Covalent Radii Chart
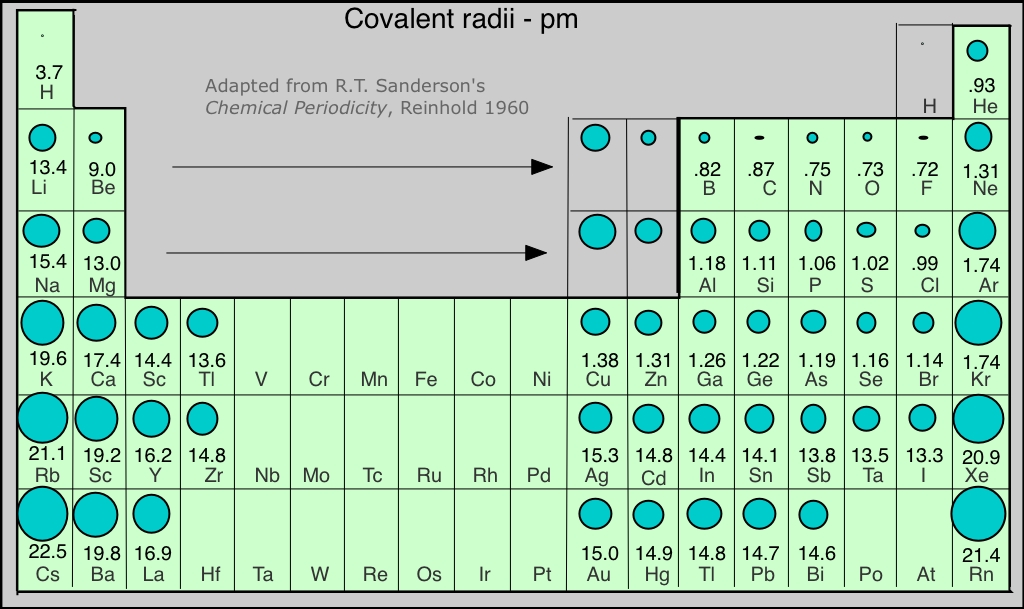
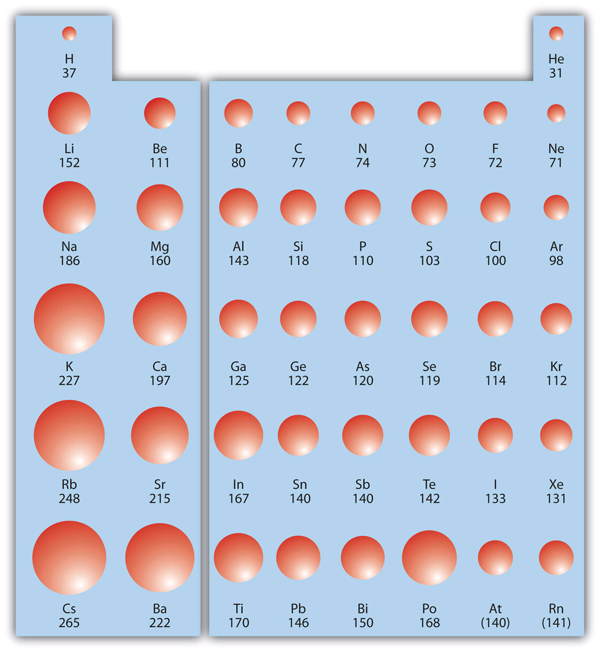
Covalent Radii Chart - In principle, the sum of the two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, r(ab) = r(a) + r(b). 1) deduced from crystallographic data for most of the elements with atomic numbers up to 96. Web covalent radius increases as we move down a group because the n level (orbital size) increases. Covalent radius mostly decreases as we move left to right across a period. Web in theory, the sum of two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, but in practice the length of the bond depends on the. Web in this web page, you will find a covalent radius chart, a visual reference of charts. Radii from each element are listed from largest to smallest, ionic charge. Web the covalent atomic radius (r cov) is half the internuclear distance in a molecule with two identical atoms bonded to each other, whereas the metallic atomic radius (r met) is. Half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. Radii are measured from bonds to c, n or o. These data show a well behaved periodic. Web in this web page, you will find a covalent radius chart, a visual reference of charts. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. The proposed radii show a well. Covalent radii are in parentheses. These data show a well behaved periodic. Web the covalent atomic radius (r cov) is half the internuclear distance in a molecule with two identical atoms bonded to each other, whereas the metallic atomic radius (r met) is. Ionic radii are also available. Moreover, different radii can be introduced for single, double and triple bonds. Web select from the following links to see visual periodicity representations for atomic radii, covalent radii, and van der waals radii. Covalent radius mostly decreases as we move left to right across a period. Web 120 rows covalent radii; Web the values of table 3 show the covalent radii from the two recent original determinations by cordero et al.[1], and. These data show a well behaved periodic. Elements above 96 are assigned a covalent radius and uncertainty of none. Web this figure shows radii (in angstroms) of atoms and ions of the first four periods of the periodic table. Web atomic radius of all the elements (complete chart) march 23, 2023. In principle, the sum of the two covalent radii. Half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. Covalent radius mostly decreases as we move left to right across a period. In principle, the sum of the two covalent radii should equal the covalent bond length between two atoms, r(ab) = r(a) + r(b). You will see a. Radii from each element are listed from largest to smallest, ionic charge. You will see a selection of chart images that show different aspects of covalent radius. 53 [citation needed] 120 or 110: Web covalent radius definition. Web 119 rows covalent (single bond) covalent (triple bond) metallic 1: Half of the single bond length between two similar atoms covalently bonded in a molecule is called the covalent radius. The covalent radius, rcov, is a measure of the size of an atom that forms part of one covalent bond. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. If the two. Web the values of table 3 show the covalent radii from the two recent original determinations by cordero et al.[1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Web in this web page, you will find a covalent radius chart, a visual reference of charts. Web this is a set of covalent atomic radii (ref. Radii from each element are listed from largest. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. Single bonds [1] single bonds [2] double bonds [2] triple bonds [2] 1: Web the values of table 3 show the covalent radii from the two recent original determinations by cordero et al.[1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Web select from the following. These data show a well behaved periodic. Web the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms that share a covalent bond. Moreover, different radii can be introduced for single, double and triple bonds (r1, r2 and r3 below), in a purely operational sense. Web 119 rows covalent (single bond) covalent (triple bond) metallic 1: In principle, the sum. Web covalent radius definition. Web this is a set of covalent atomic radii (ref. Covalent radii are in parentheses. Web the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms that share a covalent bond. It is usually measured either in picometres (pm) or angstroms (å), with 1 å = 100 pm. Ionic radii are also available. Web 119 rows covalent (single bond) covalent (triple bond) metallic 1: Atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. Web in this web page, you will find a covalent radius chart, a visual reference of charts. The differences between the two single. Single bonds [1] single bonds [2] double bonds [2] triple bonds [2] 1: Web select from the following links to see visual periodicity representations for atomic radii, covalent radii, and van der waals radii. Covalent radius mostly decreases as we move left to right across a period. If the two atoms are of the same. The covalent radius, rcov, is a measure of the size of an atom that forms part of one covalent bond. Radii from each element are listed from largest to smallest, ionic charge.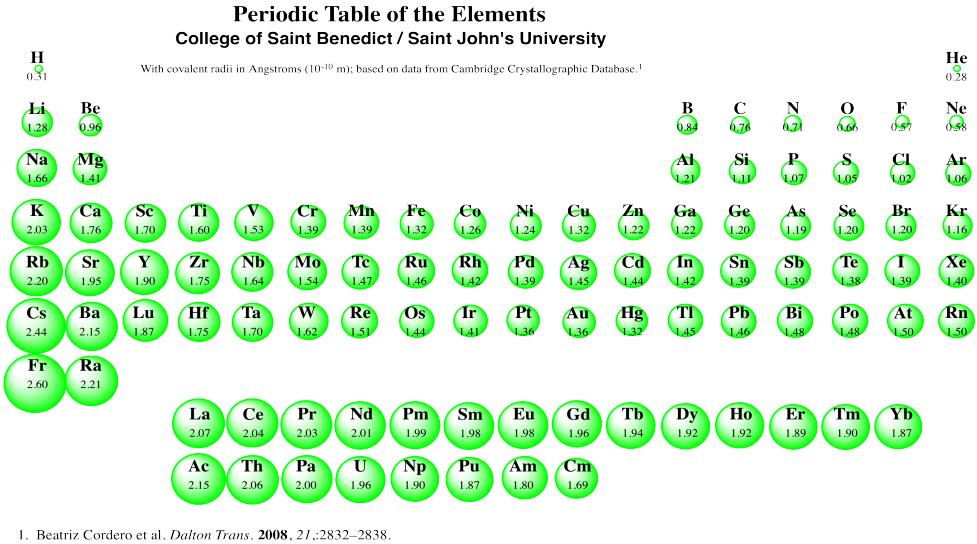
Structure & Reactivity Appendix Periodic Radii

Covalent Radius Definition and Trend

Covalent Radius Definition and Trend

Elements, Atomic Radii and the Periodic Radii

What is the Atomic Radius? EnthuZiastic
5.7 Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemistry LibreTexts
Periodic Trends Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition

1.6 Periodic Variations in Element Properties Chemistry for
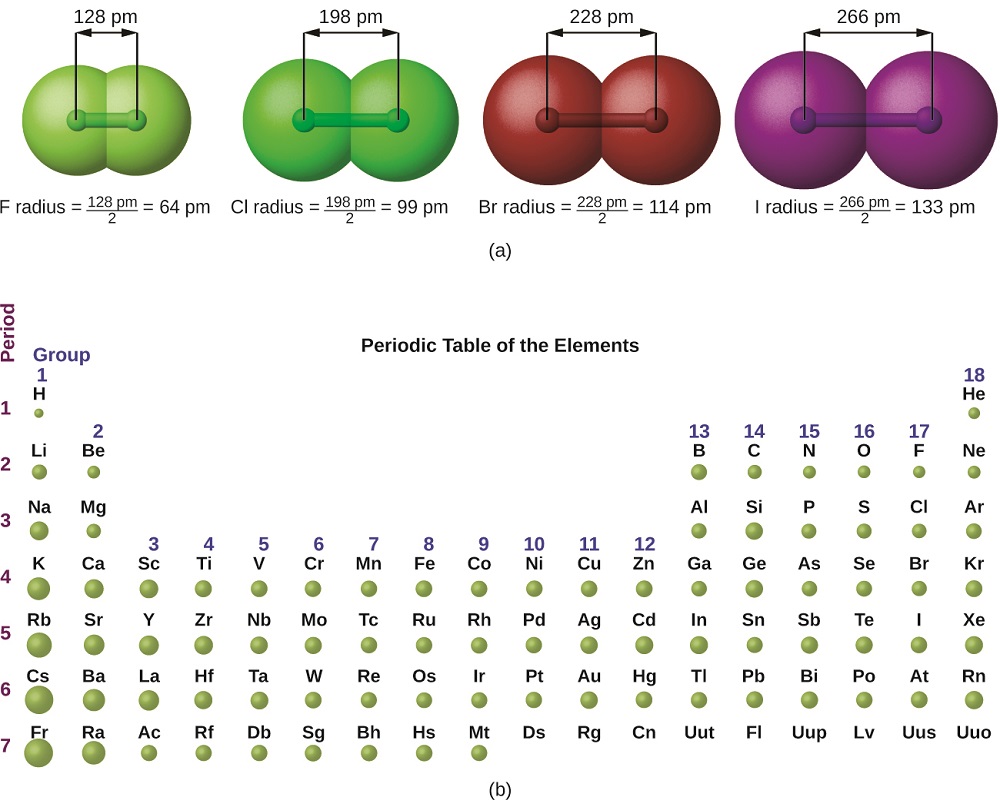
7.4 Electron Configurations, Valence Electrons, and the Periodic Table
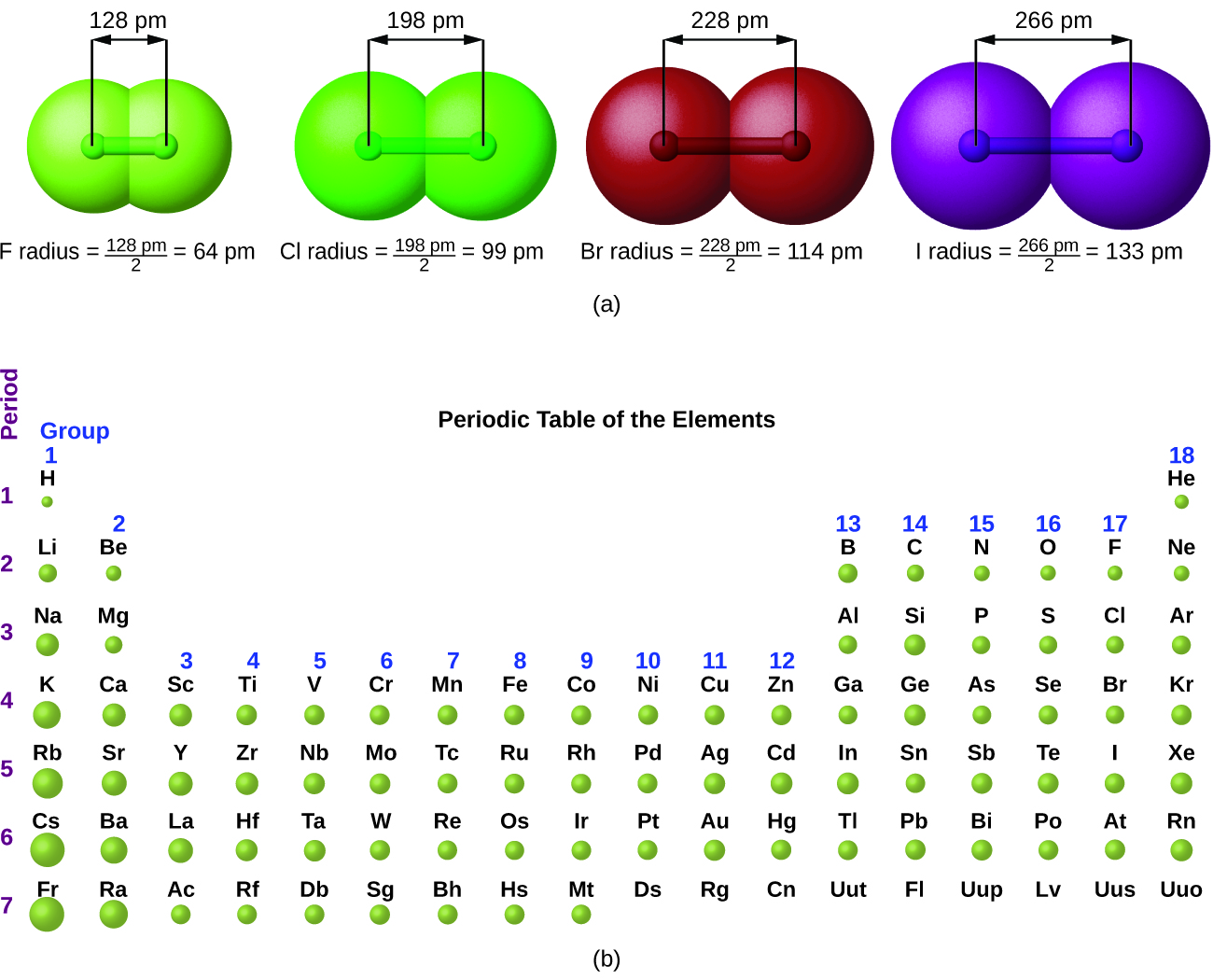
8.7 Periodic Trends and Variation of Properties General Chemistry
You Will See A Selection Of Chart Images That Show Different Aspects Of Covalent Radius.
53 [Citation Needed] 120 Or 110:
Web 120 Rows Covalent Radii;
In Principle, The Sum Of The Two Covalent Radii Should Equal The Covalent Bond Length Between Two Atoms, R(Ab) = R(A) + R(B).
Related Post: