German Cases Chart
German Cases Chart - Cases in german influence not only the form of the nouns but also the articles and adjectives associated with them. Web the four cases are nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Web the four german cases are as follows: Web there are four german cases: O grammatical cases are a form of inflection that is applied to nouns (mann), pronouns (er), articles (der), adjectives (gut) and numerals (fünf) er dankt dem guten mann. For each german case (kasus) you can find a detailed explanation, including declension, usage, verbs and prepositions forcing you to use a certain case. Depending on which textbook you use, you may find these four in a slightly different order. What if there are 2 prepositions in a sentence? Web learn how german nouns change form depending on their case, function and gender. They’re words that go before a noun (or pronoun) to provide extra information — usually something about the noun’s position in time or space. Web produced by alex stern , stella tan , sydney harper and nina feldman. Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in german. Nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. Prepositions and the german cases. (nom.) (dat.) o the case shows the function of the noun/noun group in the sentence, i.e. Nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. Prepositions and the german cases. See examples, charts and tips for mastering the nominative, genitive, dative and accusative cases. You actually know some of the nominative case already! Starting with the nominative case is the best place to start and. Often, english teachers prefer to order the cases. Knowing your cases is vital in german, as many words change depending on what case they are in. So without further ado, let’s learn the german. Web the german cases what is a case actually? Original music by elisheba ittoop , dan powell , marion lozano , sophia lanman and pat mccusker. A comprehensive description of nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive german cases with the help of german cases table and chart. Web the four cases are nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. Michelle baumgartner updated october 23, 2023 18 min. How do german cases work? Original music by elisheba ittoop , dan powell , marion lozano , sophia lanman and pat mccusker. Nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. A comprehensive description of nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive german cases with the help of german cases table and chart. The difference between definite and indefinite articles. In english, this is mostly done with word order, so it can take some getting used to! Learn the two charts on this page well, and everything else you do. Often, english teachers prefer to order the cases. So without further ado, let’s learn the german. See examples, charts, and tips for mastering the german case system. An efficient system for always knowing which declension you need. You actually know some of the nominative case already! Web there are four german cases: Nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. They’re words that go before a noun (or pronoun) to provide extra information — usually something about the noun’s position in time or space. An efficient system for always knowing which declension you need. See examples, charts and tips for mastering the nominative, genitive, dative and accusative cases. Web in this post. Web the german cases what is a case actually? Starting with the nominative case is the best place to start and. Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in german. Web in this post. The difference between definite and indefinite articles. How do german cases work? You actually know some of the nominative case already! Often, english teachers prefer to order the cases. Web in this post. Cases in german influence not only the form of the nouns but also the articles and adjectives associated with them. Web learn how german nouns change form depending on their case, function and gender. They’re words that go before a noun (or pronoun) to provide extra information —. Every time you learn a der, die, or das in front of a german noun, you’re using the nominative case — that’s knowledge and experience we can. The difference between definite and indefinite articles. Learn german cases with conversation based chunking. Michelle baumgartner updated october 23, 2023 18 min read. Starting with the nominative case is the best place to start and. How do german cases work? Correct declensions for all articles & other determiners. Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in german. Web in this post. Web learn how to identify and use the four cases of german nouns: Edited by mj davis lin. Original music by elisheba ittoop , dan powell , marion lozano , sophia lanman and pat mccusker. (he thanks the good man). You actually know some of the nominative case already! Web the german cases what is a case actually? Most german sentences include at least one case, but it’s rare that you’ll see all four cases in a single sentence.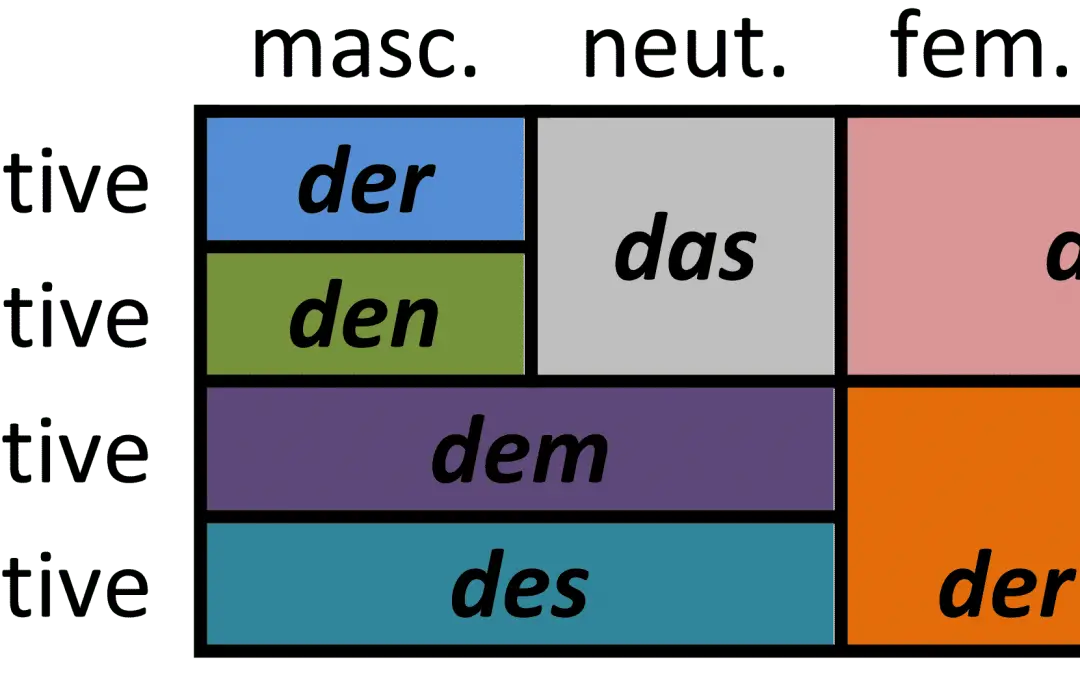
German Cases Online Courses by DAS Akademie

German grammar the 4 cases German language learning, German grammar

LOS CASOS EN ALEMÁN Nominativo, Acusativo, Dativo 123Deutsch

German Grammar Dative Case and the DER CHART YouTube

German Adjective Endings Your Essential Guide

German cases and adjective endings chart The German Professor

German Cases Learn German Cases easily with

German Cases Learn German Cases easily with
![German Cases Simply Explained A Guide to German Cases [Grammar Guide]](https://lingopie.com/blog/content/images/2022/08/German-cases-2-copia.jpg)
German Cases Simply Explained A Guide to German Cases [Grammar Guide]
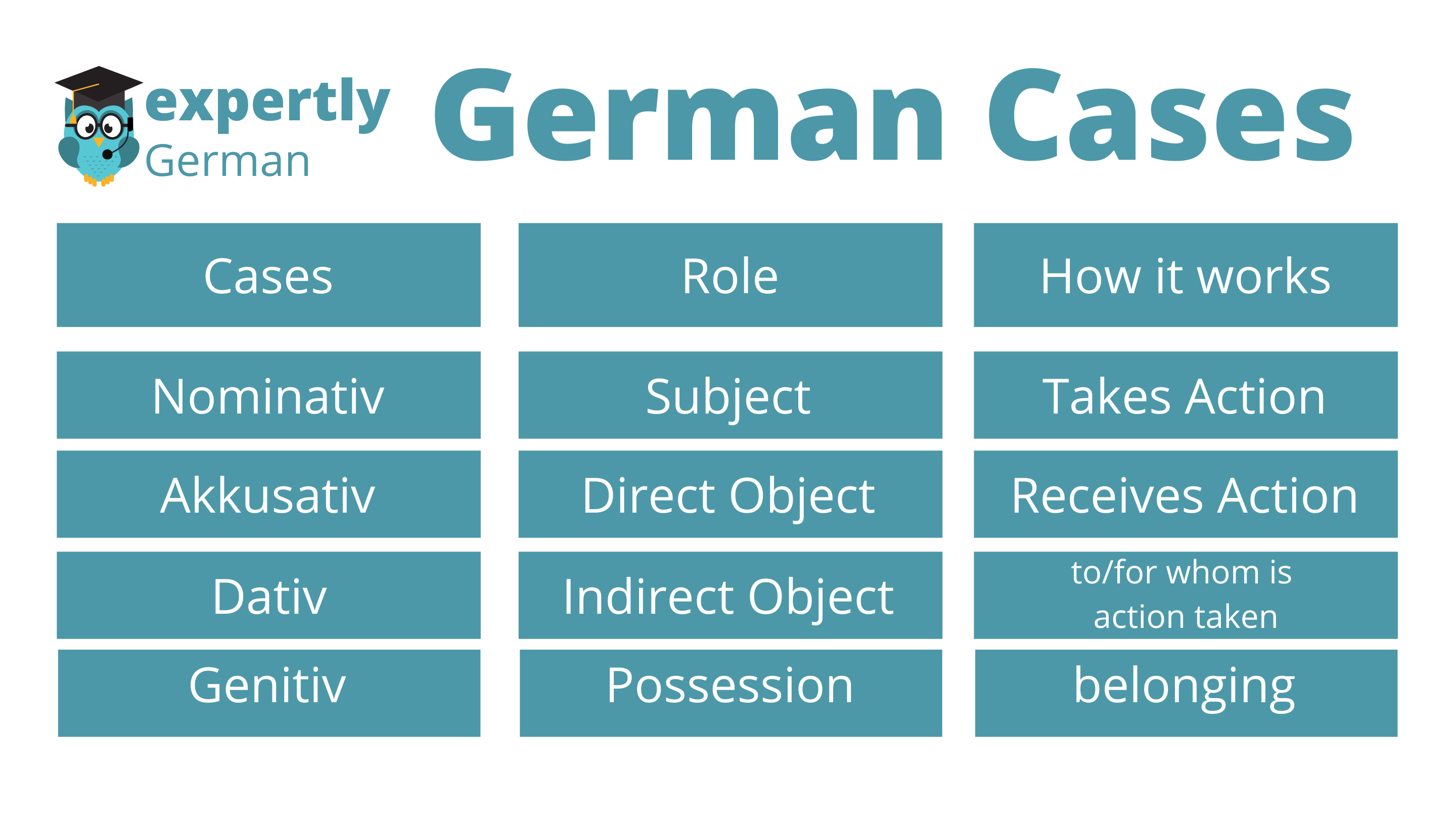
German Cases Easy Guide The four German cases
What If There Are 2 Prepositions In A Sentence?
For Each German Case (Kasus) You Can Find A Detailed Explanation, Including Declension, Usage, Verbs And Prepositions Forcing You To Use A Certain Case.
What You Need To Know.
This Chart And 2 Simple Rules Help You Choose The Right Adjective Ending.
Related Post: