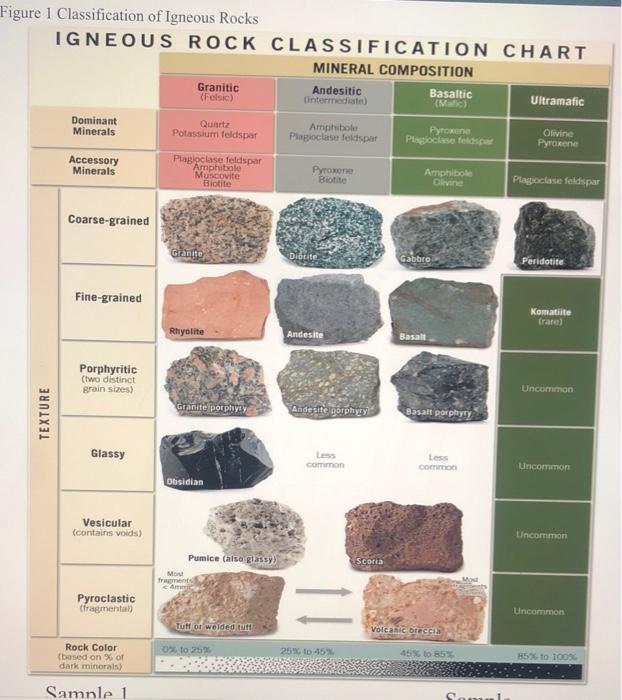
Igneous Rocks Chart
Igneous Rocks Chart - Pictures and brief descriptions of some common igneous rock types are shown on this page. Igneous rocks are those that form via the process of melting and cooling. Most igneous rocks are hard and dense. Web figure 7.13 classification diagram for igneous rocks. Here is how it works: Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. Granite boulders at joshua tree national park, california. Web in this study, we evaluated the fungal diversity present associated with cores of oligocene rocks using a dna metabarcoding approach. Web igneous rocks form when molten material cools and hardens. Intrusive rocks have larger crystals due to slower cooling, while extrusive rocks have smaller crystals resulting from rapid cooling. Web though they vary widely in composition, most igneous rocks consist of quartz, feldspars, pyroxenes, amphiboles, micas, olivines, nepheline, leucite, and apatite. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content. Igneous rocks find uses due to their durability. Web igneous rocks are classified based on. Igneous rocks find uses due to their durability. [2] magma is molten rock that flows beneath the earth's surface. Web igneous rock (igneous from latin igneus 'fiery'), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. We detected 940,969 dna reads grouped into 198 amplicon sequence variants (asvs) representing the phyla ascomycota,. Intrusive rocks have larger crystals due to slower cooling, while extrusive rocks have smaller crystals resulting from rapid cooling. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. [2] magma is molten rock that flows beneath the earth's surface. Web igneous rocks are characterized by several distinct properties:. Each of these types of rocks will have specific properties that will help you distinguish which type your igneous rock is. The word igneous derives from ignis, the latin word for “fire.” Here is how it works: Classify igneous rocks into two main types: Granite boulders at joshua tree national park, california. Web an igneous rock can be represented as a vertical line drawn through the diagram, and the vertical scale used to break down the proportion of each mineral it contains. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Determine the color (indicates mineral composition) Typically orthoclase), pyroxene (typically augite), and quartz. They may form. Web updated on june 02, 2019. Rocks hold the history of the earth and the materials that will be used to build its future. I’ll walk you through how to determine what type of igneous rock you have and provide some helpful procedures and descriptions to compare to. Composition of igneous rocks is properly identified by determination of the rock's. Igneous rocks find uses due to their durability. Typically orthoclase), pyroxene (typically augite), and quartz. Most igneous rock is buried below the surface and covered with sedimentary rock, and so we do not often see just how much igneous rock there is on earth. Composition of igneous rocks is properly identified by determination of the rock's chemical composition. The magma. Most igneous rock is buried below the surface and covered with sedimentary rock, and so we do not often see just how much igneous rock there is on earth. The word igneous derives from ignis, the latin word for “fire.” Web figure 7.13 classification diagram for igneous rocks. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size.. Determine the color (indicates mineral composition) Most igneous rocks are hard and dense. If they erupt from volcanoes onto the surface as lava, they are called extrusive rocks. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. For example, the. They may form either below or above earth’s surface. Web igneous rocks are characterized by several distinct properties: It has a composition that is intermediate between rhyolite and andesite. Classify igneous rocks into two main types: They often have a crystalline texture due to the interlocking of crystals that form as the molten rock cools. This, however, requires chemical equipment and apparatus that is unavailable in this lab. Composition refers to the rock’s specific mineralogy and chemical composition. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Most igneous rocks are hard and dense. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Estimate those proportions using the diagrams in figure 3.17, and then use figure 3.16 to determine the likely rock name for each one. In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. Web igneous rock (igneous from latin igneus 'fiery'), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria, and tuff. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. Igneous rocks are also classified according to their textures. They often have a crystalline texture due to the interlocking of crystals that form as the molten rock cools. Photos, descriptions and facts about intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. Web the qap ternary diagram is used to classify igneous rocks with visible mineral grains (phaneritic texture) from their feldspar and quartz content.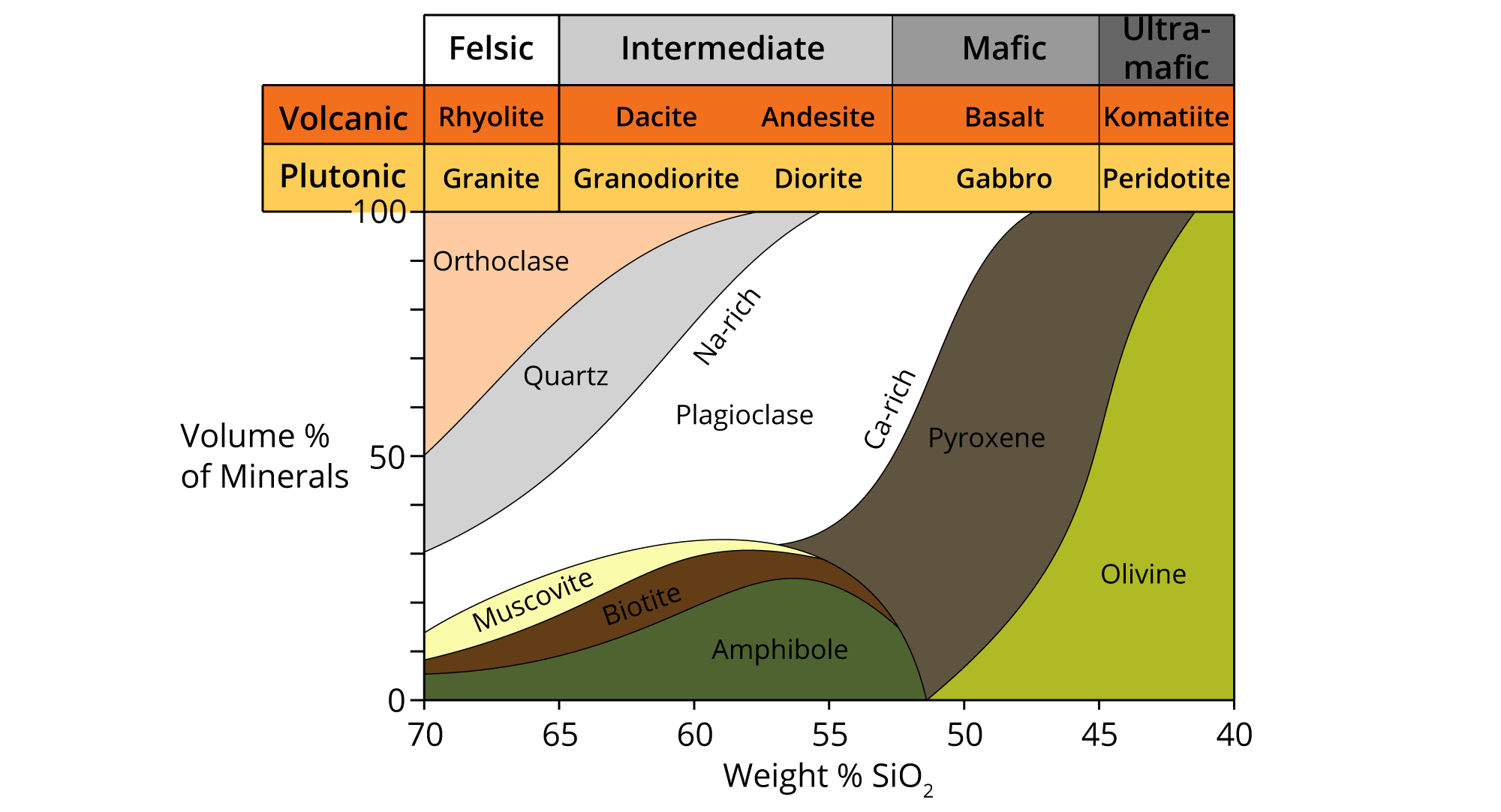
Igneous Rock Types Chart
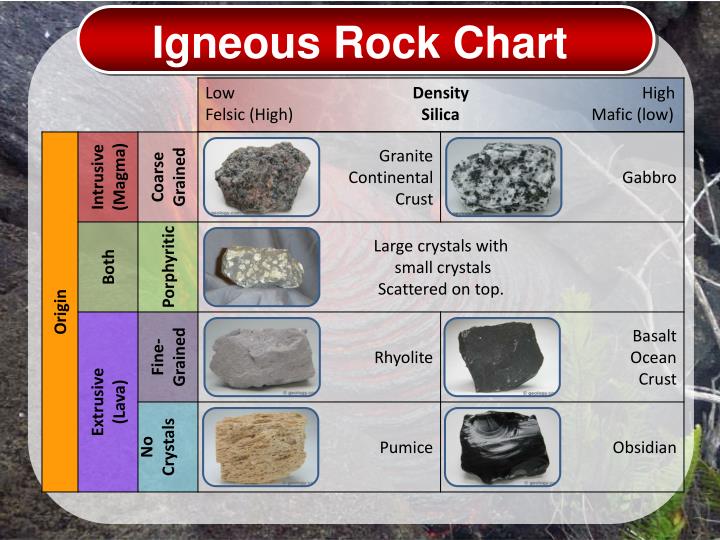
Igneous Rock Textures Chart
Solved Figure 1 Classification of Igneous Rocks IGNEOUS ROCK

Igneous Rock Chart Flinn Scientific
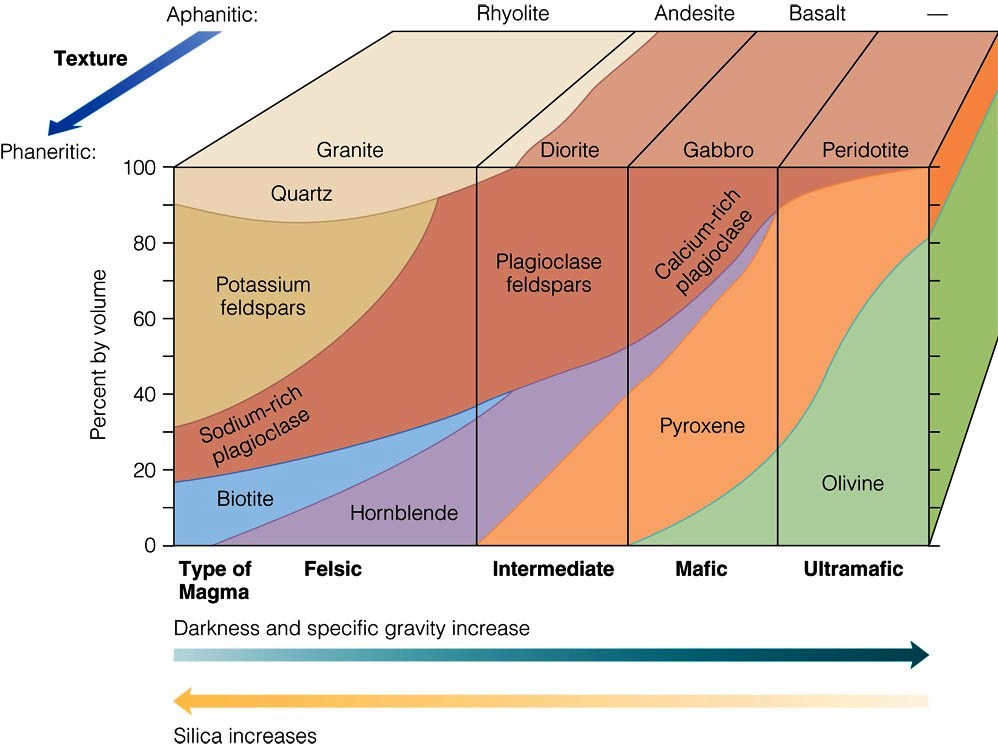
How Do Different Igneous Rocks Form From One Original Supply of Magma?
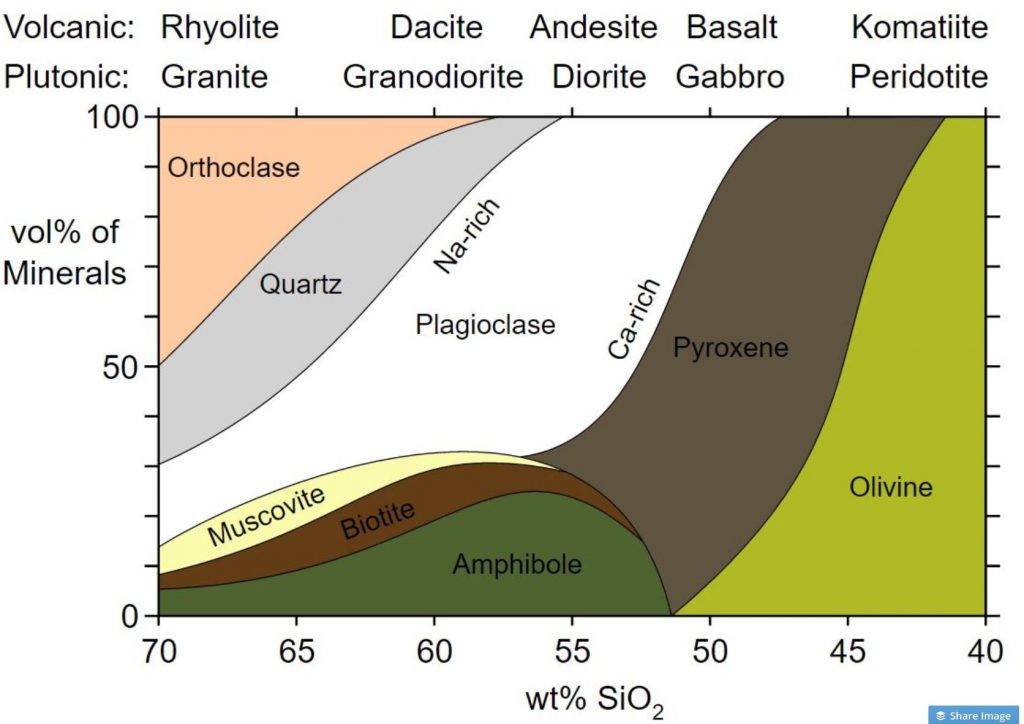
4.1 Classification of Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts
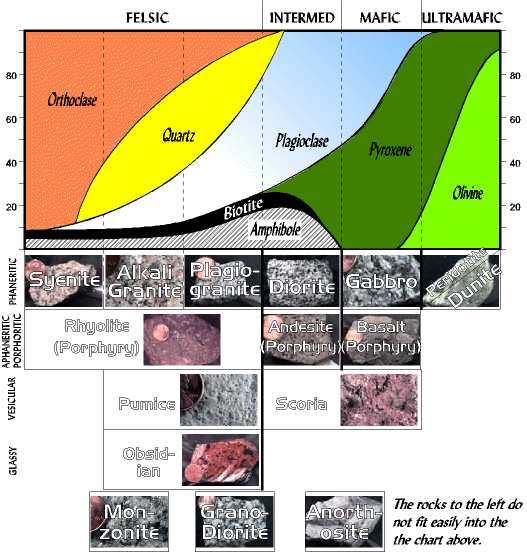
General Classification of Igneous Rocks
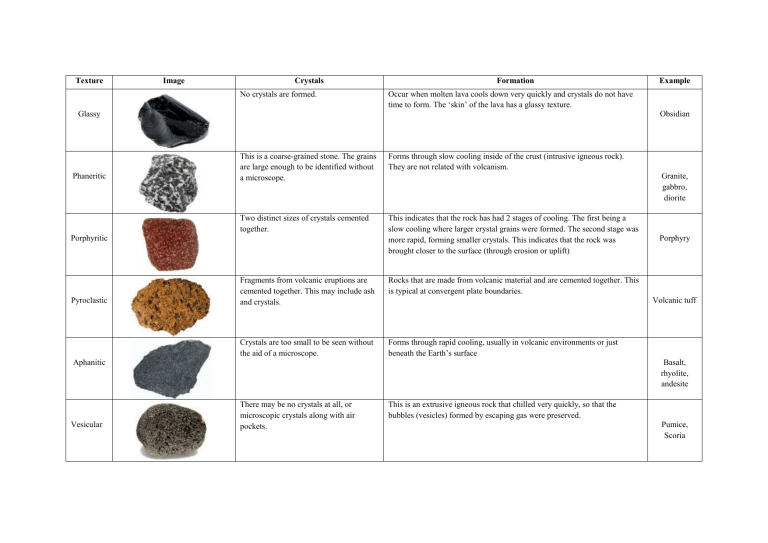
Igneous Rocks Texture Types

Igneous Rock Chart

General Classification of Igneous Rocks
Intrusive Rocks Have Larger Crystals Due To Slower Cooling, While Extrusive Rocks Have Smaller Crystals Resulting From Rapid Cooling.
Web Though They Vary Widely In Composition, Most Igneous Rocks Consist Of Quartz, Feldspars, Pyroxenes, Amphiboles, Micas, Olivines, Nepheline, Leucite, And Apatite.
It Has A Composition That Is Intermediate Between Rhyolite And Andesite.
I’ll Walk You Through How To Determine What Type Of Igneous Rock You Have And Provide Some Helpful Procedures And Descriptions To Compare To.
Related Post: