Drawing Of Transcription
Drawing Of Transcription - Addition of a 5' cap to the beginning of the rna. The transcription elongation phase begins with the release of the σ subunit from the polymerase. Transcription in eukaryotes requires the general transcription factors and the rna polymerase to form a complex at the tata box. The σ subunit of prokaryotic rna polymerase recognizes consensus sequences found in the promoter region upstream of the transcription start sight. The rna copy, or transcript, carries out the information required to create polypeptide for a protein. It occurs when the enzyme rna polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter.this signals the dna to unwind so the enzyme can ‘‘read’’ the bases. During transcription, a strand of mrna is made that is complementary to a strand of dna. Before transcription can take place, the dna double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from dna into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein. Web the process of transcription takes place in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in nucleus in eukaryotes. Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. Figure 1 shows how this occurs. The transcription elongation phase begins with the release of the σ subunit from the polymerase. Web draw a line diagram showing a segment of dna from a gene and its rna transcript, indicating which dna strand is the template, the direction of transcription and the. By controlling the production of mrna within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression. Web the rna polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. Figure 1 shows how this occurs. Before transcription can take place, the dna double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. The transcription elongation phase begins with the release. Dimensions, which can then be labeled with a particular code or set of codes. The transcription elongation phase begins with the release of the σ subunit from the polymerase. Web proteins are made from a sequence of amino acids rather than nucleotides. The dissociation of σ allows the core enzyme to proceed along the dna template, synthesizing mrna in the. Web the transcription is the first stage of gene expression by which the gene information is used to construct a functional product like protein. Web draw the process of transcription and include the following in your drawing. Before transcription can take place, the dna double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. As elongation proceeds, the dna. Before transcription can take place, the dna double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. The top part of the drawing shows transcription occurring in the nucleus of a cell: Dimensions, which can then be labeled with a particular code or set of codes. Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. As elongation proceeds, the dna is. The steps are illustrated in figure below. Web basal transcription factors are crucial in the formation of a preinitiation complex on the dna template that subsequently recruits rna polymerase ii for transcription initiation. The dissociation of σ allows the core enzyme to proceed along the dna template, synthesizing mrna in the 5' to 3' direction at a rate of approximately 40 nucleotides per second. Web draw the process of transcription and include the following in your drawing. During transcription, a strand of mrna is made that is complementary to a strand of dna.. It uses dna as a template to make an rna (mrna) molecule. By controlling the production of mrna within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression. Web the transcription initiation phase ends with the production of abortive transcripts, which are polymers of approximately 10 nucleotides that are made and released. It involves copying a gene's dna sequence. Web draw the process of transcription and include the following in your drawing. The σ subunit of prokaryotic rna polymerase recognizes consensus sequences found in the promoter region upstream of the transcription start sight. Web basal transcription factors are crucial in the formation of a preinitiation complex on the dna template that subsequently recruits rna polymerase ii for transcription initiation.. Web the transcription is the first stage of gene expression by which the gene information is used to construct a functional product like protein. Transcription is the first step of gene expression. Web draw the process of transcription and include the following in your drawing. Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. Once it reaches the terminator sequence,. Dimensions, which can then be labeled with a particular code or set of codes. Web draw the process of transcription and include the following in your drawing. As elongation proceeds, the dna is. Figure 1 shows how this occurs. Web the rna polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. The purpose of the process of transcription is to create rna, a copy of the dna sequence of a gene. Web hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (hnf1a), hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (hnf4a), and forkhead box protein a2 (foxa2) are key transcription factors that regulate a complex gene network in the liver, creating a regulatory transcriptional loop. The rna copy, or transcript, carries out the information required to create polypeptide for a protein. Bases in the copied dna, adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g), and thymine (t), form specific pairs with the bases in the mrna, except adenine (a). Transcription is the first step of gene expression. Web the process of transcription takes place in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in nucleus in eukaryotes. By controlling the production of mrna within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression. Web the transcription initiation phase ends with the production of abortive transcripts, which are polymers of approximately 10 nucleotides that are made and released. The transcription elongation phase begins with the release of the σ subunit from the polymerase. It uses dna as a template to make an rna (mrna) molecule. Addition of a 5' cap to the beginning of the rna.
Place The Descriptions In The Correct Positions On The Diagram Of Dna
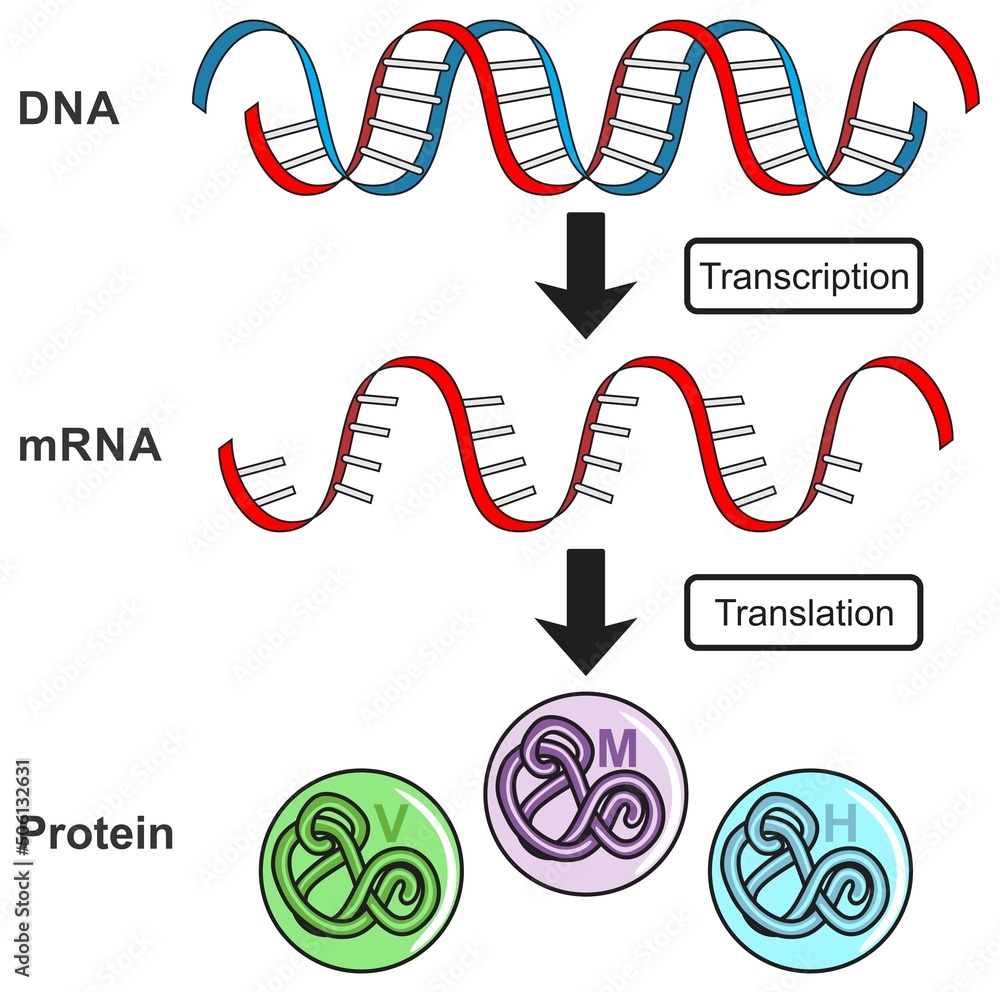
Central dogma of gene expression infographic diagram process
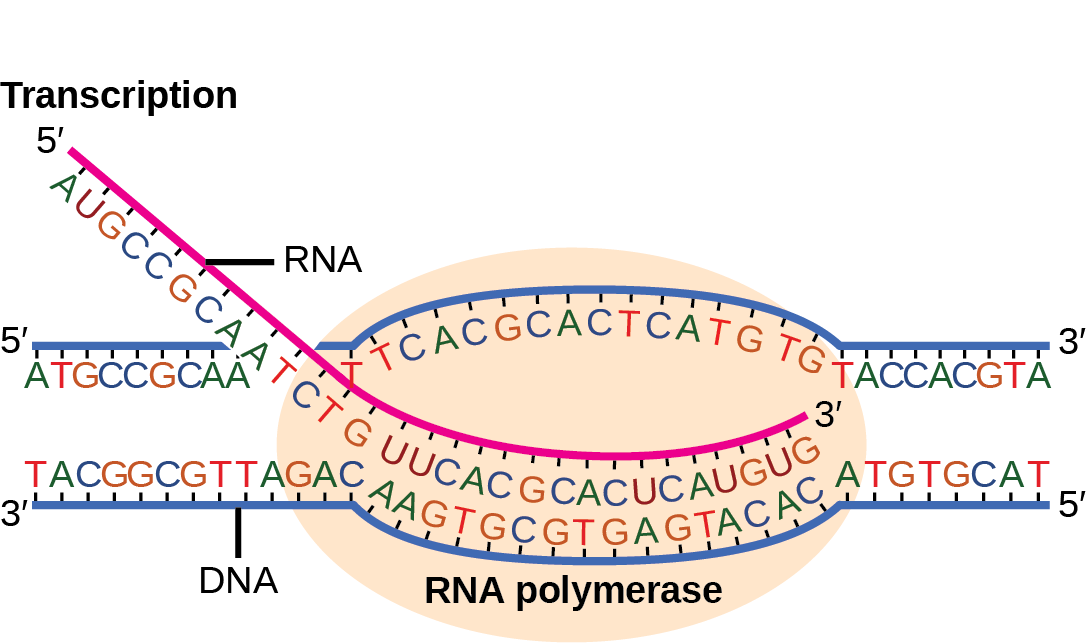
Biology 2e, Genes and Proteins, Prokaryotic Transcription
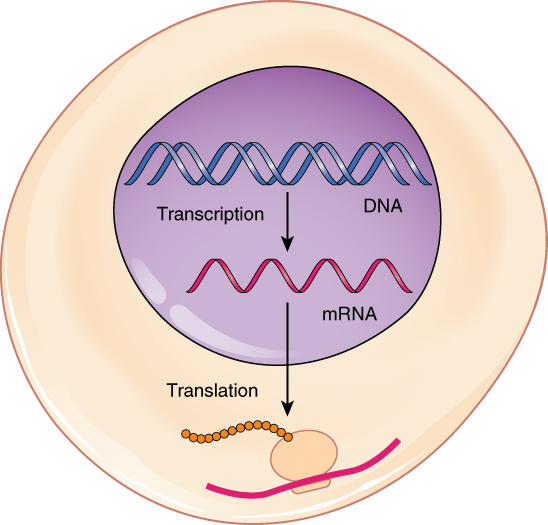
DNA Translation Introduction, Steps & Daigram
How To Draw Transcription & Translation Easy And Simple Diagrams For

Graphic representation of the bacterial transcription process
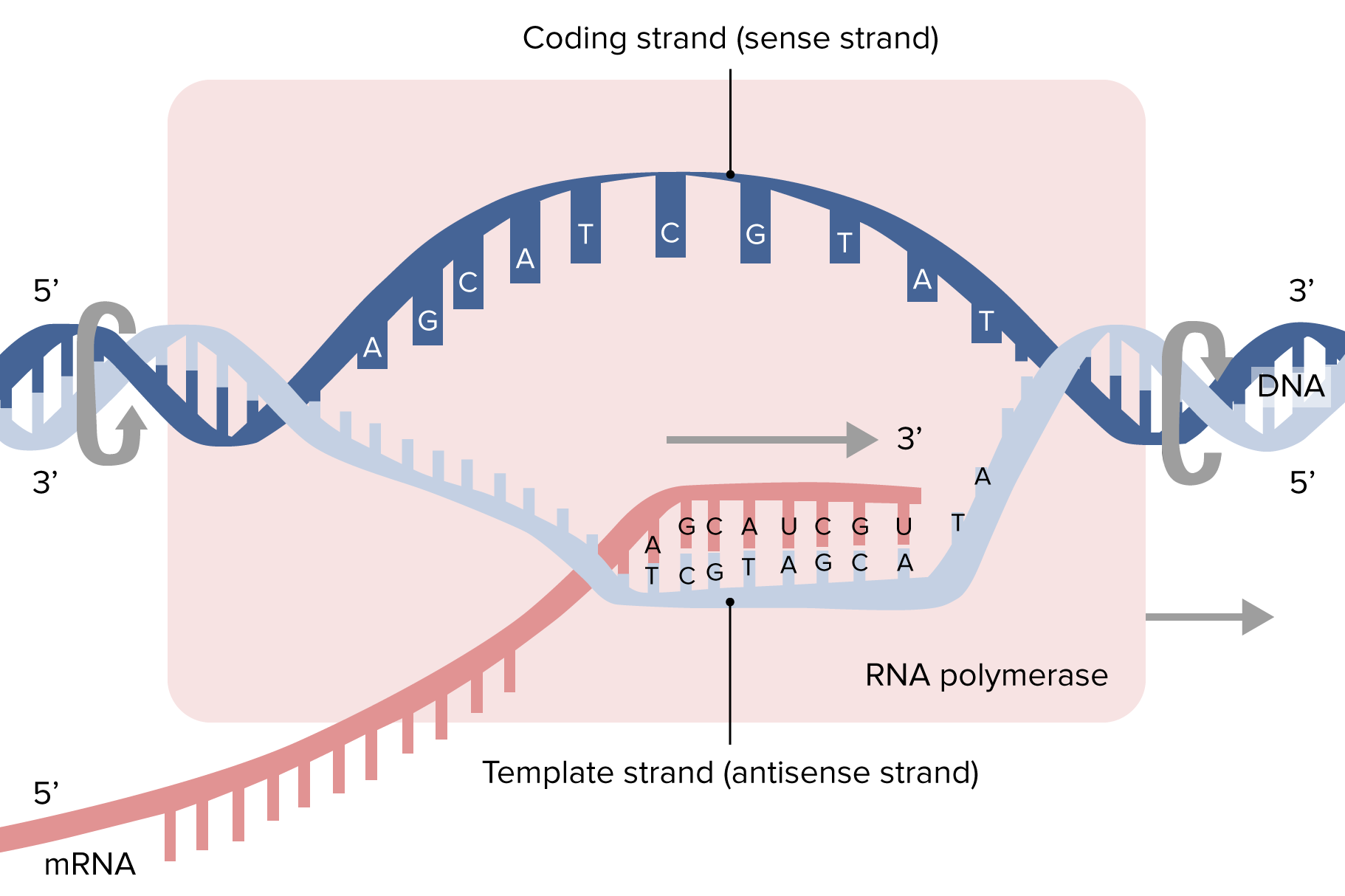
Transcription Biology Diagram
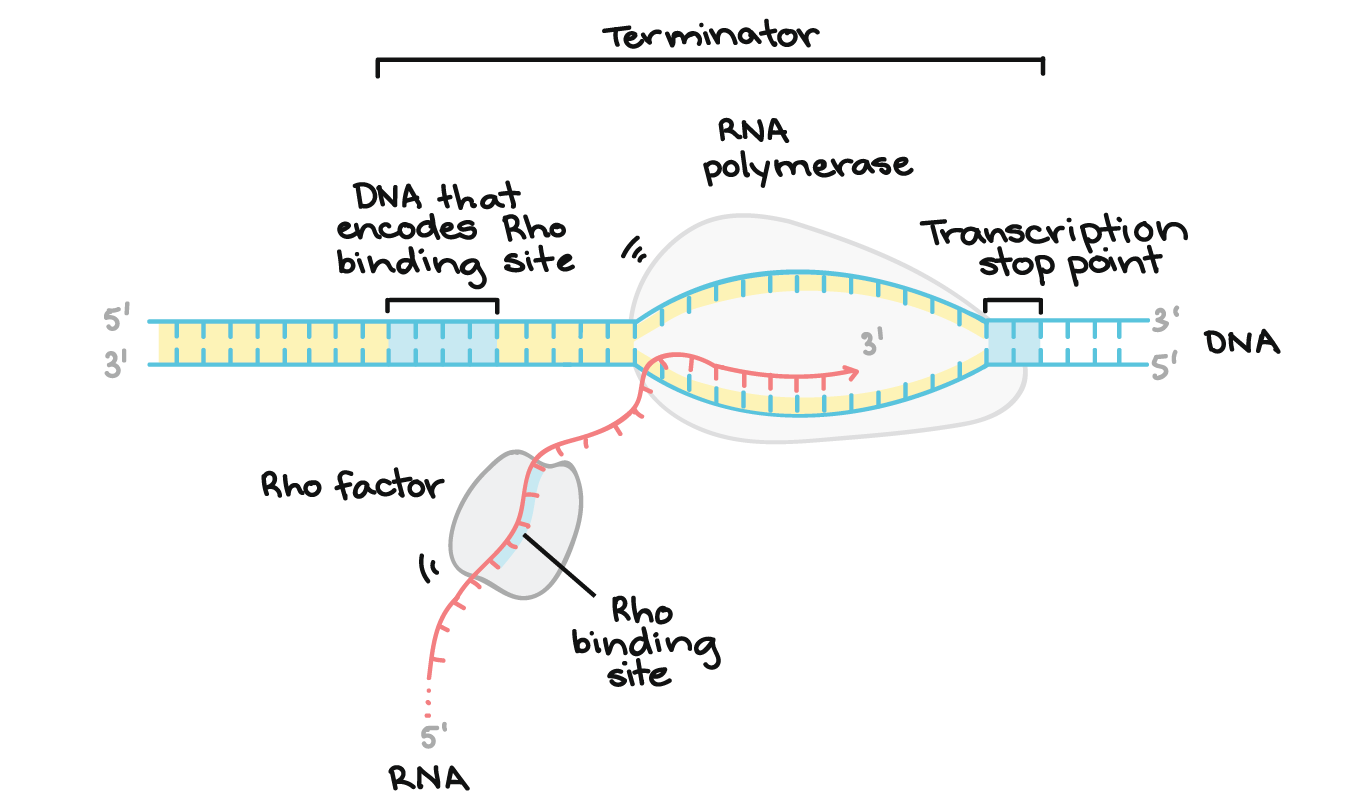
Mechanism Of Transcription Transcription MCAT Content

Draw a well labelled diagram of steps of transcription. Brainly.in
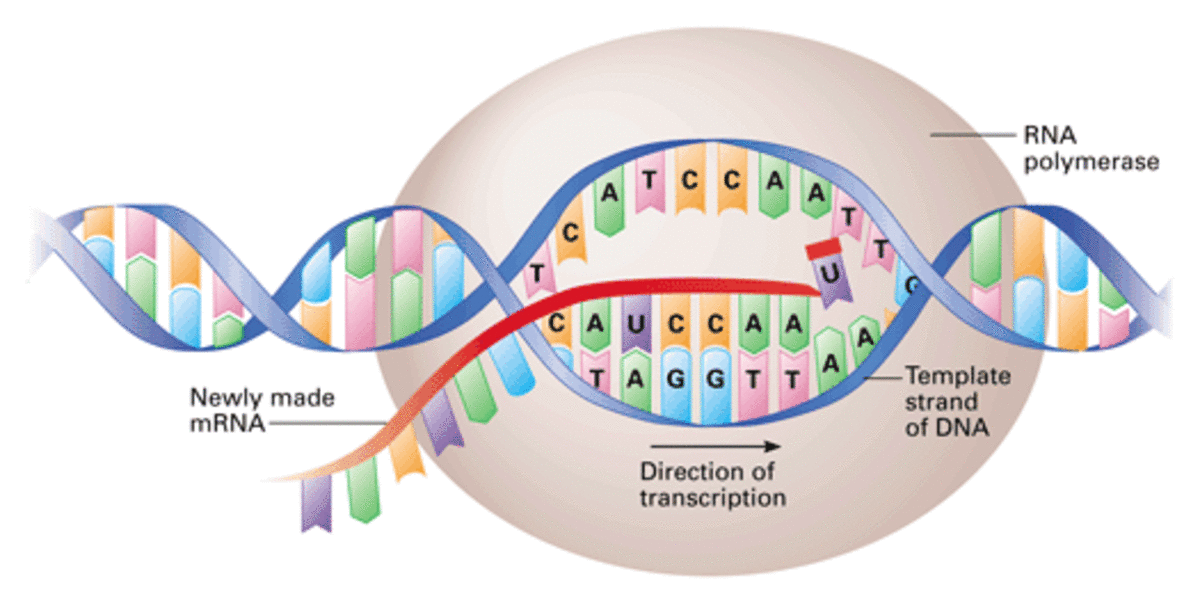
Transcription and Translation Owlcation
Transcription And Translation Are The Two Processes That Convert A Sequence Of Nucleotides From Dna Into A Sequence Of Amino Acids To Build The Desired Protein.
Transcription In Eukaryotes Requires The General Transcription Factors And The Rna Polymerase To Form A Complex At The Tata Box.
Web Basal Transcription Factors Are Crucial In The Formation Of A Preinitiation Complex On The Dna Template That Subsequently Recruits Rna Polymerase Ii For Transcription Initiation.
Web The First Step In Transcription Is Initiation, When The Rna Pol Binds To The Dna Upstream (5′) Of The Gene At A Specialized Sequence Called A Promoter (Figure 2A).
Related Post: