Draw The Shear And Moment Diagrams For The Loaded Beam
Draw The Shear And Moment Diagrams For The Loaded Beam - X 1 = 0.15m x 2 = 0.10m x 3 = 0.05m a = 0.105m step 1: ∑ m a = 0. Without there being any load applied to the beam, check that the beam is in its equilibrium position. Shear and moment diagrams the beam is. 172k views 5 years ago civil engineering/structural engineering. We go through breaking a beam into segments, and then we learn about the relatio. 5/106 draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded cantilever beam. Internal forces in beams and frames, libretexts. Web write shear and moment equations for the beams in the following problems. Web below is a simple example of what shear and moment diagrams look like, afterwards, the relation between the load on the beam and the diagrams will be discussed. Web chapter 5, problem 5/115 go tutorial draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded beam. 92k views 3 years ago statics. ∑ m a = 0. Figures 1 through 32 provide a series of shear and moment diagrams with accompanying formulas for design of beams under various static loading conditions. Find the ax, ay and by values i. Download a customised selection of the above results in a formatted pdf report. Web there are 4 steps to solve this one. R a + r b = 6 × 6 + 31 + 1 2 × 9 × 13 = 125.5 k n. What are the values of the shear force and bending moment at the middle of the. R a + r b = 6 × 6 + 31 + 1 2 × 9 × 13 = 125.5 k n. Mmax = 84 knm, σmax = 98.9 mpa. Leave all distributed forces as distributed forces and do not replace them with the equivalent point load. Post any question and get expert help quickly. Web below is a simple. To create the shear force diagram, we will use the following process. Solve for all external forces acting on the body. Draw out a free body diagram of the body horizontally. Web draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam. Figures 1 through 32 provide a series of shear and moment diagrams with accompanying formulas for design of beams. The distributed load is the slope of the shear diagram and each point load represents a jump in the shear diagram. Figures 1 through 32 provide a series of shear and moment diagrams with accompanying formulas for design of beams under various static loading conditions. Leave all distributed forces as distributed forces and do not replace them with the equivalent. Now taking moment about support a. Shear and bending moment diagrams. Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the loaded beam shown below. Without there being any load applied to the beam, check that the beam is in its equilibrium position. Draw the shear and moment diagramsfor the beam.take :a=,2,mb=,1.5,mc=,2,knmsolution :equation of equilibrium: Web the previous section presented a method to find the shear and bending moment at a single point, which is useful; The distributed load is the slope of the shear diagram and each point load represents a jump in the shear diagram. After you have the diagrams, answer the questions as a check on your work. Shear and bending moment. So in this post we’ll give you a thorough introduction to shear forces, bending moments and how to draw shear and moment diagrams. Use the 'analysis' tab to view various criteria, such as: We go through breaking a beam into segments, and then we learn about the relatio. Download a customised selection of the above results in a formatted pdf. Use the 'analysis' tab to view various criteria, such as: Shear and moment diagrams and formulas are excerpted from the western woods use book, 4th edition, and are provided herein as a courtesy of. Download a customised selection of the above results in a formatted pdf report. Web draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded beam. View the. Internal forces in beams and frames, libretexts. Web the first step in calculating these quantities and their spatial variation consists of constructing shear and bending moment diagrams, \(v(x)\) and \(m(x)\), which are the internal shearing forces and bending moments induced in. Draw out a free body diagram of the body horizontally. Let reaction at supports a and b be r. The goal of the beam analysis -determine the shear force v and I do not know how to implement the force of 15 kn Not the question you’re looking for? Draw the shear and moment diagramsfor the beam.take :a=,2,mb=,1.5,mc=,2,knmsolution :equation of equilibrium: Shear and bending moment diagrams. View the full answer step 2. Web draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam. The distributed load is the slope of the shear diagram and each point load represents a jump in the shear diagram. 172k views 5 years ago civil engineering/structural engineering. ∑ m a = 0. Web chapter 5, problem 5/115 go tutorial draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded beam. But in order to find the shear and moment at every point in the object you will need a more powerful approach. Also, draw shear and moment diagrams, specifying values at all change of loading positions and at. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Web below is a simple example of what shear and moment diagrams look like, afterwards, the relation between the load on the beam and the diagrams will be discussed. Without there being any load applied to the beam, check that the beam is in its equilibrium position.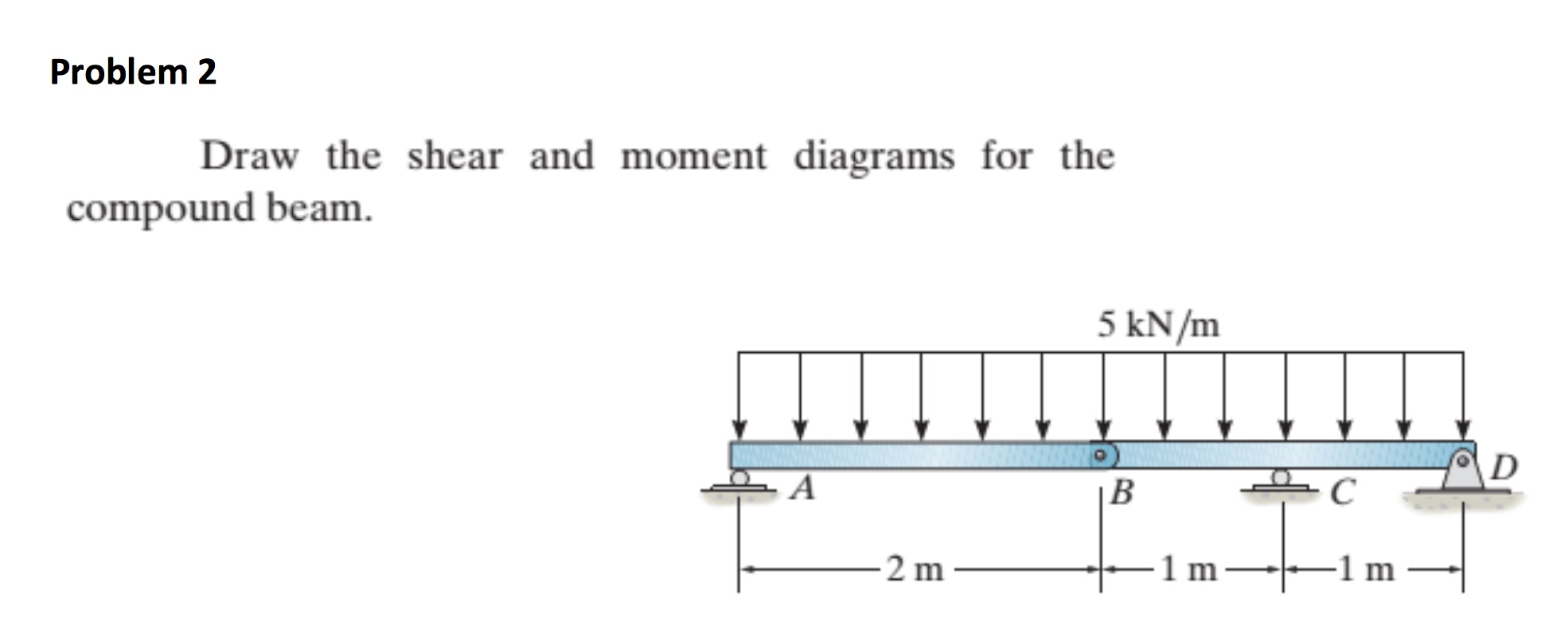
draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam chegg
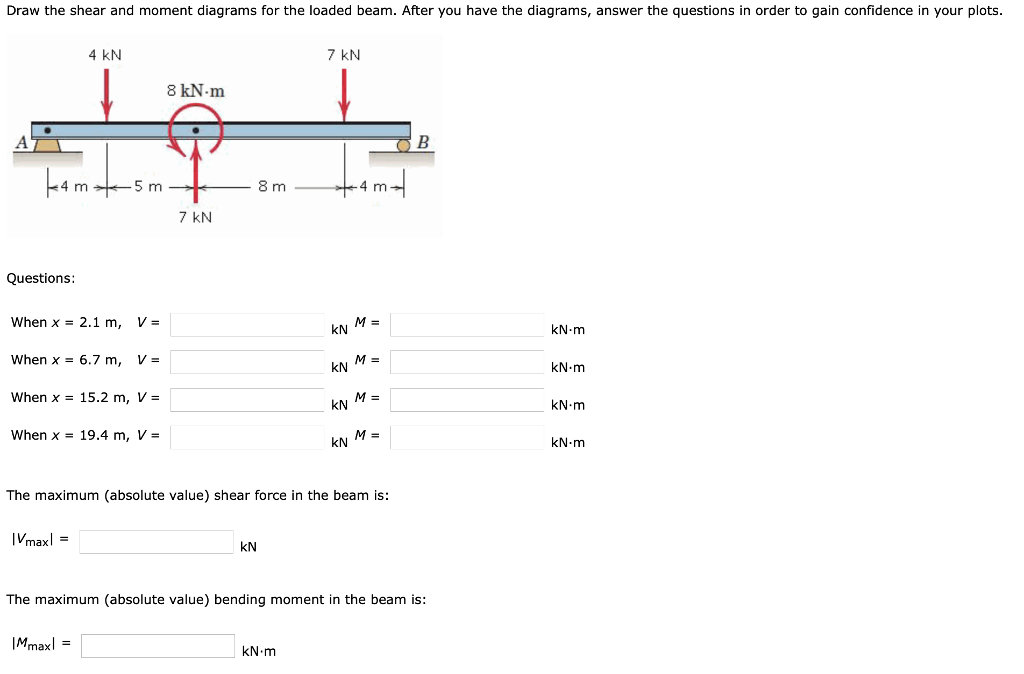
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded
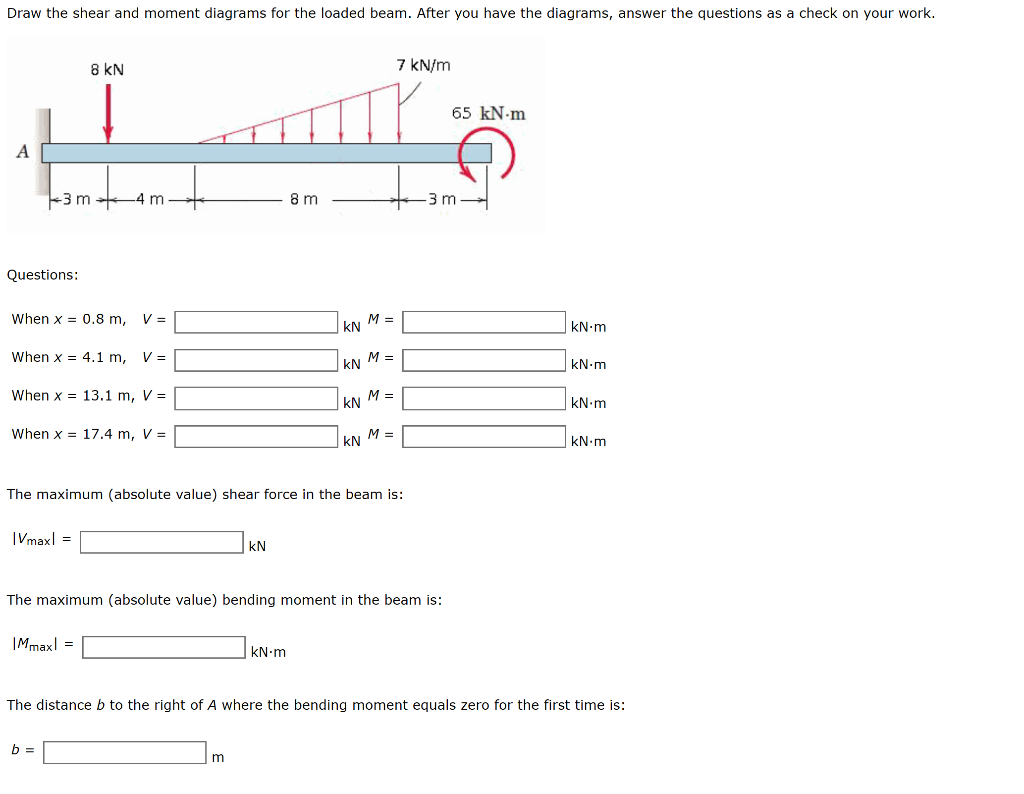
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the loaded
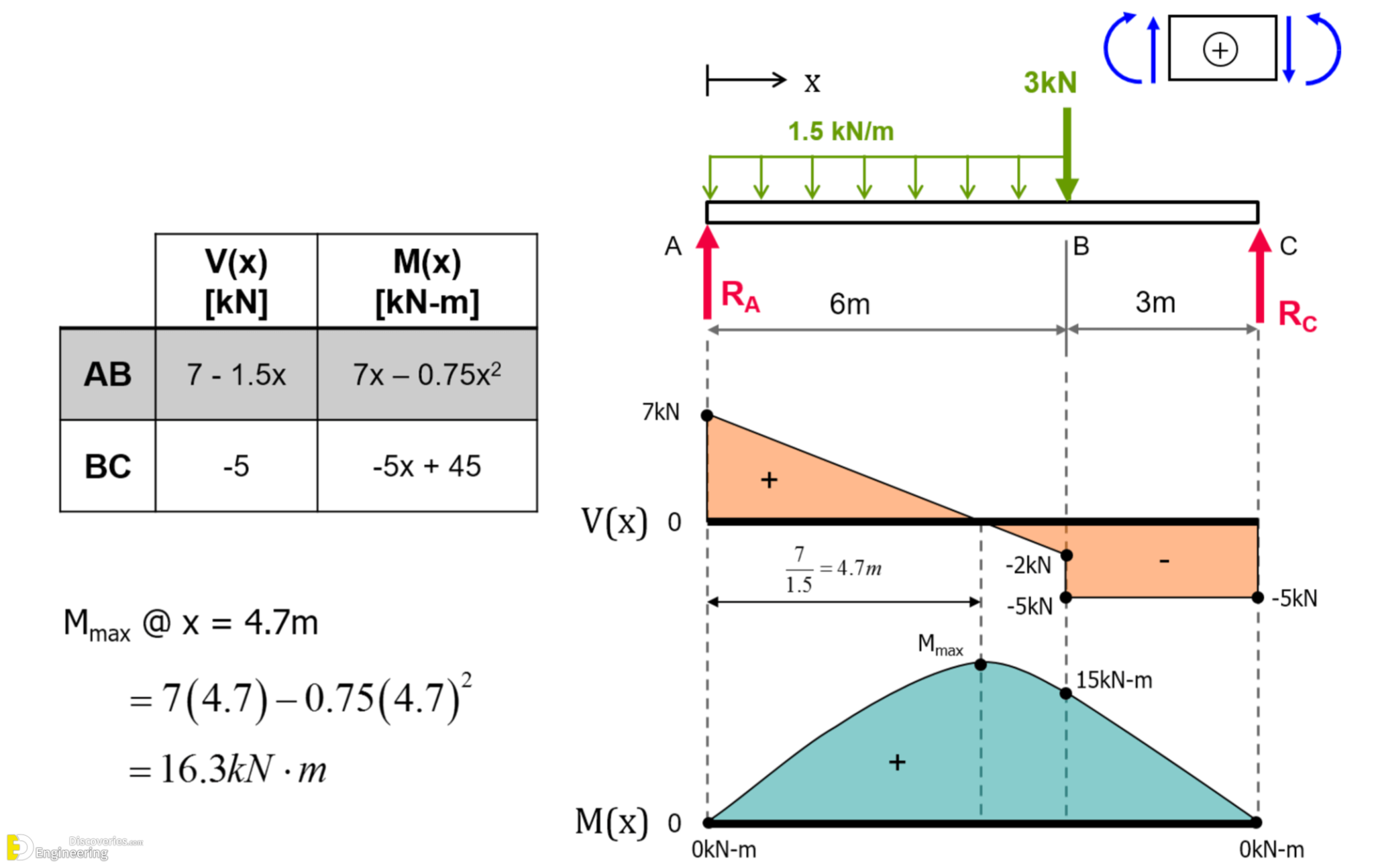
Learn How To Draw Shear Force And Bending Moment Diagrams Engineering
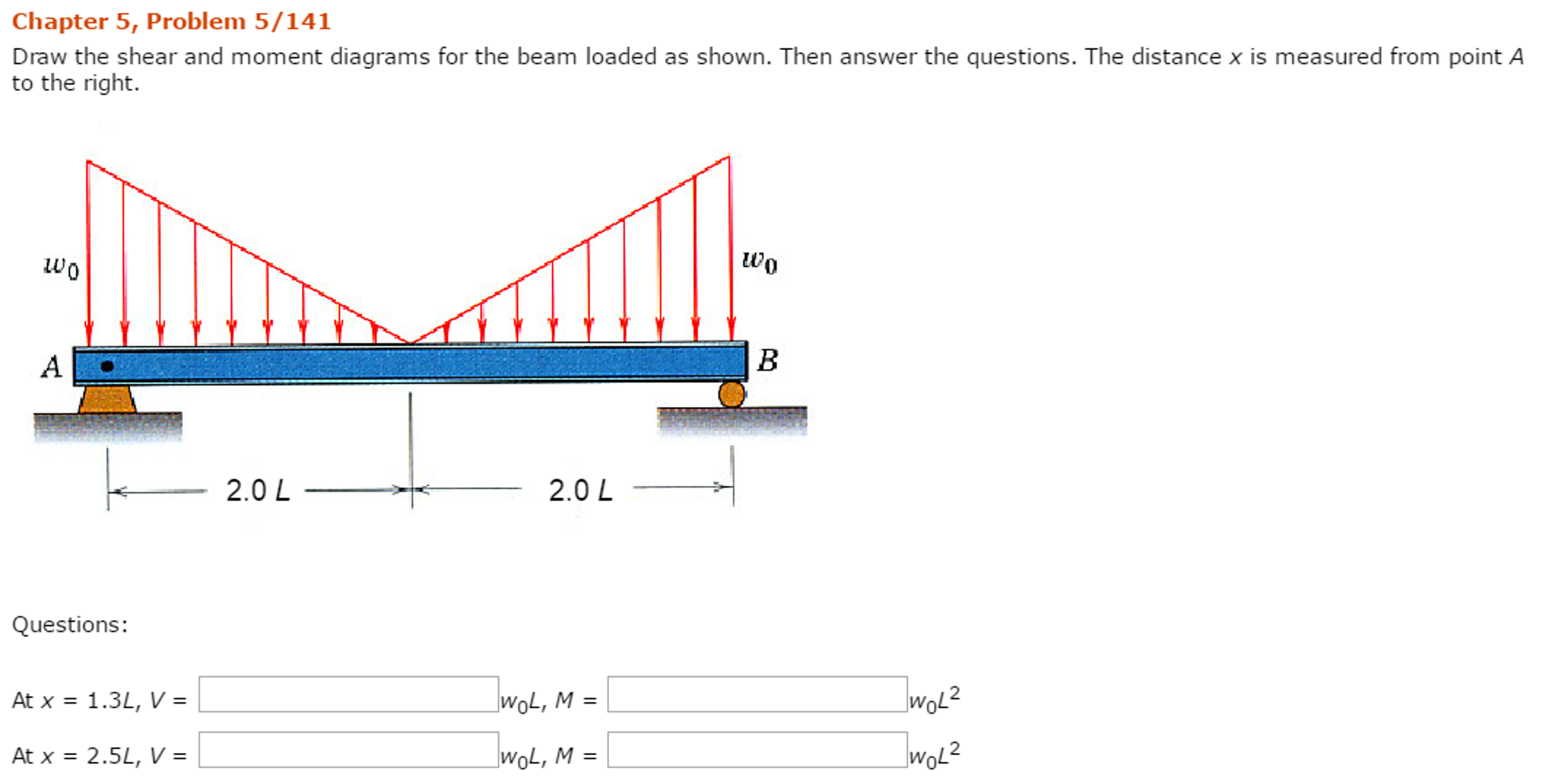
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam
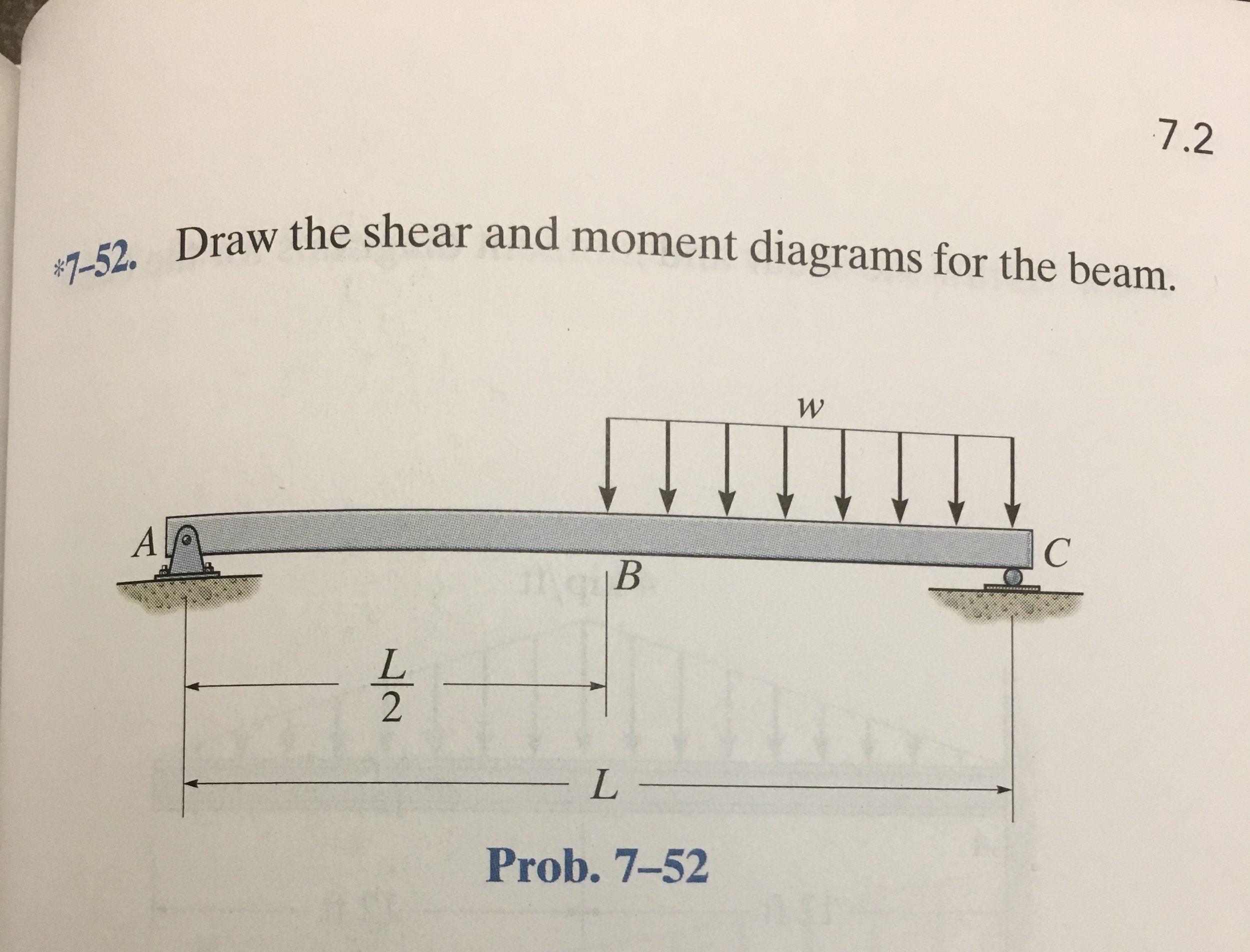
Draw The Shear Diagram For The Beam
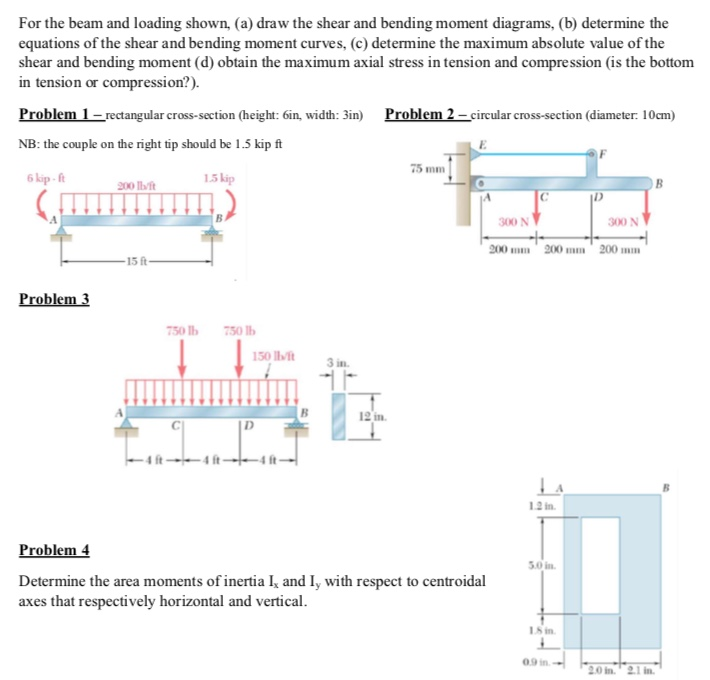
For The Beam And Loading Shown Draw Shear Bending Moment Diagrams
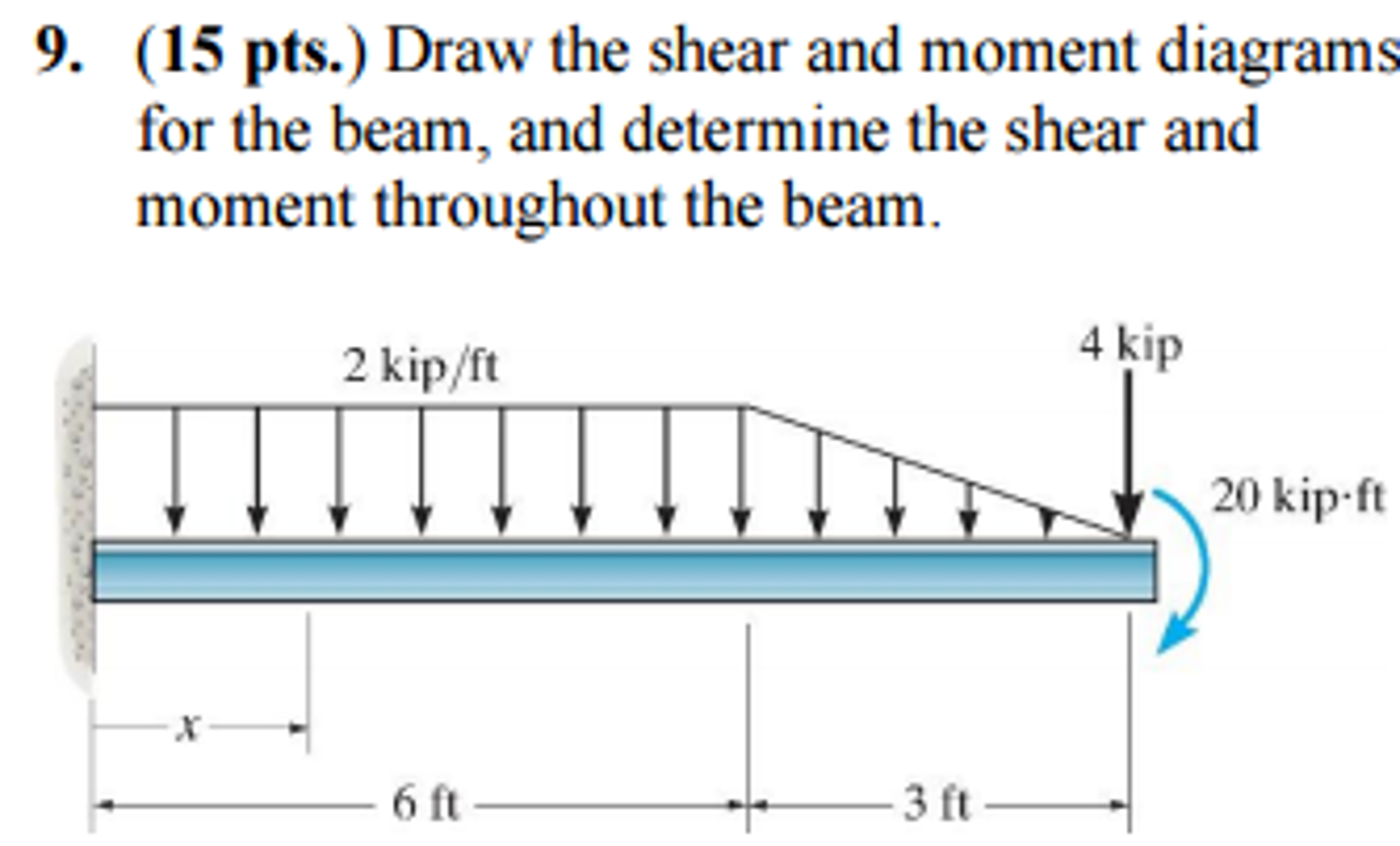
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam, and

Shear Force and Bending Moment diagram of Beam with Triangular Load
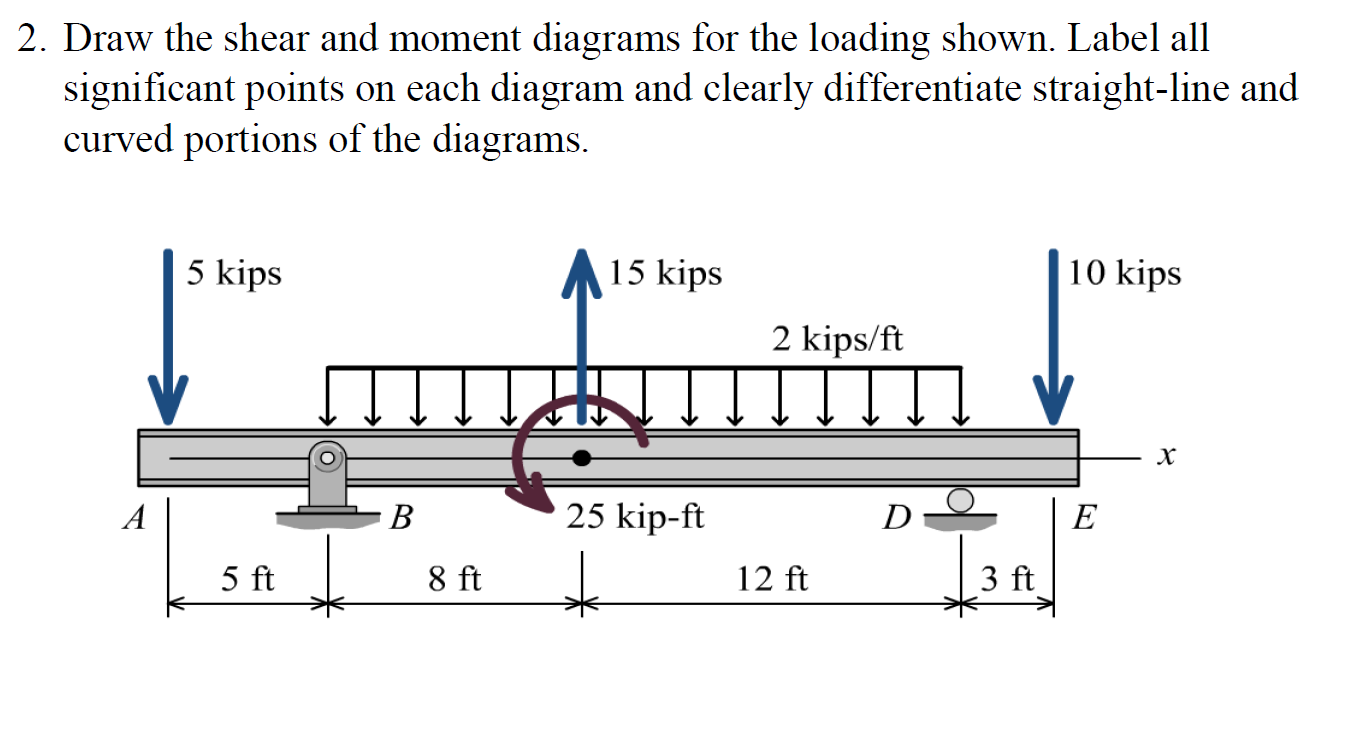
Solved 2 Draw The Shear And Moment Diagrams Of The Beam Images
Internal Forces In Beams And Frames, Libretexts.
To Create The Shear Force Diagram, We Will Use The Following Process.
Web Below Is A Simple Example Of What Shear And Moment Diagrams Look Like, Afterwards, The Relation Between The Load On The Beam And The Diagrams Will Be Discussed.
Since Δx Δ X Is Infinitely Narrow, We Can Assume That The Distributed Load Over This Small Distance Is Constant And Equal To The Value At X, X, And Call It W.
Related Post: