Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart
Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart - To determine octane to your compression, follow our. To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need about. Web the oem compression ratio is ideal for the minimum octane rating of gasoline recommended, for the factory power output levels, for factory boost levels, for emission compliance and for a driving pattern that the oem believes will be driven. Web use the standard compression ratio fuel octane chart to know the fuel suitable for your engine. Web from the 1920s to the 1970s, the evolution of engines (measured by compression ratio) and the evolution of fuels (measured by octane rating) occurred in tandem. Web calculate compression + boost for octane. Stations are required to post them on bright yellow stickers on each pump. Web bp fuel is available octane 90, 92, 95, and also diesel. An octane rating is defined as the standard measure of the performance of a motor fuel. Web the standard recommendation for street engines running on pump gas has always been to shoot for a 9.0:1 to perhaps 9.5:1 compression ratio. Web the first is a calculated number called research octane and the second is motor octane generated by actually testing the fuel in a variable compression ratio single cylinder engine. Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in the graph below) was likely due to refinery technology improvement and the addition of lead, which guards. This can reduce efficiency. Web calculate compression + boost for octane. You’ll see two common methods for measuring octane: Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in the graph below) was likely due to refinery technology improvement and the addition of lead, which guards. Web in my understanding, the compression ratio is related to the top dead center (tdc), which it will produce. In the case of rockett brand’s e85, the research number is 116 and the motor number is 108. Web generally, engines with compression ratios of 9.3 : Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in the graph below) was likely due to refinery technology improvement and the addition of lead, which guards. To determine octane to your compression, follow. Average octane rating based on refiner sales volumes and is based on a calendar year. Web in my understanding, the compression ratio is related to the top dead center (tdc), which it will produce specific compression that will compress the petrol inside ignition chamber, so it will increase temperature just before ignited by the spark. Web calculate the minimum gasoline. Web in my understanding, the compression ratio is related to the top dead center (tdc), which it will produce specific compression that will compress the petrol inside ignition chamber, so it will increase temperature just before ignited by the spark. Web from the 1920s to the 1970s, the evolution of engines (measured by compression ratio) and the evolution of fuels. These calculators are rough approximations and none of the numbers here are absolute. Many owners who operate vehicles designed to operate on 87 octane fuel experience ping and knock. Web the standard recommendation for street engines running on pump gas has always been to shoot for a 9.0:1 to perhaps 9.5:1 compression ratio. An octane rating is defined as the. Web generally, engines with compression ratios of 9.3 : An octane rating is defined as the standard measure of the performance of a motor fuel. Web a fuel with a higher octane rating can be run at a higher compression ratio without causing detonation and we know compression or boost is directly related to power. Engines with higher compression ratios. Octane rating does not relate directly to the power output or the energy. Modern engines can handle much higher compression at lower octanes. Web bp fuel is available octane 90, 92, 95, and also diesel. An octane rating is defined as the standard measure of the performance of a motor fuel. Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in. Web calculate the minimum gasoline fuel octane required based on your engine's compression ratio, maximum boost pressure, spark advance, and air fuel ratio. To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need about. Increasing pressure in the cylinder allows an engine to extract more mechanical energy from a given air/fuel mixture but requires. Engines with higher compression ratios usually require higher octane fuels. Web the oem compression ratio is ideal for the minimum octane rating of gasoline recommended, for the factory power output levels, for factory boost levels, for emission compliance and for a driving pattern that the oem believes will be driven. Then follow our mixing charts provide our calculator app, above.. There are many other factors such as head material, timing, and direct injection that come into play. Web the first is a calculated number called research octane and the second is motor octane generated by actually testing the fuel in a variable compression ratio single cylinder engine. Web bp fuel is available octane 90, 92, 95, and also diesel. Web the standard recommendation for street engines running on pump gas has always been to shoot for a 9.0:1 to perhaps 9.5:1 compression ratio. That compression made engine got hotter. Web the higher the compression ratio, the higher the octane value. To determine octane to your compression, follow our. Adding the two and dividing by two ( (r+m) / 2) produces an aki. Engines with higher compression ratios usually require higher octane fuels. Web use the standard compression ratio fuel octane chart to know the fuel suitable for your engine. Octane rating does not relate directly to the power output or the energy. The higher the octane rating, the more pressure the fuel can withstand within the compression stroke of an engine prior to igniting. These calculators are rough approximations and none of the numbers here are absolute. Web from the 1920s to the 1970s, the evolution of engines (measured by compression ratio) and the evolution of fuels (measured by octane rating) occurred in tandem. Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which would further improve engine efficiency. 1 or less will safely operate with unleaded 87 octane fuel.
leaded gasoline blend OK in 3.0TFSI to achieve 100 octane?
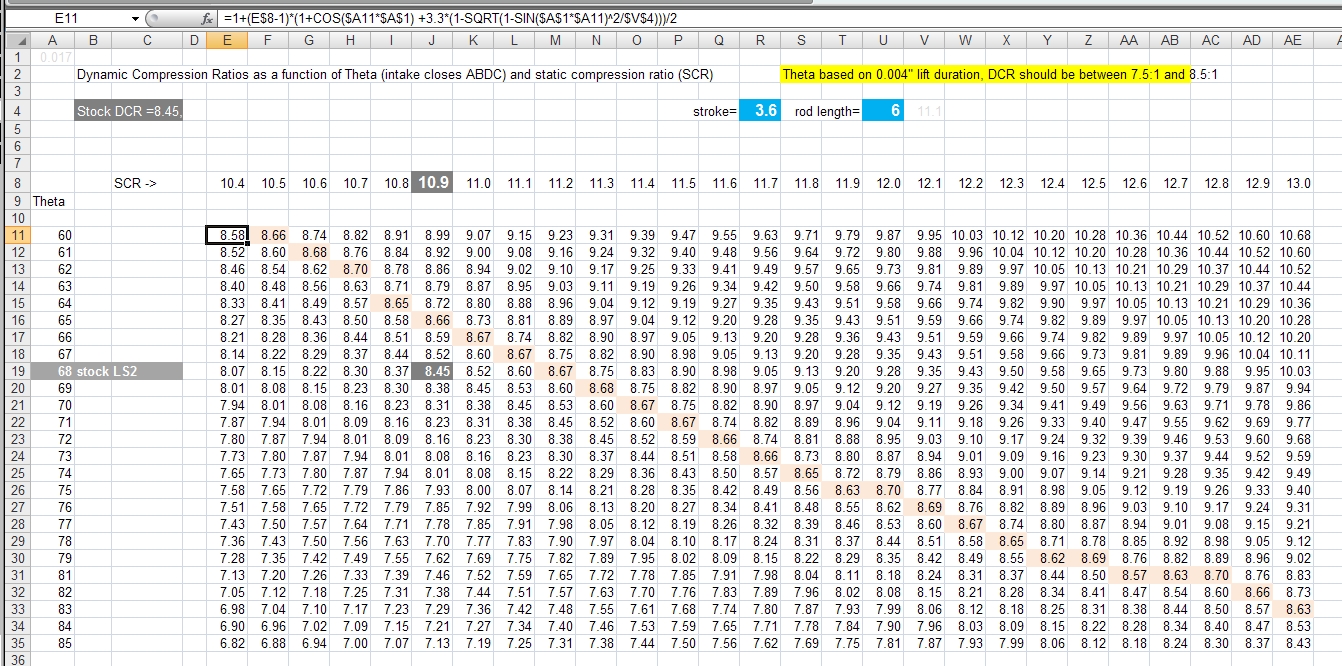
Compression Ratio To Octane Chart
The Ultimate Guide to Fuel and Octane Ratings — Auto Expert by John

Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart
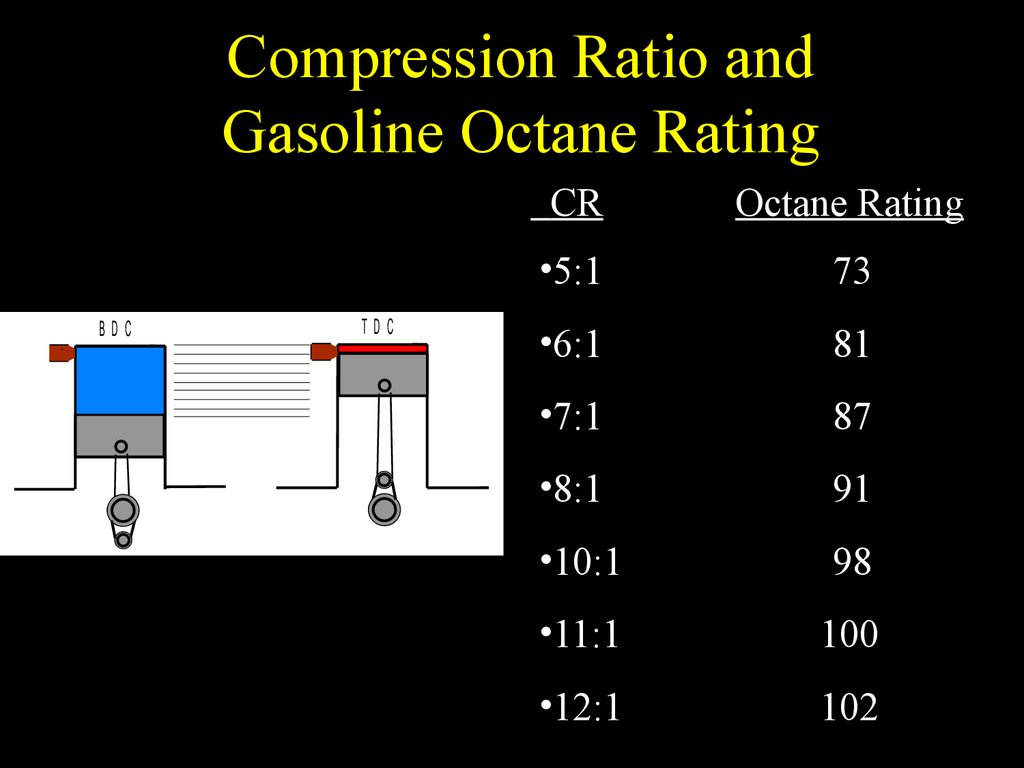
Engine Components and Operation презентация онлайн

Mechanical Engineering Octane Number
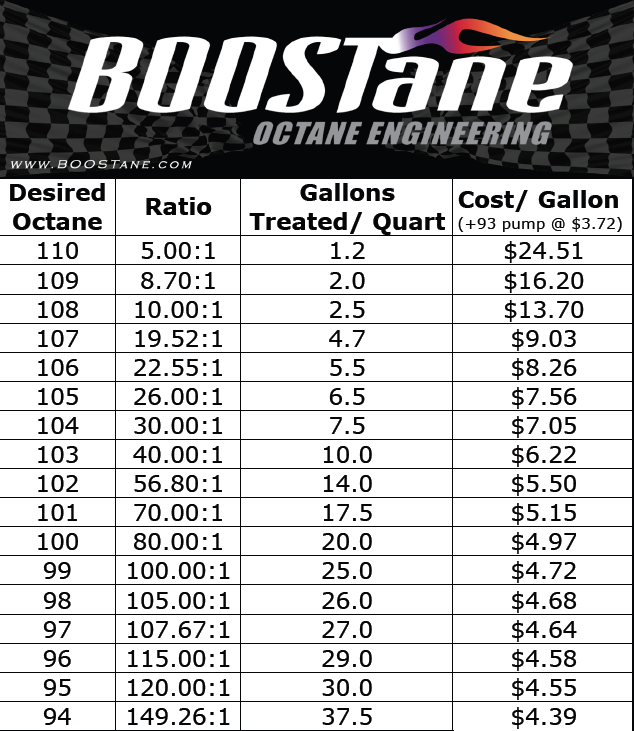
Compression Ratio Octane Chart
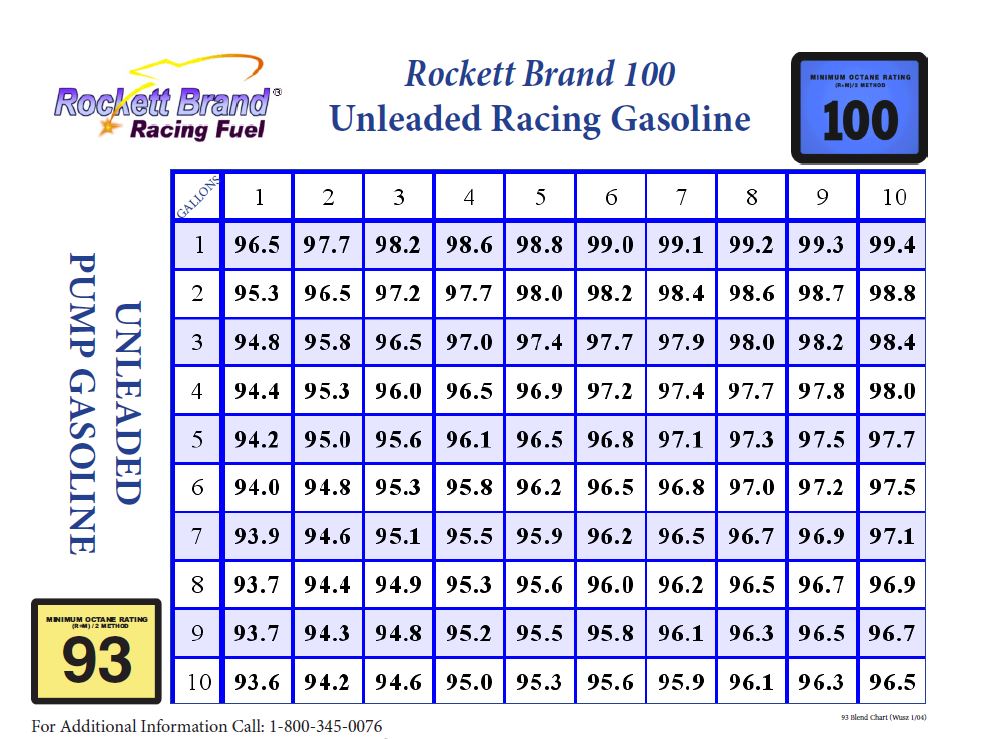
The Octane Game
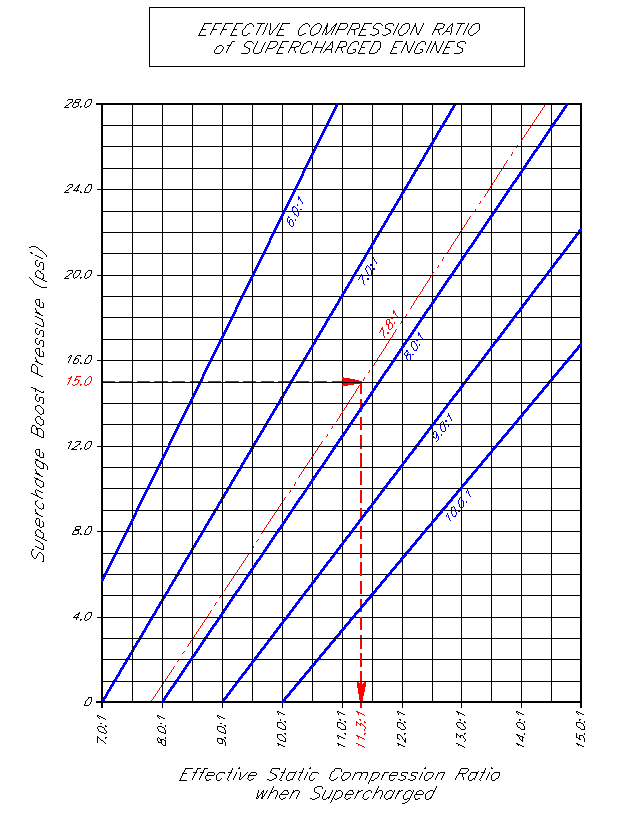
Calculate Required Octane For Compression Ratio Maniac Mechanic
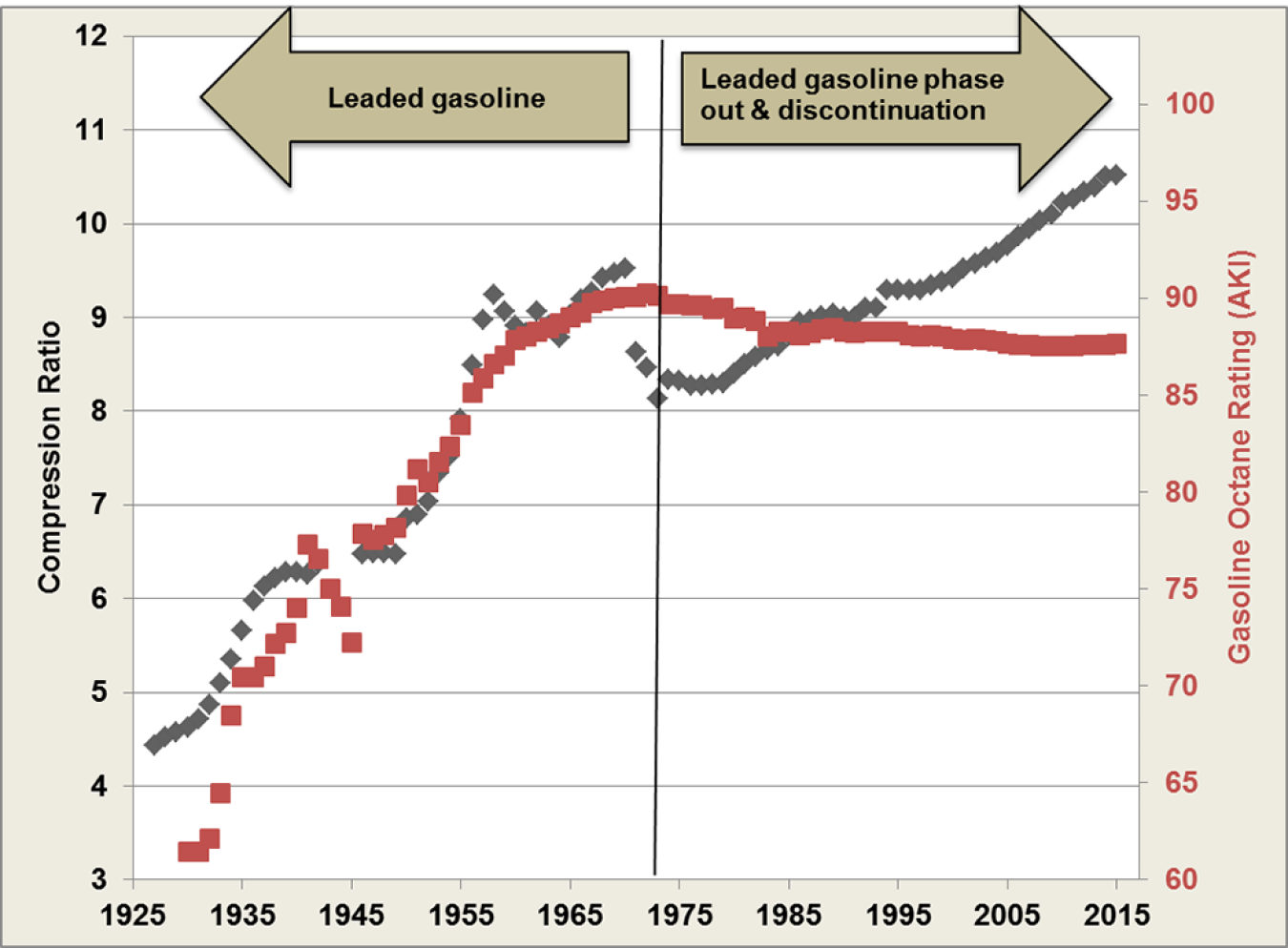
Fact 940 August 29, 2016 Diverging Trends of Engine Compression Ratio
Web In My Understanding, The Compression Ratio Is Related To The Top Dead Center (Tdc), Which It Will Produce Specific Compression That Will Compress The Petrol Inside Ignition Chamber, So It Will Increase Temperature Just Before Ignited By The Spark.
Web A Fuel With A Higher Octane Rating Can Be Run At A Higher Compression Ratio Without Causing Detonation And We Know Compression Or Boost Is Directly Related To Power.
Modern Engines Can Handle Much Higher Compression At Lower Octanes.
In The Case Of Rockett Brand’s E85, The Research Number Is 116 And The Motor Number Is 108.
Related Post: