Drawing Of Stomata
Drawing Of Stomata - Web stomata are small pores located on the surface of the leaf that allow the plant to exchange gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, as well as regulate the loss of water vapor through a process called transpiration. Web stomata must open to allow the gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen for efficient photosynthesis (see photorespiration), and light thus typically triggers stomatal opening. Web the diagram of stomata is a diagrammatical representation of a pore (stoma) or stomata found mainly on the underside of plant leaves in the epidermis, stems, and other organs that control the exchange of gases particularly carbon dioxide and oxygen between the plant and its environment. The stomata are minute pores which occur in the epidermis of the plants. In this article, it not only discusses the stomata knowledge, but helps to make stomata diagram online with ease! Web can you find any pores (gaps) in the epidermis? The epidermal cells bordering the guard cells are called accessory cells or subsidiary cells. Opening and closing of stomata. Web in plants, a stoma is a tiny pore in the surface of a leaf that is used for gas exchange. These pores are called stomata and allow carbon dioxide (\(\ce{co2}\)) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis. Web the diagram of stomata is a diagrammatical representation of a pore (stoma) or stomata found mainly on the underside of plant leaves in the epidermis, stems, and other organs that control the exchange of gases particularly carbon dioxide and oxygen between the plant and its environment. In this article, it not only discusses the stomata knowledge, but helps to. Web in plants, a stoma is a tiny pore in the surface of a leaf that is used for gas exchange. Web how to view stomata under the microscope. Hi friends, all green plants have certain primary parts, which are essential and play a. Opening and closing of stomata. Web stomata must open to allow the gas exchange of carbon. The stomata may occur on any part of a plant except the roots. Each stoma remains surrounded by two kidneys or bean shaped epidermal cells the guard cells. Web the diagram of stomata is a diagrammatical representation of a pore (stoma) or stomata found mainly on the underside of plant leaves in the epidermis, stems, and other organs that control. The stomata may occur on any part of a plant except the roots. Web stomata (singular stoma) are tiny openings or pores found in the epidermis of leaves and young stems that helps in gas exchange. They are surrounded by specialised cells and they regulate the gas exchange between the plant and it’s environment, the plant is 'breathing' through them,. Stomata are small openings that mainly occur on the underside of leaves. They provide for the exchange of gases between the outside air and the air canals within the leaf. When stomata are open, however, water vapor is lost to the external environment, increasing the rate of transpiration. Web hello everyone, how to draw stomata | draw a neat and. Web stomata are small pores located on the surface of the leaf that allow the plant to exchange gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, as well as regulate the loss of water vapor through a process called transpiration. Web stomata (singular stoma) are tiny openings or pores found in the epidermis of leaves and young stems that helps in. Opening and closing of stomata. The first time i had students do this lab, i got out razor blades (i know) and tried to have students cut off thin slices of the leaf. The stomata are minute pores which occur in the epidermis of the plants. Web stomata are small pores located on the surface of the leaf that allow. Web hello everyone, how to draw stomata | draw a neat and labeled diagram of stomata | how to draw open and closed stomatal pore | easy way to draw stomata.more. Web how to view stomata under the microscope. The first time i had students do this lab, i got out razor blades (i know) and tried to have students. Stomata are small openings that mainly occur on the underside of leaves. Most leaves are covered in these tiny pores, which allow the plants to take in carbon dioxide for use in photosynthesis and expel their waste oxygen. Learn more about the diagram of stomata along with their labellings at byju’s. When stomata are open, however, water vapor is lost. Web stomata is the tiny pores found in the epidermis of leaves and other organs. The epidermal cells bordering the guard cells are called accessory cells or subsidiary cells. Opening and closing of stomata. Web the diagram of stomata is a diagrammatical representation of a pore (stoma) or stomata found mainly on the underside of plant leaves in the epidermis,. Web how to draw open stomatal pore of stomata step by step for beginners in easy way ! In this article, it not only discusses the stomata knowledge, but helps to make stomata diagram online with ease! Web the prime two functions of stomata are: Web stomata are small pores located on the surface of the leaf that allow the plant to exchange gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, as well as regulate the loss of water vapor through a process called transpiration. Under the microscope, they appear dense or dark. Web stomate, any of the microscopic openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems. Stomata are small openings that mainly occur on the underside of leaves. Web how to draw a stomatal pore of stomata step by step in easy way for beginners who appears in board examination of class 10.more. Web hello everyone.how to draw stomata || stomata diagram || draw a neat labeled diagram of stomatahow to draw stomata,stomata diagram,stomata,draw a neat labele. Learn more about stomata and the. These pores are called stomata and allow carbon dioxide (\(\ce{co2}\)) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis. The epidermal cells bordering the guard cells are called accessory cells or subsidiary cells. Web in plants, a stoma is a tiny pore in the surface of a leaf that is used for gas exchange. Web stomata is the tiny pores found in the epidermis of leaves and other organs. Web the diagram of stomata is a diagrammatical representation of a pore (stoma) or stomata found mainly on the underside of plant leaves in the epidermis, stems, and other organs that control the exchange of gases particularly carbon dioxide and oxygen between the plant and its environment. It assists in the transpiration of water, that is, the loss of excess water from the plant in the form of water vapour.
Stomata Structure, Types, Definition, Diagram, Functions and Mechanism

Draw labelled diagrams of a closed and an open stomata
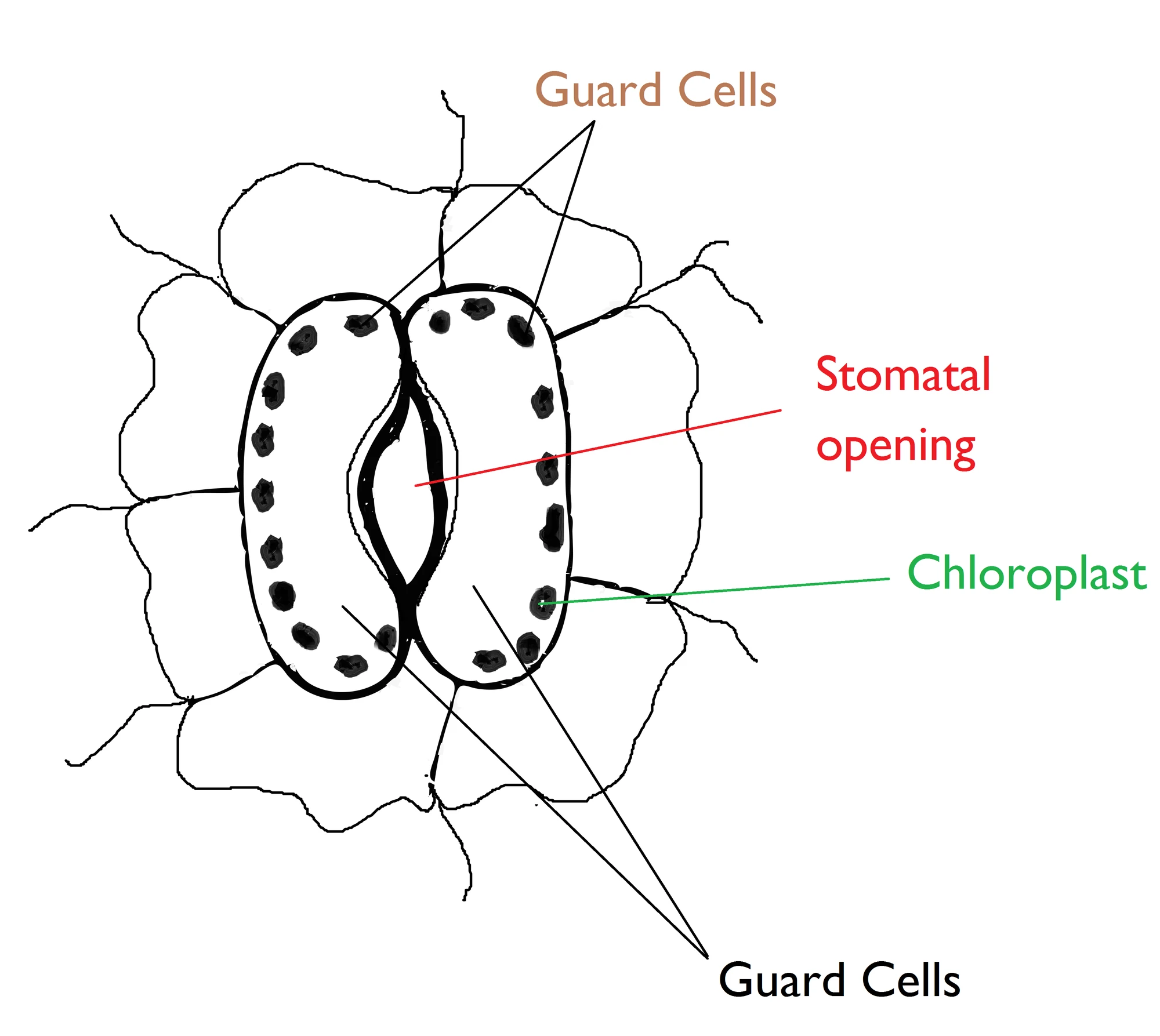
Stomata Open Science Wiki Fandom

Stomata opening and closing vector illustration VectorMine Biology

How to draw Stomata diagram easily step by step Drawing of Stomata

Stomata/opening and closing of stomata/how to draw stomata/open stomata
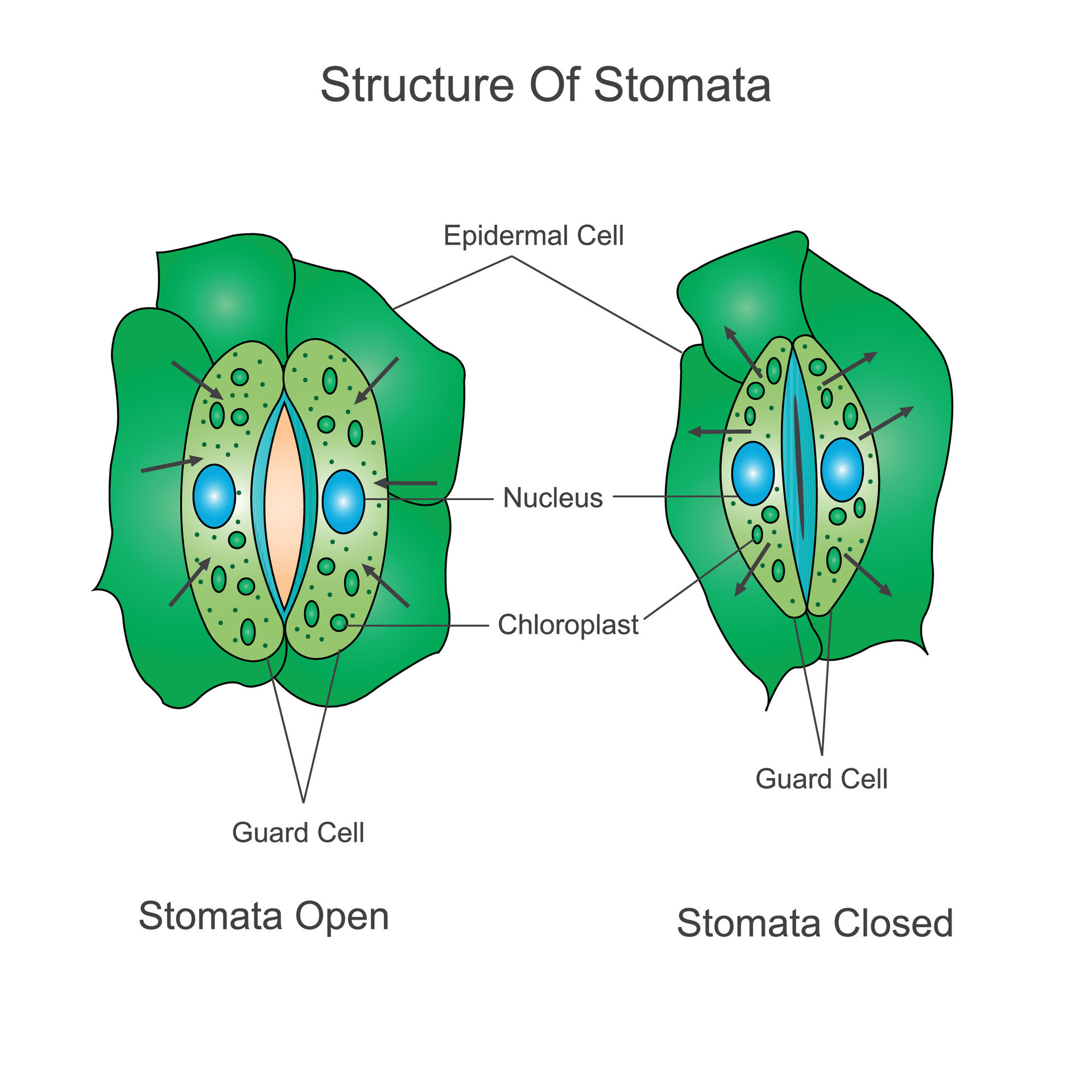
Structure of stomata. Opening and closing of stomata.Biological
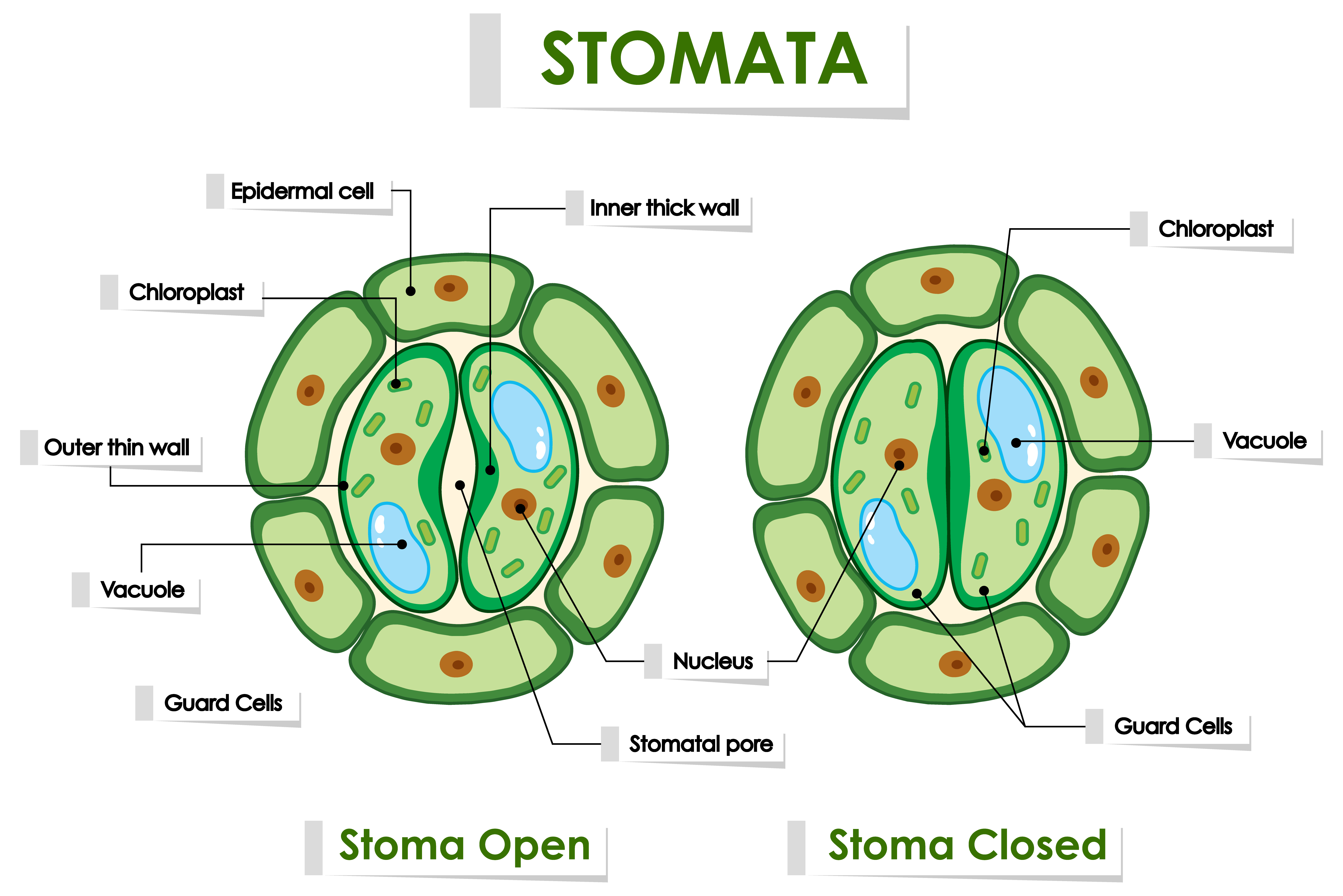
Stomata Diagram on White Background 1114668 Vector Art at Vecteezy

How To Draw a Stomata diagram and Label Step By Step Tutorial 🌿🍃
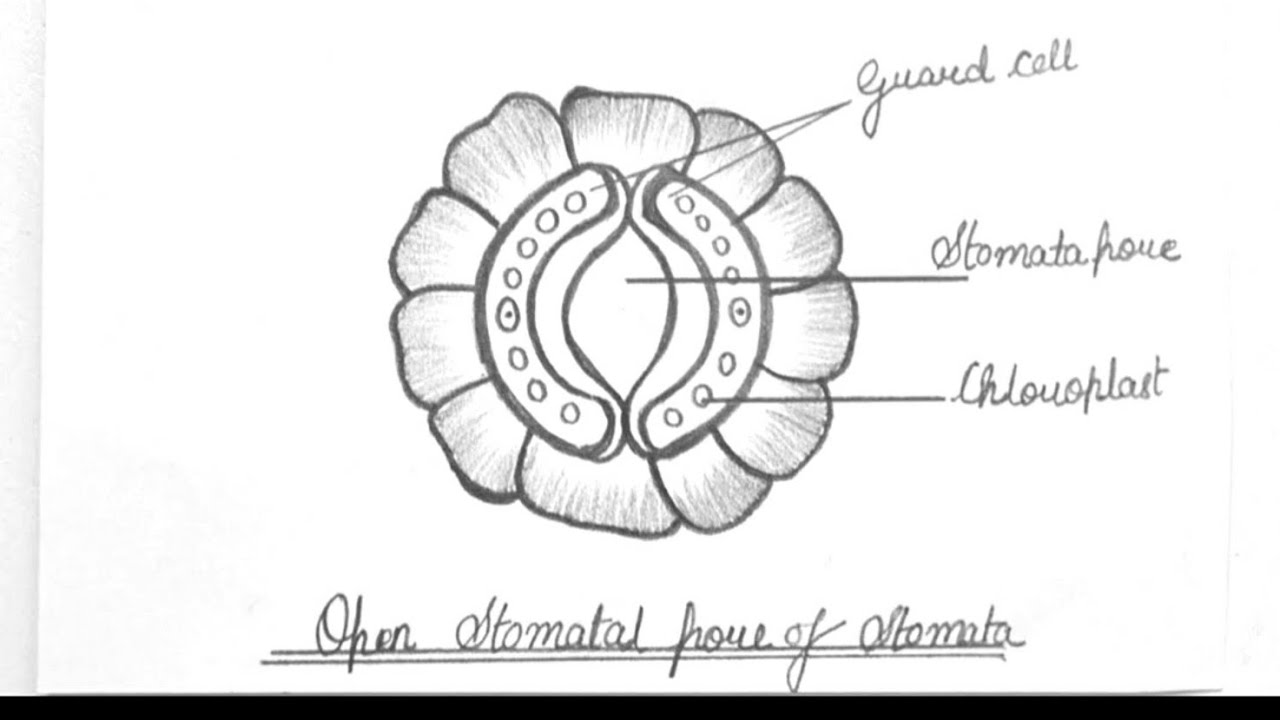
How To Draw Stomata Stomata Diagram Draw A Neat Labeled Diagram
Opening And Closing Of Stomata.
Below The Epidermis, Cells (Appearing Pink Due To Staining Of The Nuclei And Chloroplasts) Are Arranged In Columns, Forming The Palisade Mesophyll.
In This Article, Let Us Explore What Stomata Is, Its Types, Structure, And Functions Along With Its Opening And Closing.
When Stomata Are Open, However, Water Vapor Is Lost To The External Environment, Increasing The Rate Of Transpiration.
Related Post: