Chart Metamorphic Rock
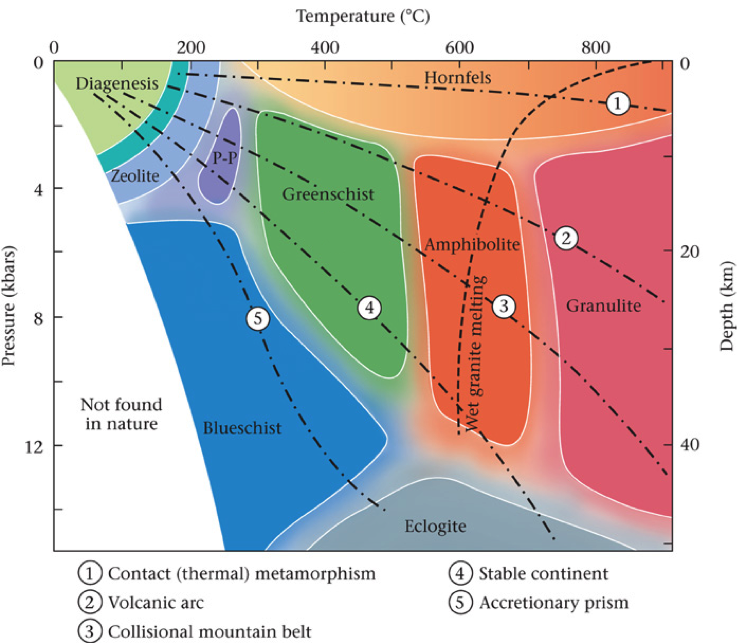
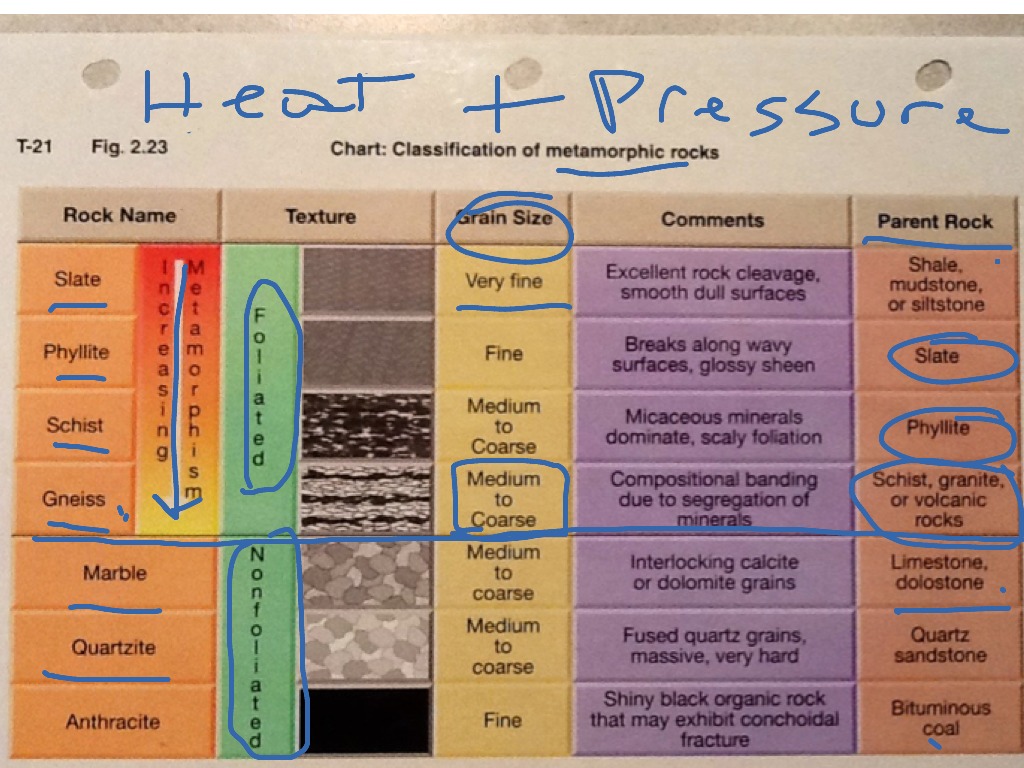
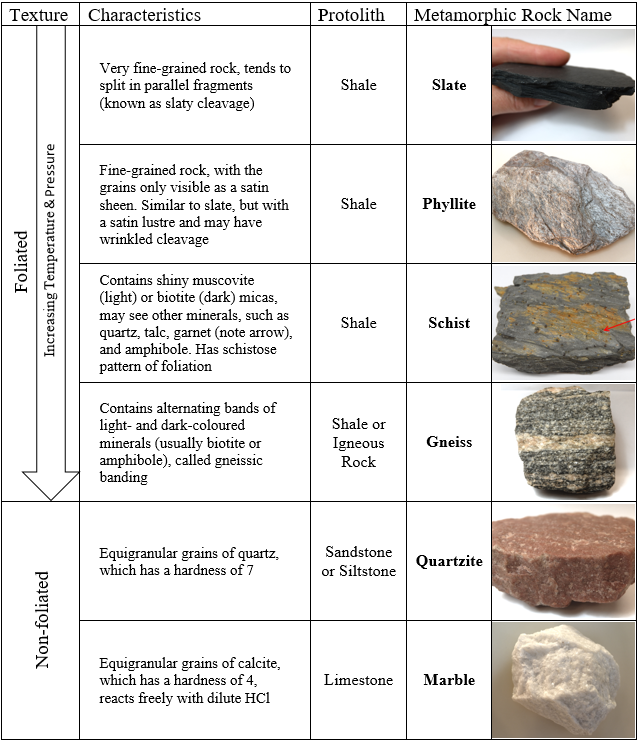
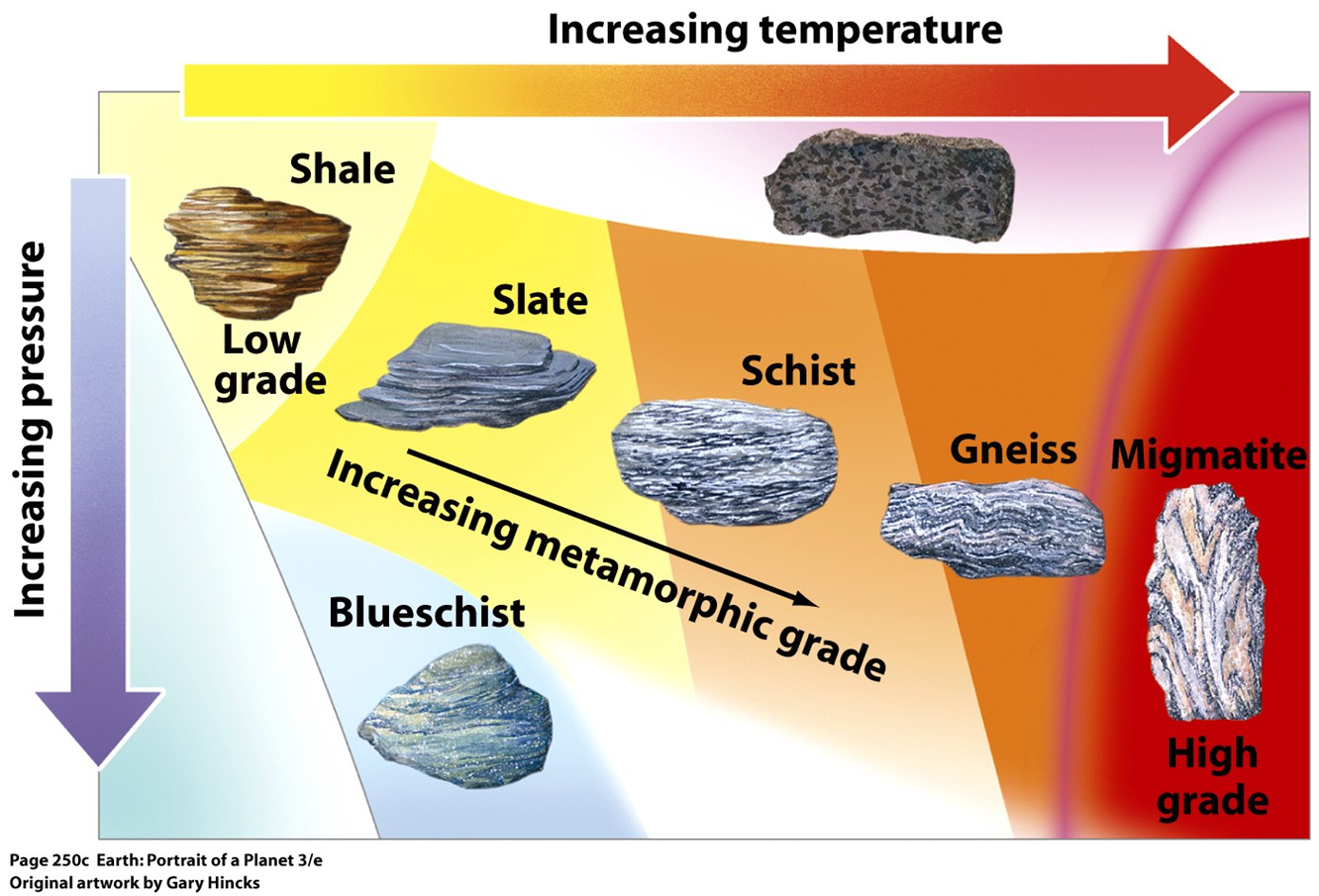
Chart Metamorphic Rock - In the rock cycle , there are three different types of rocks: Web metamorphic rocks are classified broadly into low, medium and high grades of metamorphic intensity, primarily due to the effects of heat on mineral stability. Texture is first characteristic observed in the identification process. Generalized rock identi cation chart for common metamorphic rocks. Metamorphism (meta = change, morph = form) happens when molten rock intrudes other rocks and bakes the contact zone where the molten rock touches the preexisting rock. Conditions like these are found deep within the earth or where tectonic plates meet. Those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment without directed pressure or relatively near the surface with very little pressure at all. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Web the three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. By the end of this chapter, students will be able to: Metamorphic minerals and rocks form when original parent rocks ( protoliths) undergo changes in chemistry, texture, or composition. In this chart, tfi values increase from left to right while wfi values increase from top to. This gives the geologist literally “inside information” on what occurs within the earth during such processes as the formation of new mountain ranges, the collision. Identify the properties and the names of the 8 unknown metamorphic rocks. The two sources of heat for metamorphism are the heat from a magma chamber and the geothermal gradient, which is the natural increase in. Heat and pressure are the most important causes of metamorphism. Metamorphic rocks have been modified by heat, pressure, and chemical processes, usually while buried. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Heat and pressure are the most important causes of metamorphism. There are two main types of metamorphic rocks: Web metamorphic rocks (changed rocks) are made when existing rocks are subjected to high temperatures and high pressures for long periods of time. Web the kinds of rocks that can be expected. Web there are two main types of metamorphic rocks: Conditions like these are found deep within the earth or where tectonic plates meet. Identify the properties and the names of the 8 unknown metamorphic rocks. Web what are metamorphic rocks? The higher the temperature, the more vibration occurs, and the weaker the bonds between atoms become. Identifying a metamorphic rock can sometimes be very challenging, so it helps to. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Web metamorphic rocks represent one of the three major classes of rocks, the others being igneous and sedimentary. Generalized rock identi cation chart for common metamorphic rocks. Metamorphism (meta = change, morph = form) happens when molten. Web metamorphic rocks are classified broadly into low, medium and high grades of metamorphic intensity, primarily due to the effects of heat on mineral stability. Web explain the relationships among slate, phyllite, schist, and gneiss in terms of metamorphic grade. Explain how metamorphic facies relate to plate tectonic processes. Exposure to these extreme conditions has altered the mineralogy, texture, and. Texture is first characteristic observed in the identification process. The two sources of heat for metamorphism are the heat from a magma chamber and the geothermal gradient, which is the natural increase in. Metamorphic minerals and rocks form when original parent rocks ( protoliths) undergo changes in chemistry, texture, or composition. Metamorphic rocks have been modified by heat, pressure, and. The two sources of heat for metamorphism are the heat from a magma chamber and the geothermal gradient, which is the natural increase in. Heat causes atoms to vibrate; Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. Identify and describe the three principal metamorphic agents. Web metamorphic rocks represent one of the three major classes of rocks, the. Some rocks, such as granite, do not change much at the lower metamorphic grades because their minerals are still stable up to several hundred degrees. In the rock cycle , there are three different types of rocks: Web classification of metamorphic rocks. Web what are metamorphic rocks? These are the rocks that form by the effects of heat, pressure, and. In the rock cycle , there are three different types of rocks: Web the study of metamorphic rocks (now exposed at the earth's surface following erosion and uplift) provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the earth's crust. Heat and pressure are the most important causes of metamorphism. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions. In the rock cycle , there are three different types of rocks: Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. Identify and describe the three principal metamorphic agents. These are the rocks that form by the effects of heat, pressure, and shear upon igneous and sedimentary rocks. Web the study of metamorphic rocks (now exposed at the earth's surface following erosion and uplift) provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the earth's crust. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Conditions like these are found deep within the earth or where tectonic plates meet. Texture is first characteristic observed in the identification process. Web metamorphic rocks are generally dense with very low porosity and permeability (nelson et al., 2000; Web metamorphic rocks represent one of the three major classes of rocks, the others being igneous and sedimentary. Metamorphic minerals and rocks form when original parent rocks ( protoliths) undergo changes in chemistry, texture, or composition. Web metamorphic grade is important, not just because different kinds of rocks and minerals form at different temperatures, but because temperature affects chemical reaction rates. Web metamorphic rocks are an important topic in geology. Metamorphic fluids flowing through a rock may cause significant changes in some cases. Explain how metamorphic facies relate to plate tectonic processes. Those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment without directed pressure or relatively near the surface with very little pressure at all.
MR15PM Collection of 15 Metamorphic Rocks PM.jpg (1778×1357) Rock

Rock Collection And ID Chart 18 Rocks Igneous, Metamorphic, Sedimentary

Overview of Metamorphic Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science

Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Rock Chart

Metamorphic Rock Chart Flinn Scientific
Metamorphic rocks, minerals, grade, and facies Lucky Sci
Metamorphic rock chart Science, Geology ShowMe

American Educational Identifying Metamorphic Rock Chart
Igneous Metamorphic And Sedimentary Rocks Chart
Classifications of Rocks Sedimentary, Igneous and Metamorphic
Metamorphic Rocks Have Been Modified By Heat, Pressure, And Chemical Processes, Usually While Buried Deep Below Earth's Surface.
Heat Causes Atoms To Vibrate;
Web Metamorphic Rocks Provide A Record Of The Processes That Occurred Inside Earth As The Rock Was Subjected To Changing Physical And Chemical Conditions.
By The End Of This Chapter, Students Will Be Able To:
Related Post: