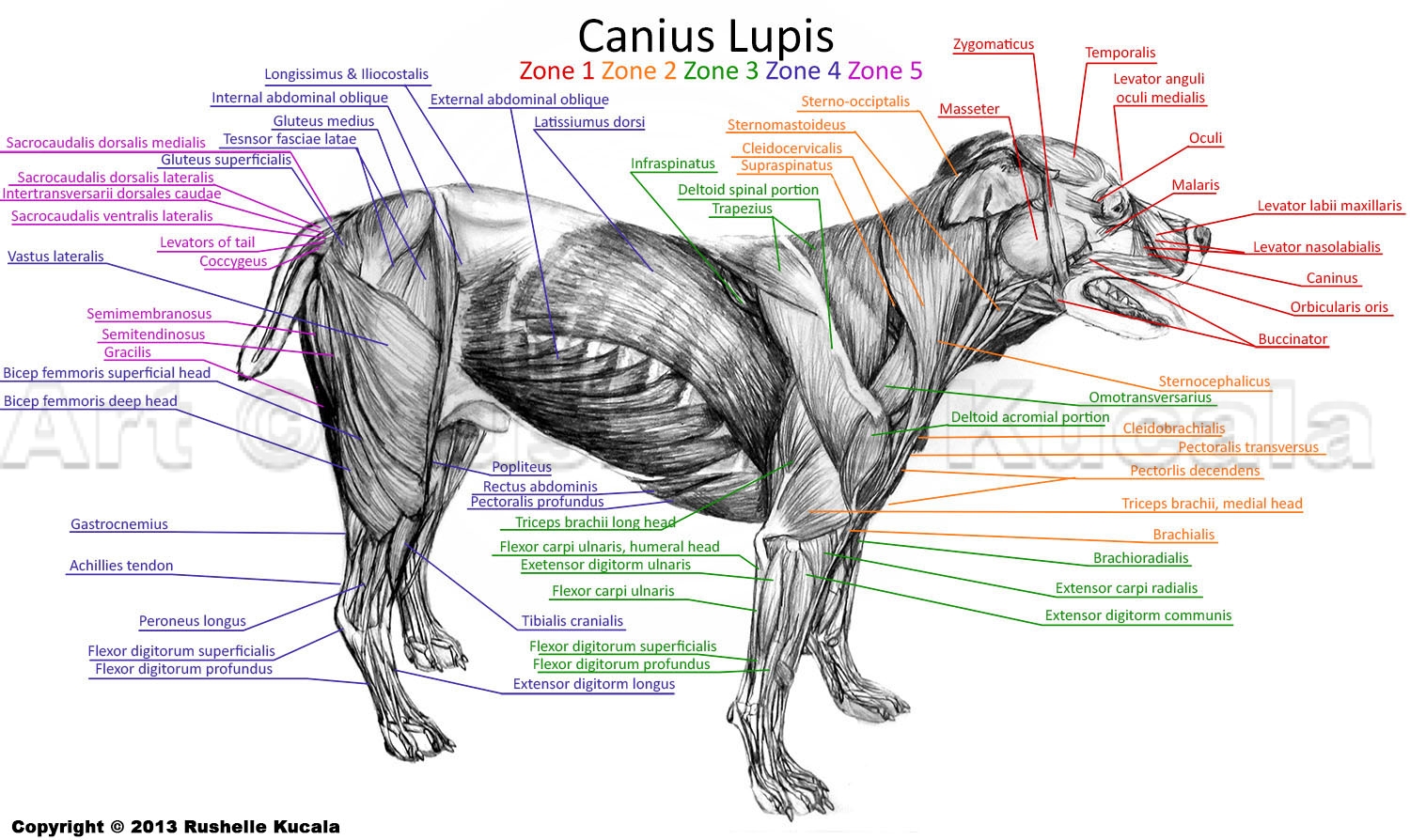
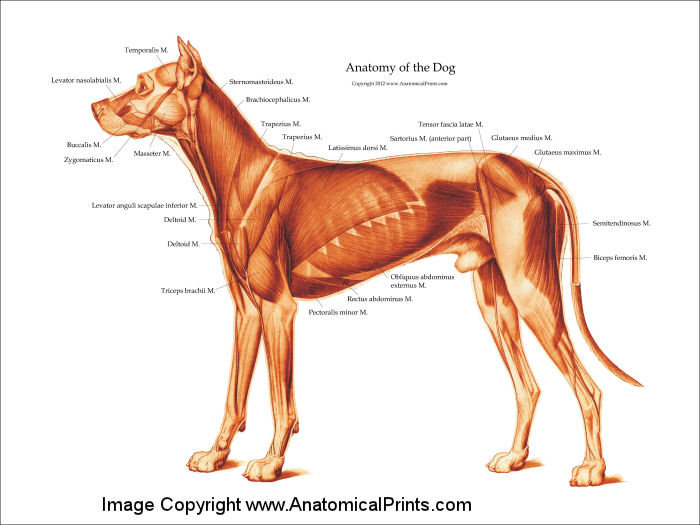
Dog Muscle Chart
Dog Muscle Chart - The following is a list of the muscles in the dog, along with their origin, insertion, action and innervation. Web anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: Filadendron / e+ via getty images. Muscle loss at other sites can be more variable. Again, the amount of muscles an individual dog has depends on the breed and the individual. Bones provide rigid structure to the body and shield internal organs from damage. Web muscle condition score is assessed by visualization and palpation of the spine, scapulae, skull, and wings of the ilia. As judges, we tend to focus less on muscles than the bony landmarks and angles, yet, it is the dog’s musculature that holds everything together an facilitates its movement. Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Muscles help facilitate movement and provide stabilisation in dogs. Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. Components of the musculoskeletal system in dogs. The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Again, the amount of muscles an individual dog has depends on the breed and the individual. These are the muscles that. Web understand dog anatomy with our canine charts and models, including skeletons and pathology models. As we can see in the image below, the majority of a dog's muscles are concentrated in the front of their body. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movement, while smooth and cardiac muscles control involuntary functions. Web dogs are digitigrade animals and bear weight. By identifying weak areas, you can prevent injuries and promote overall health. A dog’s body is made up of several interconnected organ systems, each with its own critical functions. Figure 1 recommended criteria for muscle condition scoring using visual examination and palpation. Is your dog suffering from a muscle injury? The following is an overview of some major muscles and. Muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). Web this canine musculature anatomy wall chart illustrates the features of the muscles of a dog in beautiful detail. The following muscles play important roles in a dog's ability to bark: Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated. Those on the pad surface of the manus align the flexor tendons. Each breed has unique muscle structure and groups. Web body and muscle condition score. Muscle loss at other sites can be more variable. Muscles in dogs enable them to run, jump, play, and perform everyday activities. Web dog anatomy is not very difficult to understand if a labeled diagram is present to provide a graphic illustration of the same. Web dogs have three main types of muscle: Web body and muscle condition score. Muscles help facilitate movement and provide stabilisation in dogs. Web dogs are digitigrade animals and bear weight on digits ii to v, with the main weight bearing occurring on digits iii and iv. These are the muscles that are attached to the bones and are responsible. That is exactly what you will find in this dogappy article. Web a dog can have between 200 and over 400 muscles. Barking is a complex behaviour that involves the coordinated activity of several muscles in a dog's respiratory and vocal tract systems. A dog’s body is made up of several interconnected organ systems, each with its own critical functions.. Filadendron / e+ via getty images. Originates on the first sternebrae and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus. Web the purpose of this document is to provide students of canine anatomy a simple reference for muscular origins, insertions, actions and nerve innervations without having to search through the overwhelming verbiage that accompanies most canine anatomy texts. Each type. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movement, while smooth and cardiac muscles control involuntary functions. The following muscles play important roles in a dog's ability to bark: Web dogs are digitigrade animals and bear weight on digits ii to v, with the main weight bearing occurring on digits iii and iv. Muscles help facilitate movement and provide stabilisation in dogs.. We know how much it sucks to see your favourite pup down for the count. Web dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. By identifying weak areas, you can prevent injuries and promote overall health. Reproduced with the kind permission of the world small animal veterinary association (wsava). A dog’s body is made up of several interconnected organ. The following muscles play important roles in a dog's ability to bark: Web this canine musculature anatomy wall chart illustrates the features of the muscles of a dog in beautiful detail. Web the front leg of a dog consists of the clavicle, scapula (arm), radius and ulna (forearm), carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges (forepaw). The following is an overview of some major muscles and their actions: Extrinsic muscles of the thoracic limb and related structures: Optimizing training and exercise routines based on muscle anatomy can enhance performance. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movement, while smooth and cardiac muscles control involuntary functions. Web muscle condition score is assessed by visualization and palpation of the spine, scapulae, skull, and wings of the ilia. Muscles help facilitate movement and provide stabilisation in dogs. We know how much it sucks to see your favourite pup down for the count. Muscle condition score is graded as normal, mild loss, moderate loss, or severe loss. Web a dog can have between 200 and over 400 muscles. Canine muscular anatomy is similar in function and organisation to that of humans with some unique differences in structure. It both adducts the limb and also prevents. Here are presented scientific illustrations of the canine muscles and skeleton from different anatomical standard views (lateral, medial, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral / palmar.). Web anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: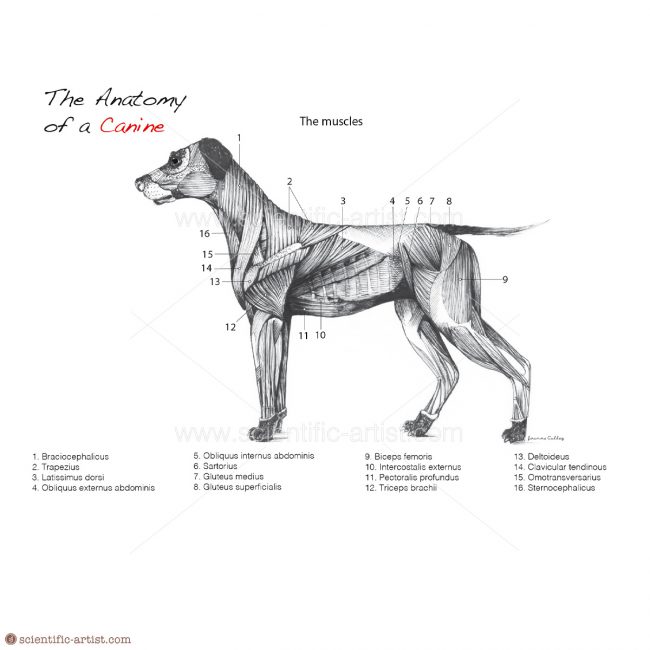
Canine Muscular Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated ubicaciondepersonas
Dog Muscle Anatomy by TheDragonofDoom on DeviantArt

dog_muscles.jpg (1600×1035) Animal Anatomy Pinterest Anatomy
Dog Anatomical Chart Muscles

Dog muscles DogGroomingDIY Dog anatomy, Vet medicine, Vets

Dog Muscular And Skeletal Chart Clinical Charts and Supplies

Canine Muscle Chart Large Animal Massage Awareness

Pin on Animal anatomy

canine muscular anatomy Dog Muscles Diagram

Canine Muscular Anatomy Chart Dog Muscles Poster Laminated
As Judges, We Tend To Focus Less On Muscles Than The Bony Landmarks And Angles, Yet, It Is The Dog’s Musculature That Holds Everything Together An Facilitates Its Movement.
What Muscles Enable A Dog To Bark?
Dogs Have Different Types Of Muscles, Including Skeletal Muscles, Smooth Muscles, And Cardiac Muscles.
Web Dogs Are Digitigrade Animals And Bear Weight On Digits Ii To V, With The Main Weight Bearing Occurring On Digits Iii And Iv.
Related Post: