Earths Atmosphere Pie Chart
Earths Atmosphere Pie Chart - Web the atmosphere of earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet earth that is retained by earth's gravity. Numbers are mainly from 2000, with co 2 and methane from 2019, and do not represent any single source. Web this lesson was written for aqa syllabus to describe the development of the earth's atmosphere. Averaged throughout the entire atmosphere, water vapor makes up about 0.4% of the total. Web composition of earth's atmosphere by molecular count, excluding water vapor. The chemical formulas at the right show the major species of interest in the various regions. Composition of earth’s atmosphere other gases. Click on the image to find out what the atmosphere is made of. Web this pie chart shows the percentages of the main gases in air. The earth's atmosphere is essential to the survival of many living creatures on the planet. These variable components include water vapor, dust particles, and ozone. Use the pie chart template to complete a chart of the gases in the atmosphere. Hint each segment is 5% find the answers at the end of the blog. Numbers are mainly from 2000, with co 2 and methane from 2019, and do not represent any single source. The concentration. Composition of earth’s atmosphere other gases. Averaged throughout the entire atmosphere, water vapor makes up about 0.4% of the total. Layers upon layers of gas surrounding. That is essentially what the earth’s atmosphere is like: Web composition of earth's atmosphere by molecular count, excluding water vapor. Pie chart showing the composition of clean air. Web below is a pie chart with a graphical representation of dry air. That is essentially what the earth’s atmosphere is like: Water vapor is excluded from this total. The dry composition of the atmosphere is mostly nitrogen and oxygen. The main divisions of the atmosphere are defined by the elevations at which the sign of the temperature gradient changes. What percentages do you think they make up? Web from largest to smallest, earth’s atmosphere composition contains nitrogen, oxygen, argon, co2 and trace gases. Web composition of earth's atmosphere by molecular count, excluding water vapor. Web below is a pie. These variable components include water vapor, dust particles, and ozone. Click on the image to find out what the atmosphere is made of. Web the atmosphere of earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet earth that is retained by earth's gravity. The chemical formulas at the right show the major species of interest in the various regions. The. Web describe the major gaseous components of the atmosphere. It also contains small amounts of argon and carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases, such as helium, neon, methane, krypton, and hydrogen. Web what the atmosphere is. Water vapor is shown as a slice that can be up to 2% of the total. Web gases in earth's atmosphere. The main divisions of the atmosphere are defined by the elevations at which the sign of the temperature gradient changes. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1%. Explain why engineers need to know the composition of air. Web from largest to smallest, earth’s atmosphere composition contains nitrogen, oxygen, argon, co2 and trace gases. Web. The remaining gases include carbon dioxide, water vapour and trace quantities of the noble gases. Earth & it's atmosphere 2. Web the proportion of gases in the air has not changed much in 200 million years. Web the atmosphere of earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet earth that is retained by earth's gravity. Web below is a. The remaining gases include carbon dioxide, water vapour and trace quantities of the noble gases. It contains a storyboard activity, a pie chart activity and a researc. The main divisions of the atmosphere are defined by the elevations at which the sign of the temperature gradient changes. Web the proportion of gases in the air has not changed much in. Web structure of the atmosphere. Web the common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air. The remaining gases include carbon dioxide, water vapour and trace quantities of the noble gases. The dry composition of the atmosphere is mostly nitrogen and oxygen. It contains a storyboard activity, a pie chart activity and a researc. Hint each segment is 5% find the answers at the end of the blog. The hadean eon and atmosphere composition of earth. What percentages do you think they make up? Explain relative sizes of fractions and percentages. Web the proportion of gases in the air has not changed much in 200 million years. Use a circle graph (pie chart) to describe and interpret the atmospheric composition. Averaged throughout the entire atmosphere, water vapor makes up about 0.4% of the total. Lower pie represents trace gases that together compose about 0.0434% of the atmosphere (0.0442% at august 2021 concentrations). It contains a storyboard activity, a pie chart activity and a researc. Pie chart showing the composition of clean air. Web gases in earth's atmosphere. Composition of earth’s atmosphere other gases. 3.9 billion years ago there was no oxygen in the atmosphere. The pie chart below shows the percentages of gases that make up the. The chemical formulas at the right show the major species of interest in the various regions. Web file:composition of earth's atmosphere en.svg is a vector version of this file.
Gases in Earth's Atmosphere Center for Science Education

PPT Meteorology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2374709
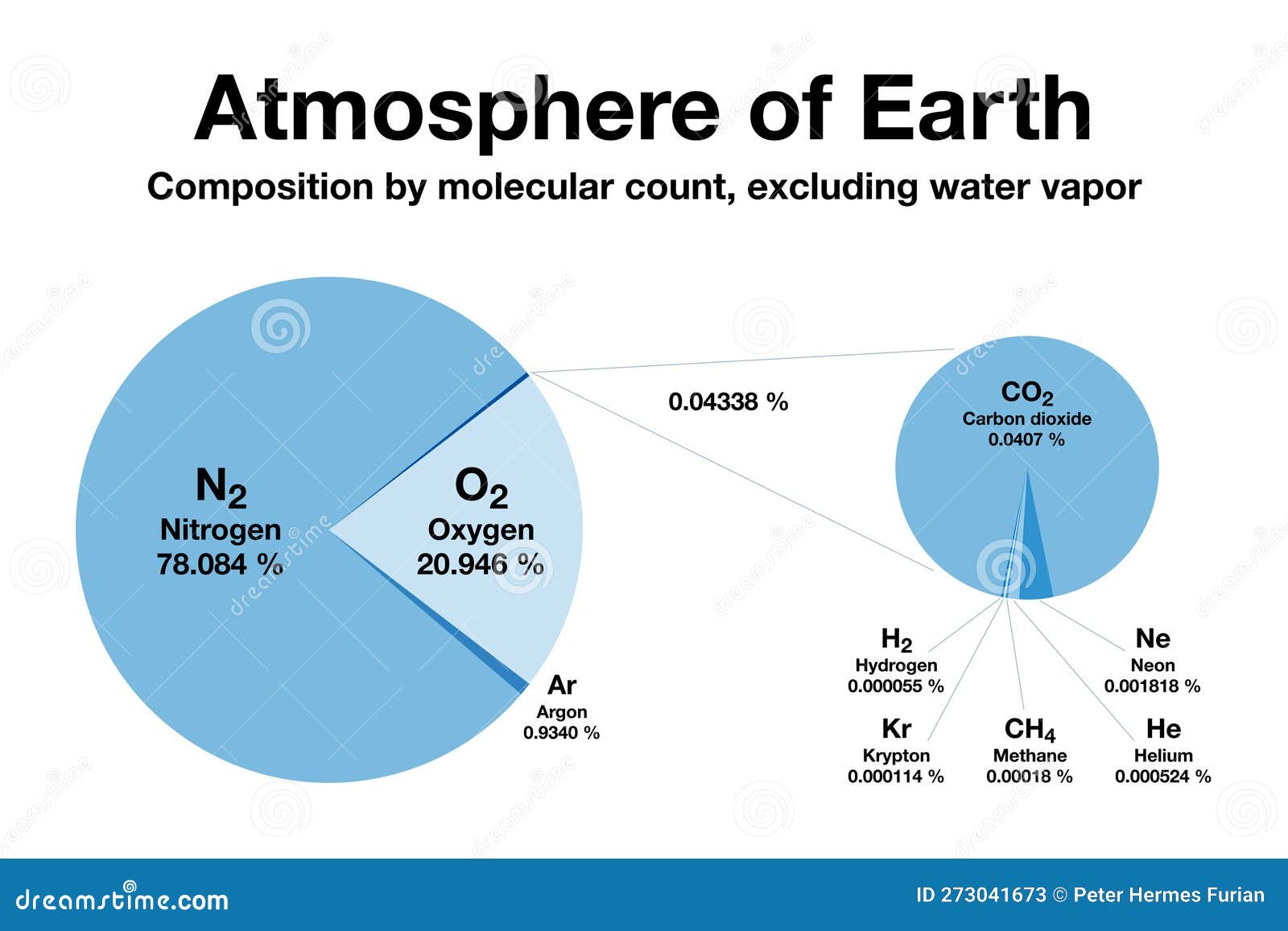
Atmosphere of Earth, Composition by Molecular Count, Excluding Water
Scientific Explorer Earth's Atmosphere Part 2 Composition

Pie Chart Showing Percentage Earths Atmosphere Stock Illustration

Pie Chart Diagram of the Composition of the Atmosphere on Stock
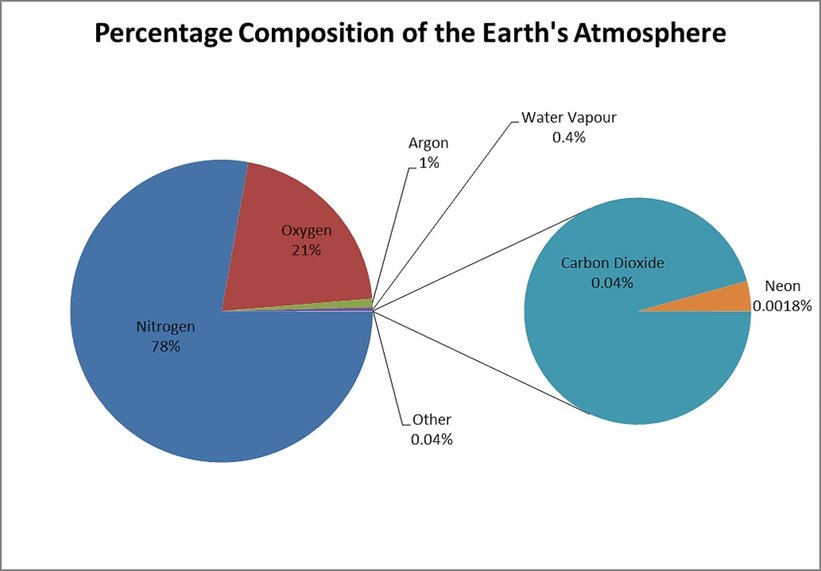
Gases In Earth's Atmosphere Pie Chart

Atmosphere Of Earth Pie Chart Nitrogen Gas PNG, Clipart, Angle, Area

Earth's Atmosphere Key Stage Wiki
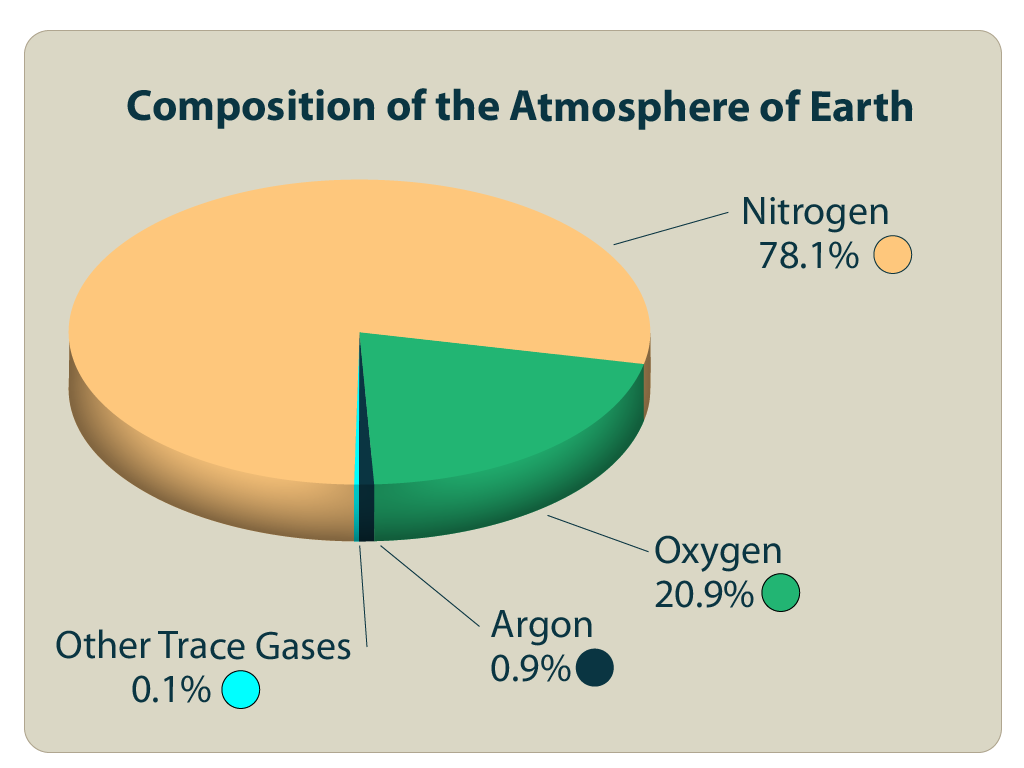
The Layered Earth
Imagine A Layer Cake, Wrapping Around The Earth.
Explain Why Engineers Need To Know The Composition Of Air.
Water Vapor Is Shown As A Slice That Can Be Up To 2% Of The Total.
The Atmosphere Protects Life On Earth By Absorbing Ultraviolet Solar Radiation, Warming The Surface Through Heat Retention (Greenhouse Effect), And Reducing Temperature Extremes Between Day And Night (The Diurnal Temperature Variation).
Related Post: