Galvanic Chart For Metals
Galvanic Chart For Metals - Web view this chart of galvanic compatibility. Web what is galvanic corrosion: Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences of 0.2 volts or more suggest a galvanic corrosion risk. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. These fi lms give them exceptionally good corrosion resistance, although they are among the most active metals. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for corrosion. The following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will occur. Galvanic series relationships are useful as a guide for selecting metals to be joined, will help the selection of metals having minimal tendency to interact galvanically, or will indicate the need or degree of protection to be applied to lessen the expected potential interactions.in general, the further apart the materials are in the galvanic. Web the table below is the galvanic series of metals, alloys and graphite in seawater (most noble at top) in flowing seawater, at ‘normal’ temperature. Web this chart will help you to determine which metals are more noble than other metals. Web fastener material selection based on the galvanic series of metals to minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on. Web the galvanic series of metals (right) lists metals and alloys in decreasing order of electrical activity. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. To use the chart, align the metal to be assessed (for the risk of corrosion) in the left column with the contact metal listed in the. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and. Water) is necessary to promote galvanic corrosion. Electric current flows from plus to minus. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Web however, you can. The relative position of two metals on such a series gives a good indication of. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web this chart will help you to determine which metals are more noble than other metals. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. This chart is designed to assist in broadly. Web a chart depicting the galvanic series for some common metals in a frequently encountered conducting solution, seawater, is included in figure 1. Galvanic series relationships are useful as a guide for selecting metals to be joined, will help the selection of metals having minimal tendency to interact galvanically, or will indicate the need or degree of protection to be. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. The position of zinc on the galvanic series, above most other metals, means that it will corrode preferentially if it contacts any of these metals and moisture is present. The list begins with the more active (anodic) metal and proceeds down. Metals nearer. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Maximum recommended voltage difference is 0,2v: The relative position of two metals on such a series gives a good indication of. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. The relative position of two metals on such a series gives a good indication of. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. When two metals. Maximum recommended voltage difference is 0,2v: Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Aluminum 1100, 3003, 3004, 5052, 6053. Galvanic series relationships are useful as a guide for selecting metals to be joined, will help. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for corrosion. Web all metals can be classified into a galvanic series representing the electrical potential they develop in a given electrolyte against a standard reference electrode. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences of 0.2 volts or more suggest a galvanic corrosion risk. Web fastener. Use this chart below to better understand what metals will work best together without potential for galvanic corrosion: Water) is necessary to promote galvanic corrosion. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for corrosion. Zn, ag/agcl and cu/cuso4 reference electrodes galvanic series chart. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Galvanic series relationships are useful as a guide for selecting metals to be joined, will help the selection of metals having minimal tendency to interact galvanically, or will indicate the need or degree of protection to be applied to lessen the expected potential interactions.in general, the further apart the materials are in the galvanic. The list begins with the more active (anodic) metal and proceeds down. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Aluminum 1100, 3003, 3004, 5052, 6053. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will occur. Web fastener material selection based on the galvanic series of metals to minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the substrates. Electric current flows from plus to minus. Web however, you can completely avoid galvanic corrosion by choosing matching metal anchors. Web this chart will help you to determine which metals are more noble than other metals. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg.
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals Video Bokep Ngentot
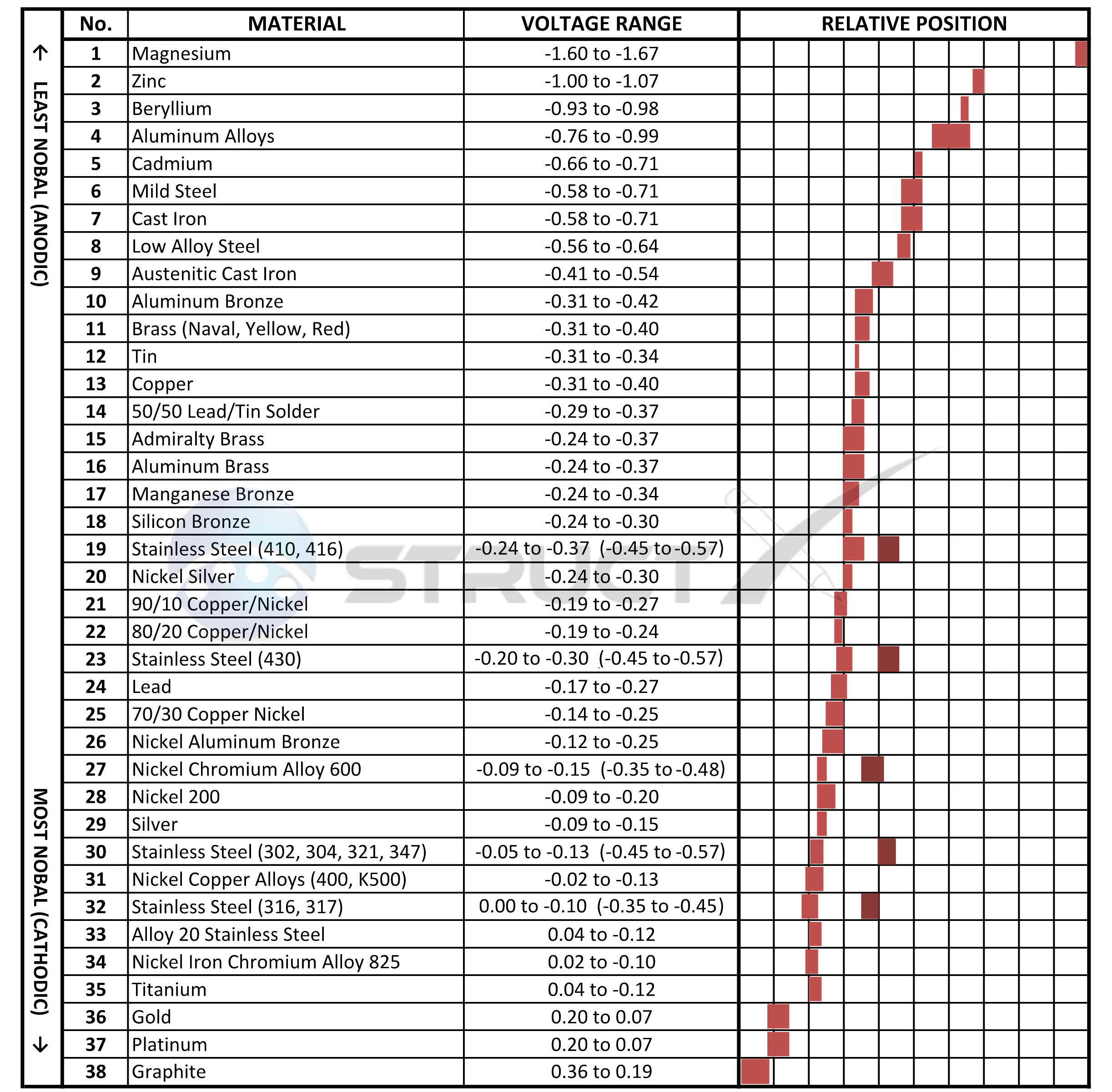
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)

Galvanic Chart Of Metals
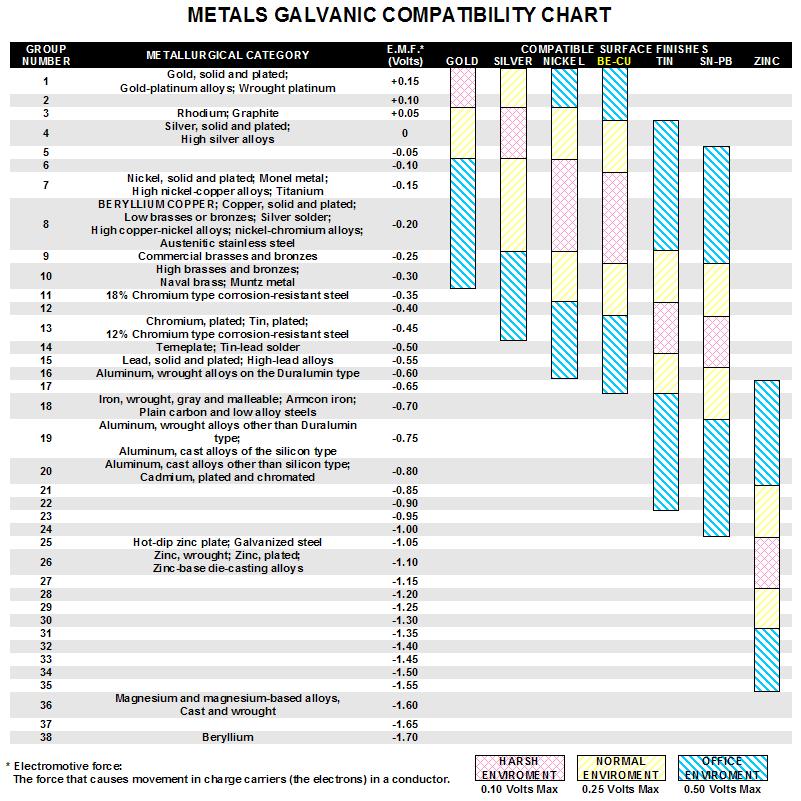
Omega Shielding Products Metals Galvanic Compatibility Chart

The Galvanic Series the essential guide EngineeringClicks
![Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel](https://engineerexcel.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/galvanic-corrosion-chart.png)
Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel
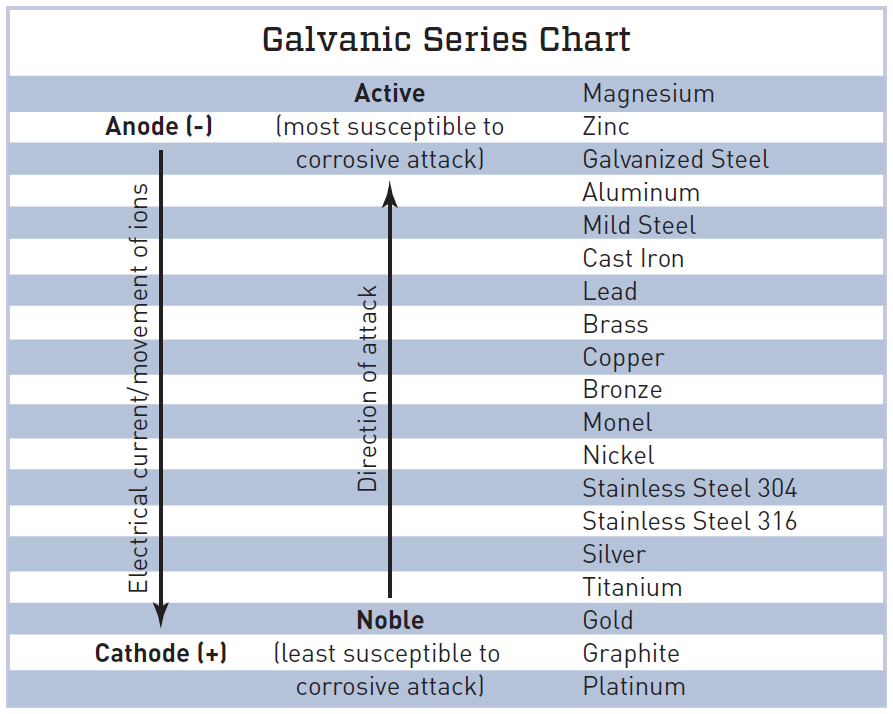
Separating Galvanic Metals JLC Online

Metals Galvanic Compatibility Chart Online Shopping

An Introduction to the Galvanic Series Galvanic Compatibility and

Galvanic Chart Of Metals
Web Galvanic Corrosion (Some Times Called Dissimilar Metal Corrosion) Is The Process By Which The Materials In Contact With Each Other Oxidizes Or Corrodes.
Web The Galvanic Series Of Metals (Right) Lists Metals And Alloys In Decreasing Order Of Electrical Activity.
Web The Table Below Is The Galvanic Series Of Metals, Alloys And Graphite In Seawater (Most Noble At Top) In Flowing Seawater, At ‘Normal’ Temperature.
Web The Galvanic Series Chart Below Shows Metals And Their Electrochemical Voltage Range (Relative Activity In Flowing Sea Water).
Related Post: