Drawing Of Cell Membrane
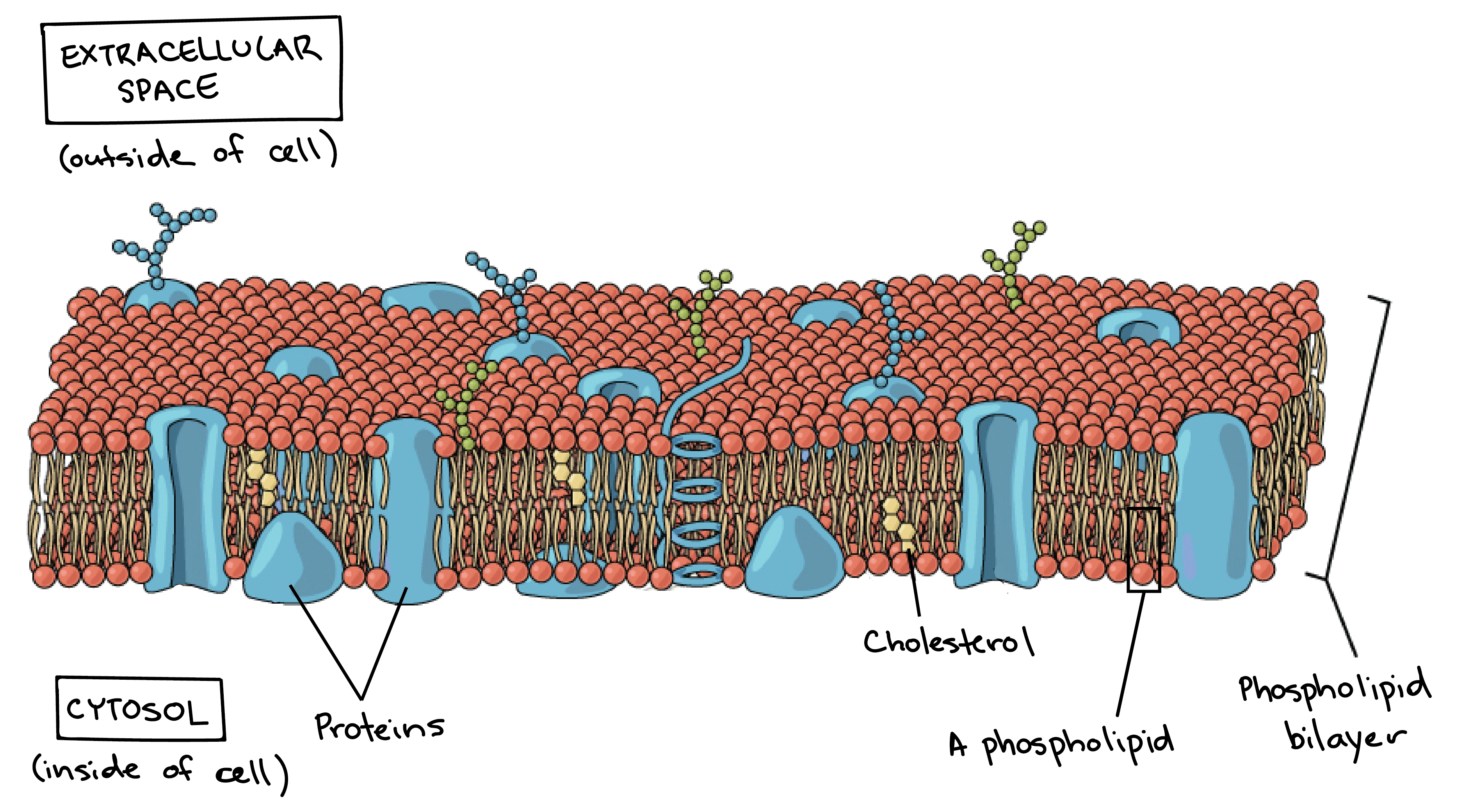
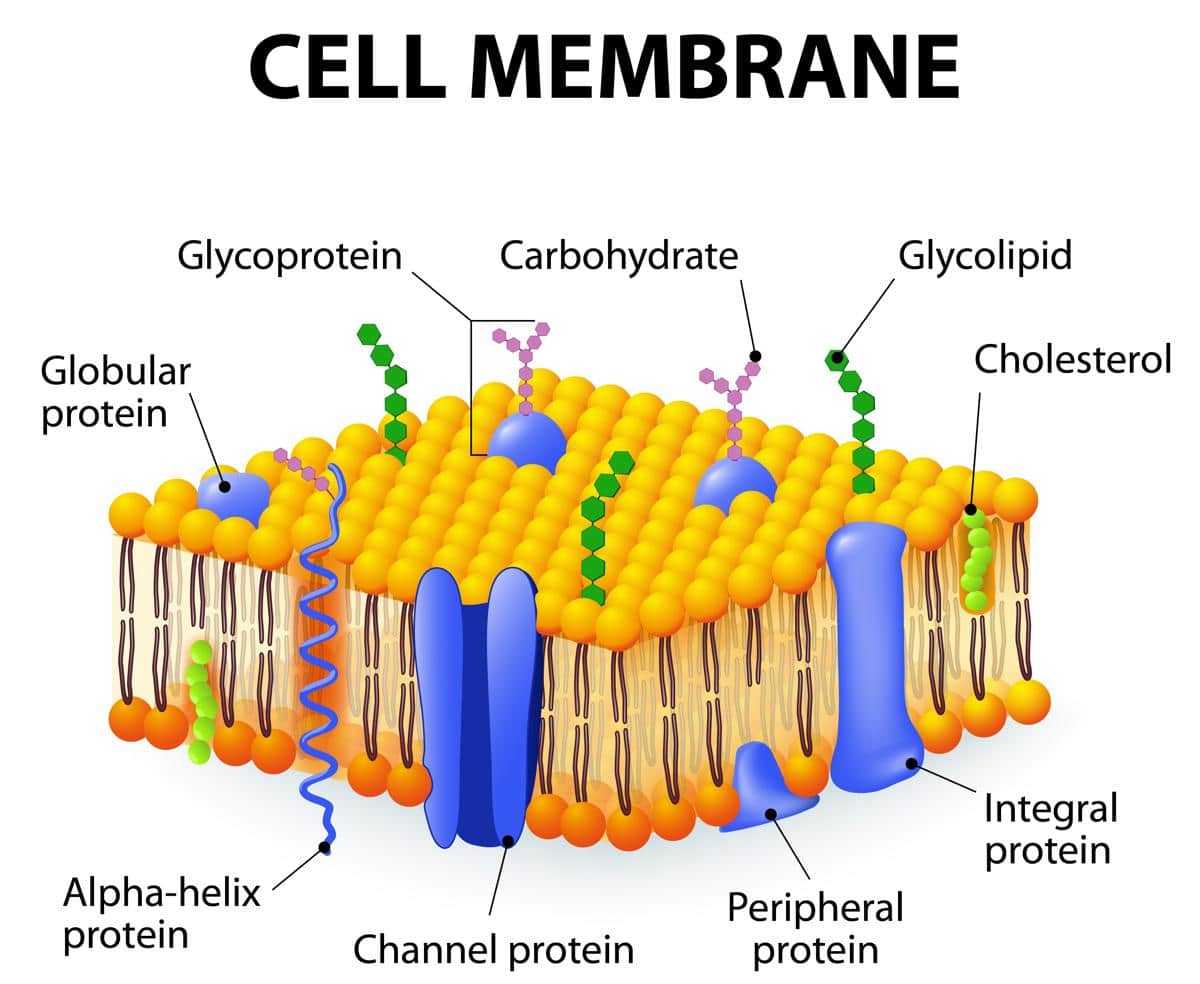
Drawing Of Cell Membrane - Web what are cellular membranes made of? In other words, a diagram of the membrane (like the one below) is just a snapshot of a dynamic process in which phospholipids and proteins. It is very easy drawing detailed method to help you. Describe how molecules cross the cell membrane based on their properties and concentration gradients. With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed. Web the fluid mosaic model explains the structure of cell membranes. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Fundamentals of biology ii (lumen) 9: A 3d diagram of the cell membrane. Web the fluid mosaic model explains the structure of cell membranes. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids, which have a hydrophilic phosphate head, a glycerol backbone, and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. The. Web cell membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell. What you’ll learn to do: Web describe the structure of cell membranes. The membrane bilayer contains many kinds of phospholipid molecules,. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Structure and function of the cell membrane. A cell’s plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. In other words, a diagram of the membrane (like the one below) is just a snapshot of a dynamic process in which phospholipids and proteins. Structure of the cell membrane. Web what is. Web a drawing showing the three main cell membrane components and how they are arranged in a cell membrane. These membranes are composed of phospholipids, forming a bilayer with hydrophilic heads facing outwards and hydrophobic tails facing inwards. Web the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells. It is very easy drawing detailed method to help you. 9k views 11 months ago easy science drawing. Web cell membrane, thin. Web the fluid mosaic model explains the structure of cell membranes. Web the fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins, and cholesterol are embedded within this bilayer, creating a diverse mosaic.. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Web the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The phospholipids form a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed. In other words, a diagram of the membrane (like the one below) is just a snapshot of a dynamic process in which phospholipids. What you’ll learn to do: 2.4.2 explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes. 9k views 11 months ago easy science drawing. Describe how molecules cross the cell membrane based on their properties and concentration gradients. Web this cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials. Describe the structure and function of membranes, especially the phospholipid bilayer. With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed. Describe the structure of cell membranes. A simplified rough guide of the dry weight is shown in table 1. Web the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or. With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The cell membrane functions as a barrier, keeping cell constituents in and unwanted substances out, and as a gate, allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. How to draw cell membrane easily/cell membrane drawing. Describe how molecules cross the cell membrane based on their properties and concentration gradients. A simplified rough guide of the dry weight is shown in table 1. It is very easy drawing detailed method to help you. Web a drawing showing the three main cell membrane components and how they are arranged in a cell membrane. Fundamentals of biology ii (lumen) 9: The phospholipid heads face outward, one layer exposed to the interior of the cell and one layer exposed to the exterior (figure 2). Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two phospholipid layers, or a type of lipid with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails inside. Web according to the fluid mosaic model, the plasma membrane is a mosaic of components—primarily, phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins—that move freely and fluidly in the plane of the membrane. Web describe the structure of cell membranes. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The lipid tails of one layer face the lipid tails of the other layer, meeting at the interface of the two layers. Web cell membranes are fluid.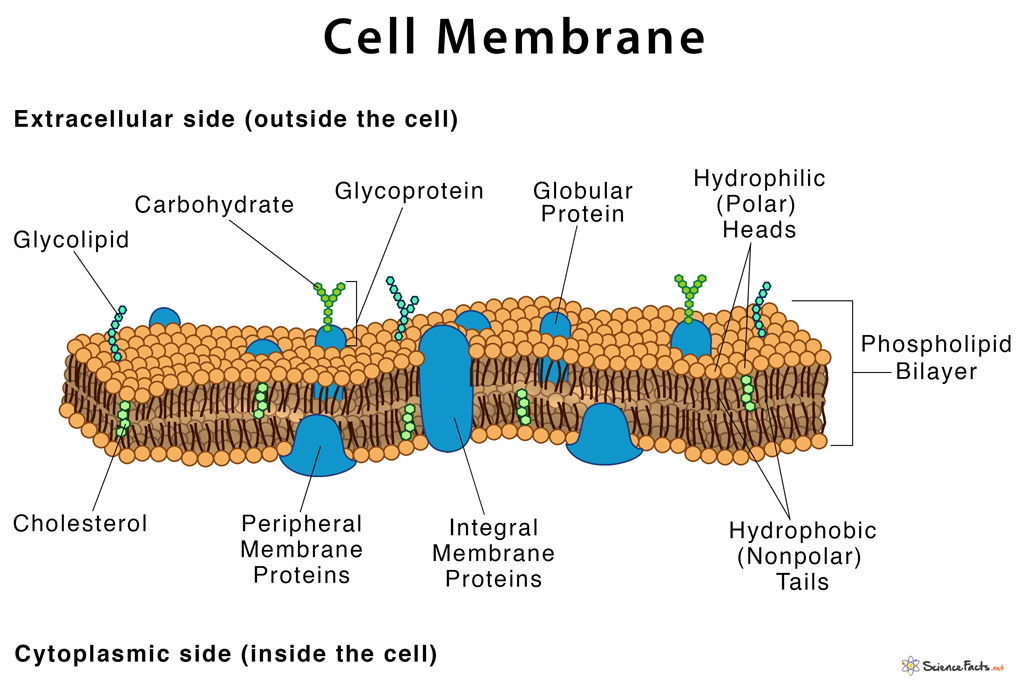
Cell Membrane Definition, Structure, & Functions with Diagram

Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level
Structure Of Plasma Membrane Diagram / Components And Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
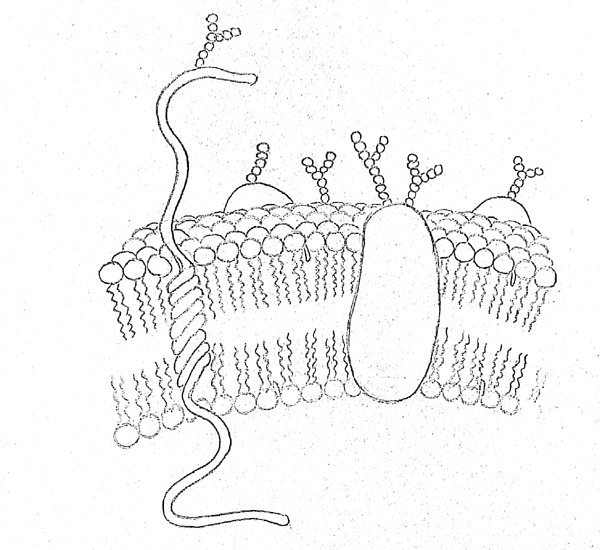
DRAW IT NEAT How to draw plasma membrane (Cell membrane)

Schematic Diagram of a Cell Membrane Cell Structure Function
Cell Organelles BIOLOGY JUNCTION

Cell membrane definition, structure, function, and biology
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure

TJ. Schematic diagram of typical membrane proteins in a biological
2.4.2 Explain How The Hydrophobic And Hydrophilic Properties Of Phospholipids Help To Maintain The Structure Of Cell Membranes.
9K Views 11 Months Ago Easy Science Drawing.
It Is Made Of A Phospholipid Bilayer, Along With Other Various Lipids, Proteins, And Carbohydrates.
A 3D Diagram Of The Cell Membrane.
Related Post: