Climb Gradient Chart
Climb Gradient Chart - Web learn how to determine the required rate of climb based on the climb gradient for instrument departure procedures. This web page does not contain. Web here is the rate of climb chart: Given a required climb or descent in feet per minute and ground speed in knots, compute the target vsi reading with required climb/descent multiplied. Web to calculate climb gradient, you divide the altitude gain required (in feet) by the horizontal distance traveled (in feet) and then multiply the result by 100 to convert it to a. Web afm charts allow calculation of the mtow that meets the minimum regulatory climb gradient. See examples, charts, and formulas for different. Web a rate of climb/descent table is provided for use in planning and executing climbs or descents under known or approximate ground speed conditions. Web to calculate it manually, divide your rate of climb by your ground speed and multiply by 60 to convert it to feet per hour. Web this table provides a rate of climb or descent in feet per minute below the groundspeed in knots for the gradient shown in percent (%) at the left. And how challenging are various. These charts take into consideration the runway characteristics of slope and. Web there, the takeoff minimums on runway 14 require a climb gradient of 610 feet per nautical mile to over 2,000 feet above the airport elevation of 6,882 feet msl. This web page does not contain. These requirements are part of. And how challenging are various. Considering that the aircraft is in approach configuration (intermediate flaps), if a missed approach is executed with one engine becoming. These requirements are part of. 75 ÷ 60 * 200 =. See examples, charts, and formulas for different. The rate of climb table in the tpp book should. Ground speed = 75 knots; Web learn how to calculate various performance parameters for aviation, such as temperature conversion, crosswind component, load factor, stall speed, and more. And how challenging are various. Climb gradient required = 200 feet per mile; Web the climb gradient is now half of what it was before: Web the climb gradient is the percentage of the rise over run (100% if you are climbing at 45 degrees) that your aircraft is climbing at while the rate of climb is the speed at which you. Web a rate of climb/descent table is provided for use in. Ground speed = 75 knots; Considering that the aircraft is in approach configuration (intermediate flaps), if a missed approach is executed with one engine becoming. These charts take into consideration the runway characteristics of slope and. Web a rate of climb/descent table is provided for use in planning and executing climbs or descents under known or approximate ground speed conditions.. 75 ÷ 60 * 200 =. Web determine the required rate of climb necessary to achieve the gypsm three’s published climb gradient. The rate of climb table in the tpp book should. This web page does not contain. And how challenging are various. Web learn how to determine the required rate of climb based on the climb gradient for instrument departure procedures. Edited nov 21, 2018 at 5:42. Web to calculate it manually, divide your rate of climb by your ground speed and multiply by 60 to convert it to feet per hour. Web ground speed (gs) (knots) ÷ 60 * climb gradient. And how challenging are various. Considering that the aircraft is in approach configuration (intermediate flaps), if a missed approach is executed with one engine becoming. Ground speed = 75 knots; Web we explain the significance of standard climb gradients (200 feet per nautical mile), and their variations at different airports. Web learn how to determine the required rate of climb. Web determine the required rate of climb necessary to achieve the gypsm three’s published climb gradient. The video provides guidance on how to locate these. Web first, you can figure out your descent rate to the stepdown fix, start descending at that rate, and then increase your rate of descent once you cross the stepdown. See examples, charts, and formulas. Web to calculate it manually, divide your rate of climb by your ground speed and multiply by 60 to convert it to feet per hour. Web learn how to calculate various performance parameters for aviation, such as temperature conversion, crosswind component, load factor, stall speed, and more. The video provides guidance on how to locate these. Alternatively, you can use. 75 ÷ 60 * 200 =. However, we are also required to accelerate to a speed called vfs (final segment climb speed). You then need to check on your aircraft tables if, depending on. Web the climb gradient is the percentage of the rise over run (100% if you are climbing at 45 degrees) that your aircraft is climbing at while the rate of climb is the speed at which you. Edited nov 21, 2018 at 5:42. These requirements are part of. See examples, charts, and formulas for different. Web ground speed (gs) (knots) ÷ 60 * climb gradient (feet per mile) example: Given a required climb or descent in feet per minute and ground speed in knots, compute the target vsi reading with required climb/descent multiplied. And how challenging are various. Web a rate of climb/descent table is provided for use in planning and executing climbs or descents under known or approximate ground speed conditions. Web to calculate it manually, divide your rate of climb by your ground speed and multiply by 60 to convert it to feet per hour. Web first, you can figure out your descent rate to the stepdown fix, start descending at that rate, and then increase your rate of descent once you cross the stepdown. Web the 40:1 surface is calculated out to 22.09 nautical miles from the runway end within an arc of 180° centered along the runway centerline extended. Web learn how to determine the required rate of climb based on the climb gradient for instrument departure procedures. Climb gradient required = 200 feet per mile;
Departure Procedure Climb Gradient And Calculating Your Rate Of Climb
Climbing And Bouldering Grading Systems Push Climbing

Climbing route grading Everything you need to know 5c Climbers
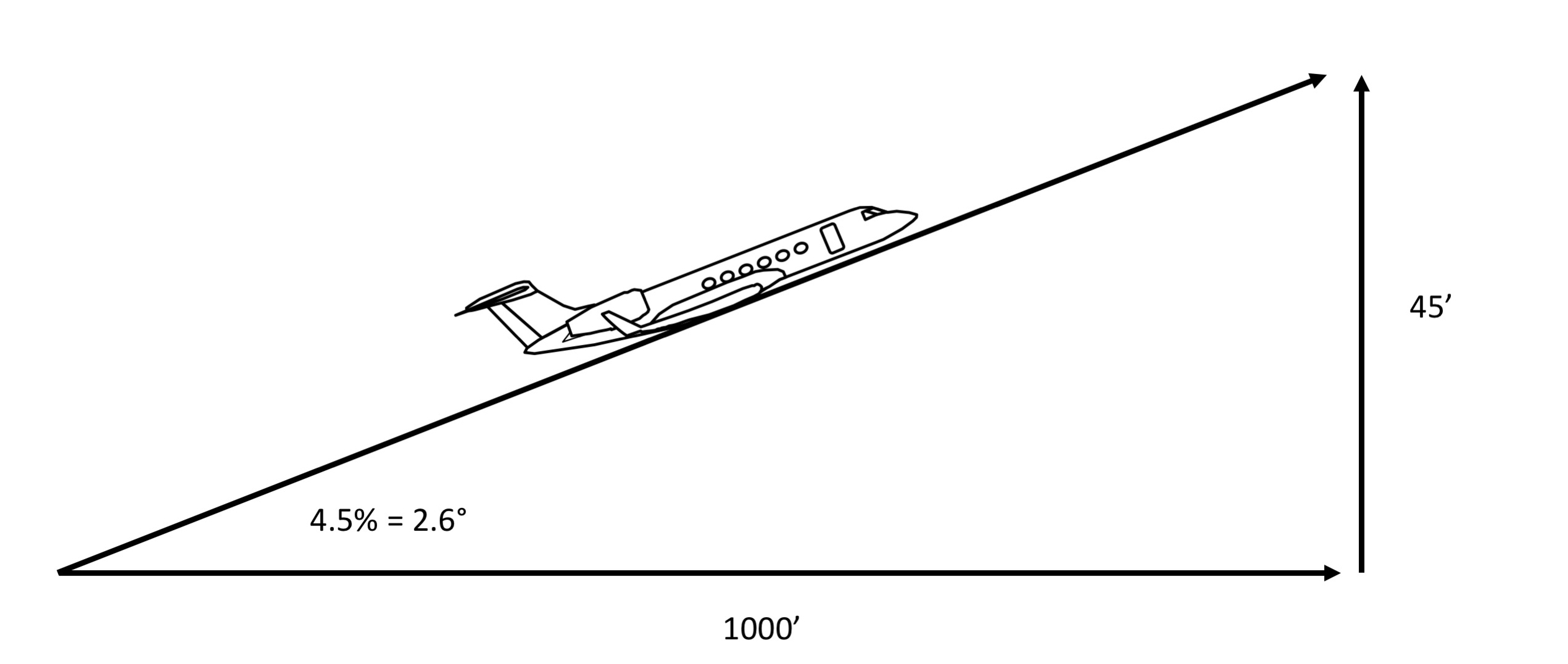
Takeoff Climb Gradient

Departure Procedure Climb Gradient And Calculating Your Rate Of Climb

Departure Procedure Climb Gradient And Calculating Your Rate Of Climb
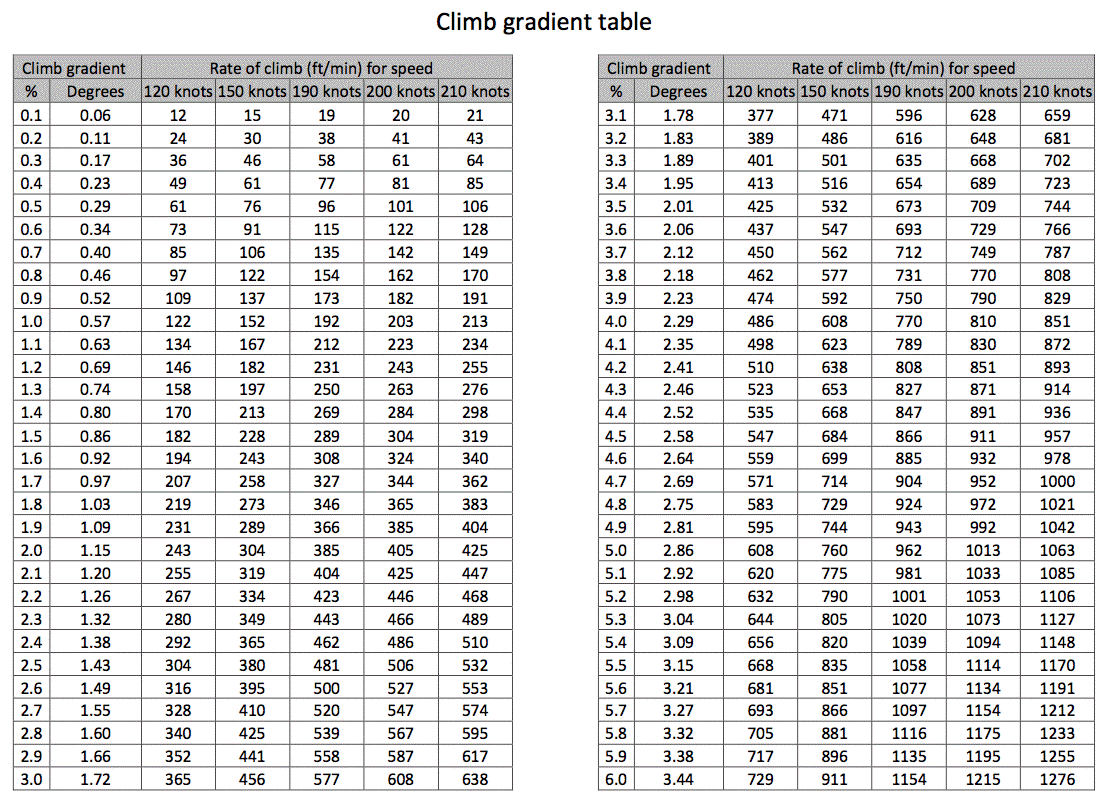
FAA Climb Gradient Chart
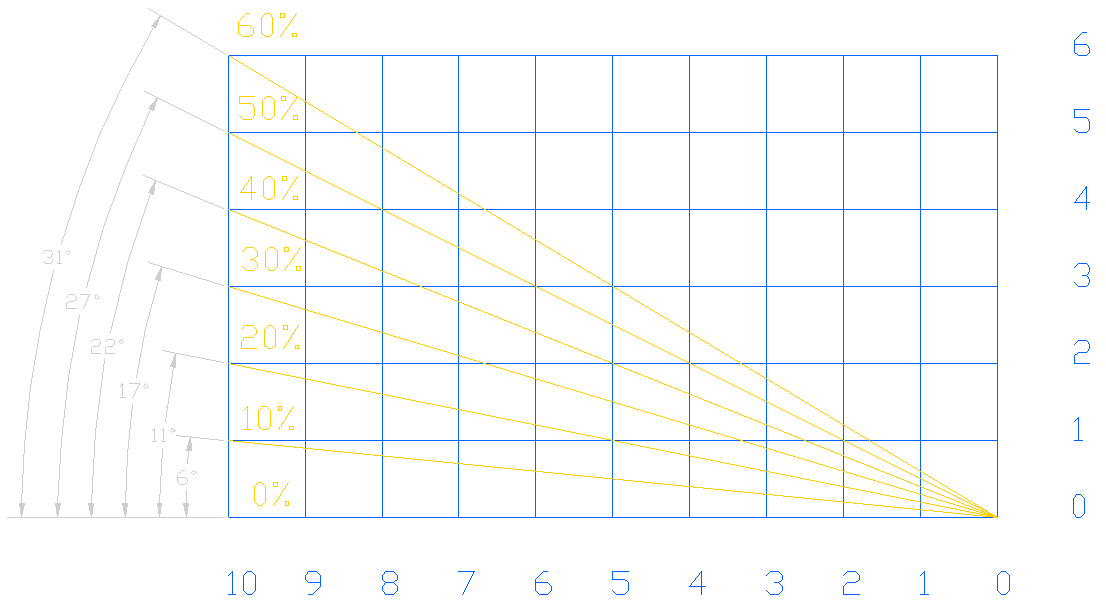
HILL CLIMBING ABILITY RATIOS SLOPES CALCULATIONS

FAA Climb Gradient Chart
Climb gradients at 44, 58, 88, and 100 power available in takeoff
Considering That The Aircraft Is In Approach Configuration (Intermediate Flaps), If A Missed Approach Is Executed With One Engine Becoming.
The Rate Of Climb Table In The Tpp Book Should.
Web There, The Takeoff Minimums On Runway 14 Require A Climb Gradient Of 610 Feet Per Nautical Mile To Over 2,000 Feet Above The Airport Elevation Of 6,882 Feet Msl.
Ground Speed = 75 Knots;
Related Post: