Carbon Monoxide Level Chart
Carbon Monoxide Level Chart - 3% (nonsmokers) 10% (smokers) [2] differential diagnosis. During prolonged or high exposures, symptoms. But if they're used in a partly closed or closed space, the carbon monoxide level can be a danger. Sudden chest pain may occur in people with angina. Web large amounts of co can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate. Web updated 24 may 2022. Web carbon monoxide (co) is an odorless, colorless gas that can cause sudden illness and death if inhaled. Between 51 ppm and 100 ppm; Web as co levels increase and remain above 70 ppm, symptoms become more noticeable and can include headache, fatigue and nausea. Treatment is likely to start right away for anyone brought to an emergency room with suspected carbon monoxide poisoning. Starting in 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010. Between 51 ppm and 100 ppm; Average levels in homes without gas stoves vary from 0.5 to 5 parts per million (ppm). Web levels > 20% commonly cause vague dizziness, generalized weakness, difficulty concentrating, and impaired judgment. But if they're used in a partly closed or closed space, the carbon monoxide. 3% (nonsmokers) 10% (smokers) [2] differential diagnosis. In hemodynamically stable patients, venous samples are accurate and commonly used [ 47,48 ]. Steps to reduce exposure to carbon monoxide. Less than 2%, or 0.02. Web carbon monoxide (co) is an odorless, colorless gas that can cause sudden illness and death if inhaled. If your levels are higher, you may have co intoxication or poisoning. For information on co standards, sources, health effects, and programs to reduce co, please see our carbon monoxide pollution page. Starting in 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010. Average levels in homes without gas stoves vary from 0.5 to 5 parts per million (ppm). What makes indoor. Health and safety issues in natural disasters. American industrial hygiene association (aiha): Atsdr toxicological profile for carbon monoxide. Steps to reduce exposure to carbon monoxide. At sustained co concentrations above 150 to 200 ppm, disorientation, unconsciousness, and death are possible. The concentration of co, measured in parts per million (ppm) is a determining factor in the symptoms for an average, healthy adult. Web acute exposure guideline levels (aegls): Web levels in homes. 4% to 5%, or 0.04 to 0.05. 6% to 8%, or 0.06 to 0.08. Web large amounts of co can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate. 3% (nonsmokers) 10% (smokers) [2] differential diagnosis. Carbon monoxide detectors, venting of gas appliances, maintenance of exhaust systems [1] treatment. Web these are the normal ranges for co levels in the blood: Levels near properly adjusted gas stoves are often. Cyanide toxicity, alcoholic ketoacidosis, aspirin poisoning, upper respiratory tract infection [2] [4] prevention. Web as co levels increase and remain above 70 ppm, symptoms become more noticeable and can include headache, fatigue and nausea. Web large amounts of co can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate. Web october 3, 2021 by josh. Web updated 24 may 2022. 6% to 8%, or 0.06 to 0.08. 3% (nonsmokers) 10% (smokers) [2] differential diagnosis. Carbon monoxide poisoning is common. Average levels in homes without gas stoves vary from 0.5 to 5 parts per million (ppm). For information on co standards, sources, health effects, and programs to reduce co, please see our carbon monoxide pollution page. 4% to 5%, or 0.04 to 0.05. Less than 2%, or 0.02. What makes indoor air unhealthy? Web as co levels increase and remain above 70 ppm, symptoms become more noticeable and can include headache, fatigue and nausea. Tests that may provide clues. If your levels are higher, you may have co intoxication or poisoning. Greater than 101 ppm if someone is experiencing symptoms when will carbon monoxide levels set off your alarm? Carbon monoxide (co) is an odorless, colorless and tasteless but dangerous gas. Cdc carbon monoxide (co) poisoning: Tests that may provide clues. Web large amounts of co can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate. At sustained co concentrations above 150 to 200 ppm, disorientation, unconsciousness, and death are possible. Health and safety issues in natural disasters. Greater than 101 ppm if someone is experiencing symptoms when will carbon monoxide levels set off your alarm? Web as co levels increase and remain above 70 ppm, symptoms become more noticeable and can include headache, fatigue and nausea. Web acute exposure guideline levels (aegls): What makes indoor air unhealthy? American industrial hygiene association (aiha): Web the diagnosis of co poisoning is made in patients with known or suspected co exposure in conjunction with an elevated carboxyhemoglobin (cohb) level measured by cooximetry of a blood gas sample. Average levels in homes without gas stoves vary from 0.5 to 5 parts per million (ppm). In hemodynamically stable patients, venous samples are accurate and commonly used [ 47,48 ]. Web updated 24 may 2022. Carbon monoxide (co) is an odorless, colorless and tasteless but dangerous gas. Less than 2%, or 0.02. 3% (nonsmokers) 10% (smokers) [2] differential diagnosis.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels are showing a startling increase

What to Know about Carbon Monoxide HB McClure Company
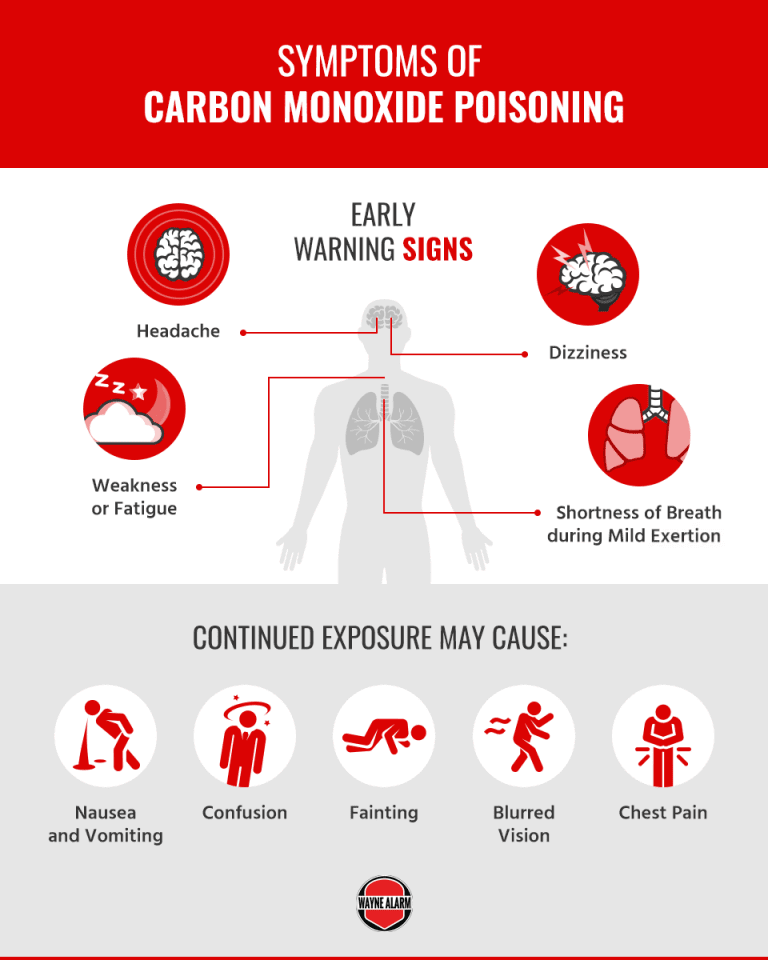
10 Common Causes of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Wayne Alarm
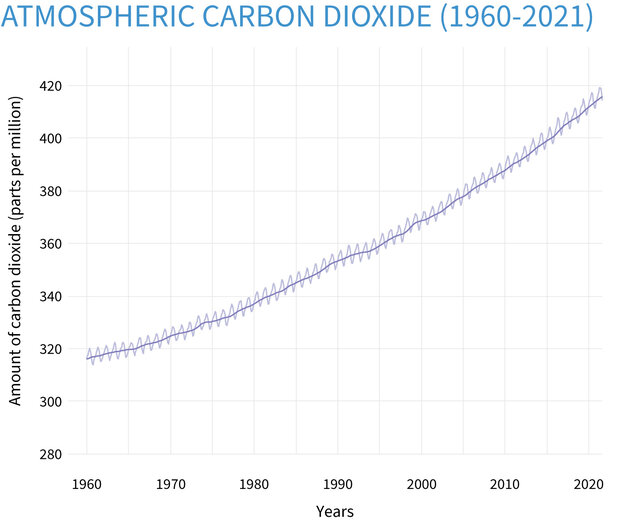
Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide NOAA Climate.gov

Carbon dioxide in atmosphere at record level

Three sickened by carbon monoxide in Near West Side apartment

Carbon Monoxide Levels Chart

Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Nursing Priorities and Treatment

CO2 levels Carbon dioxide hit the highest level in human history The
Graphic Carbon Dioxide Concentration Climate Change Vital Signs of
Adult Heavy Smokers (More Than 2 Packs A Day):
Web Carbon Monoxide (Co) Is An Odorless, Colorless Gas That Can Cause Sudden Illness And Death If Inhaled.
Steps To Reduce Exposure To Carbon Monoxide.
During Prolonged Or High Exposures, Symptoms.
Related Post: