Drawing Of Ribosomes
Drawing Of Ribosomes - They are structures containing approximately equal. As catalysts they speed the time of reactions, as fibers they provide support, and many proteins function in specific tasks, like contracting muscle cells. Web it's an educational video from 9th biology ptb.in this video, you will learn how to draw diagram of ribosomes in cell?ribosomes, structure of ribosomes, how. Web ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. This chain of amino acids then folds to form a complex 3d structure. Ribosomes occur both as free particles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. The colored balls at the top of this diagram represent different amino acids. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell’s genetic material, or dna, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. A single pancreas cell can synthesize 5 million molecules. Web this space forms near the part of dna with instructions for making ribosomes, the molecules responsible for making proteins. Web this space forms near the part of dna with instructions for making ribosomes, the molecules responsible for making proteins. Ribosomes occur both as free particles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and as particles attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. This chain of amino acids then folds to form a complex 3d structure. Even before. The tinier subunit is the place the mrna binds and it decodes, whereas the bigger subunit is the place the amino acids are included. Web ribosomes are made of proteins and ribonucleic acid (abbreviated as rna), in almost equal amounts. They act as bridges, matching a codon in an mrna with the amino acid it codes for. The nucleus (plural,. Web it's an educational video from 9th biology ptb.in this video, you will learn how to draw diagram of ribosomes in cell?ribosomes, structure of ribosomes, how. Even before an mrna is translated, a cell must invest energy to build each of its ribosomes. The small particles that came to be known as. This chain of amino acids then folds to. Web the function of a ribosome in any cell is to produce proteins. As catalysts they speed the time of reactions, as fibers they provide support, and many proteins function in specific tasks, like contracting muscle cells. Web ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. They are. Ribosomes read mrna blueprints and piece together proteins, with the help of transfer rna (trna) support workers that bring them the right amino acid each step of the way. Web ribosomes found in higher plant and animal cells are oblate or spheroids in shape, having a diameter of 150 to 200 a 0. A peptide bond links the carboxyl end. In our analogy, the robots making our product are made in a special corner of the blueprint room, before being released to the factory. Ribosomes read mrna blueprints and piece together proteins, with the help of transfer rna (trna) support workers that bring them the right amino acid each step of the way. As catalysts they speed the time of. In eukaryotes, the nucleolus is. 1 is an electron micrograph showing clusters of ribosomes. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger rna molecules to form polypeptide chains. A single pancreas cell can synthesize 5 million molecules. Trnas ( transfer rnas) carry amino acids to the ribosome. They also catalyze the reaction that links amino acids to make a new protein. They play a crucial role in the process of prot. This chain of amino acids then folds to form a complex 3d structure. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus, and exit the nucleus with nuclear pores. Web ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in. Ribosomes are tiny spheroidal dense particles (of 150 to 200 a 0 diameters) that are primarily found in most prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus, and exit the nucleus with nuclear pores. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger rna molecules to form polypeptide chains. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses. These clusters, called polysomes, are held together by messenger rna (mrna). Web the shape of a protein is what gives the protein its specific function. The exact size of the ribosomes varies, depending on the cell type and whether the cell is resting or participating in cell division. A peptide bond links the carboxyl end of one amino acid with. These clusters, called polysomes, are held together by messenger rna (mrna). A single pancreas cell can synthesize 5 million molecules. Web a bacterial ribosome is about 250 nm in diameter and consists of two subunits, one large and one small. It comprises of two sections, known as subunits. The exact size of the ribosomes varies, depending on the cell type and whether the cell is resting or participating in cell division. Web this reaction is catalyzed by ribosomes and generates one water molecule. Ribosomes read mrna blueprints and piece together proteins, with the help of transfer rna (trna) support workers that bring them the right amino acid each step of the way. All proteins start as deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna. Ribosomes consist of two major components: They are sites of protein synthesis.; Web ribosomes provide a structure in which translation can take place. Web figure 3.4.1 3.4. A eukaryotic ribosome is composed of nucleic acids and about 80 proteins and has a molecular mass of about 4,200,000 da. Web the function of a ribosome in any cell is to produce proteins. Even before an mrna is translated, a cell must invest energy to build each of its ribosomes. As the ribosome collects a new amino acid, it attaches this amino acid to the chain of amino acids it has just pieced together by performing a chemical reaction.
The structure ribosome functions Royalty Free Vector Image
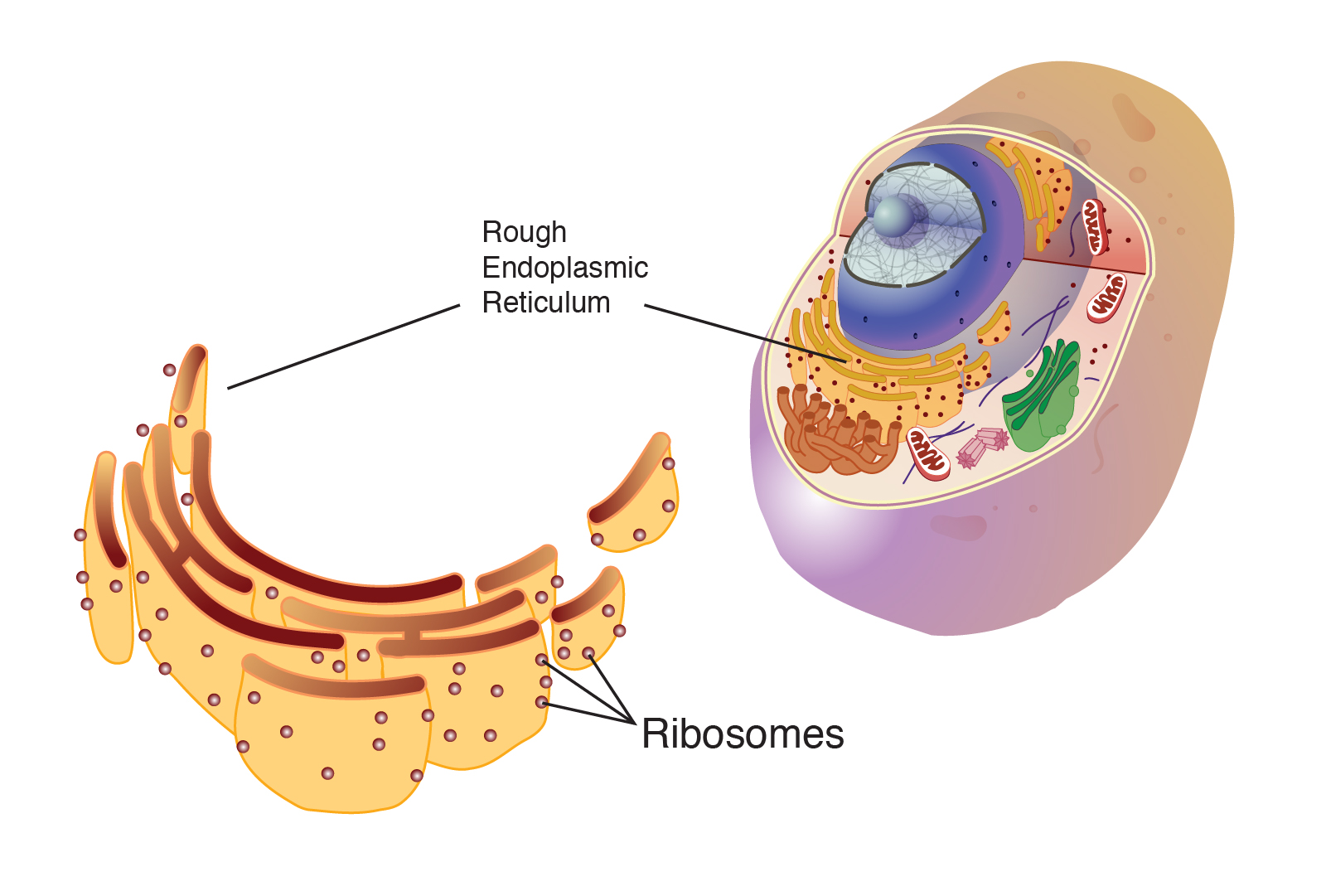
Ribosome
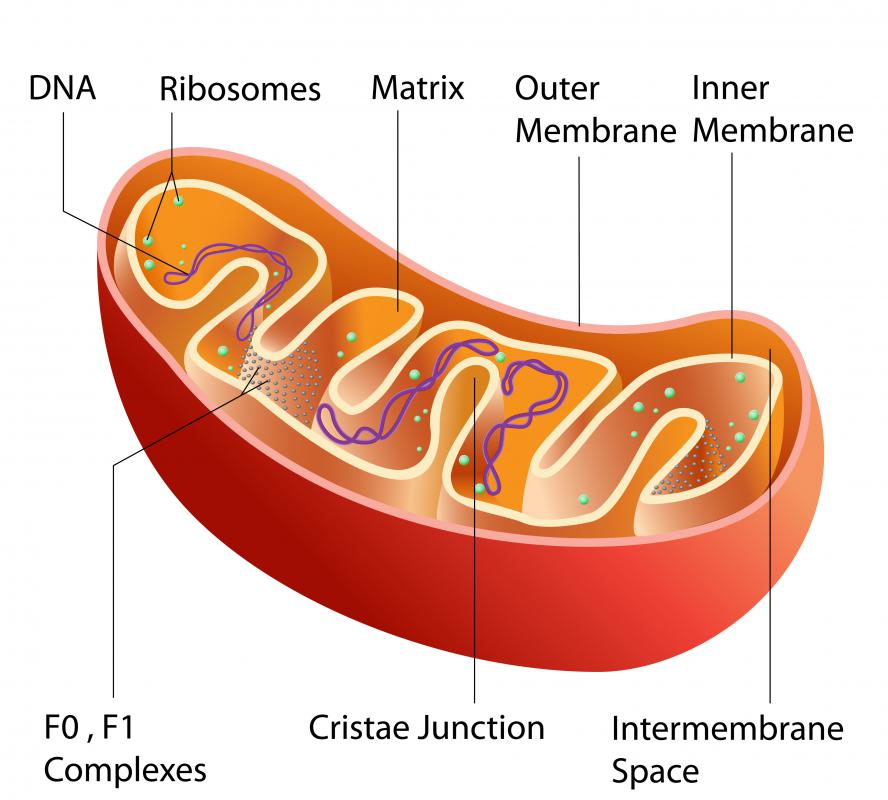
What is a Ribosome? (with pictures)
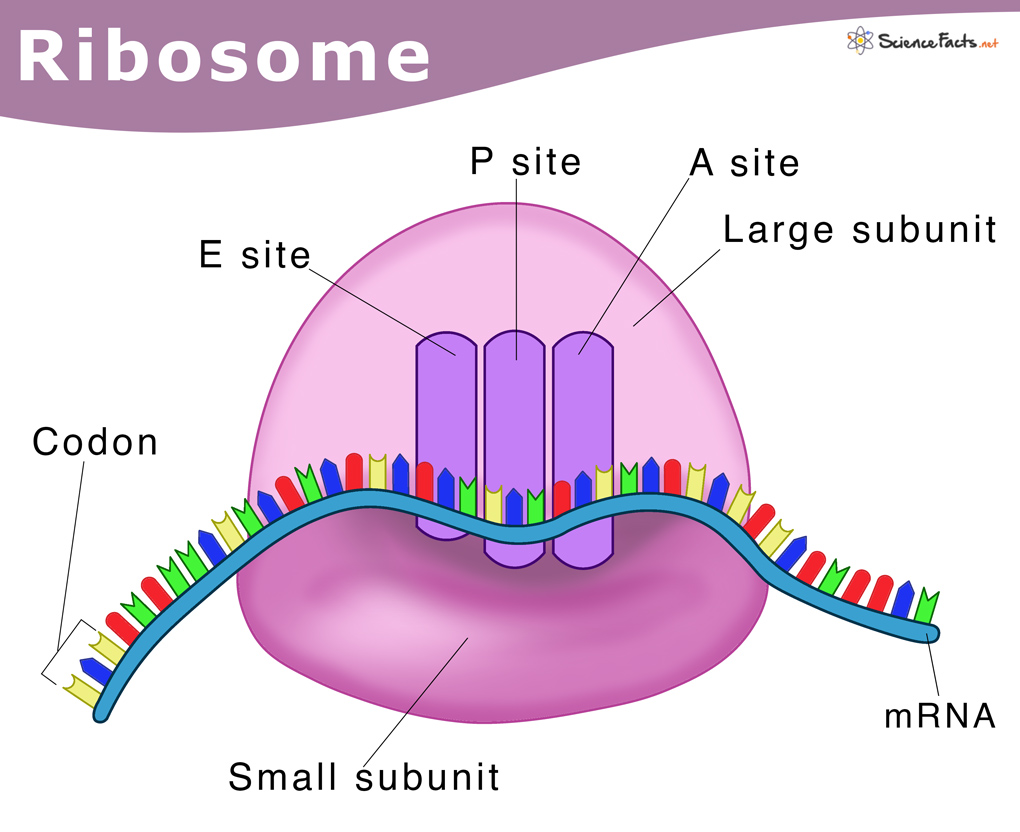
Ribosomes Definition, Structure, & Functions, with Diagram
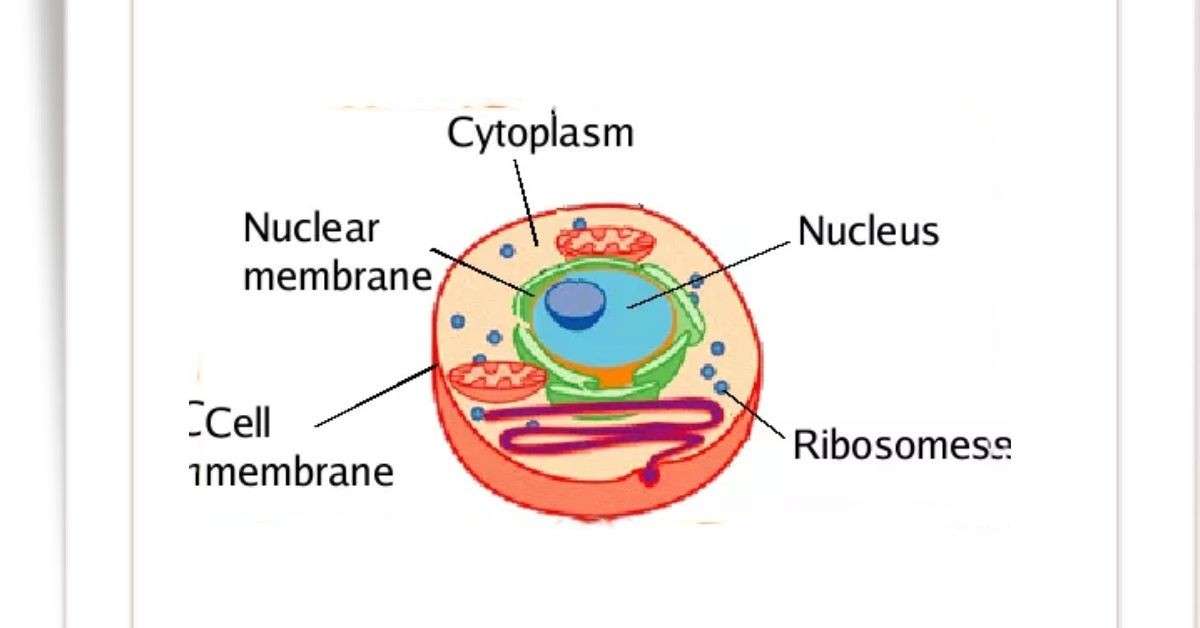
Ribosome Types, Structure and Functions Biology Educare
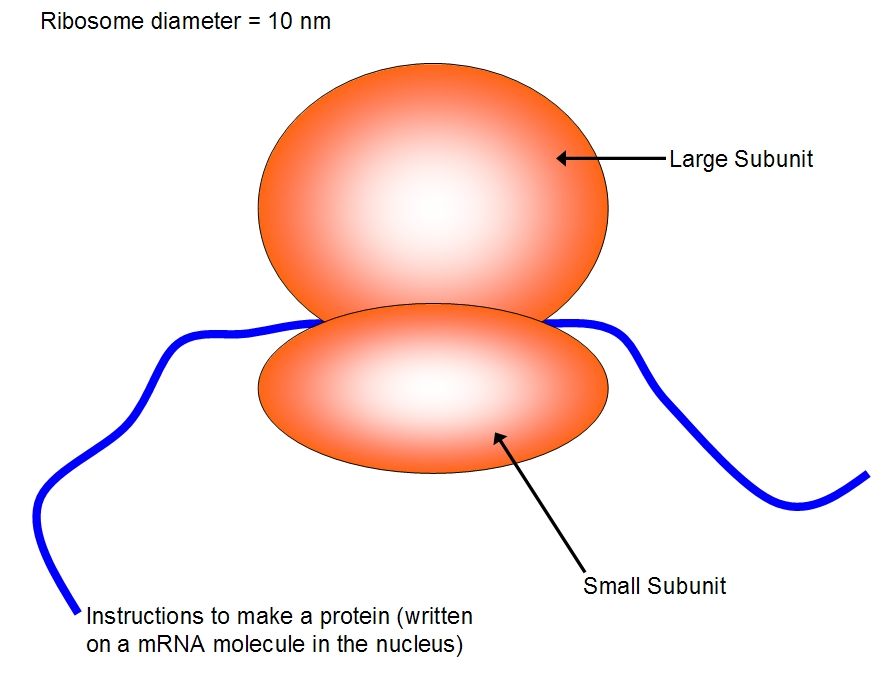
Ribosomes
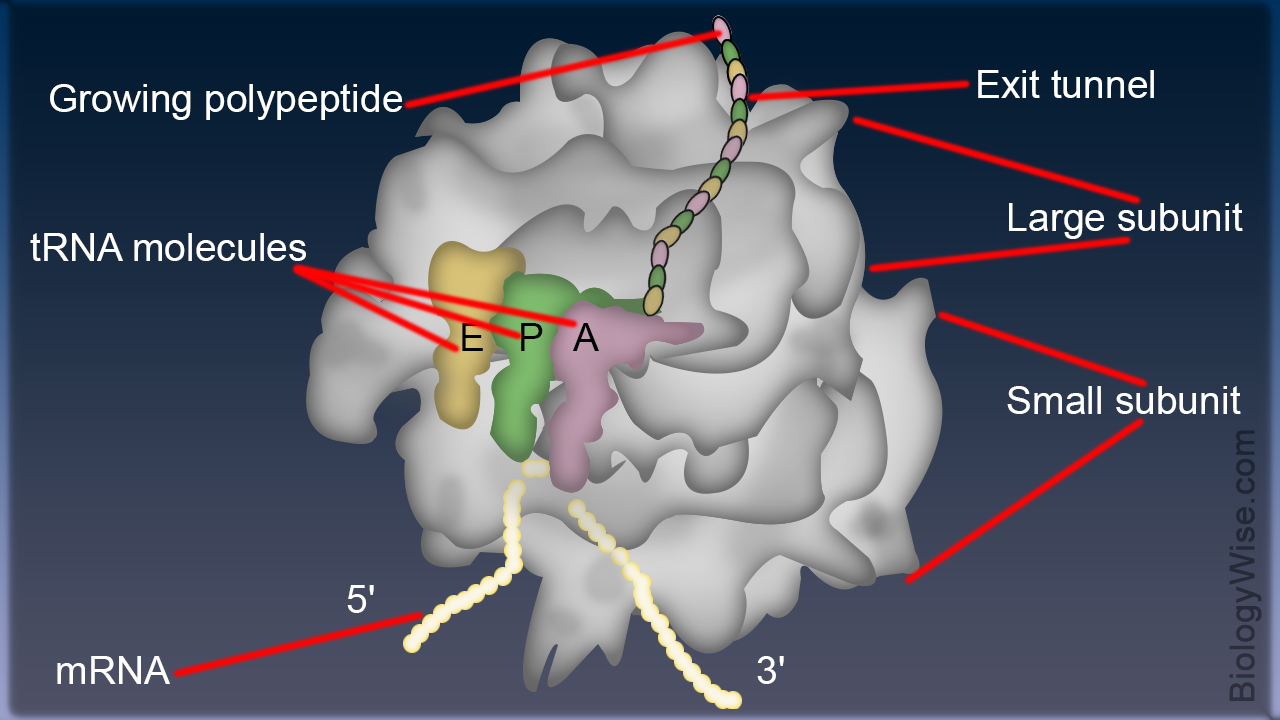
Structure of Ribosome

The structure ribosome infographics on Royalty Free Vector

The structure of the ribosome Infographics Vector Image
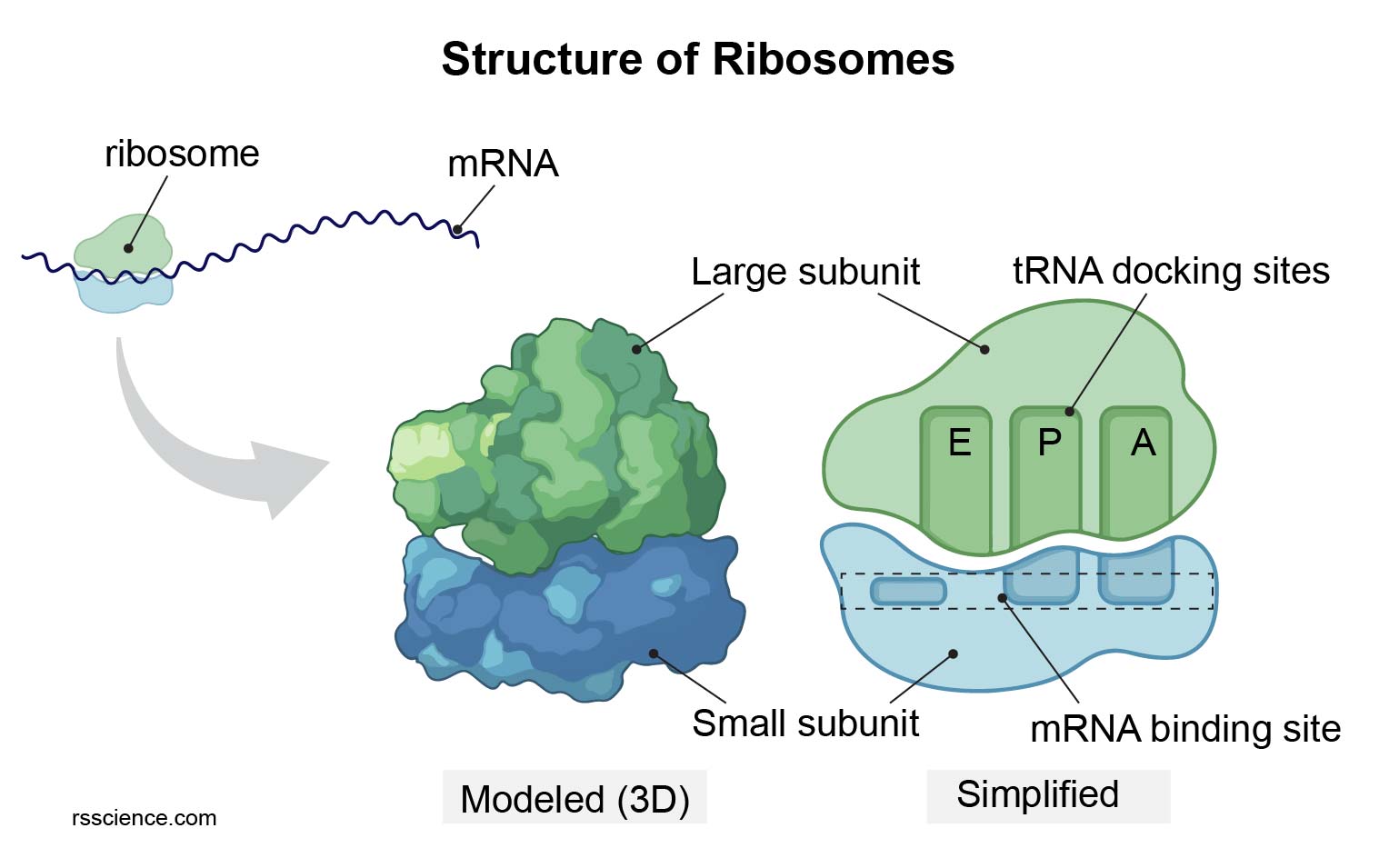
Ribosome protein factory definition, function, structure and biology
1 Is An Electron Micrograph Showing Clusters Of Ribosomes.
Ribosomes Link Amino Acids Together In The Order Specified By The Codons Of Messenger Rna Molecules To Form Polypeptide Chains.
Web The Shape Of A Protein Is What Gives The Protein Its Specific Function.
They Are Structures Containing Approximately Equal.
Related Post: