Draw A Human Epithelial Cell And An Elodea Cell
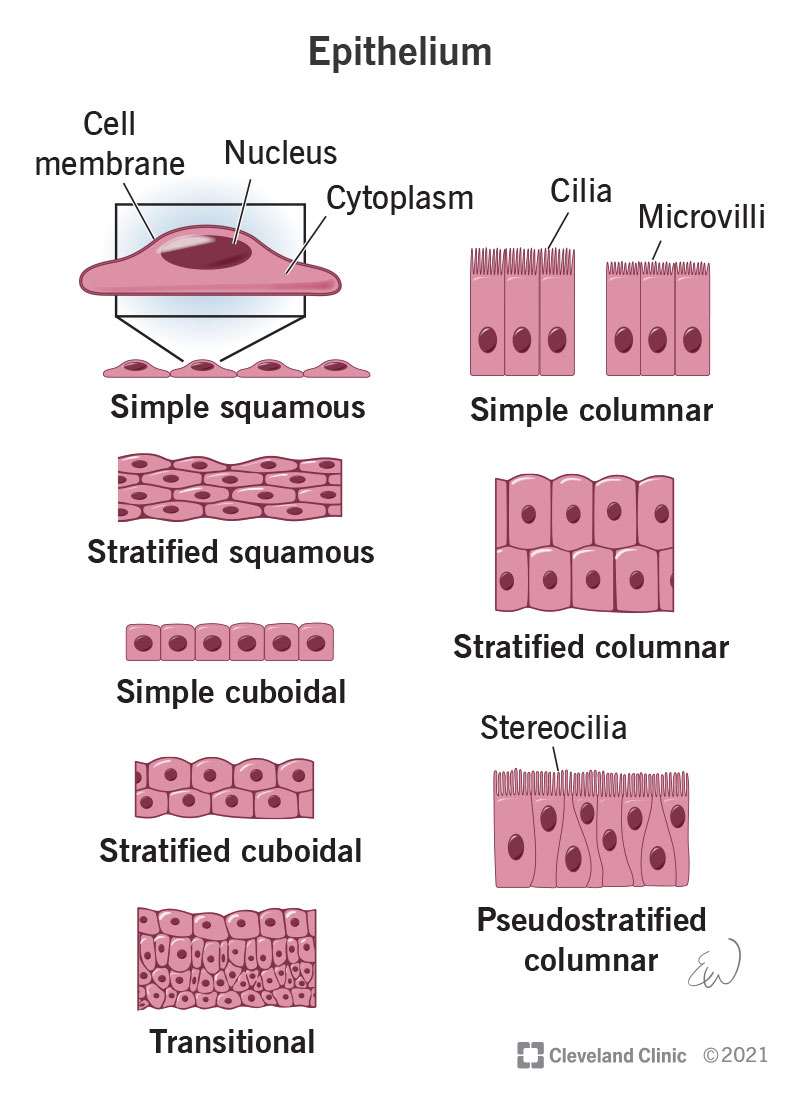
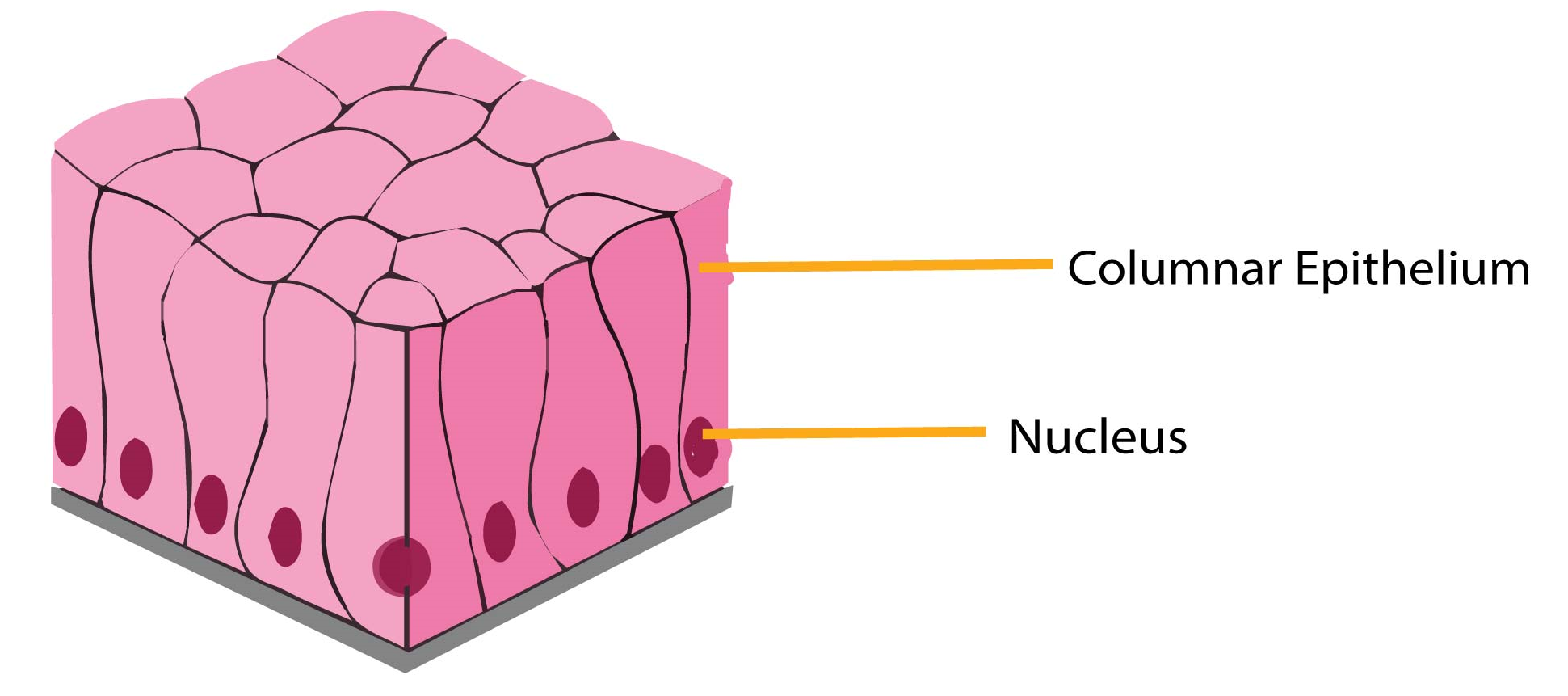
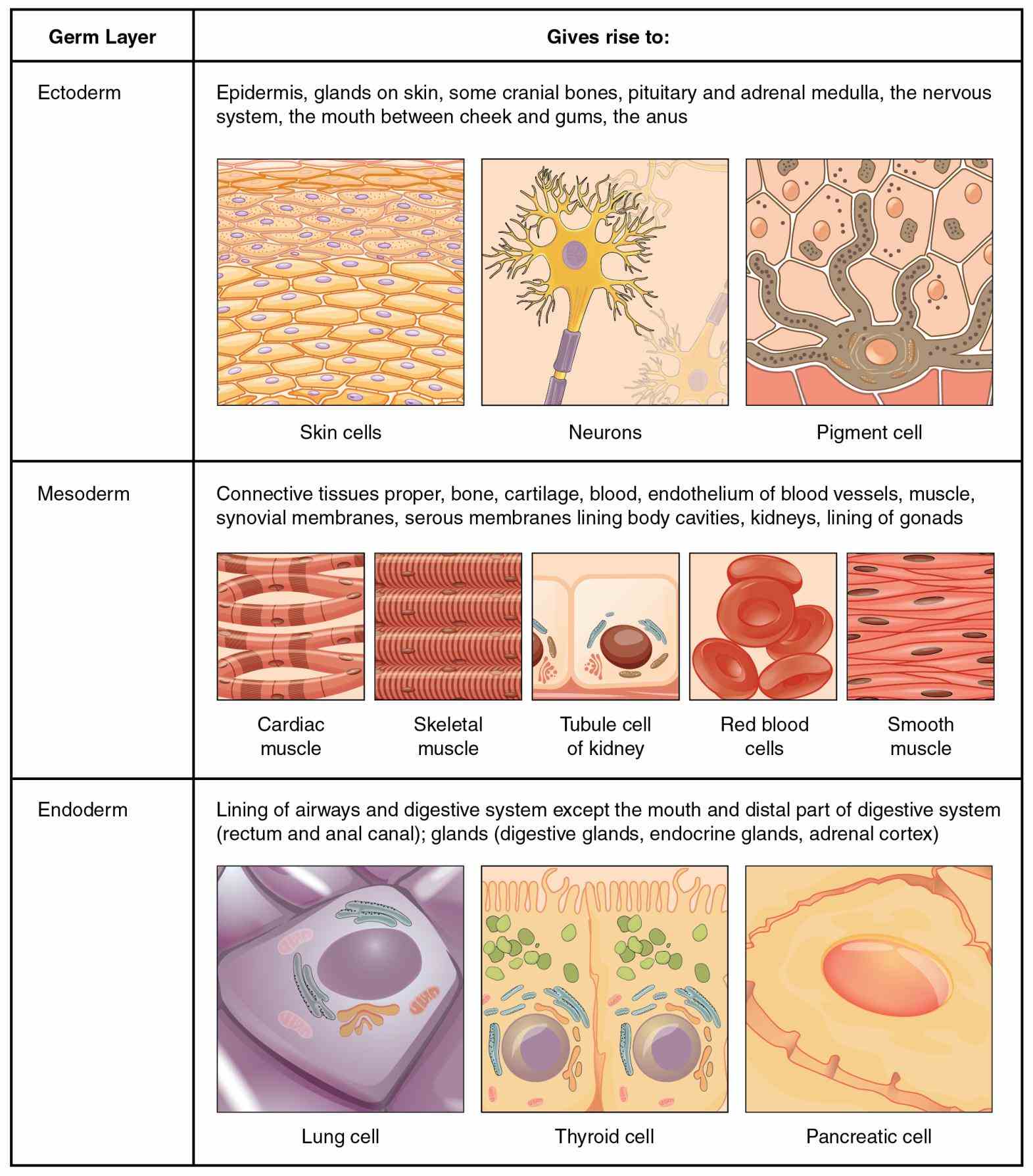
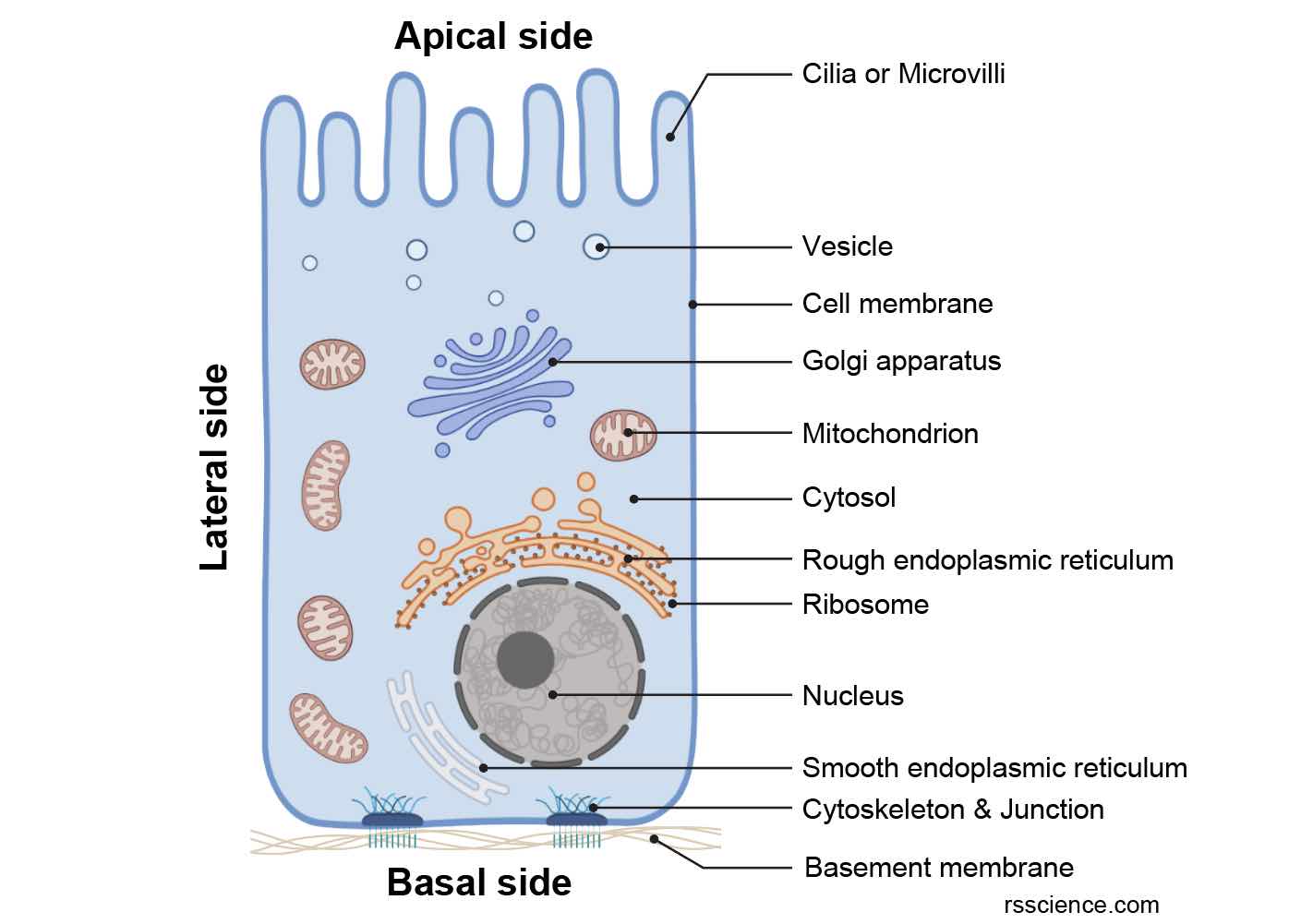
Draw A Human Epithelial Cell And An Elodea Cell - Prepare cheek cell and plant cell slide. A squamous epithelial cell looks flat under a microscope. Observe the cells under normal conditions, and make a sketch of what you see. Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (d) is composed of many layers of folded membrane. A columnar epithelial cell looks like a column or a tall rectangle. Elodea is a water plant that grows abundantly in ponds around spokane. This human cheek cell is a good example of a typical animal cell. Learn to efficiently use the compound light microscope. Distinguish between tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and gap junctions. It has a prominent nucleus and a flexible cell membrane which. Using the forceps, gently tear off a small piece of a leaf from elodea. Label the cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, nucleus (if you see it), central vacuole, and tonoplast. What purpose do epithelial cells serve? While observing the leaf under the microscope, wick a solution of 6% nacl (sodium chloride) across the slide. Just oustide the nucleus, the. Wet mount of human epithelial cell (cheek cell) exercise 6: Human cells tend to be a little. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (c). Distinguish between simple epithelia and stratified epithelia, as well as between squamous, cuboidal, and. Wet mount of an elodea leaf cell. Discover how chloroplasts while undergoing photosynthesis; Draw a cell from the azolla in the space below. A new study shows that cell size, in conjunction with specific signaling pathways, controls apoptosis within developing tissues. Web in the lab the cell of the biology lab primer, you will: Make the individual cells 20 mm wide. Prepare a wet mount of one leaf from the water plant elodea using the water in which it is kept. Illustrations of how to prepare a wet mount slide (mader 2001). Web in this lab you will look at two types of cells, a human cheek cell and an elodea cell and see how they are similar and how they. Elodea is a water plant that grows abundantly in ponds around spokane. Learn to make whole mounts of cells from plant and animal tissues. The nucleolus (a) is a condensed region within the nucleus (b) where ribosomes are synthesized. A micrograph of a cell nucleus. Observation of plant cells (elodea cells) exercise 7: Structures found on some epithelial cells are an adaptation to specific functions. Web in the lab the cell of the biology lab primer, you will: A cell wall, a nucleus, a cell membrane and a cytoplasm. Wet mount of human epithelial cell (cheek cell) exercise 6: Web the onion and elodea cells are interconnected like a brick formation, whereas cheek. They will be used today for you to observe a eukaryotic animal cells and its nucleus. This human cheek cell is a good example of a typical animal cell. Epithelial cells form from ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which explains why epithelial line body cavities and cover most body and organ surfaces. A micrograph of a cell nucleus. Label the cell. The nucleolus (a) is a condensed region within the nucleus (b) where ribosomes are synthesized. Web in this lab you will look at two types of cells, a human cheek cell and an elodea cell and see how they are similar and how they are different. Use the scanning (4x) objective to focus. As you can see in the image,. Draw a cell from the azolla in the space below. Web this elodea leaf cell exemplifies a typical plant cell. Use the scanning (4x) objective to focus. It has a prominent nucleus and a flexible cell membrane which. Using the forceps, gently tear off a small piece of a leaf from elodea. Illustrations of how to prepare a wet mount slide (mader 2001). A columnar epithelial cell looks like a column or a tall rectangle. Learn to efficiently use the compound light microscope. Distinguish between tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and gap junctions. A cuboidal epithelial cell looks close to a square. Explain the structure and function of epithelial tissue. Stain cells to improve the visibility of specific organelles. Nucleus, nucleoli, nuclear envelope, cytoplasm, and cell wall. A micrograph of a cell nucleus. Web find the cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, and cytoplasm. Conduct a gram stain to visualize plaque bacteria Wet mount of an elodea leaf cell. Figure 2 human cheek cells. Water will flow out of the elodea cells by osmosis, shrinking the cell membrane away from the stiff cell wall (plasmolysis). Cells with smaller sizes and relatively smaller sizes compared to their neighbors exhibit an increased likelihood of undergoing apoptosis. What purpose do epithelial cells serve? Prepare cheek cell and plant cell slide. Observe the structures of elodea, alium and human cells. Review the major organelles of eukaryotes; Web there are three basic shapes used to classify epithelial cells. Web paper towels or tissues.
Diagram Of Elodea Cell
Describe various types of epithelial tissues with the help of labeled
Epithelium What It Is, Function & Types

How Do Human Epithelial Cells And Elodea Cells Differ HOWDOZD
[Solved] 3 Draw a human epithelial cell and an Elodea cell. Label the
[Solved] 3 Draw a human epithelial cell and an Elodea cell. Label the
Epithelial Tissues And Their Functions Anatomy
Epithelium Definition, Characteristics, Cell Structures, Types, and

Diagram Of Elodea Cell
[Solved] 3 Draw a human epithelial cell and an Elodea cell. Label the
A Cell Wall, A Nucleus, A Cell Membrane And A Cytoplasm.
Place The Elodea Leaf Into The Drop Of Water On Your Slide.
A New Study Shows That Cell Size, In Conjunction With Specific Signaling Pathways, Controls Apoptosis Within Developing Tissues.
Web Epithelial Cells Make Up Primary Tissues Throughout The Body.
Related Post: