Epididymal Cyst Size Chart
Epididymal Cyst Size Chart - Spermatoceles are also known as spermatic cysts. All scrotal lumps should be checked by a doctor to make sure they are 9. Cysts may develop in the upper pole of the epididymis and present as a painless scrotal mass. Last reviewed 1 jan 2018. (hydroceles and epididymal cysts) are very common, especially as men. They are usually of lymphatic origin 2. Web other names for spermatoceles include spermatic cysts or epididymal cysts. Spermatoceles are benign cystic dilations of the epididymis. It feels like a smooth, firm pea sized lump in the scrotum on top of the testicle. Web south devon & torbay. Epididymal cysts do not interfere with reproduction. Web most lumps found in the scrotum are not cancer. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm. (hydroceles and epididymal cysts) are very common, especially as men. Web small epididymal cysts are typically left alone. Web we describe the clinical characteristics of men with these lesions and hypothesize that men with spermatoceles seek intervention when the lesion approximates the size of a testicle. If there is a confirmed diagnosis of epididymal cyst (for example clinically or following ultrasound of the scrotum): They are usually asymptomatic but may cause some anxiety to the patient. The cysts. Diagnose by ultrasound demonstrating a well defined simple cyst. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm. Even if there isn’t pain, it can be scary to notice a lump around your testicle. Usually idiopathic but cystic dilation from outflow obstruction may play a role. Web we describe the clinical. They tend to be benign (not cancerous). They may be present for years and never cause trouble. Many men feel them and are concerned that they have testicular cancer, but a doctor can usually tell the difference by examination and/or using an ultrasound scan. Web other names for spermatoceles include spermatic cysts or epididymal cysts. (hydroceles and epididymal cysts) are. Web from birth onwards (male). [3] the fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Even if there isn’t pain, it can be scary to notice a lump around your testicle. Web we describe the clinical characteristics of men with these lesions and hypothesize that men with spermatoceles seek intervention when the lesion approximates the. Usually idiopathic but cystic dilation from outflow obstruction may play a role. Occasionally, epididymal cysts can cause symptoms (such as pain, ache or a “dragging” sensation) in which case intervention may. Epididymal cysts can become infected and cause pain and discomfort. Epididymal cysts do not interfere with reproduction. They may be present for years and never cause trouble. Web most lumps found in the scrotum are not cancer. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm. These cysts are benign (not cancerous), typically painless, and can. How should i manage an epididymal cyst or spermatocele? Web size ranges from a few millimeters up to 2 cm. They are usually of lymphatic origin 2. They may be present for years and never cause trouble. Spermatoceles don’t typically hurt, so you may not notice a lump right away. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm. Cysts may develop in the upper pole of the epididymis and present. Noncancerous and generally painless, a spermatocele usually is filled with milky or clear fluid that might contain sperm. We present a single institution series of men undergoing spermatocelectomy. [4] spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa [5] and they can vary in size from several millimeters to many centimeters. Usually idiopathic but cystic dilation from outflow obstruction may play a role.. Web most epididymal cysts are fairly small, less than 0.5 cm to 1 cm in size, and cause no symptoms at all. Web south devon & torbay. Reassure the person it is a common harmless finding, is usually asymptomatic, and rarely needs treatment. How should i manage an epididymal cyst or spermatocele? [4] spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa [5]. Web an epididymal cyst contains fluid, and a spermatocele contains seminal fluid and sperm (o’kelly, 2019). Spermatoceles don’t typically hurt, so you may not notice a lump right away. If there is a confirmed diagnosis of epididymal cyst (for example clinically or following ultrasound of the scrotum): They are quite common and don't usually require treatment. Reassure the person it is a common harmless finding, is usually asymptomatic, and rarely needs treatment. What are spermatoceles (spermatic cysts)? They tend to be benign (not cancerous). Cysts are relatively common and can occur anywhere on the body, including the scrotum. Often manifests as a palpable mass. Many men feel them and are concerned that they have testicular cancer, but a doctor can usually tell the difference by examination and/or using an ultrasound scan. Web most epididymal cysts are fairly small, less than 0.5 cm to 1 cm in size, and cause no symptoms at all. You can view 4 more pages before signing in. Epididymal cysts are common and rarely require treatment. Web from birth onwards (male). Inflammation or fluid tension on the wall of epididymal cysts can also cause pain. Varicose veins within the scrotum (varicocele) are also common.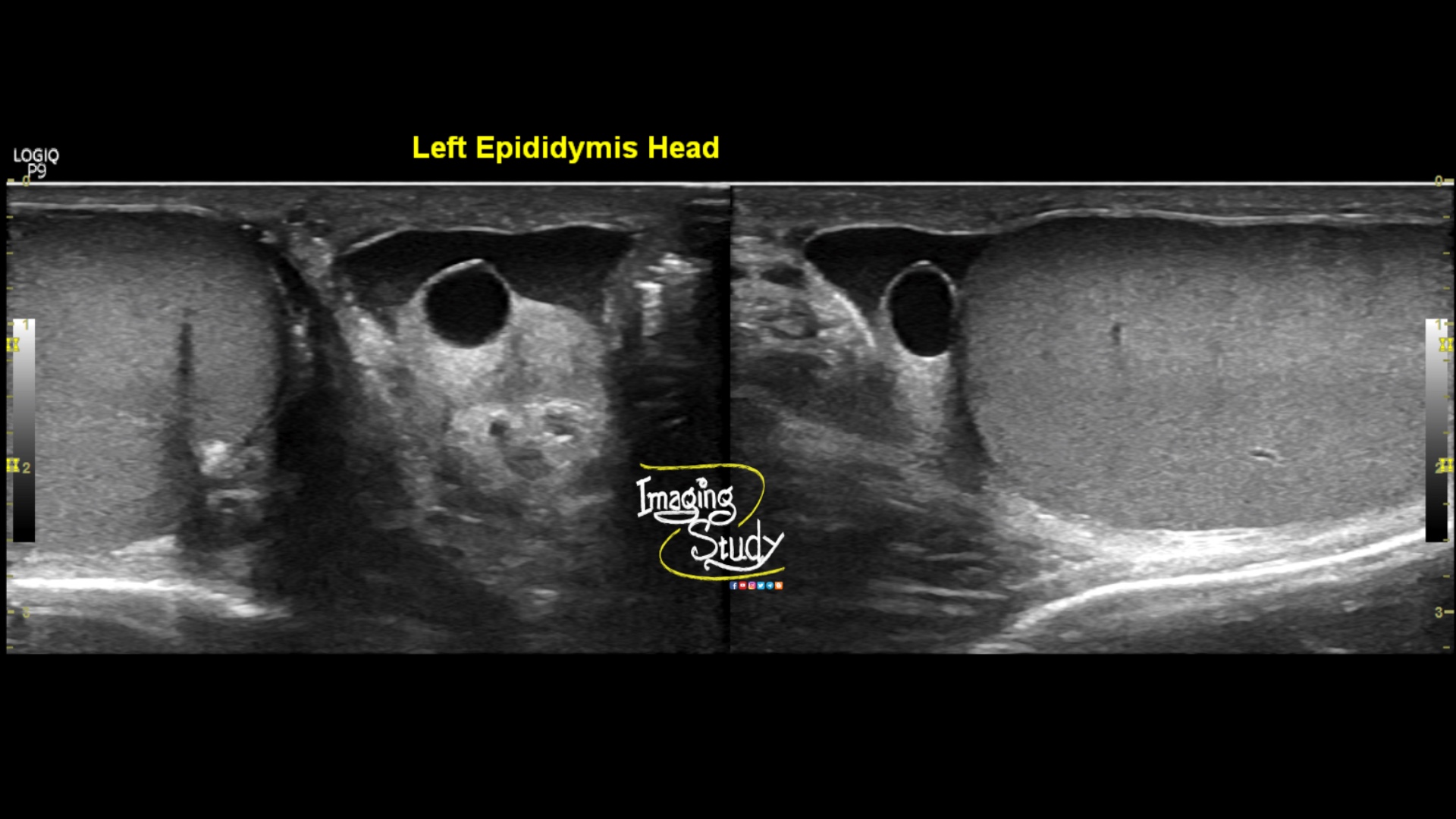
Case 24 Epididymal Cyst

Epididymal Cyst Diagram

How to diagnose Male Infertility Urology

Epidermoid Cyst of the Testicle Urology
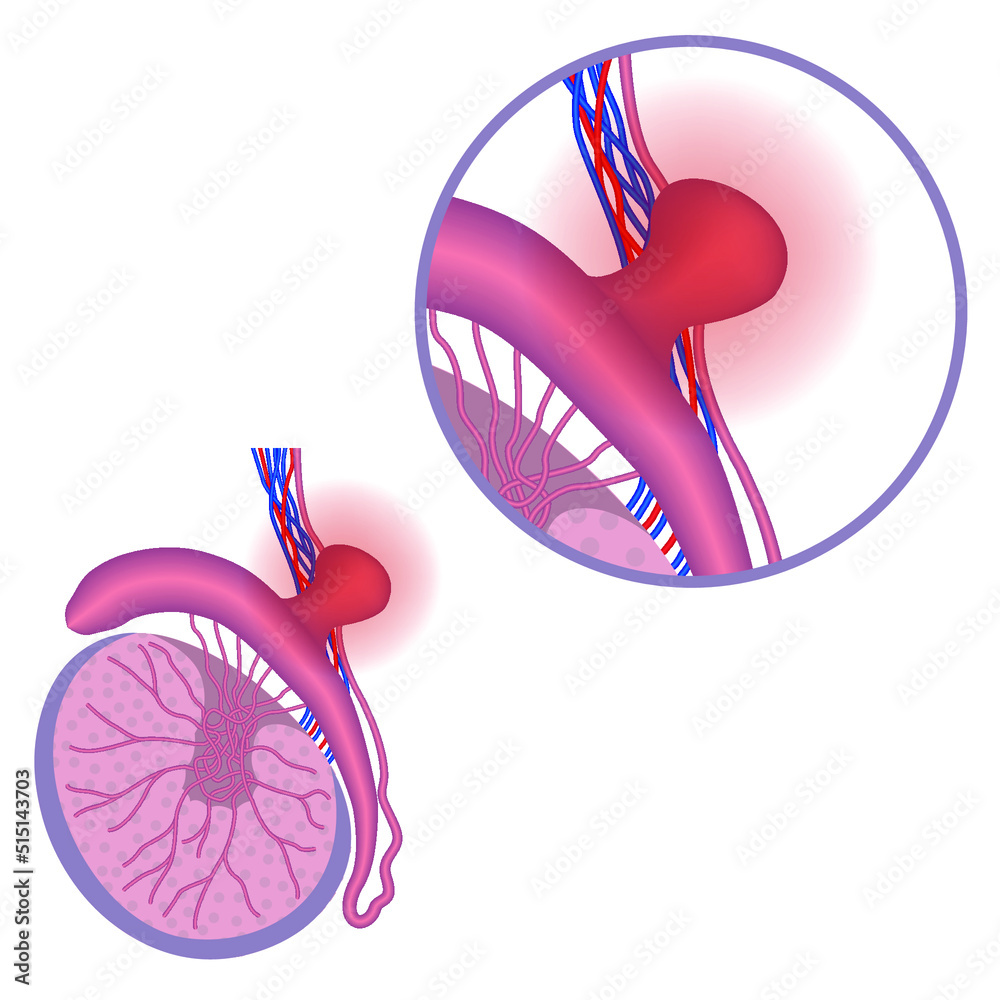
Spermatocele. Epididymal cyst. Anatomy of the male reproductive system

Epididymal Cyst Size Chart

Epididymal Cyst Diagram
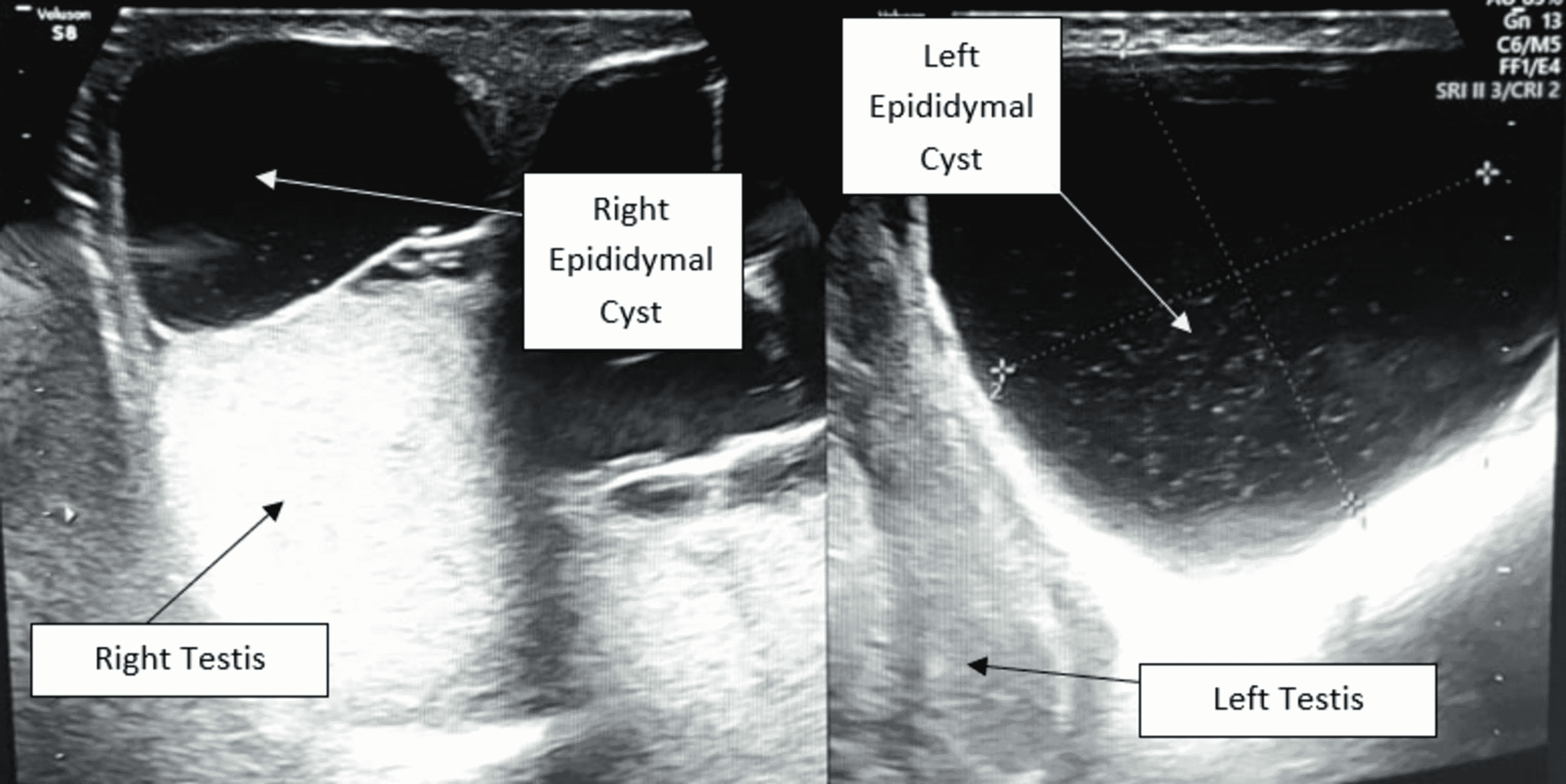
Epididymal Cyst Size Chart

Epididymal Cyst Causes, Symptoms, and Types of Treatment
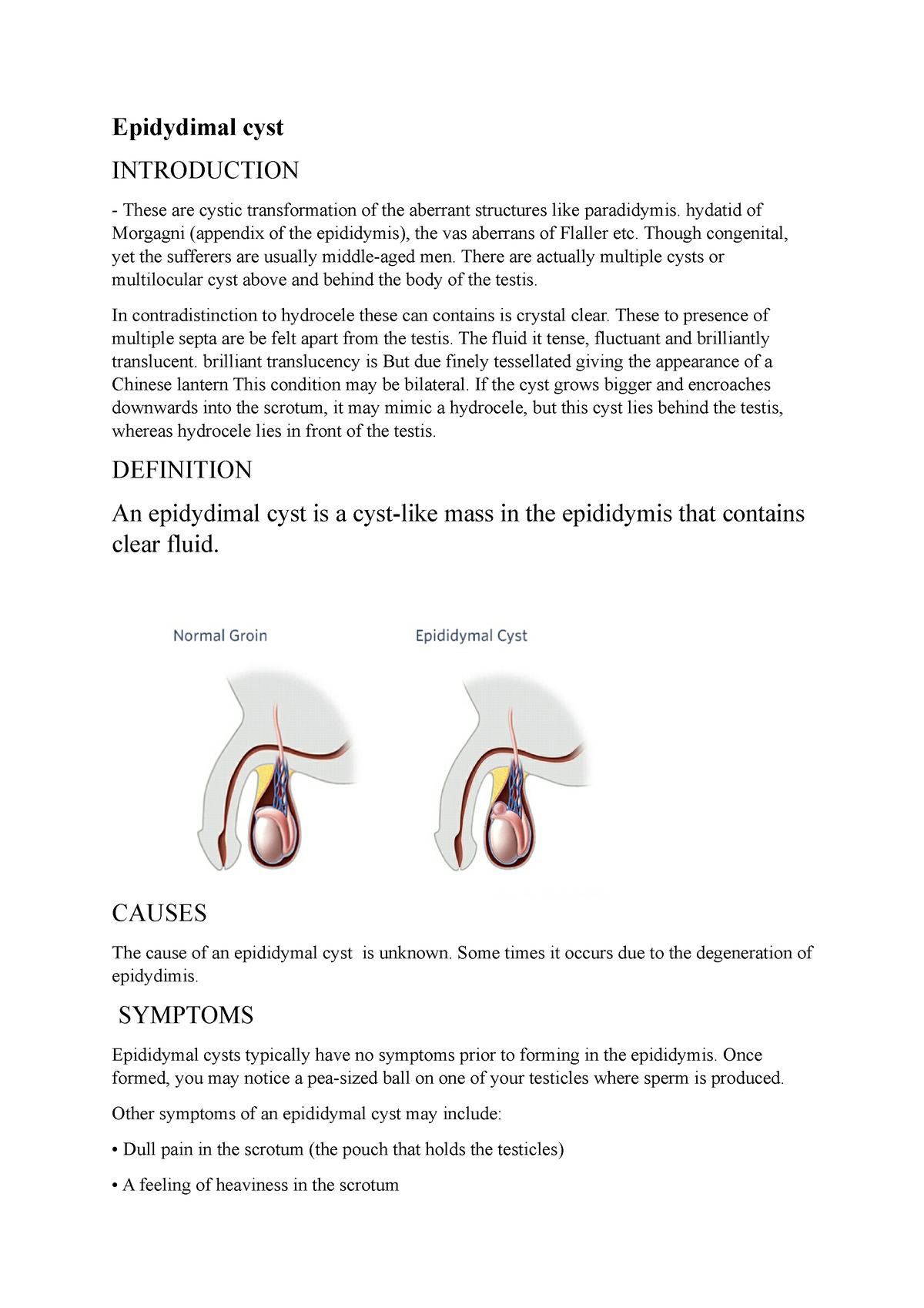
A brief note on Epididymal cyst Epidydimal cyst INTRODUCTION These
Benign Dilatation Of The Efferent Ductules In The Rete Testis Or Head Of The Epididymis.
They Are Usually Asymptomatic But May Cause Some Anxiety To The Patient.
Epididymal Cysts Do Not Interfere With Reproduction.
Occasionally, Epididymal Cysts Can Cause Symptoms (Such As Pain, Ache Or A “Dragging” Sensation) In Which Case Intervention May.
Related Post: