Chart Rocks And Minerals
Chart Rocks And Minerals - Web photographs and information for a large collection of igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. A rock is a solid collection of minerals. Additionally, you can use identification resources like books and flow charts. Web a basic guide to common uk rock types, detailing igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Web rocks are classified based on how they were formed. Finally, compare the properties of your rock to those of known rock types while looking for other identifying characteristics. Web rock, in geology, naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of one or more minerals. Igneous (rocks crystallizing from molten material), sedimentary (rocks composed of products of mechanical weathering (sand, gravel, etc.) and chemical weathering (things precipitated from solution ), and metamorphic (rocks produced by alteration of other rock. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Examples of minerals are feldspar, quartz, mica, halite, calcite, and amphibole. The three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Such aggregates constitute the basic unit of which the solid earth is composed and typically form recognizable and mappable volumes. Web photographs and information for a large collection of igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. The three. Examples of minerals are feldspar, quartz, mica, halite, calcite, and amphibole. Web on the following pages are descriptions of the properties and uses of the rocks and minerals in the teachers‘ kit. The three major classes of rock are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock. Web an interactive reference guide to rocks, minerals, and gemstones. The gallery of minerals has examples. This chart shows the relative abundance of the common rock forming minerals in some of earth's most abundant rock types. A simplified classification diagram for igneous rocks based on their mineral compositions. Web photographs and information for a large collection of igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. The three major classes of rock. Terminology can be referenced in the illustrated glossary of terms that is located at the end of the descriptive information. Web interactive guide to hundreds of rocks and minerals. But there are certain things you can do to help identify your rock. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. Examples of minerals are. Web in this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the basic concepts, terminology, and practical techniques to help you navigate the diverse realm of mineralogy and petrology, share essential tools, and provide tips to enhance your rock identification skills. Examples of minerals are feldspar, quartz, mica, halite, calcite, and amphibole. Write these traits down, then compare the mineral’s traits to those. The gallery of minerals has examples of common minerals that are categorized by type. Write these traits down, then compare the mineral’s traits to those of known mineral types. Web a mineral is an inorganic, crystalline solid. Web please pay it forward. Rocks are classified by their mineral and chemical composition, by the texture of the constituent particles and by. A rock is a solid collection of minerals. Web a mineral is a pure substance with a specific composition and structure, while a rock is typically a mixture of several different minerals (although a few types of rock may include only one type of mineral). Web discover key characteristics that can help you identify your rock or mineral. Next, test. The rocks and minerals are presented in alphabetical order with their assigned numbers shown to the left. Terminology can be referenced in the illustrated glossary of terms that is located at the end of the descriptive information. Each has a thumbnail picture of the specimen and a brief description of it. The three major classes of rock are igneous, sedimentary,. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. Web please pay it forward. Examples of minerals are feldspar, quartz, mica, halite, calcite, and amphibole. Web in this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the basic concepts, terminology, and practical techniques to help you navigate the diverse realm of mineralogy and petrology, share essential tools, and. Web a mineral is an inorganic, crystalline solid. Basalt and gabbro account for most of the rock in the oceanic crust, granite (rhyolite) and andesite (diorite) represent abundant rock types of the continental crust. A mineral is formed through natural processes and has a definite chemical composition. But there are certain things you can do to help identify your rock.. The gallery of minerals has examples of common minerals that are categorized by type. Web discover key characteristics that can help you identify your rock or mineral. A mineral is formed through natural processes and has a definite chemical composition. Each has a thumbnail picture of the specimen and a brief description of it. A rock is a solid collection of minerals. The rocks and minerals are presented in alphabetical order with their assigned numbers shown to the left. A simplified classification diagram for igneous rocks based on their mineral compositions. The three major classes of rock are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock. Write these traits down, then compare the mineral’s traits to those of known mineral types. These indicators separate rocks into igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic. The three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Minerals can be identified by their characteristic physical properties such as crystalline structure, hardness, streak, and cleavage. Such aggregates constitute the basic unit of which the solid earth is composed and typically form recognizable and mappable volumes. Web on the following pages are descriptions of the properties and uses of the rocks and minerals in the teachers‘ kit. There are three main types of rock, classified by how they are sourced and formed: Web a mineral is a pure substance with a specific composition and structure, while a rock is typically a mixture of several different minerals (although a few types of rock may include only one type of mineral).
Crystals and Minerals Chart at The Crystal Healing Shop

Rocks And Minerals Chart

MOHS Hardness Scale Rock and Mineral Collection ID chart Rocks and

Mineral Rock Chart With Pictures
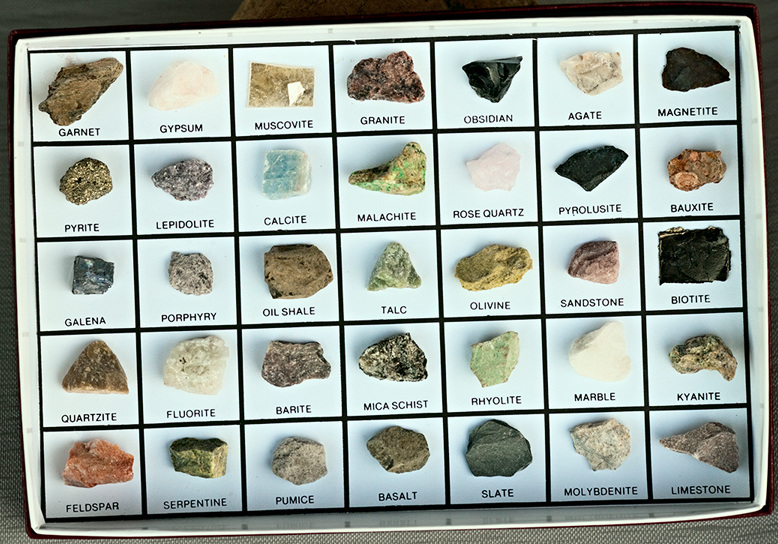
Rocks and Minerals Information on the earth

Rocks And Minerals Chart

Rocks and Minerals of U.S. Reference Collection (24 pcs.) Main Photo

Rocks and Minerals Activities and Anchor Chart Anchor charts, Rocks
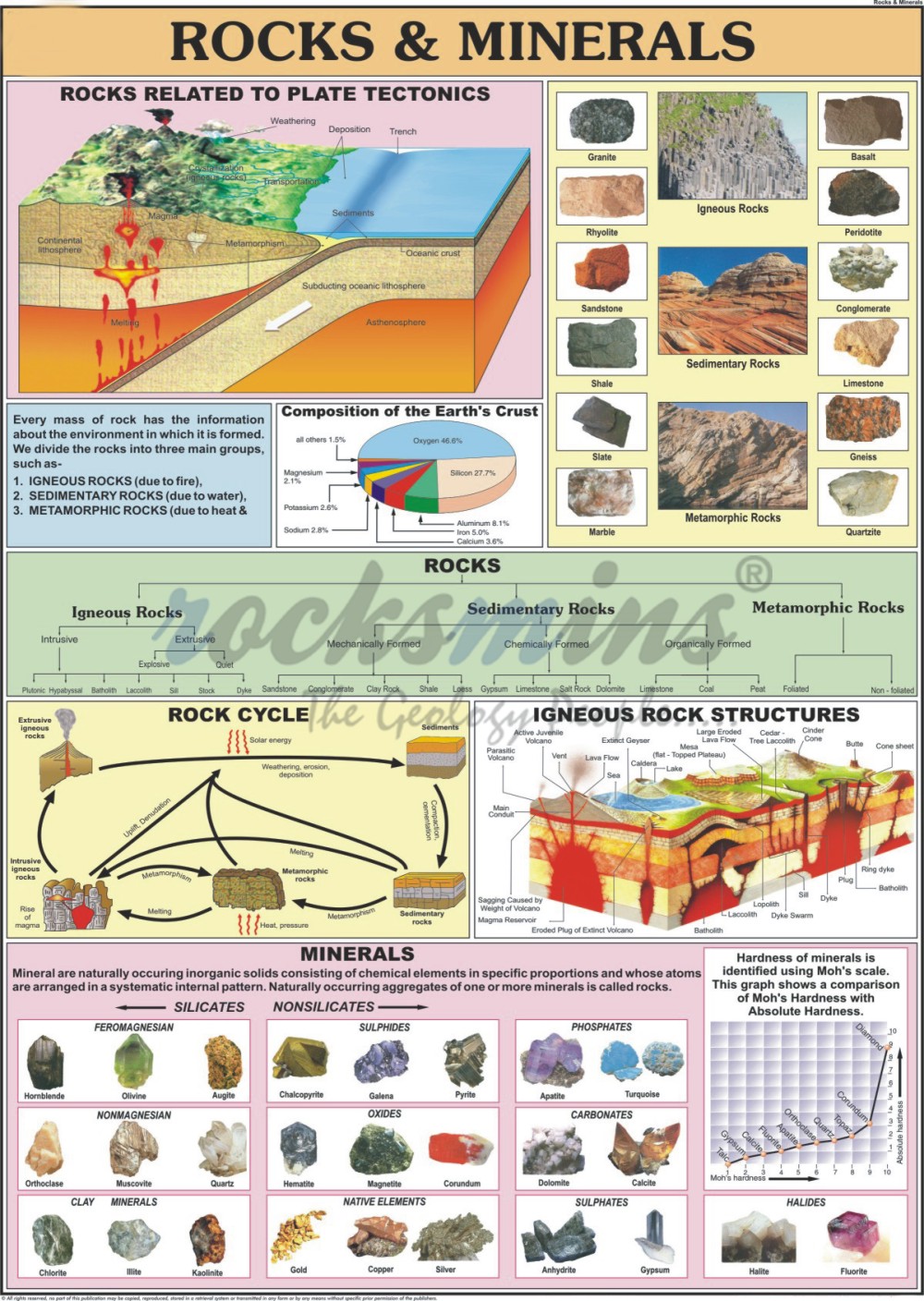
GEOLOGY CHARTS Rocks & Minerals Charts, Structure of Earth Charts

Rocks And Minerals Chart Identification
These Rocks Change Forms Via The Rock Cycle.
Terminology Can Be Referenced In The Illustrated Glossary Of Terms That Is Located At The End Of The Descriptive Information.
Examples Of Minerals Are Feldspar, Quartz, Mica, Halite, Calcite, And Amphibole.
Note That Glassy Igneous Rocks Pumice And Obsidian Are Not Included On This Diagram.
Related Post: