C Chart Six Sigma
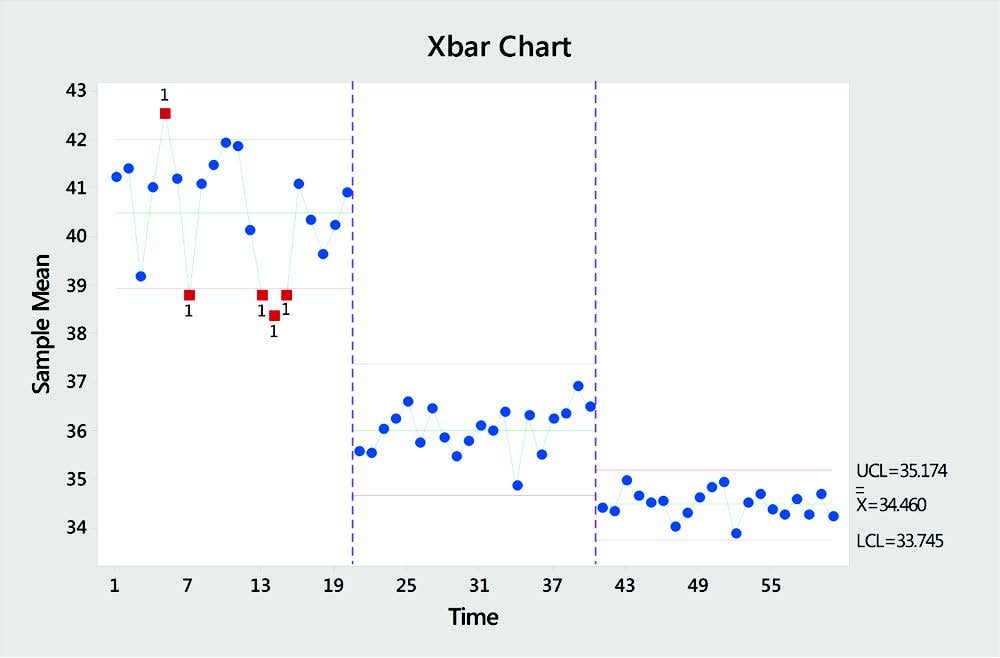
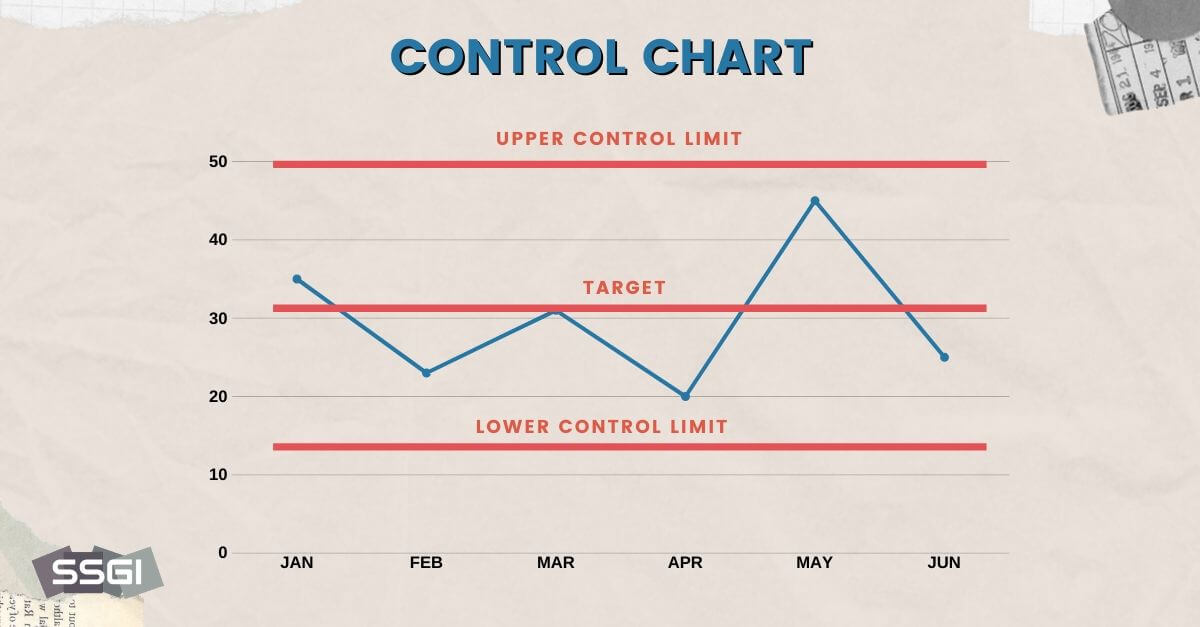
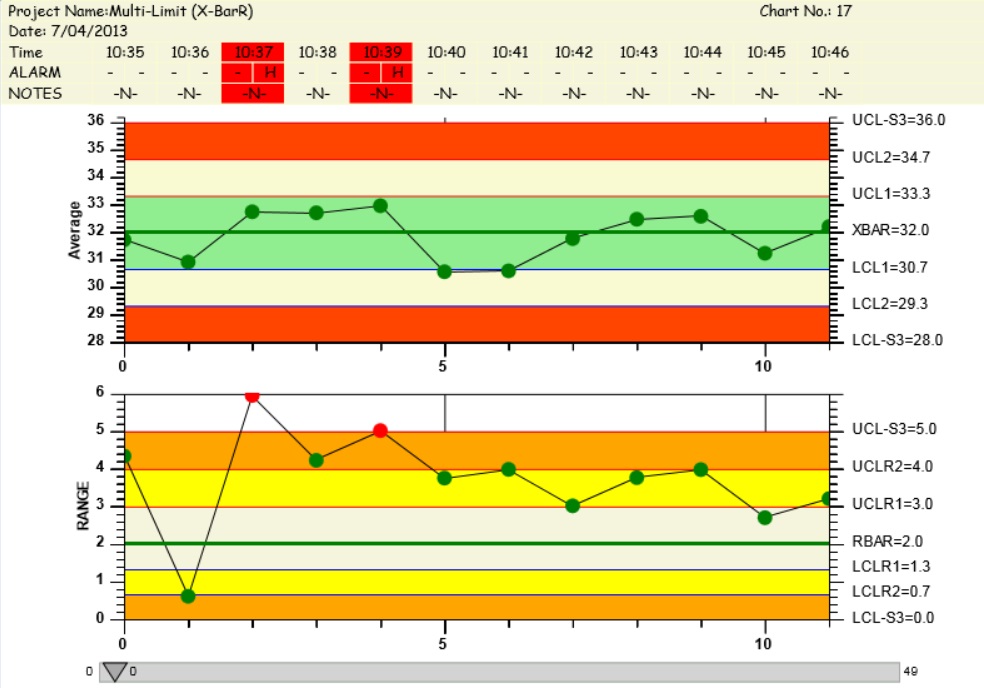
C Chart Six Sigma - There are four types of attribute charts: Control charts are a simple yet powerful tool that helps us understand if a process is “stable or in control.” control charts are used in the control phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze, improve, and control) process. The center line is the average number of nonconformities. Web the c chart measures the number of nonconformities per “unit” and is denoted by c. C chart, n chart, np chart, and u chart. This “unit” is commonly referred to as an inspection unit and may be “per day” or “per square foot” of some other predetermined sensible rate. Control charts generally have three parts: Control charts dealing with the number of defects or nonconformities are called c charts (for count). Web the seven six sigma chart types include: Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. Every item in the sample is evaluated for only the number of defects, flaws, or occurrences, etc. Here’s a brief overview of control charts and how they can be used in six sigma. Control charts are graphical representations of process data over time. Deciding between a green belt or a black belt to lead a six sigma project depends on. A control chart always has a central line for the average, an upper line for the upper control limit, and a lower line for the lower control limit. Plotted statistic for the c attribute control chart. Each chart has its specific use and is suitable for analyzing different data types. Control charts are a simple yet powerful tool that helps. C chart is also known as the control chart for defects (counting of the number of defects). On occasion, it also serves as a positive indicator. In six sigma studies, we read control charts in the control phase, like the statistical process cont control chart (spc chart). This chart is used when the number of samples of each sampling period. The c chart is used when the data can only be whole numbers, as in counting, it is known as attribute, or discrete data. Plotted statistic for the c attribute control chart. Deciding between a green belt or a black belt to lead a six sigma project depends on the project's size and complexity. Web what are control charts in. Web the interviewer wants to understand if you know the roles of different six sigma belt levels. Constant (fixed) sample size (subgroup size) develop upper and lower control limits (ucl and lcl) and determine the performance of a process over time. Web the c chart is a control chart for the number of nonconformities (defects or concerns) per inspection unit.. This “unit” is commonly referred to as an inspection unit and may be “per day” or “per square foot” of some other predetermined sensible rate. Web what are control charts in six sigma? Plotted statistic for the c attribute control chart. Web the control chart is a graph used to study how a process changes over time. Control charts are. Web a c control chart is a statistical tool used to monitor the number of defects in a process over time. C chart is also known as the control chart for defects (counting of the number of defects). C chart, n chart, np chart, and u chart. Web what are control charts in six sigma? Plotted statistic for the c. This control chart should be used when the following conditions exist: Special cause variation does not always indicate the negative part of the process, sometimes it reflects a good indication for the process too. In six sigma studies, we read control charts in the control phase, like the statistical process cont control chart (spc chart). Web a c control chart. Web developed in the 1920s by walter a. The c chart is used when the data can only be whole numbers, as in counting, it is known as attribute, or discrete data. This chart is used when the number of samples of each sampling period is essentially the same. This allows us to see how the process behaves over time.. Web developed in the 1920s by walter a. On occasion, it also serves as a positive indicator. Web what is a c chart? A c chart is a control chart for monitoring the number of defects per sample. Control charts generally have three parts: Green belts handle smaller projects or are part of teams in larger projects. There is a difference between a defect and defective, as there is between a nonconformity and nonconforming unit. Web what is a c chart? The c chart is used when the data can only be whole numbers, as in counting, it is known as attribute, or discrete data. Web control charts are an essential tool used in six sigma to monitor process stability and improve quality. Special cause variation may not always represent the bad aspect of the process; It is generally used to monitor the number of defects in constant size units. By understanding how control charts work, you can more effectively use them to improve your process and product quality. Every item in the sample is evaluated for only the number of defects, flaws, or occurrences, etc. On occasion, it also serves as a positive indicator. In order to see the special cause variation, we need a control chart. Web the interviewer wants to understand if you know the roles of different six sigma belt levels. Web the c chart is a control chart for the number of nonconformities (defects or concerns) per inspection unit. Each point on the chart represents the total number of nonconformities in a subgroup. Special cause variation does not always indicate the negative part of the process, sometimes it reflects a good indication for the process too. Web an attribute chart is a type of control chart for measuring attribute data (vs.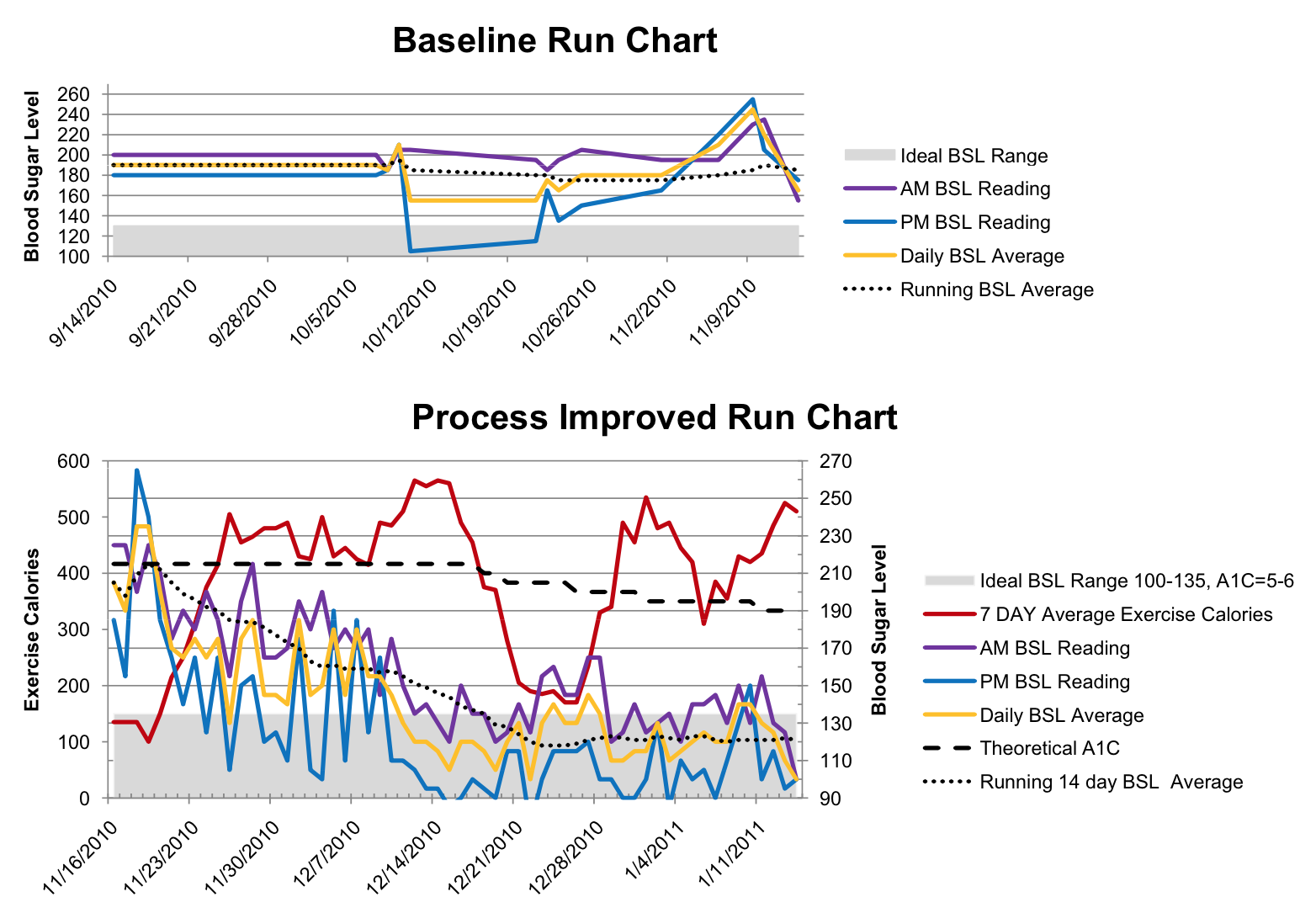
10 C CHART IN SIX SIGMA, SIX CHART SIGMA IN C Chart & Formation

Six Sigma Road Map Lean six sigma, Six sigma tools, Business process
5 More Critical Six Sigma Tools A Quick Guide

What is Control Charts in Six Sigma and How to Create them?
Lean Six Sigma The Definitive Guide (2020) SSGI

What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma Levels Methodology Tools

Article Everything You Wanted to Know About Six Sigma
22 C CHART IN SIX SIGMA, IN C CHART SIX SIGMA Chart & Formation
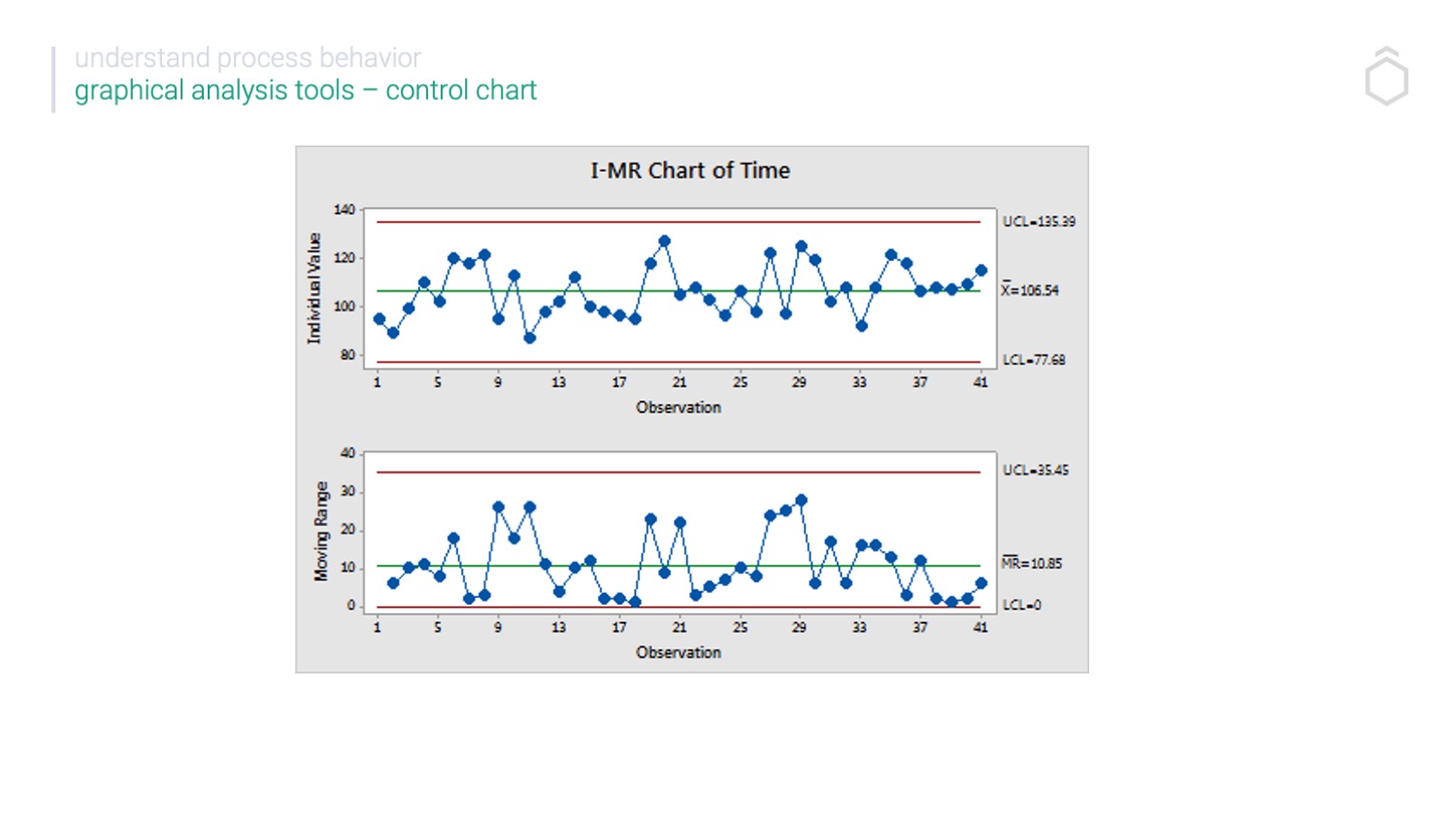
6 Sigma Control Chart Introduction Toolkit from Leanscape
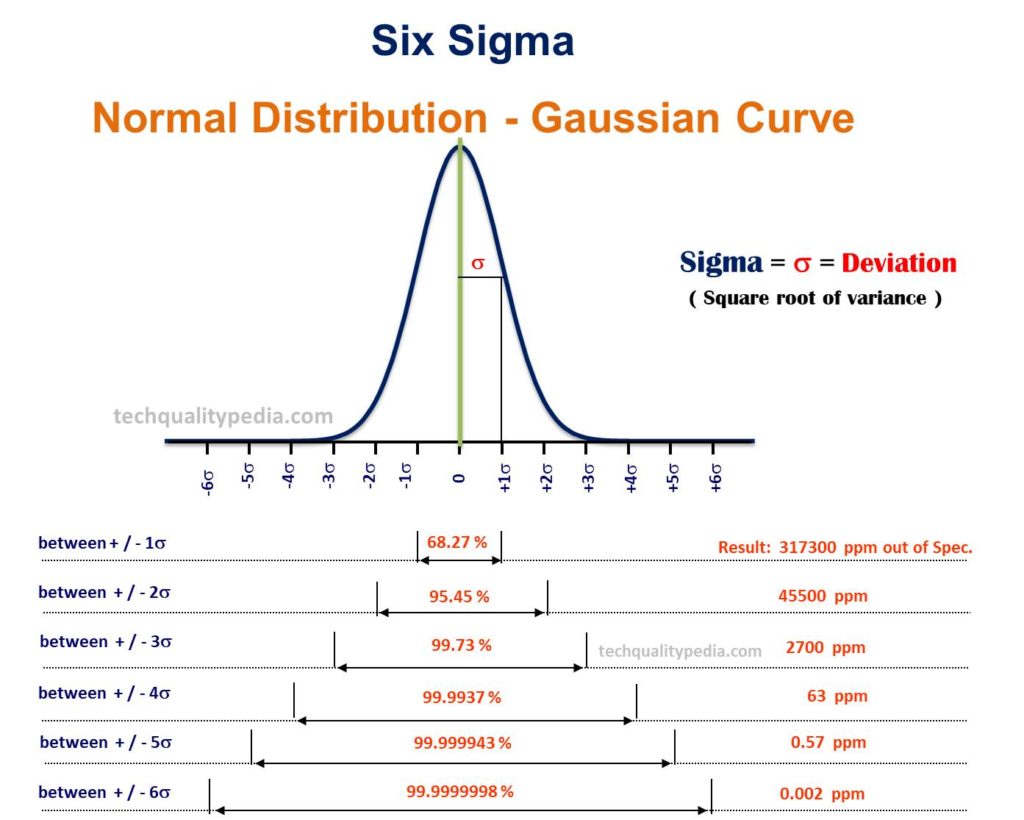
What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma Levels Methodology Tools
They Show Whether The Manufacturing Process Is Stable And Operating Within Expected Parameters Through The Use Of Statistical Limits.
The C Chart Is Especially Easy To Make Because The Number Of Defects Is Plotted Directly On The Control Chart.
A Control Chart Always Has A Central Line For The Average, An Upper Line For The Upper Control Limit, And A Lower Line For The Lower Control Limit.
Control Charts Are Graphical Representations Of Process Data Over Time.
Related Post: