Compressibility Factor Chart
Compressibility Factor Chart - The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Web the compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor \(z\), equal to \(\frac{pv}{rt}\), where \(v\) is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure \(p_r\) for several values of the reduced temperature \(t_r\). At high temperatures (tr > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy. Ρ = [ p mw gas] / [ r × z × t] where. Web compressibility factor, usually defined as z = pv/rt, is unity for an ideal gas. Web the compressibility factor ( z) is used to calculate the mass density (ρ) of a gas or dense phase fluid using the following equation: If we only know the temperature and pressure, we can still calculate it using a compressibility chart. Z = gas compressibility factor. 1 definition and physical significance. Typical units are in 2 /lbf, ft 2 /lbf, 1=atm, and 1/kpa. Ρ = mass density of fluid. For real gases, the compressibility factor may be very different from one. The compressibility factor is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the to account for the behavior. Web a compressibility factor chart shows how real gases deviate from ideal gases by plotting the compressibility factor z against different values of pressure for different. Ρ = mass density of fluid. 2 generalized compressibility factor graphs for pure gases. The calculator falls under the category of thermodynamics calculators, primarily used in the field of chemistry and engineering. 1 definition and physical significance. In most engineering work, the compressibility factor is used as a correction factor to ideal behavior. 1 definition and physical significance. Web the compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor \(z\), equal to \(\frac{pv}{rt}\), where \(v\) is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure \(p_r\) for several values of the reduced temperature \(t_r\). [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] it is a measure of how much the thermodynamic properties of a real gas deviate from those. Web figure 1 shows the essential features of a generalized compressibility factor chart. Web a compressibility factor chart shows how real gases deviate from ideal gases by plotting the compressibility factor z against different values of pressure for different temperatures. Correlations based on the equation. `z = (p*v_m)/ (r*t)` where: Z = pv¯¯¯¯ rt z = p v ¯ r. Web a compressibility factor chart shows how real gases deviate from ideal gases by plotting the compressibility factor z against different values of pressure for different temperatures. At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. Z = gas compressibility factor. P v = n r u t (1) where. Web the compressibility. R = ideal gas constant. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] it is a measure of how much the thermodynamic properties of a real gas deviate from those expected of an ideal gas. Web in a perfect or ideal gas the correlations between pressure, volume, temperature and quantity of gas can be expressed by the ideal gas law. The compressibility chart. Web the compressibility factor ( z) is used to calculate the mass density (ρ) of a gas or dense phase fluid using the following equation: Web the compressibility factor is given by: Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas. Web the compressibility factor ( z) is used to calculate the mass density (ρ) of a gas or dense phase fluid using the following equation: Mw gas = molecular weight of gas stream. P = pressure of the gas. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature.. Web compressibility factor, usually defined as z = pv/rt, is unity for an ideal gas. It is simply defined as the ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at the same temperature and pressure. At high temperatures (tr > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy. Web in. Web the compressibility factor ( z) is used to calculate the mass density (ρ) of a gas or dense phase fluid using the following equation: Web the compressibility factor is given by: Ρ = [ p mw gas] / [ r × z × t] where. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Figures. At very low pressure (pr << 1), gases behave as an ideal gas regardless of temperature. Ρ = [ p mw gas] / [ r × z × t] where. The calculator falls under the category of thermodynamics calculators, primarily used in the field of chemistry and engineering. 2 generalized compressibility factor graphs for pure gases. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Web figure 1 shows the essential features of a generalized compressibility factor chart. These have been extended [see, e.g., liley (1987)] to include the saturated liquid. Web the compressibility factor chart plots the compressibility factor , equal to , where is the volume per mole, versus the reduced pressure for several values of the reduced temperature. 1 definition and physical significance. Web in 1941 standing and katz (1) presented a compressibility factor chart based on binary mixtures and saturated hydrocarbon vapor data. This chart is generally reliable for sweet natural gases and correctable for those containing hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide (2). This chart brings the following information: Z = pv¯¯¯¯ rt z = p v ¯ r t. The compressibility factor is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the to account for the behavior. Web learn how to read a compressibility chart, how to figure out the compressibility factor, what reduced pressure, reduced temperature, and pseudo reduced speci. Z = gas compressibility factor.
3.2 Real gas and compressibility factor Introduction to Engineering

Compressibility Factor of Natural Gas Download Scientific Diagram

Standing and Katz’s compressibility factor chart Download Scientific
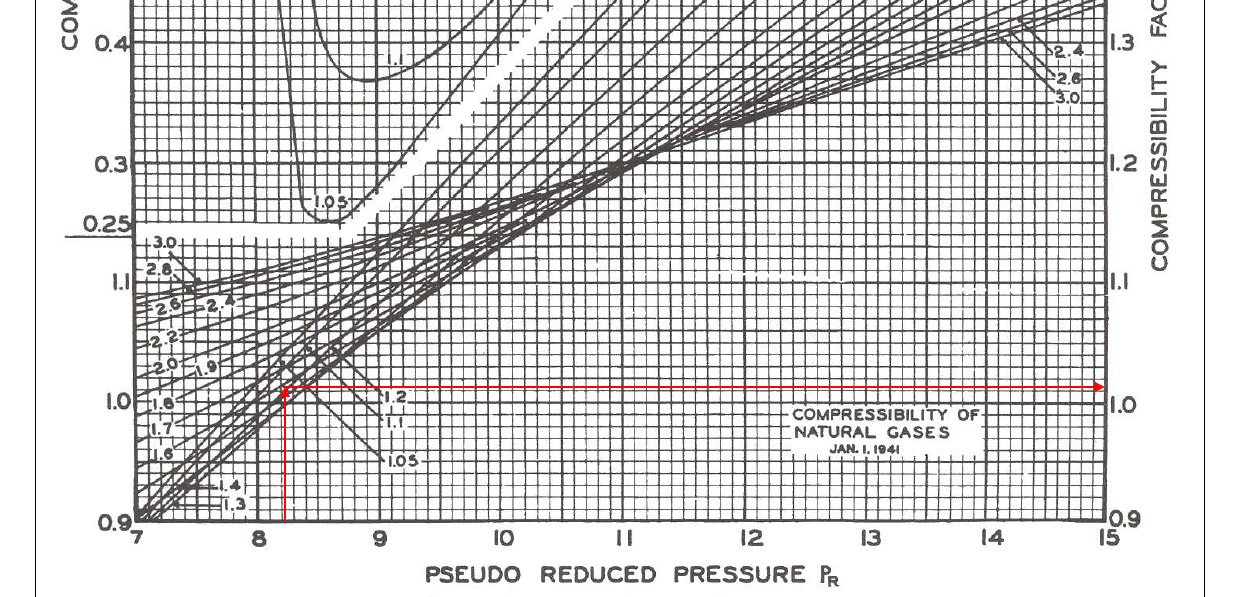
Determine Compressibility Factor with Present of CO2 and H2S
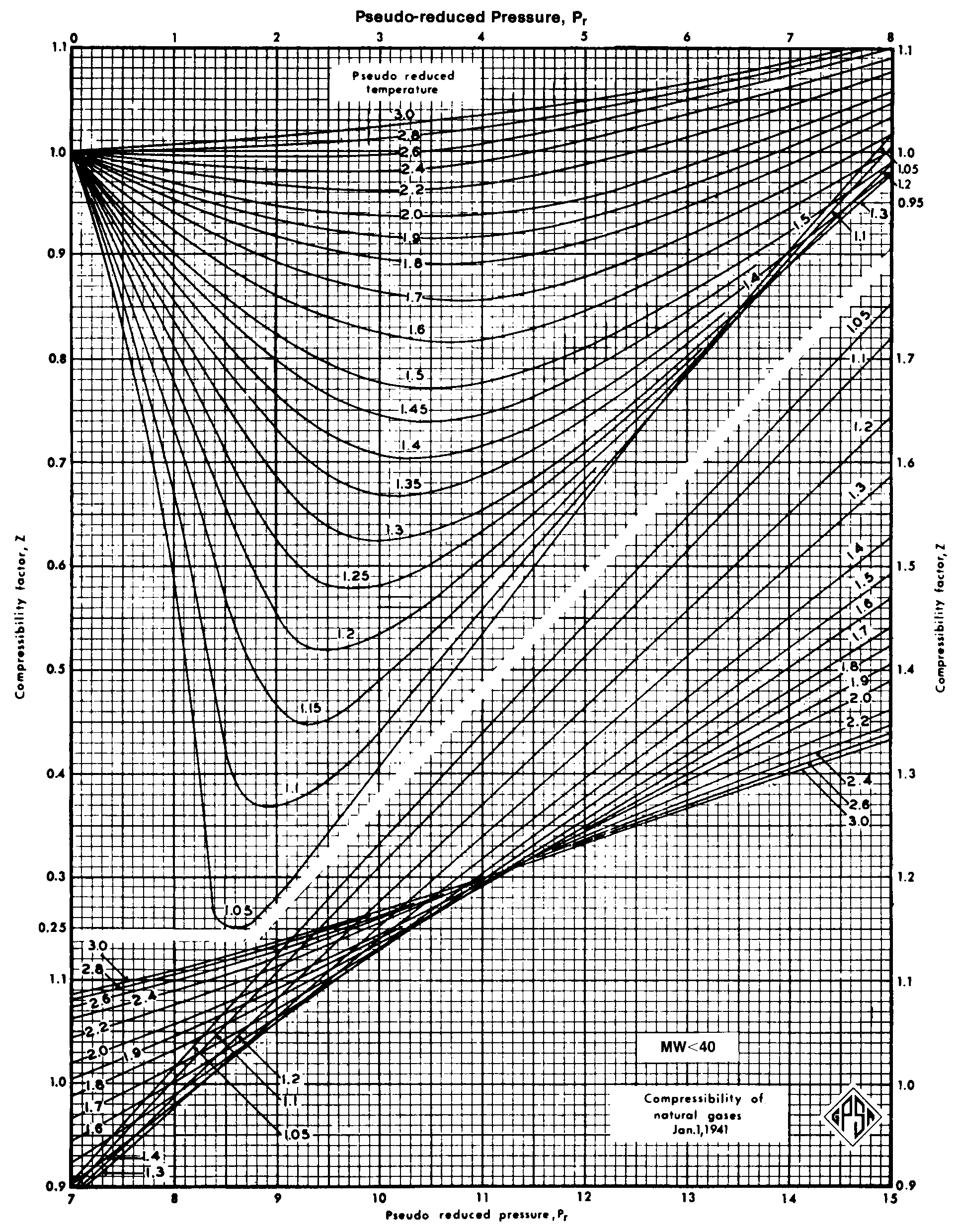
Determine Compressibility Factor, Z Factor Engineering Units

Chapter 3 Physical Properties of Fluids Gas Compressibility Factor
Generalized Compressibility Chart PDF Thermodynamics
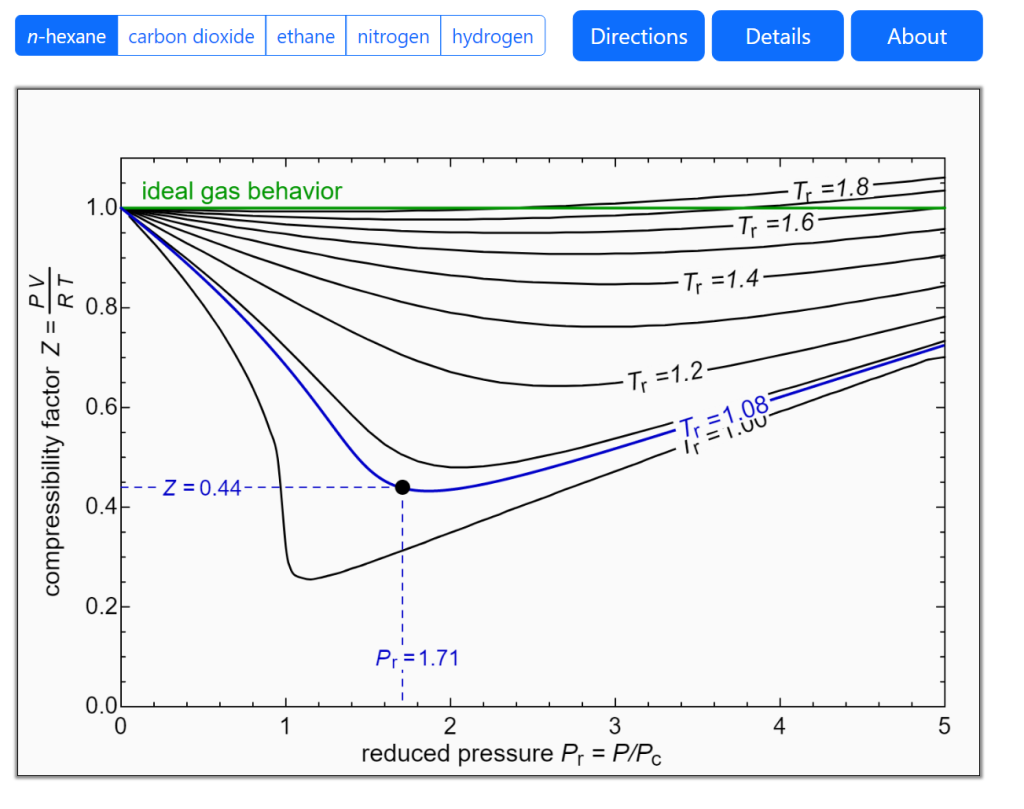
compressibilityfactorcharts LearnChemE

Reading Compressibility Factor Charts YouTube
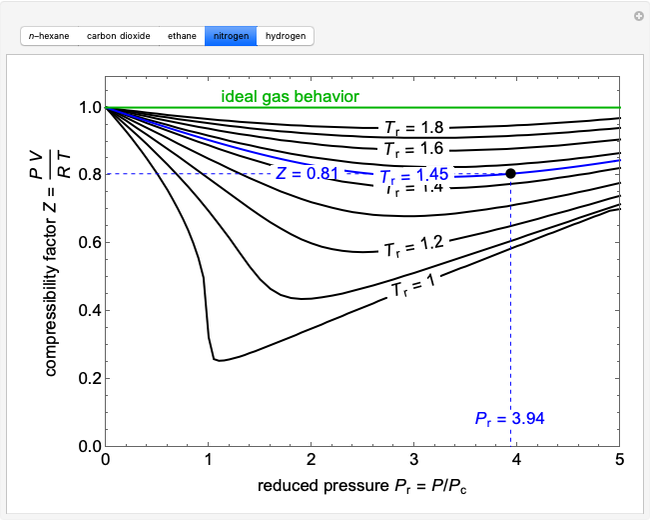
Compressibility Factor Charts Wolfram Demonstrations Project
If We Only Know The Temperature And Pressure, We Can Still Calculate It Using A Compressibility Chart.
Web The Compressibility Factor Is Given By:
It Is Valid For Many Substances, Especially Those That Have Simple Molecular Structures.
The Compressibility Chart Calculator Is A Specialized Calculator That Calculates The Compressibility Factor (Z) Of A Gas Using Its Pressure, Volume, And Temperature.
Related Post:
