Countersink Size Chart
Countersink Size Chart - First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see the left side of the chart). Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimetres apart from the countersink angle. This is the nominal diameter of the countersink for the fastener. In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. Web use this chart to find out what size countersunk hole to use for ansi 82 degree machine fasteners. Countersink modeling and selectable sizes. For example, an ansi metric m4 machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 4.5 mm, a countersunk diameter of 9.4 mm, and a countersunk angle of 90°. Countersink depth is typically measured from the surface of the material to the bottom of the countersink hole. These resources will provide you with information on the recommended drill bit sizes for different screw or. Occasionally, a countersink is used simply as a method of chamfering or deburring a hole. Machined countersinks are created with a drill press and formed countersinks are made with punch press tooling—the best option depends on your project and part geometry. This is for iso screws and bolts. Web want the head of each screw to sit flush with your wood surface? Web what is the difference? V 11/32 ±0.005 х 82॰ Modeling rules for countersunk holes. Web countersink hole size charts. Tables 1, 2, and 3 below list typical countersink dimensions for socket flat head screws to sit flush with the surface they are sunk into: Countersink depth is typically measured from the surface of the material to the bottom of the countersink hole. Web countersink depth is the depth of. First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see the left side of the chart). Machined countersinks are created with a drill press and formed countersinks are made with punch press tooling—the best option depends on your project and part geometry. Countersink angle = 82॰ that, along with the stated tolerance, gives a solution for the callout: This. Web want the head of each screw to sit flush with your wood surface? Web use this chart to find out what size countersunk hole to use for ansi socket flat head fasteners. It is considered good practice to countersink or break the edges of holes that are smaller than f (max.) in parts having a hardness which approaches, equals,. This is for iso screws and bolts. Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimetres apart from the countersink angle. What controls the location of the screw? Countersink depth is typically measured from the surface of the material to the bottom of the countersink hole. Countersink angle = 82॰ that,. Web a countersink is an angled taper applied to a hole that allows a fastener (usually a flat head screw or similar) to sit even with, or below the surface which has been countersunk. This is for ansi metric countersinks. Machined countersinks are created with a drill press and formed countersinks are made with punch press tooling—the best option depends. Web this chart shows the dimensions of counterbore and countersink holes for different screw sizes, in metric units (millimeters). What controls the location of the screw? The purpose of a countersink is to allow a fastener, typically a flathead screw, to sit slightly below the surface of the part. First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see. Pilot hole diameter = 5/27; Web a countersink is an angled taper applied to a hole that allows a fastener (usually a flat head screw or similar) to sit even with, or below the surface which has been countersunk. When a conical shape element is detected, it will be identified as a countersink. Web diameter and depth:the diameter of the. The countersink symbol is used to indicate that a countersink hole feature is required. Web want the head of each screw to sit flush with your wood surface? A screw placed in a countersunk hole is located by the angle. Countersink modeling and selectable sizes. Tables 1, 2, and 3 below list typical countersink dimensions for socket flat head screws. This is for iso screws and bolts. Machined countersinks are created with a drill press and formed countersinks are made with punch press tooling—the best option depends on your project and part geometry. V 11/32 ±0.005 х 82॰ Understand the types and use of countersink drill bit, countersink vs counterbore hole and check out the countersink size chart for holes/bits.. The purpose of a countersink is to allow a fastener, typically a flathead screw, to sit slightly below the surface of the part. Our reference chart has the drill bit for each screw size Web countersink hole size charts. Web what is the difference? The countersunk hole is recognized through two steps below. The countersink symbol is used to indicate that a countersink hole feature is required. For example, an ansi inch 9/16″ 100 degree machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 5/8″, a countersunk diameter of 1 10/69″, and a countersunk angle of. This is the nominal diameter of the countersink for the fastener. Pilot hole diameter = 5/27; V 11/32 ±0.005 х 82॰ Tables 1, 2, and 3 below list typical countersink dimensions for socket flat head screws to sit flush with the surface they are sunk into: A screw placed in a countersunk hole is located by the angle. First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see the left side of the chart). In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. Web countersink depth is the depth of a countersink hole, which is a conical hole cut into a material to allow the head of a countersunk screw or bolt to be flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimetres apart from the countersink angle.
Metric Countersink Dimensions Chart
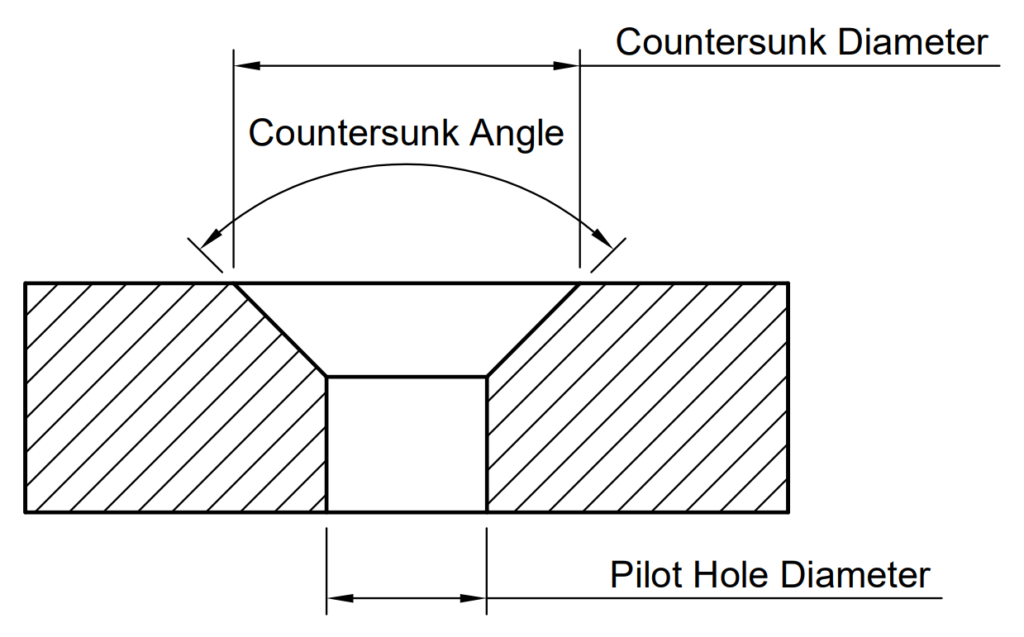
Countersunk Hole Size for Machine Screw (ANSI Metric)

Countersink Size Chart Metal

Countersink Holes Chart for Drilling Wood Screws Drill Bit Size Guide
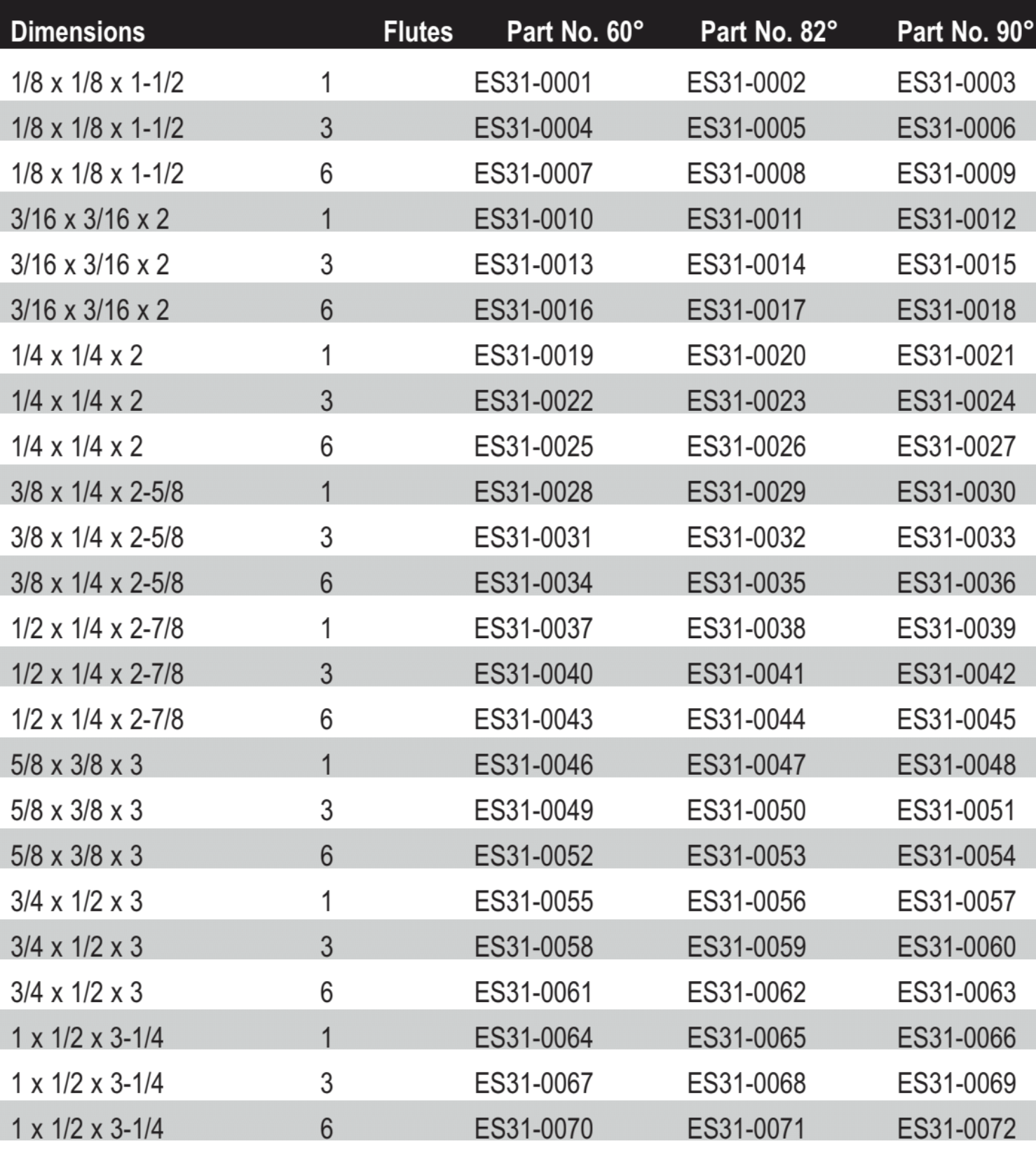
Countersink Size Chart Metal
HSM Machining
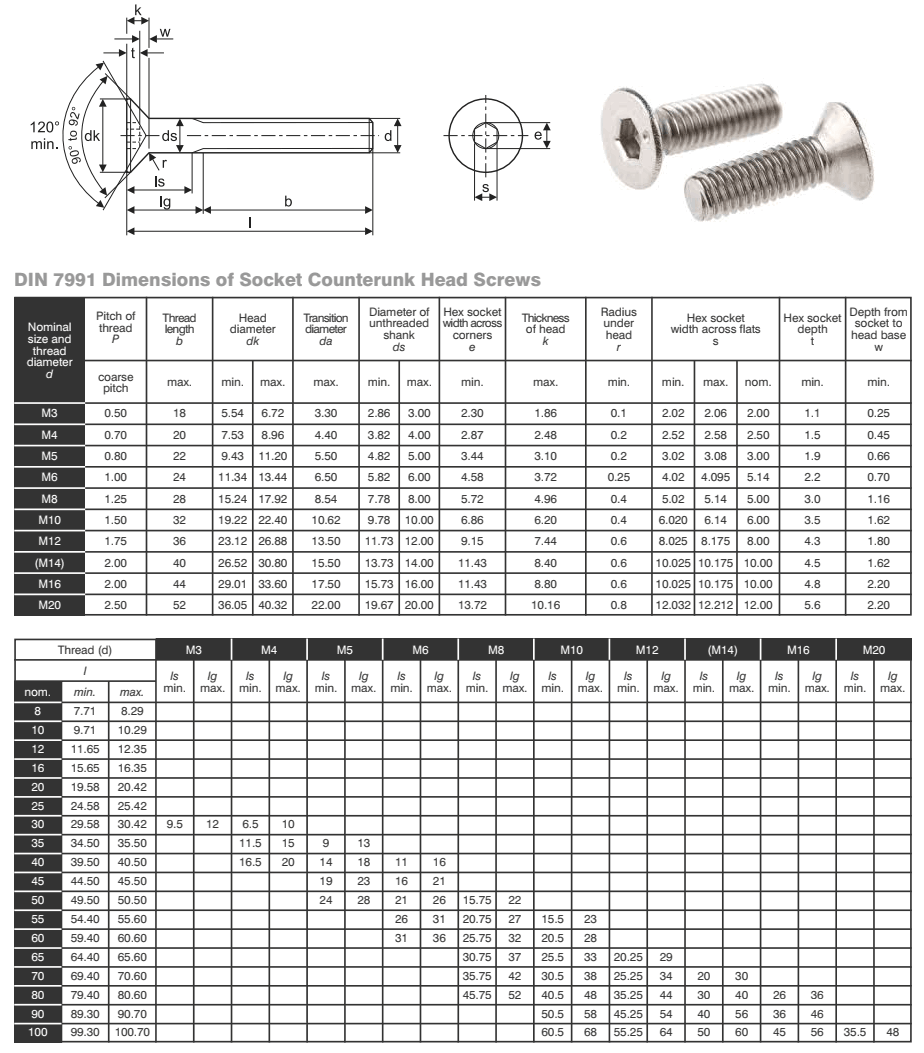
to West Coast Fasteners Pty Ltd West Coast Fasteners Perth
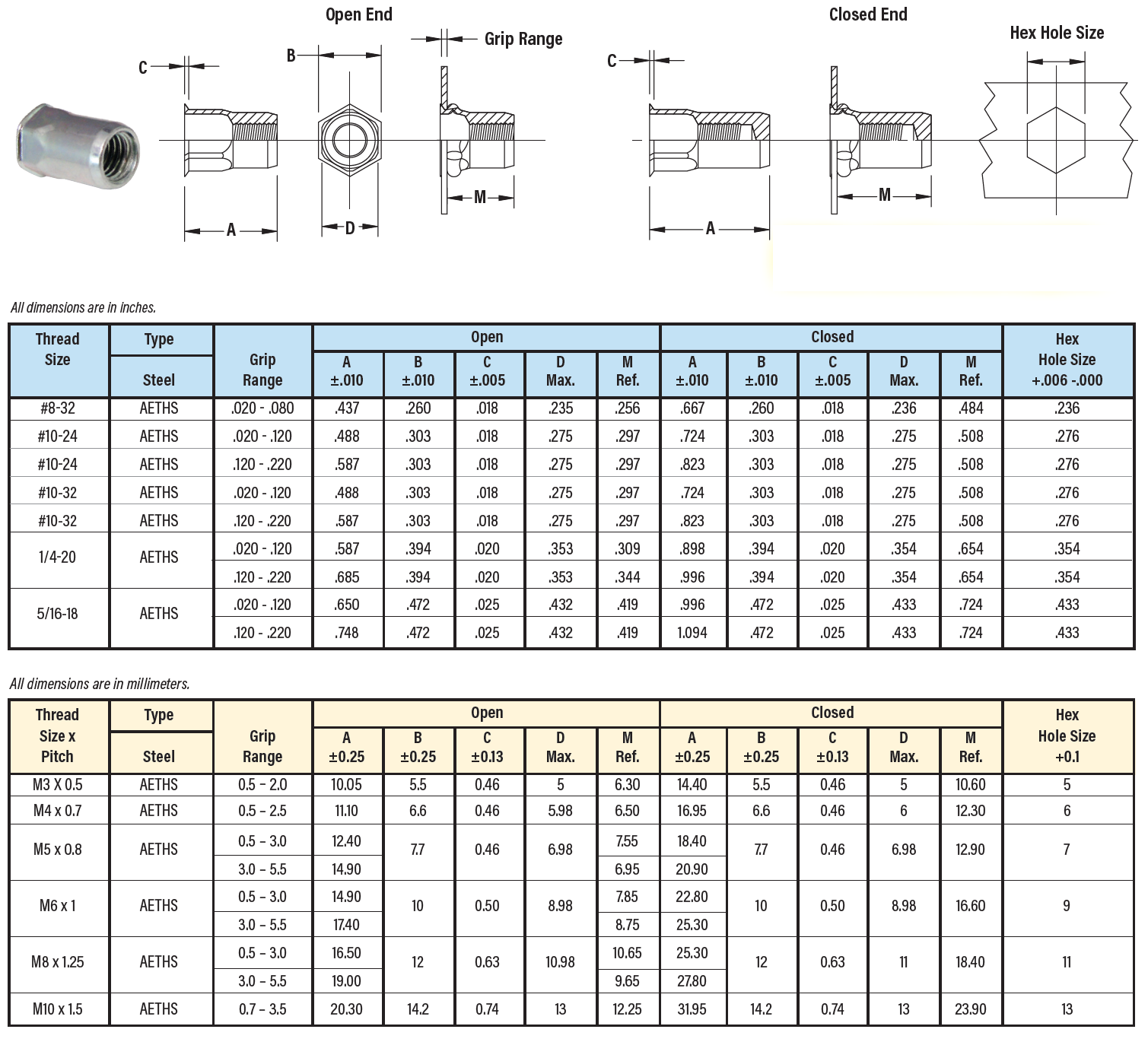
Standard Countersunk Hole Diameters Home Interior Design
Counterbore and Countersink Dimensions Chart

Countersink 90° d1=10,4mm d2=6mm DamenCNC B.V.
Web Countersunk Hole Size Chart For Socket Flat Head Fasteners (Ansi Inch) Using The Above Table, Given #6 Fastener With A Loose Fit, We Have:
It Is Considered Good Practice To Countersink Or Break The Edges Of Holes That Are Smaller Than F (Max.) In Parts Having A Hardness Which Approaches, Equals, Or Exceeds The Screw Hardness.
Modeling Rules For Countersunk Holes.
Web A Countersink Is An Angled Taper Applied To A Hole That Allows A Fastener (Usually A Flat Head Screw Or Similar) To Sit Even With, Or Below The Surface Which Has Been Countersunk.
Related Post:
