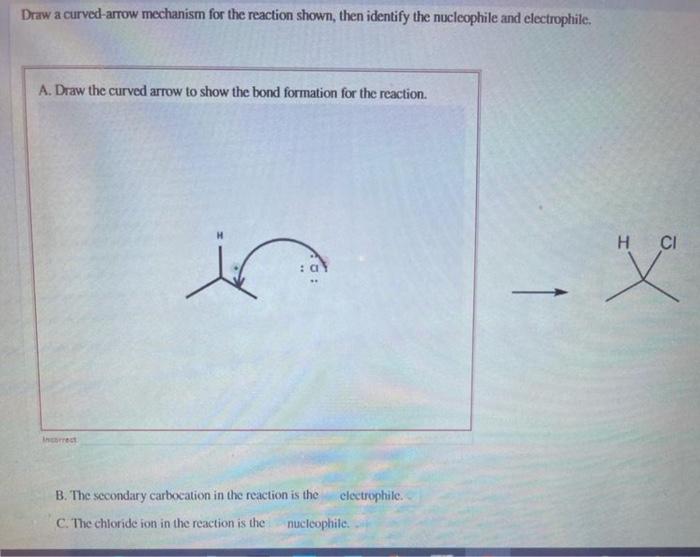
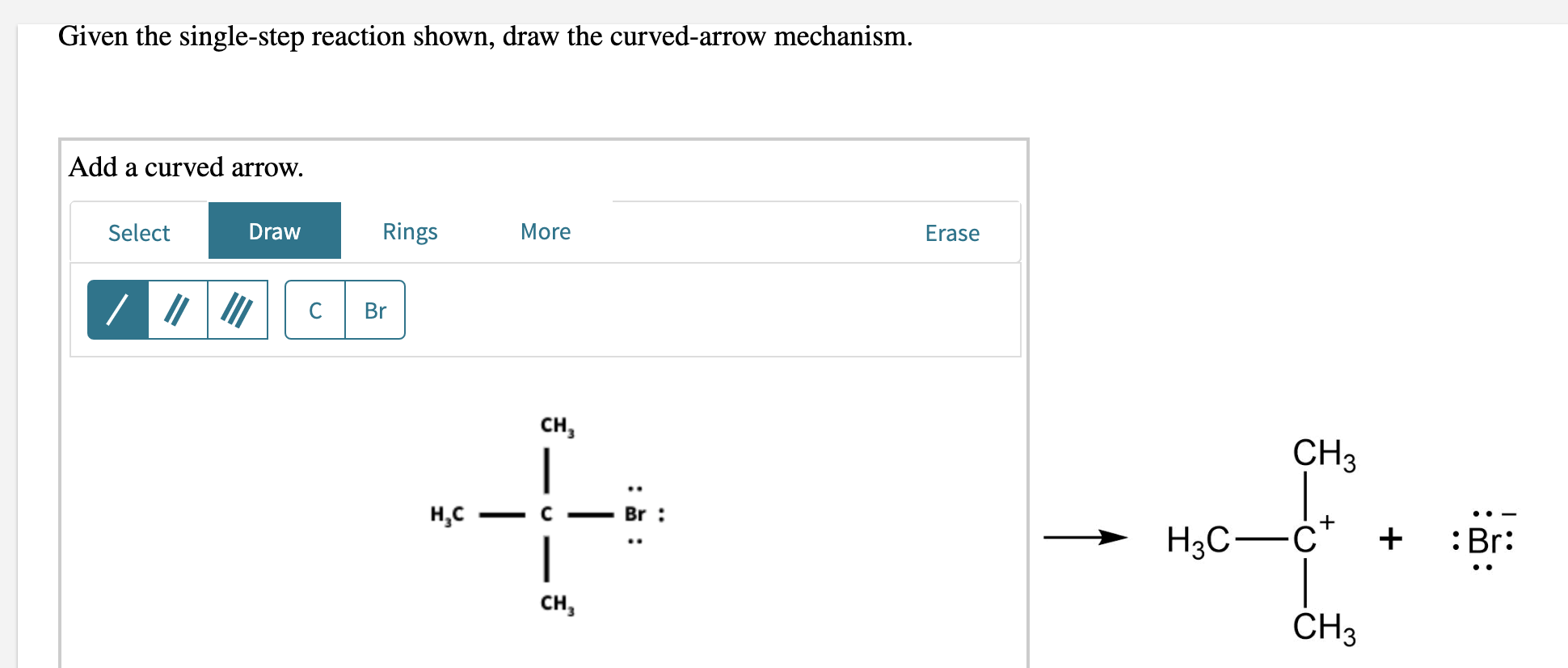
Given The Singlestep Reaction Shown Draw The Curvedarrow Mechanism
Given The Singlestep Reaction Shown Draw The Curvedarrow Mechanism - Here we can see that we are having a 3 degree alkyl halide and in the product side we are getting a 3 degree carbocation. This absence of a mechanism suggests that the reaction is considered to occur without detailing the individual steps involving electron movement. This problem has been solved! There are 2 steps to solve this one. The final curved arrow mechanism would look something like this: The movement of electrons is depicted Select the properties of the sn1 reaction mechanism. Draw any resulting intermediates or transition states. After completing this section, you should be able to use curved (curly) arrows, in conjunction with a chemical equation, to show the movement of electron pairs in a simple polar reaction, such as electrophilic addition. Web after completing this section, you should be able to use curved (curly) arrows, in conjunction with a chemical equation, to show the movement of electron pairs in a simple polar reaction, such as electrophilic addition. Here’s the best way to solve it. There are 2 steps to solve this one. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. This problem has been solved! The movement of electrons is depicted Here’s the best way to solve it. The movement of electrons is For the following sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. Select draw rings more erase 7 i 1 с br ch3 ch, | h₂cc + hc che ch, 5 2 0. This absence of a. Web chemistry questions and answers. The nucleophile (hydroxide ion) attacks the electrophilic carbon (carbon attached to the bromine atom). Web chemistry questions and answers. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Here we can see that we are having a 3 degree alkyl halide and in the product side we are. 100% (21 ratings) share share. The movement of electrons is Web chemistry questions and answers. Here’s the best way to solve it. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below. 100% (21 ratings) share share. Here’s the best way to solve it. \ table [ [ select , , templates,more,erase ] , [ 1 , iii, b r , , ] ] The final curved arrow mechanism would look something like this: There are 2 steps to solve this one. The movement of electrons is depicted Select draw rings more erase 7 i 1 с br ch3 ch, | h₂cc + hc che ch, 5 2 0. This absence of a mechanism suggests that the reaction is considered to occur without detailing the individual steps involving electron movement. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps. The nucleophile (hydroxide ion) attacks the electrophilic carbon (carbon attached to the bromine atom). Here we can see that we are having a 3 degree alkyl halide and in the product side we are getting a 3 degree carbocation. Curved arrows are a formal notation to help us understand the electron flow in organic reactions. This problem has been solved!. This problem has been solved! The movement of electrons is depicted Web chemistry questions and answers. Web after completing this section, you should be able to use curved (curly) arrows, in conjunction with a chemical equation, to show the movement of electron pairs in a simple polar reaction, such as electrophilic addition. Web curved arrows in organic reaction mechanisms. The nucleophile (hydroxide ion) attacks the electrophilic carbon (carbon attached to the bromine atom). The movement of electrons is The movement of electrons is depicted Select draw rings more erase 7 i 1 с br ch3 ch, | h₂cc + hc che ch, 5 2 0. After completing this section, you should be able to use curved (curly) arrows, in. Select the properties of the sn1 reaction mechanism. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Here’s the best way to solve it. Web chemistry questions and answers. 100% (21 ratings) share share. Curved arrows are a formal notation to help us understand the electron flow in organic reactions. Here we can see that we are having a 3 degree alkyl halide and in product side we are getting a 3 degree carbocation. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Here’s the best way to solve it. 100% (9 ratings) share share. The final curved arrow mechanism would look something like this: For the following sn1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step. The nucleophile (hydroxide ion) attacks the electrophilic carbon (carbon attached to the bromine atom). Here’s the best way to solve it. Web chemistry questions and answers. This problem has been solved! Web chemistry questions and answers. This problem has been solved! Select the properties of the sn1 reaction mechanism. We are asked to draw the curved arrow mechanism after a single step of reaction. There are 2 steps to solve this one.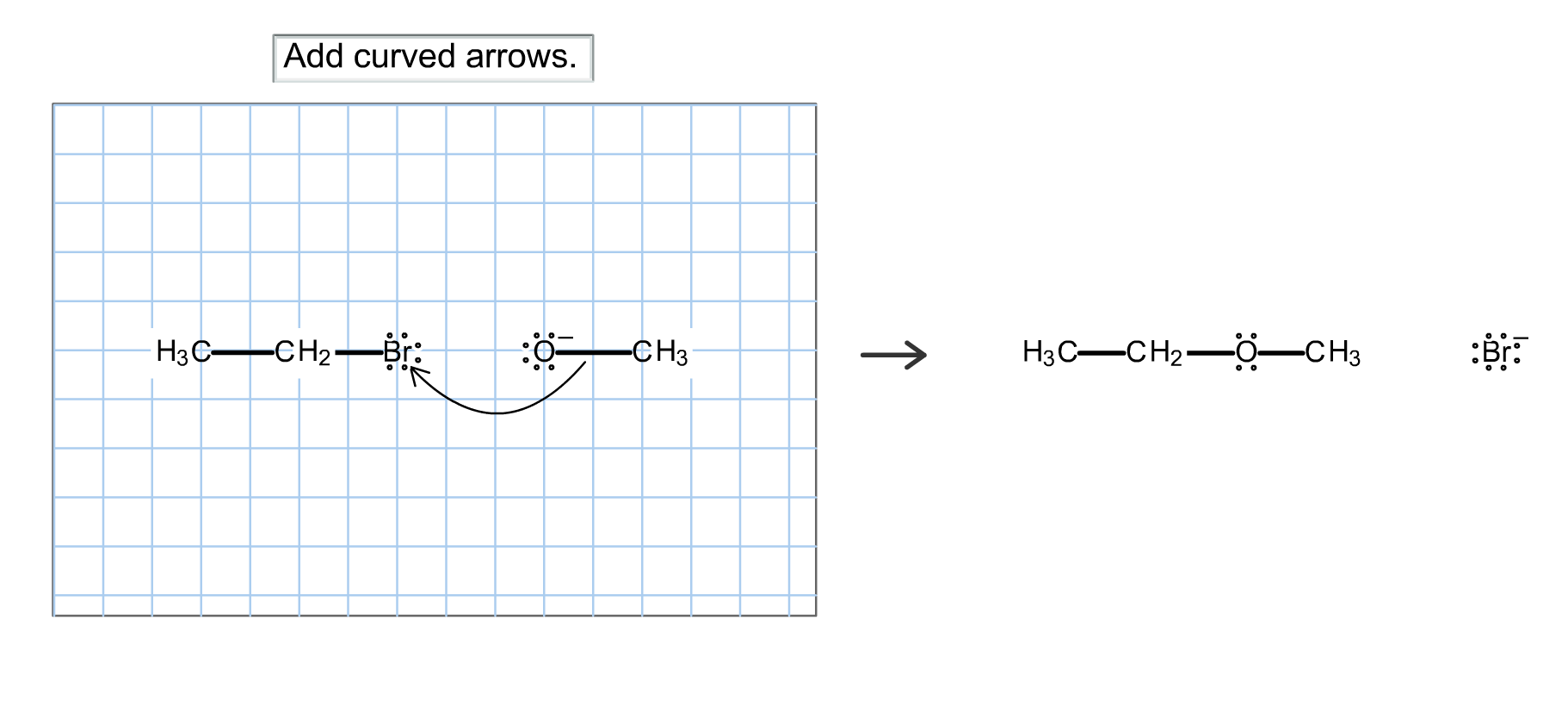
Given the following singlestep reaction, draw the curvedarrow

Solved Given The Following Singlestep Reaction, Draw The...
Solved Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the
Solved Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the
[Solved] Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the c
Solved Draw a curvedarrow mechanism for the reaction shown,
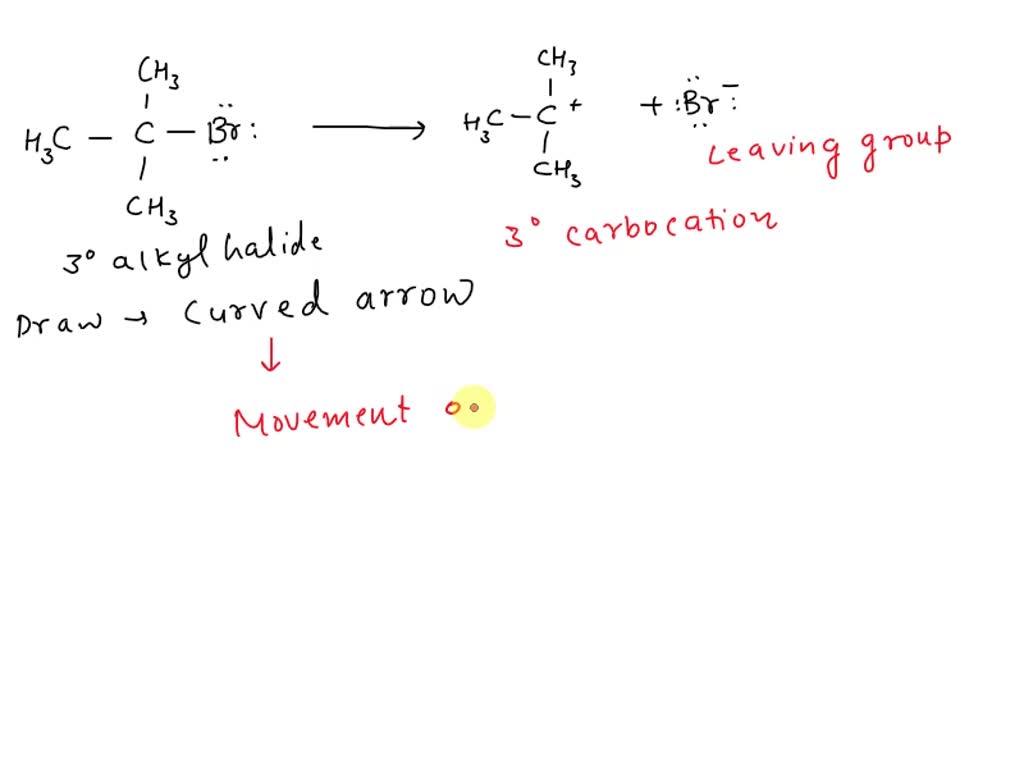
SOLVED Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the curvedarrow
Solved Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the

Given The Following Single Step Reaction Draw The Curved Arrow Mechanism
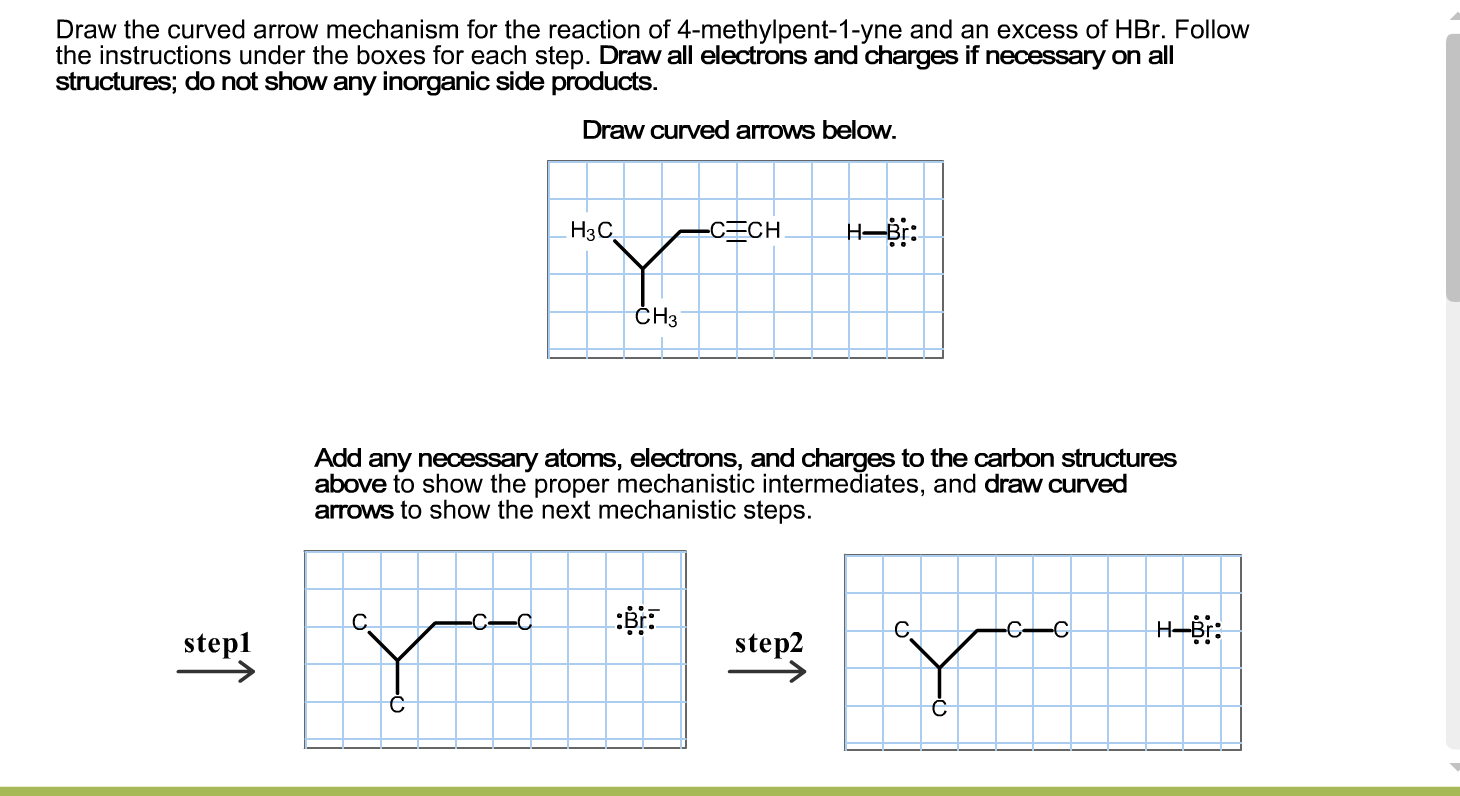
Solved Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction of
After Completing This Section, You Should Be Able To Use Curved (Curly) Arrows, In Conjunction With A Chemical Equation, To Show The Movement Of Electron Pairs In A Simple Polar Reaction, Such As Electrophilic Addition.
Add Curved Arrows Select Draw Rings More Erase Ch, H, Cbr :
There Are 2 Steps To Solve This One.
This Problem Has Been Solved!
Related Post:
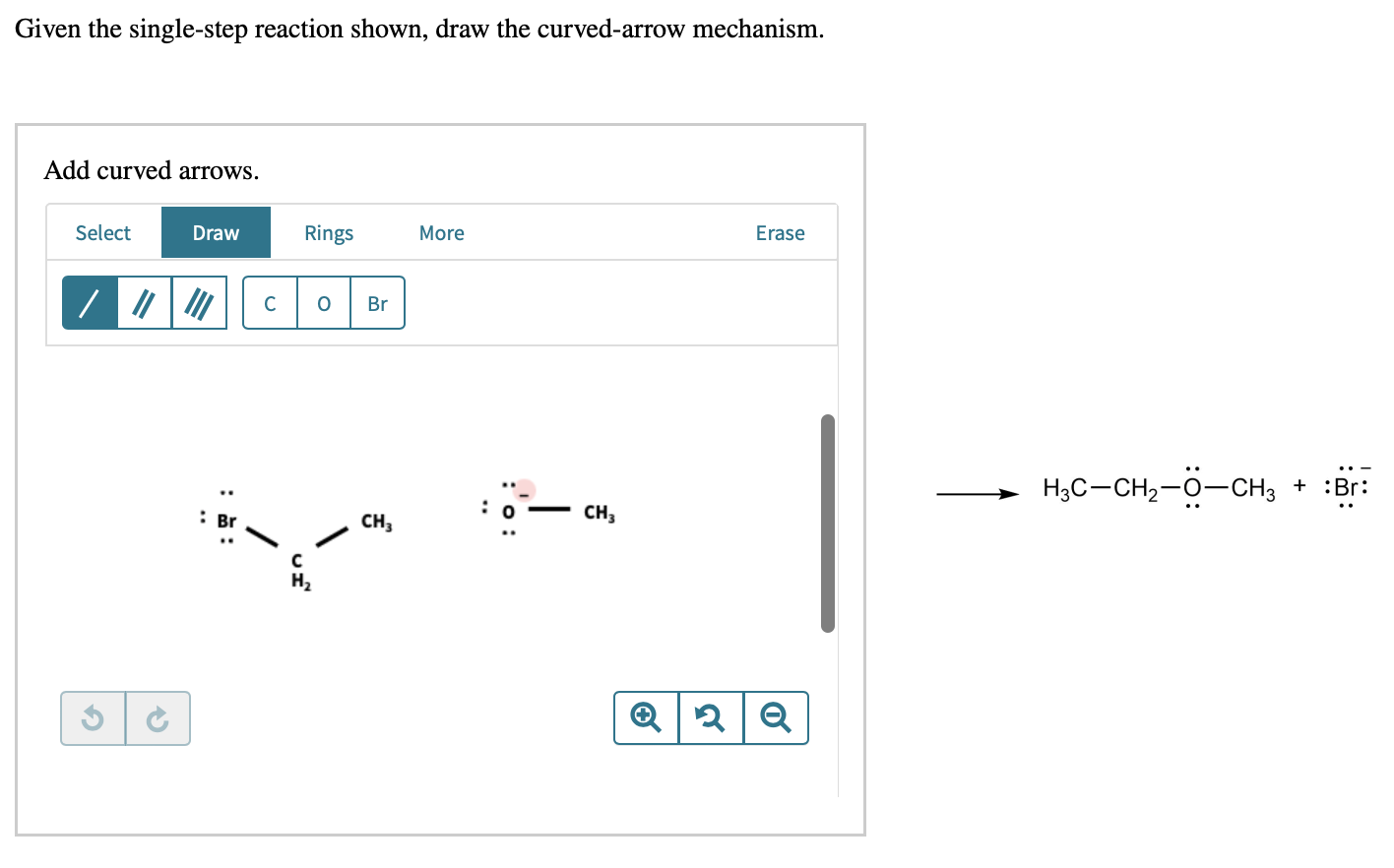
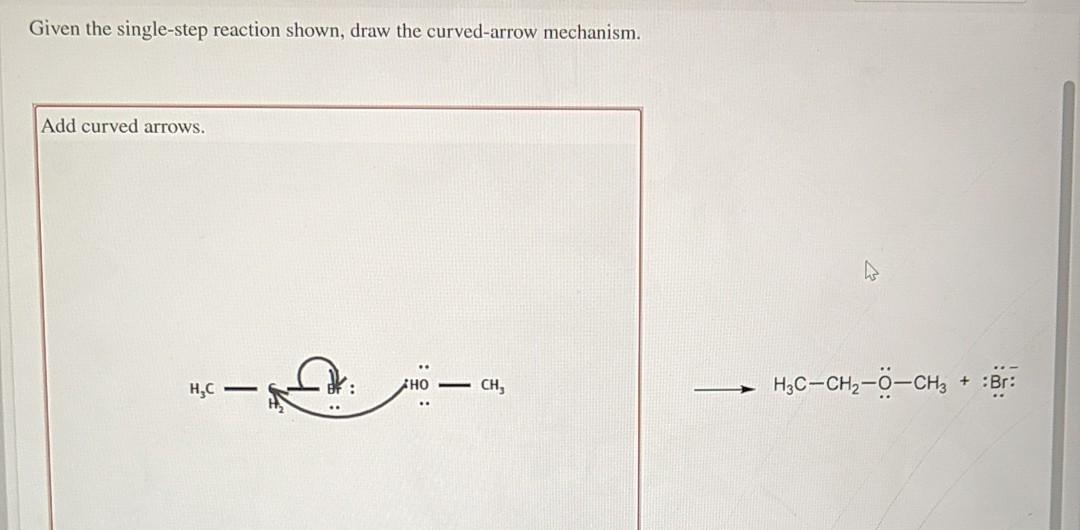
![[Solved] Given the singlestep reaction shown, draw the c](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/481/4814ee7a-6b17-4b4c-8b28-58951673ea46/phpg5VEYo)