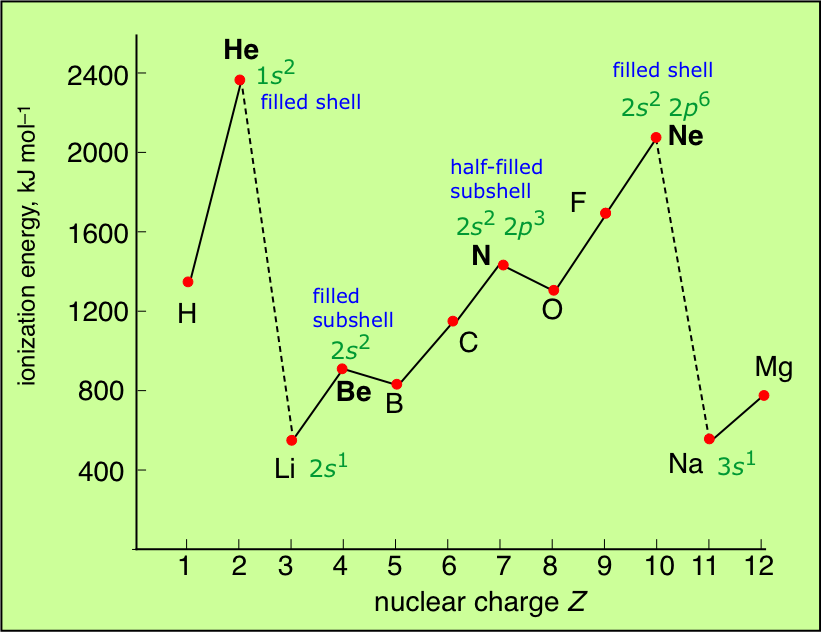
Which element has the highest first ionization energy? Socratic

Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
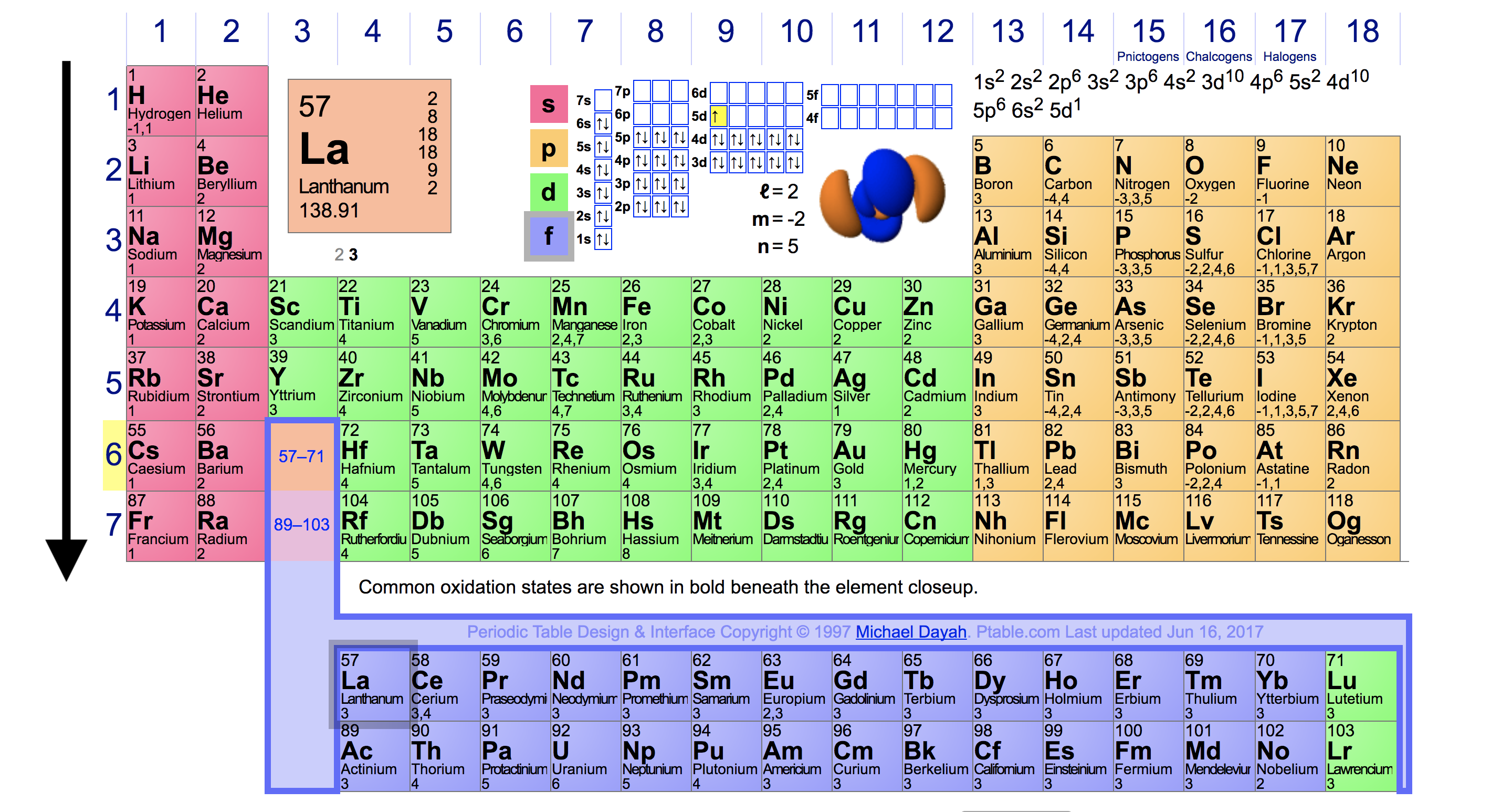
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
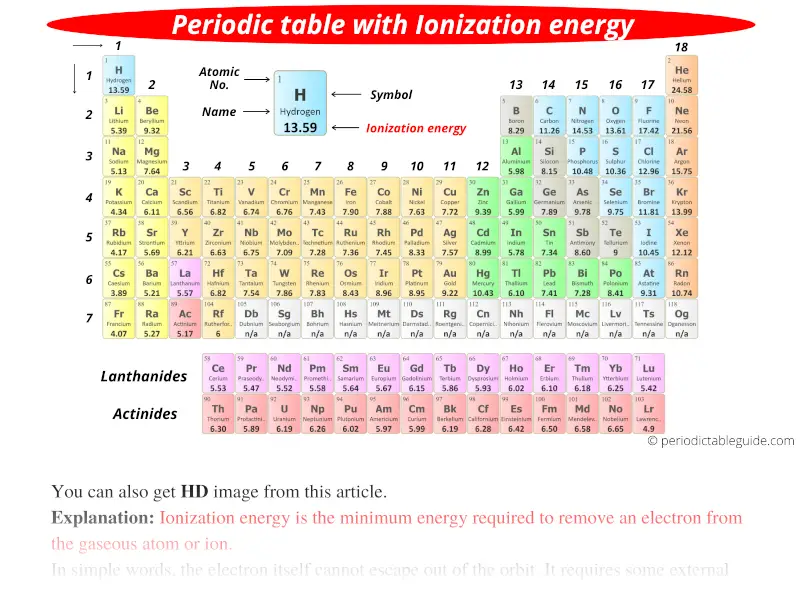
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
Web Ionization Is The Process Of Removing An Electron From A Neutral Atom (Or Compound).
Web Definition Of Ion And Ionization Energy, And Trends In Ionization Energy Across A Period And Down A Group.
Because Positive Charge Binds Electrons More Strongly, The Second Ionization Energy Of An Element Is Always Higher Than The First.
Unlike Atomic Radii, We Can And Do Measure Ionization Energies In The Gas Phase, When The Atom Or Ion Is Not Interacting With Anything Else.
Related Post:
