Free Energy Of Formation Chart
Free Energy Of Formation Chart - Temperatures where either the metal or oxide melt or vaporize are marked on the diagram. This page introduces gibbs free energy (often just called free energy), and shows how it can be used to predict the feasibility of reactions. Web calculate the standard free energy change at room temperature, using (a) standard free energies of formation and (b) standard enthalpies of formation and standard entropies. Do the results indicate the reaction to be spontaneous or nonspontaneous under standard conditions? Web the standard gibbs free energy of formation (g f °) of a compound is the change of gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature, usually 298. An atlas of charts for high‐temperature chemical calculations. Reed and julius klerer 1972 j. A pure element in its standard state has a standard free energy of formation of zero. Journal of the electrochemical society , volume 119 , number 12 citation t. These values are valid for the temperature 25 c. Web the standard gibbs free energy of formation (g f °) of a compound is the change of gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature, usually. Web free energy of formation is negative for most metal oxides, and so the diagram is drawn with ∆g=0 at the top of the diagram, and the values of ∆g shown are all negative numbers. The change in free energy, δg, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system.. Web gibbs free energy and spontaneity. Web standard gibb's energies of formation for. Web the standard free energy of formation of a substance is the free energy change that occurs when 1 mole of the substance is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. An atlas of charts for high‐temperature chemical calculations. Web calculate standard free energy change. Web gibbs free energy, denoted g, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. A pure element in its standard state has a standard free energy of formation of zero. Web definition and explanation of the terms standard state and standard enthalpy of formation, with listing of values for standard enthalpy and gibbs free energy of formation, as well as. Web an introduction to gibbs free energy. The standard gibbs free energy change, δg°, indicates the thermodynamic favorability of a physical or chemical process. Reed and julius klerer 1972 j. What is the heat absorbed or released when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its respective elements in their standard states? When δg° < 0, the process is. Web standard gibb's energies of formation for. When δg° < 0, the process is thermodynamically favored. Web free energy of formation is negative for most metal oxides, and so the diagram is drawn with ∆g=0 at the top of the diagram, and the values of ∆g shown are all negative numbers. Web gibbs free energy, denoted g, combines enthalpy and. Web gibbs free energy, denoted g, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. All standard state, 25 °c and 1 bar (written to 1 decimal place). Web calculate the standard free energy change at room temperature, using (a) standard free energies of formation and (b) standard enthalpies of formation and standard entropies. This page introduces gibbs free energy (often. Name δh f ° (kj/mol) δg f ° (kj/mol) s° (j/mol k) h 2 (g) 0: Reed and julius klerer 1972 j. Where h is enthalpy, t is temperature (in kelvin, k ), and s is the entropy. Web gibbs free energy, denoted g, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. The change in free energy, δg, is equal. Journal of the electrochemical society , volume 119 , number 12 citation t. Web calculate the standard free energy change at room temperature, using (a) standard free energies of formation and (b) standard enthalpies of formation and standard entropies. The standard gibbs free energy change, δg°, indicates the thermodynamic favorability of a physical or chemical process. An atlas of charts. Web the standard free energy of formation of a substance is the free energy change that occurs when 1 mole of the substance is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. Web the standard gibbs free energy of formation of a compound is the change of gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of that. The change in free energy, δg, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. This page introduces gibbs free energy (often just called free energy), and shows how it can be used to predict the feasibility of reactions. Web introduction to gibbs free energy (video) | khan academy. If you have already read the page about how to do this with total entropy changes, you will find a little bit of repetition on this page. Web definition and explanation of the terms standard state and standard enthalpy of formation, with listing of values for standard enthalpy and gibbs free energy of formation, as well as standard entropy and molar heat capacity, of 370 inorganic compounds. Explain how temperature affects the spontaneity of some processes. Web calculate standard free energy change for a process using senthalpies of formation and the entropies for its reactants and products. The figures include nomographs for equilibrium partial pressures. Name δh f ° (kj/mol) δg f ° (kj/mol) s° (j/mol k) h 2 (g) 0: Its symbol is δ f g˚. Web gibbs free energy, denoted g, combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. Reed and julius klerer 1972 j. Web standard gibb's energies of formation for. What is the heat absorbed or released when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its respective elements in their standard states? Web standard heats and free energies of formation and absolute entropies of elements and inorganic compounds. The standard gibbs free energy of formation at 25°c (298,15 k) for 1 mol of the substance in its given state (g= gas and l= liquide) from its elements in their standard state (stable forms at 1 bar and 25°c) s°: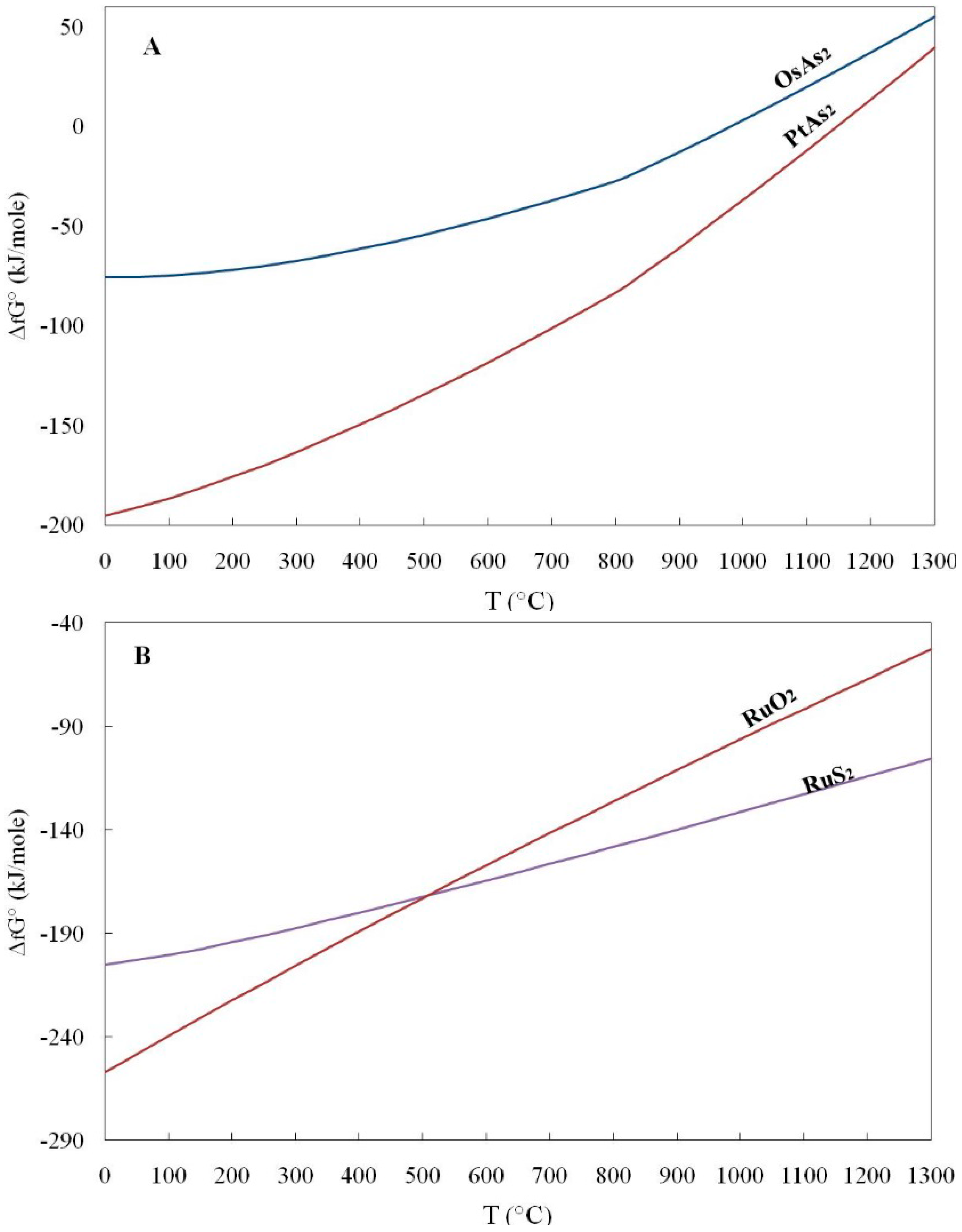
Standard Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation Table slideshare
Geosciences Free FullText Gibbs Free Energy of Formation for

Standard Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation Table slideshare

Gibbs Free Energy Definition, Equation, Unit, and Example

Gibbs free energy of formation values for various oxides. Download

Standard Gibbs free energy of formation, standard enthalpy of formation
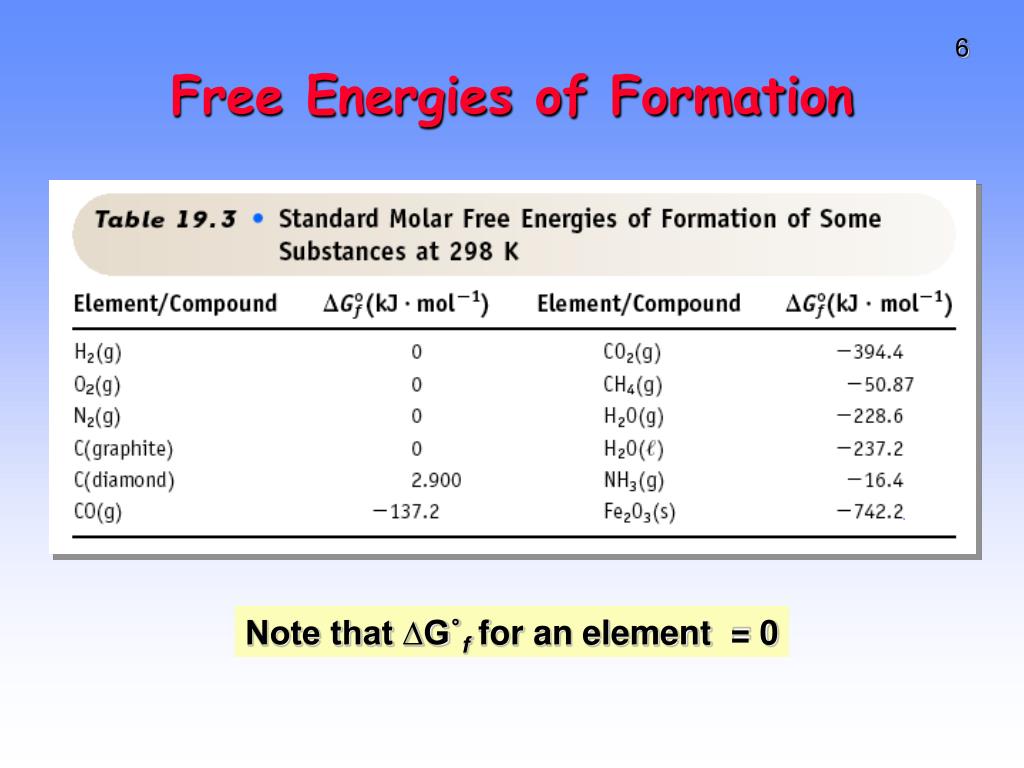
PPT Gibbs Free Energy, G PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
![[PDF] Gibbs Free Energy of Formation for Selected Platinum Group](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1dbf18616943ea1a81a4ada05098657bbd1510ba/2-Table1-1.png)
[PDF] Gibbs Free Energy of Formation for Selected Platinum Group

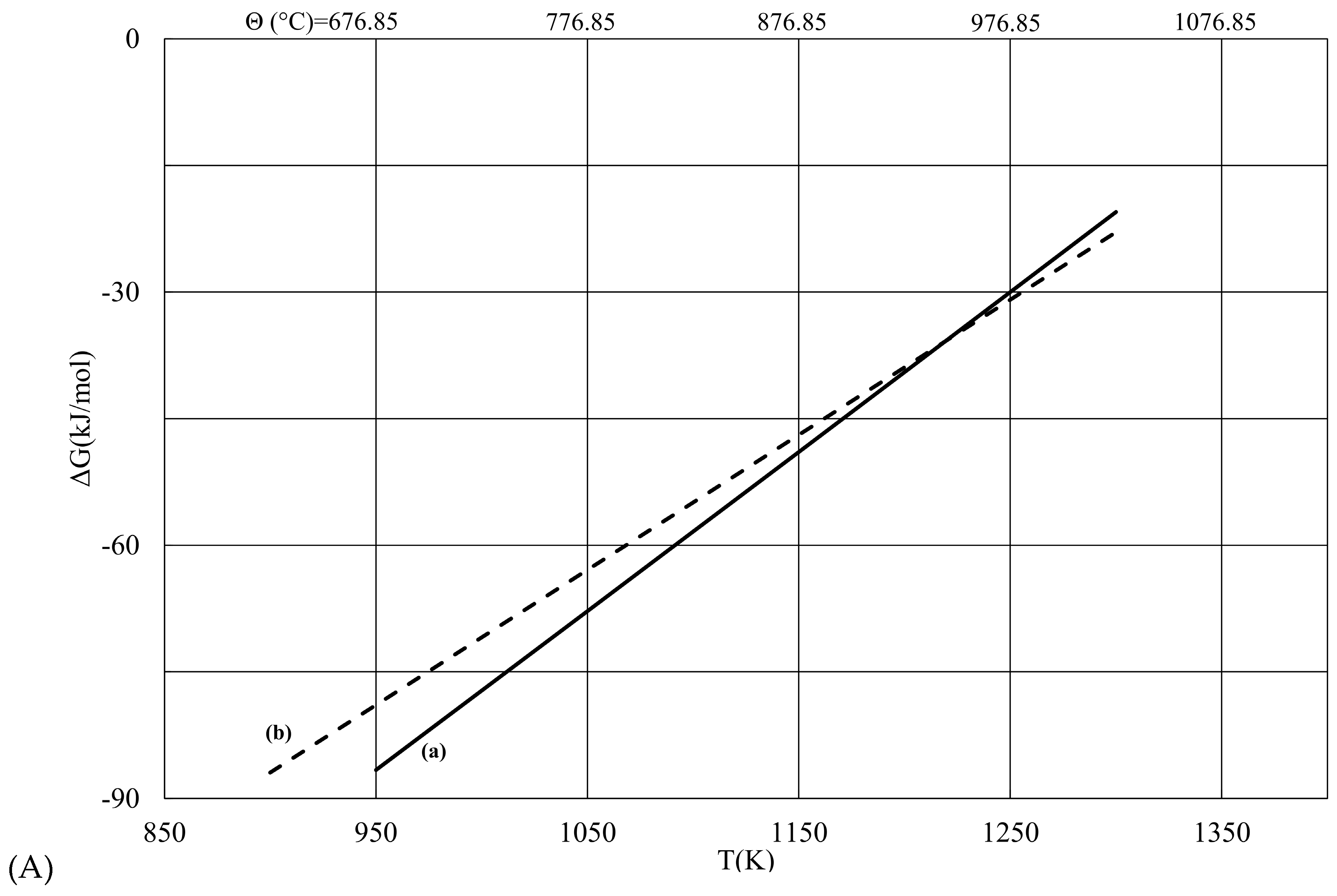
Gibbs free energy of formation for selected chemicals. The point [5
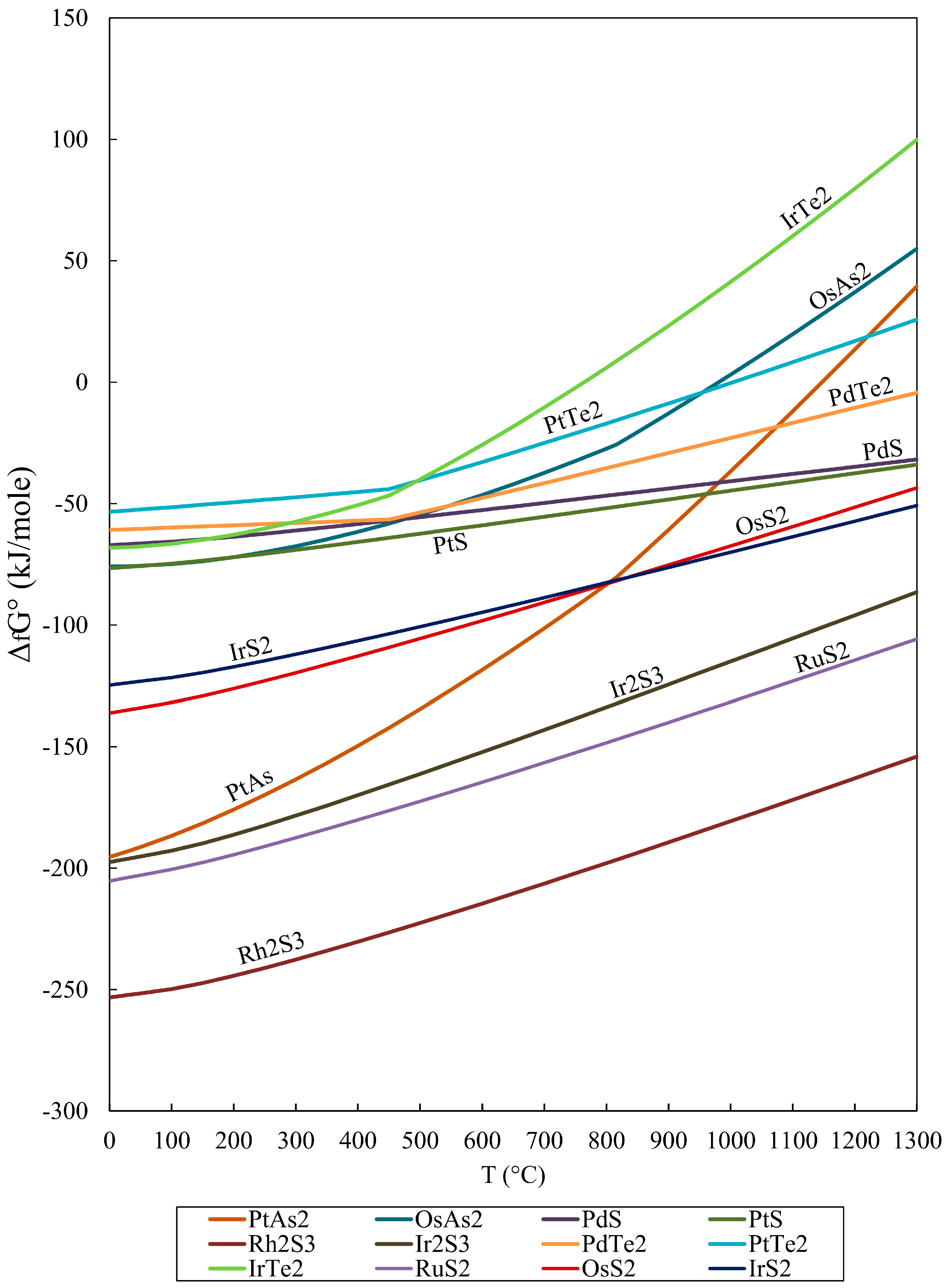
Standard Gibbs Free Energy Of Formation Table slideshare
Web An Introduction To Gibbs Free Energy.
Journal Of The Electrochemical Society , Volume 119 , Number 12 Citation T.
Where H Is Enthalpy, T Is Temperature (In Kelvin, K ), And S Is The Entropy.
Web The Standard Free Energy Of Formation Of A Substance Is The Free Energy Change That Occurs When 1 Mole Of The Substance Is Formed From Its Constituent Elements In Their Standard States.
Related Post: