Chemical Weathering Drawing
Chemical Weathering Drawing - Complete the following table by indicating which process is primarily responsible for each of the described chemical weathering changes: Unlike mechanical weathering, it either dissolves the minerals or converts them into other. Updated on february 18, 2019. Web mechanical and chemical weathering: There are three types of weathering: Chemical weathering involves the chemical alteration of minerals within rocks, forming new minerals and soluble salts. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers. Learn the definition of chemical weathering, the different types and. Web by extension, in the language of the specialists of the critical zone, chemical weathering may be defined as that set of processes which alter a rock into a layer of chemically and physically transformed superficial material (i.e., regolith) which is susceptible to evolve (soil or karst) with time following biogeochemical processes. Web weathering is traditionally subdivided into two sets of processes: This happens through weathering, erosion, and deposition. Geochemistry and isotope geochemistry of rivers chevron_right. Breaking a rock through physical weathering increases the effective surface area in which chemical weathering can occur, and through changing the composition of rocks in chemical weathering, the durability of a rocks. The main processes of chemical weathering are hydrolysis, oxidation, and dissolution. No rock on. Web chemical weathering breaks down rocks by forming new minerals that are stable at the earth’s surface. Physical weathering, the mechanical breakdown or disintegration of the bedrock itself into particles large and small. Web by extension, in the language of the specialists of the critical zone, chemical weathering may be defined as that set of processes which alter a rock. This happens through weathering, erosion, and deposition. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Once a rock has been broken down, a process called erosion transports the bits of rock and mineral away. Unlike mechanical weathering, it either dissolves the minerals or converts them into other. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers. Calcite to calcium and bicarbonate ions; Chemical weathering, the chemical decomposition of some or all of the constituent minerals or the bedrock. Chemical weathering, also known as decomposition or decay, is the breakdown of rock by chemical mechanisms. Natural forces like wind, water, and ice erode rocks. Web model the process of mechanical and chemical weathering, drawing conclusions from their. Complete the following table by indicating which process is primarily responsible for each of the described chemical weathering changes: Chalk is a great material to use to demonstrate weathering because chalk is a soft sedimentary rock made of calcite. The movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Mechanical weathering is caused by wind, sand, rain, freezing,. Salt, sidewalk chalk, plastic container with a lid, teaspoon For example, buildings, statues, and monuments are subject to erosion through chemical weathering from reactions to rainwater. Temperature changes also play a role, making rocks expand and contract and sometimes break. Dissolution is the process where minerals dissolve in water. Web mechanical and chemical weathering: Author danielle sands view bio. Determine which environments and climates are most likely to promote different types of. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers. Web weathering describes the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on the surface of earth. Chemical weathering, also known as decomposition or decay, is the breakdown of rock by chemical mechanisms. No rock on earth is hard. This type of weathering contributes to soil formation. Web updated on october 29, 2019. The main processes of chemical weathering are hydrolysis, oxidation, and dissolution. Model weathering with salt and chalk. Web weathering is traditionally subdivided into two sets of processes: Water, ice, acids, salts, plants, animals, and changes in temperature are all agents of weathering. Chalk is a great material to use to demonstrate weathering because chalk is a soft sedimentary rock made of calcite. For example, buildings, statues, and monuments are subject to erosion through chemical weathering from reactions. The movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Web exercise 5.2 chemical weathering. Determine which environments and climates are most likely to promote different types of. For example, buildings, statues, and monuments are subject to erosion through chemical weathering from reactions to rainwater. Web updated on october 29, 2019. Rain dislodges soil particles, leading to mechanical weathering. Weathering occurs when water breaks down rocks and soil to create sediment. Web mechanical and chemical weathering: Water, a powerful force, shapes our world through weathering and erosion. This happens through weathering, erosion, and deposition. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Physical weathering occurs when existing rocks are mechanically broken into smaller pieces with little or no chemical change. Web chemical weathering breaks down rocks by forming new minerals that are stable at the earth’s surface. Breaking a rock through physical weathering increases the effective surface area in which chemical weathering can occur, and through changing the composition of rocks in chemical weathering, the durability of a rocks. Chemical weathering involves the chemical alteration of minerals within rocks, forming new minerals and soluble salts. For example, buildings, statues, and monuments are subject to erosion through chemical weathering from reactions to rainwater. The movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Calcite to calcium and bicarbonate ions; Biological weathering is caused by the actions of plants and animals as they grow, nest, and burrow. As water accumulates, it moves soil and rock particles, causing erosion. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers.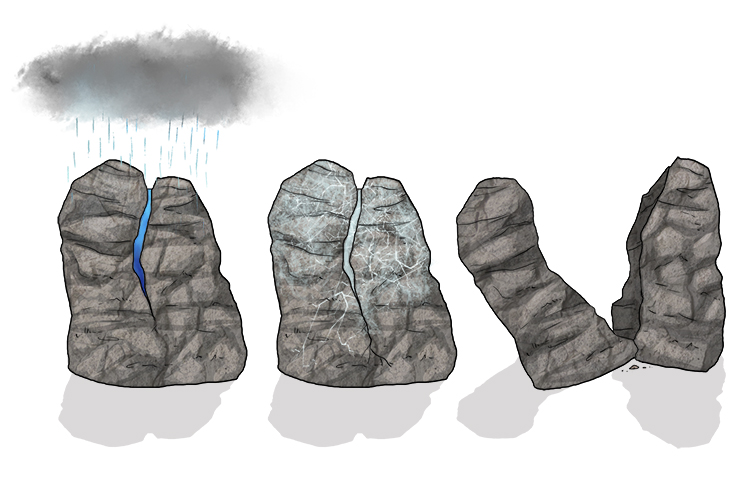
Chemical Weathering
Climate a geological perspective

PPT Ch 5 Weathering & Erosion PowerPoint Presentation, free

PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1186156

Geology Chemical weathering, 6th grade science, Earth science
/examples-of-chemical-weathering-607608_FINAL-54f8c4d63ed94e0eab454dc5e96cabff.png)
4 manieren waarop chemische verwering rock verandert

Science Lesson Mechanical and Chemical Weathering YouTube
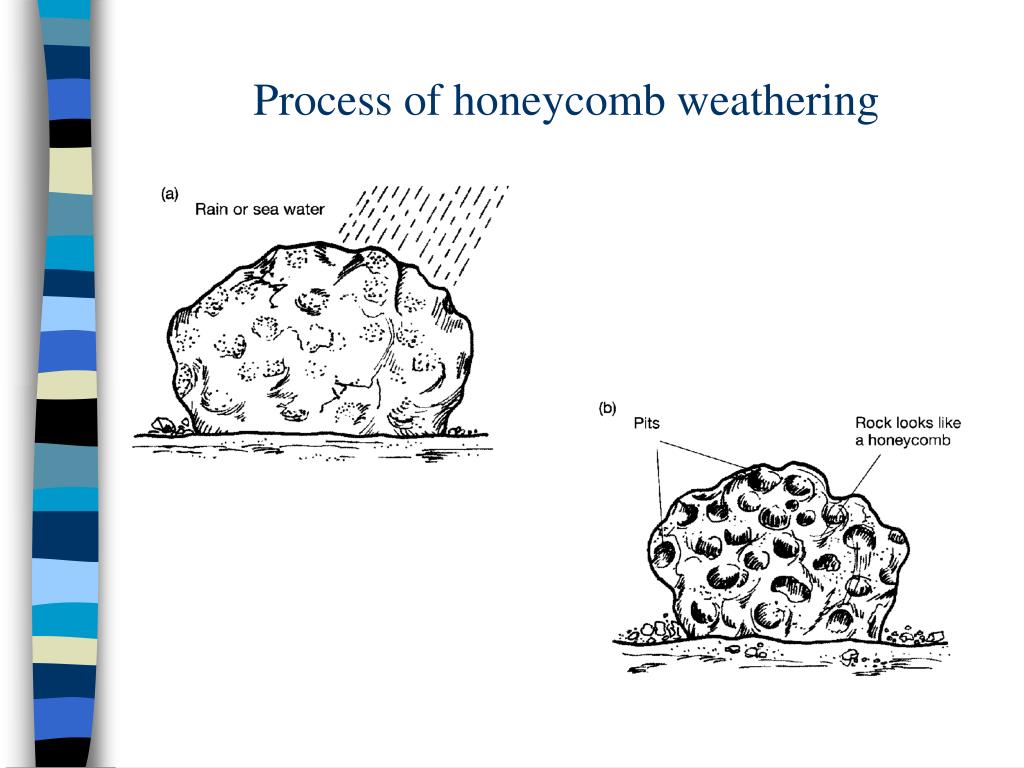
PPT Types of Chemical Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free

PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1600140
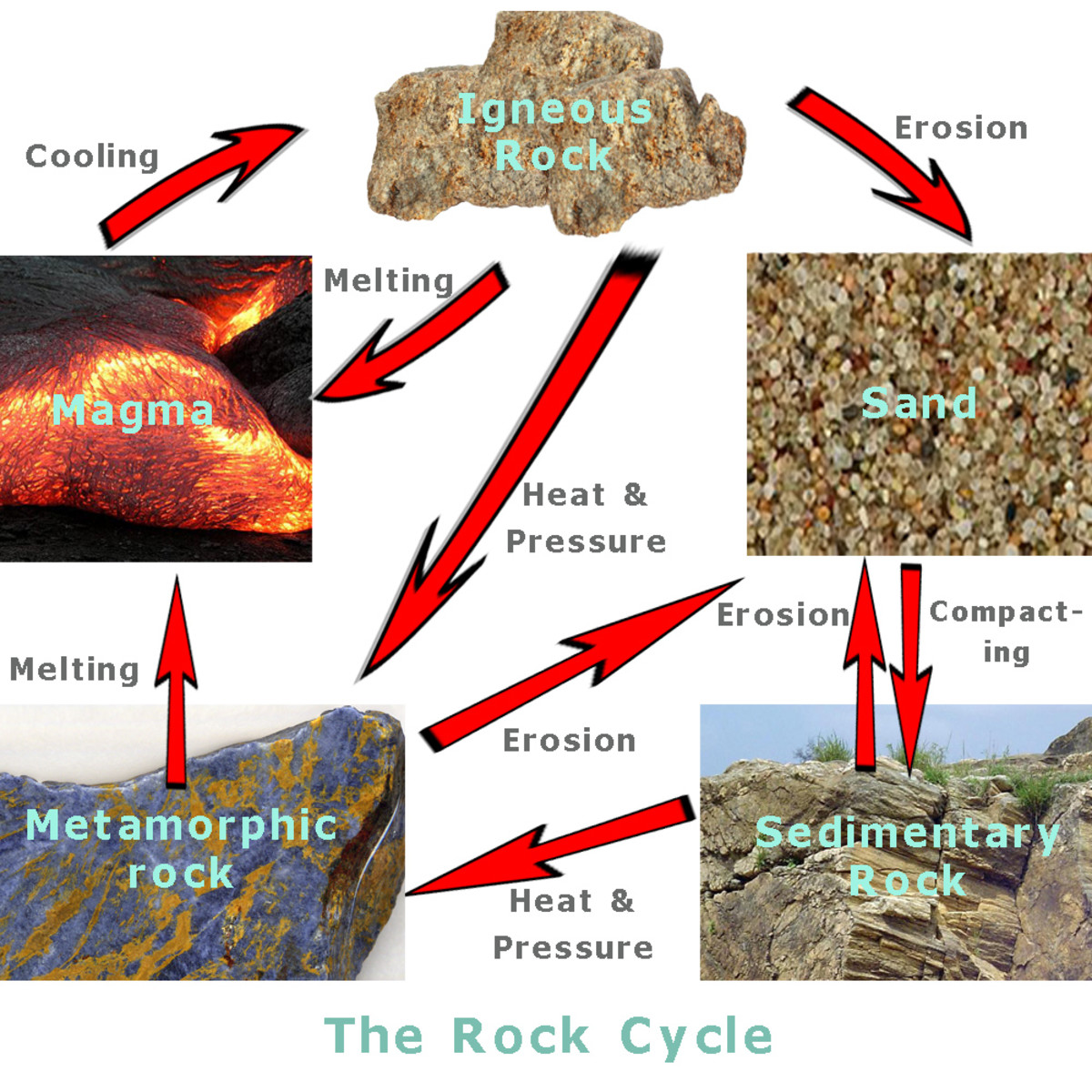
Chemical Weathering A Great Natural Force Owlcation
Water, Carbon Dioxide, And Oxygen Are Important Agents Of Chemical Weathering.
This Can Happen Through Dissolution By Water Or By Chemical Reactions.
There Are Three Types Of Weathering Which Affect Rock:
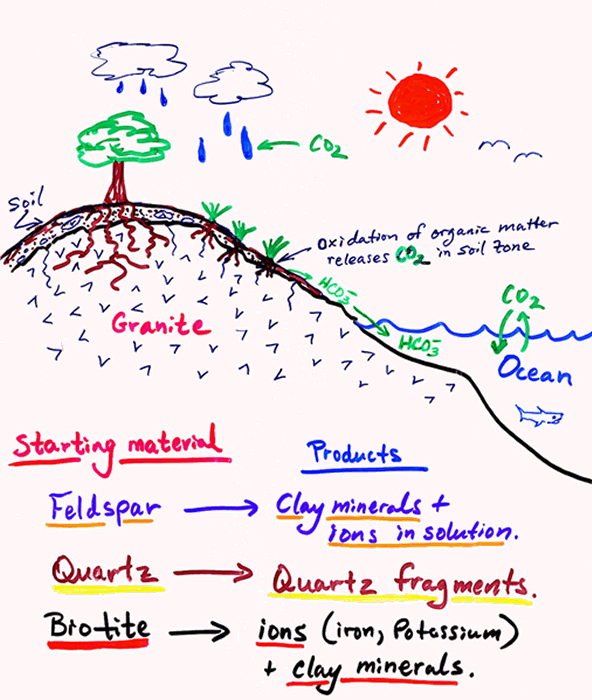
Web By Extension, In The Language Of The Specialists Of The Critical Zone, Chemical Weathering May Be Defined As That Set Of Processes Which Alter A Rock Into A Layer Of Chemically And Physically Transformed Superficial Material (I.e., Regolith) Which Is Susceptible To Evolve (Soil Or Karst) With Time Following Biogeochemical Processes.
Related Post: