Hyponatremia Flow Chart
Hyponatremia Flow Chart - Web hyponatremia is considered mild when the sodium concentration is 130 to 134 meq per l, moderate when 125 to 129 meq per l, and severe when less than 125 meq per l. The cause of hyponatraemia is often multifactorial. Web hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 meq/l, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally. Web hyponatremia can be classified according to the volume status of the patient as hypovolemic, hypervolemic, or euvolemic. Then check plasma osmolality to determine if true or false hyponatremia. Web hyponatraemia is defined as serum sodium 125 mmol/l are asymptomatic. Investigation of hyponatraemia in adults. Cortisol (9am level) thyroid function tests. In healthy individuals, the ingestion of water does not lead to hyponatremia because suppressed release of antidiuretic hormone (adh), also called vasopressin, allows excess water to be excreted in a. Web hyponatraemia is a serum sodium concentration Web acute hyponatremia is characterized by onset of symptoms <48h. Hyponatremia (serum sodium hyponatremia</strong> has been associated with an increased risk of mortality. Web hyponatraemia, defined as a serum sodium concentration !135 mmol/l, is the most common disorder of body fluid and electrolyte balance encountered in clinical practice. Common problem in icu (30% of patients have a na < 134mmol/l). Common problem in icu (30% of patients have a na < 134mmol/l) independent predictor of mortality in icu. Web hyponatremia is considered mild when the sodium concentration is 130 to 134 meq per l, moderate when 125 to 129 meq per l, and severe when less than 125 meq per l. Acute — duration of less than 48 hours. Hyponatraemia. The cause of hyponatraemia is often multifactorial. Web hyponatremia, which is defined as a plasma na + concentration <135 mm, is a very common disorder, occurring in up to 22% of hospitalized patients. In healthy individuals, the ingestion of water does not lead to hyponatremia because suppressed release of antidiuretic hormone (adh), also called vasopressin, allows excess water to be. Web the most common classification system for hyponatremia is based on volume status: Web hyponatraemia, defined as a serum sodium concentration !135 mmol/l, is the most common disorder of body fluid and electrolyte balance encountered in clinical practice. Web hyponatremia, which is defined as a plasma na + concentration <135 mm, is a very common disorder, occurring in up to. Web follow chronic hyponatraemia flow chart on page 3. Hyponatraemia and rapid fluid shifts can result in cerebral oedema causing neurological symptoms. Severe — serum sodium concentration less than 125 mmol/l. Web acute hyponatremia is characterized by onset of symptoms <48h. An aberrantly low sodium may result from drawing electrolytes upstream from a hypotonic infusion. 1 this may explain why management of hyponatremia is still suboptimal, as also recently illustrated by a hyponatremia registry. Acute — duration of less than 48 hours. Web our approach to treating patients with hyponatremia depends upon the duration of the hyponatremia, the severity of the hyponatremia, the presence and severity of symptoms, and the presence of preexisting intracranial pathology. An aberrantly low sodium may result from drawing electrolytes upstream from a hypotonic infusion. Web hyponatremia is a lab diagnosis. Hypovolemic (decreased total body water with greater decrease in sodium level), euvolemic (increased total body. Common problem in icu (30% of patients have a na < 134mmol/l) independent predictor of mortality in icu. Hyponatremia (serum sodium hyponatremia</strong> has been associated. Chronic — duration of 48 hours or more. Web our approach to treating patients with hyponatremia depends upon the duration of the hyponatremia, the severity of the hyponatremia, the presence and severity of symptoms, and the presence of preexisting intracranial pathology such as recent traumatic brain injury, recent intracranial surgery or hemorrhage, or an intracranial. If na <125 mmol/l or. Common problem in icu (30% of patients have a na < 134mmol/l) independent predictor of mortality in icu. Patients with acute hyponatremia develop neurologic symptoms resulting from cerebral edema induced by water movement into the brain. Then check plasma osmolality to determine if true or false hyponatremia. Web first step, repeat serum sodium measurement! Hyponatremia can be seen in patients. The rate of onset of hyponatraemia can be classified as: An aberrantly low sodium may result from drawing electrolytes upstream from a hypotonic infusion. Hypervolemic hyponatremia may be caused by congestive heart failure,. Web hyponatraemia, defined as a serum sodium concentration !135 mmol/l, is the most common disorder of body fluid and electrolyte balance encountered in clinical practice. Chronic —. Web hyponatremia is considered mild when the sodium concentration is 130 to 134 meq per l, moderate when 125 to 129 meq per l, and severe when less than 125 meq per l. 1 this may explain why management of hyponatremia is still suboptimal, as also recently illustrated by a hyponatremia registry. Web follow chronic hyponatraemia flow chart on page 3. This disorder is almost always the result of an increase in circulating avp and/or increased renal sensitivity to avp, combined with an intake of free water; Web hyponatraemia is a serum sodium concentration Web hyponatraemia is defined as serum sodium 125 mmol/l are asymptomatic. Hyponatremia can be seen in patients with euvolemia, hypovolemia, or hypervolemia. Cortisol (9am level) thyroid function tests. Web hyponatremia, which is defined as a plasma na + concentration <135 mm, is a very common disorder, occurring in up to 22% of hospitalized patients. Sodium is low, but plasma osmolality is normal (e.g. Web hyponatremia is a lab diagnosis. Web hyponatremia (serum sodium [s na] <136 mmol/l) is a common water balance disorder that often poses a diagnostic or therapeutic challenge. A notable exception is hyponatremia due. Hypovolemic (decreased total body water with greater decrease in sodium level), euvolemic (increased total body. Web our approach to treating patients with hyponatremia depends upon the duration of the hyponatremia, the severity of the hyponatremia, the presence and severity of symptoms, and the presence of preexisting intracranial pathology such as recent traumatic brain injury, recent intracranial surgery or hemorrhage, or an intracranial. The rate of onset of hyponatraemia can be classified as: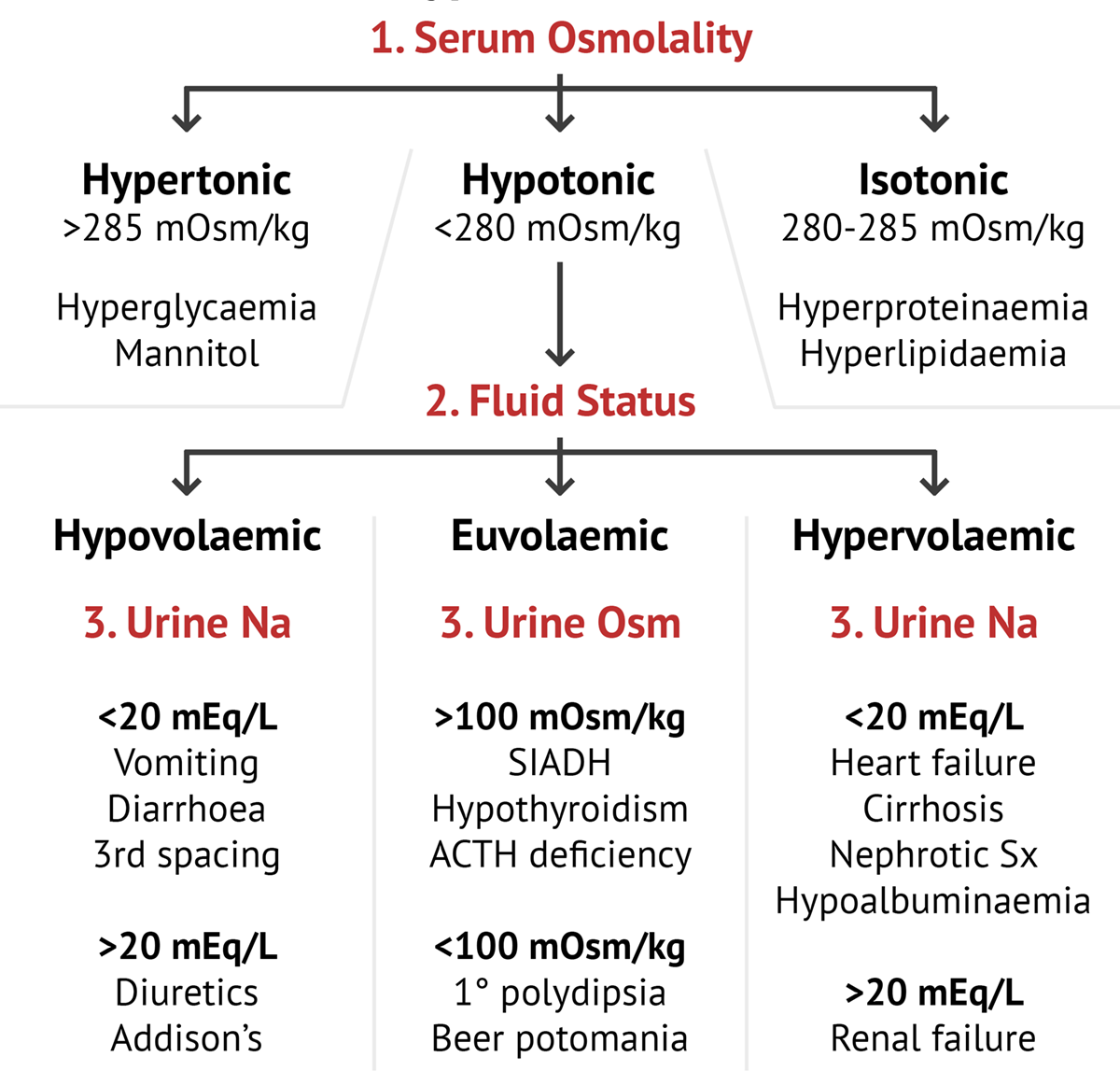
Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia Hyponatremia Electrolytes Nursing Images

Hyponatremia Differential Diagnosis Algorithm Hypovolemic Grepmed My

Hyponatremia Flow Chart Curbsiders Images And Photos vrogue.co

Hyponatremia Flowchart Images and Photos finder

Hyponatremia Stages

Hyponatremia Ddx

Hyponatremia Rapid Reviews Videos EM Cases
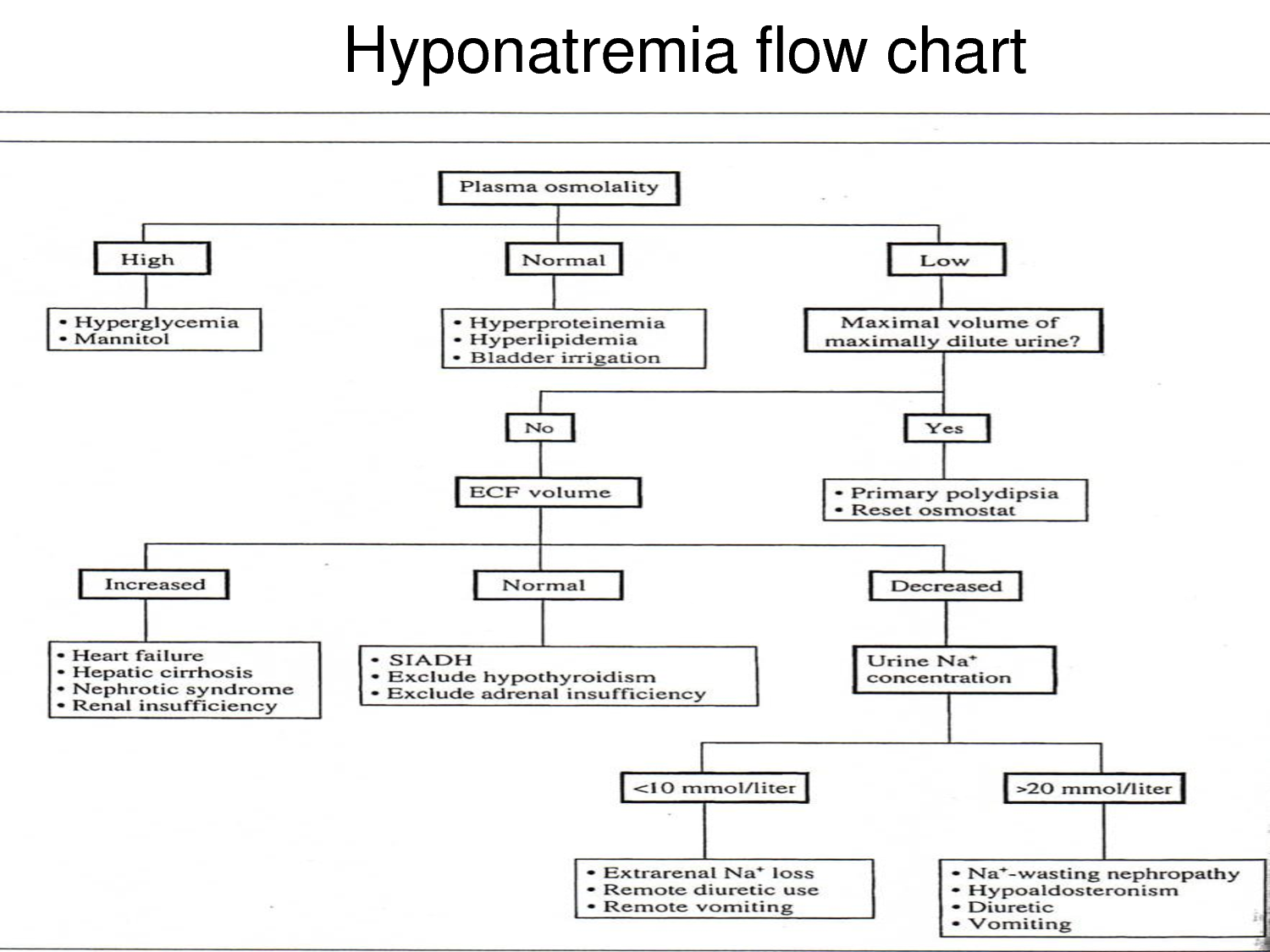
Hyponatremia Workup Chart
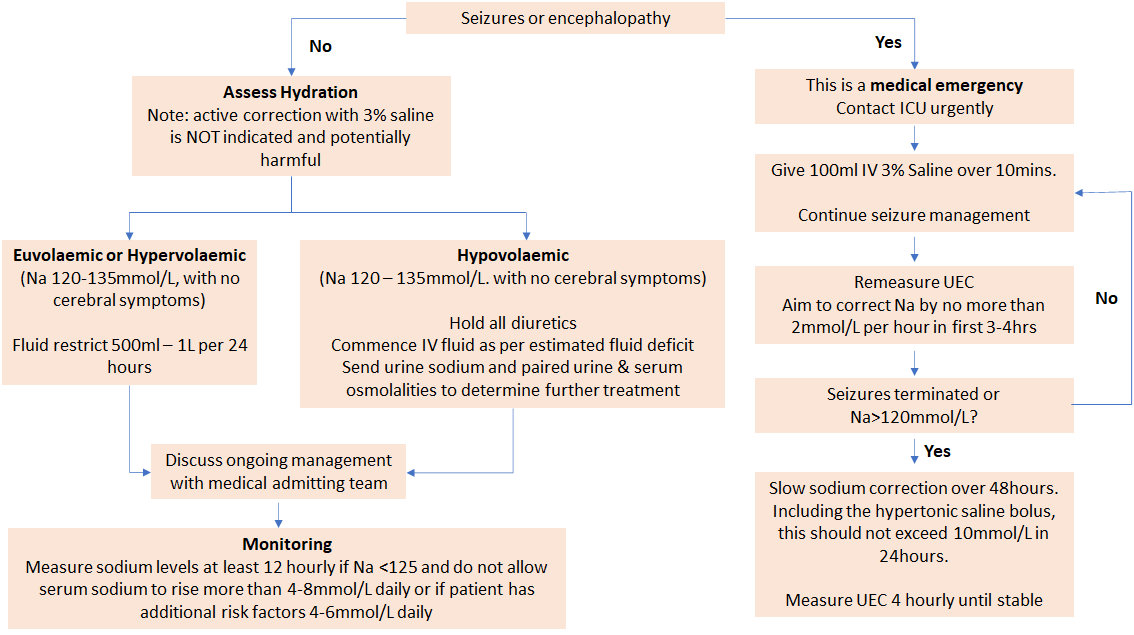
Sodium Hyponatraemia Emergency Care Institute
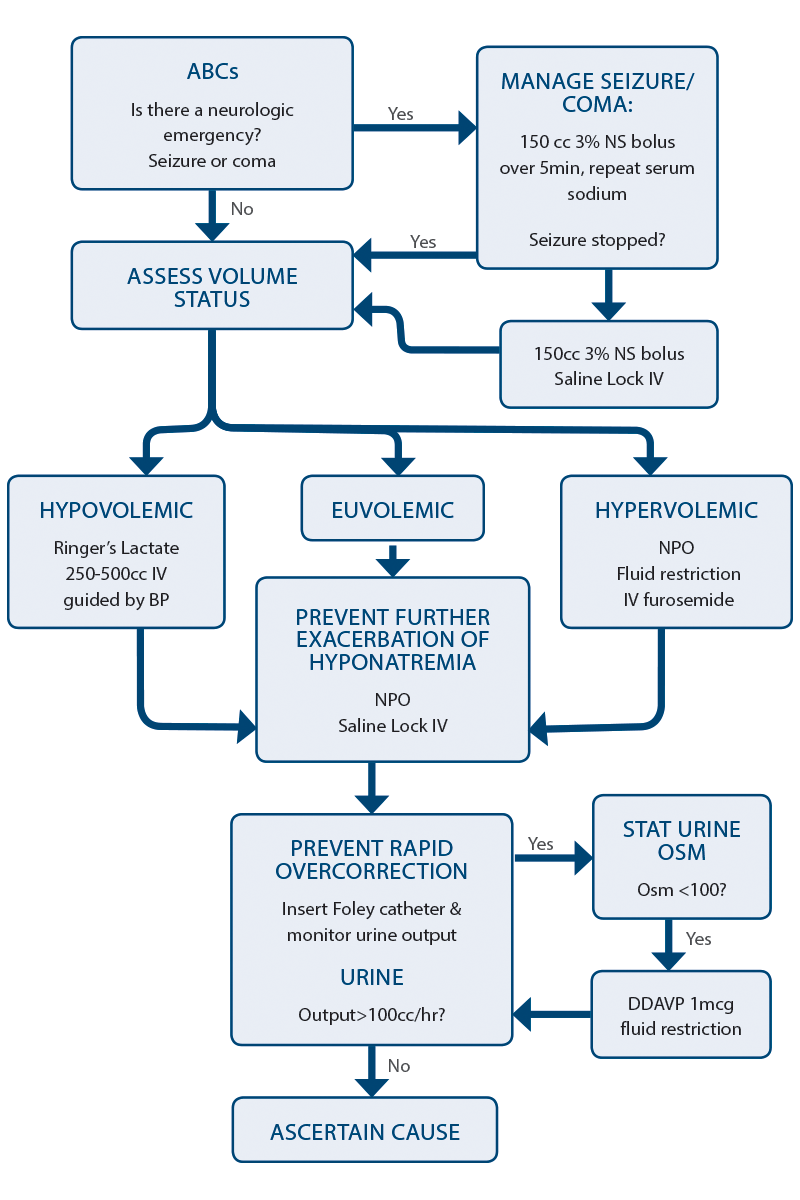
Hyponatremia Flowchart
Severe — Serum Sodium Concentration Less Than 125 Mmol/L.
Hyponatraemia And Rapid Fluid Shifts Can Result In Cerebral Oedema Causing Neurological Symptoms.
Common Causes Are Fluid Overload From Ccf Or Dehydration From Intercurrent Illnesses And Correct Identification Will Dictate Treatment (See Flow Chart Below).
An Aberrantly Low Sodium May Result From Drawing Electrolytes Upstream From A Hypotonic Infusion.
Related Post: