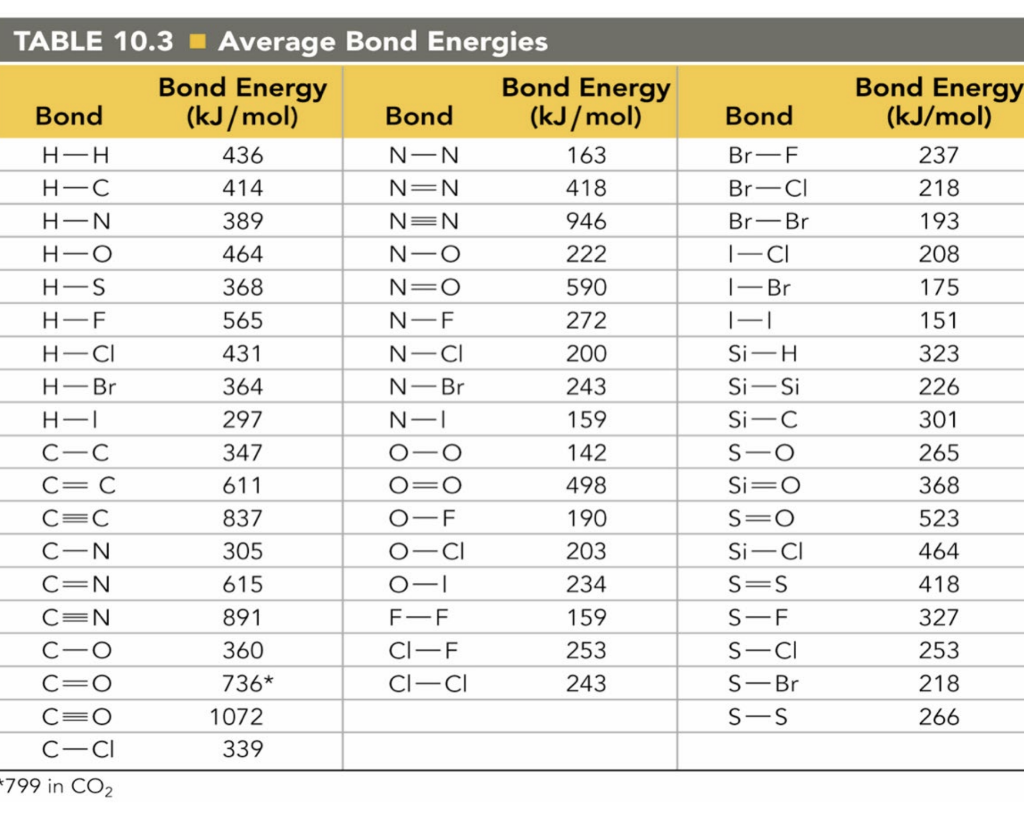
Bond Energies Chart
Bond Energies Chart - In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of ionic bonds, which is related to the lattice energy of a compound. Bond energies and bond lengths. Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break one. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. It is also called average bond enthalpy or mean bond enthalpy. Bond length and bond energy. Web bond energy (be) is the average amount of energy required to break all the chemical bonds between the same two types of atoms in a molecule (e.g., carbon and hydrogen, hydrogen and oxygen). R.t.sanderson, polar covalence , 1983 r.t.sanderson, chemical bonds and bond energy , 1976 Bond order is the number of electron pairs that hold two atoms together. This page introduces bond energies and looks at how they can be used to estimate the enthalpy change for some simple reactions. In this article, we'll explore two different concepts that help describe that energy: All energy values are listed in terms of (kj/mol) using the bond energy formula above, any value in the equation can be determined by adding the bond energies within a molecule. Intramolecular force and potential energy get 3 of 4 questions to level up! That means that. Cottrell, the strengths of chemical bonds, 2nd ed., butterworths, london, 1958; That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break one. All energy values are listed in terms of (kj/mol) using the bond energy formula above, any. Web properties of atoms, radicals, and bonds 4.41 table 4.11 bond dissociation energies the bond dissociation energy (enthalpy change) for a bond a 9b which is broken through the reaction ab : Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. To define and used average bond energies. This distance is the bond length between the atoms. Web. Bond energies are also called bond enthalpies, and in the past have been known as bond strengths. We can calculate a more general bond energy by finding the average of the bond energies of a specific bond in different molecules to. To define and used average bond energies. Bond energies and bond lengths. Typical units are kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Energy is released when chemical bonds are formed because atoms become more stable. All energy values are listed in terms of (kj/mol) using the bond energy formula above, any value in the equation can be determined by adding the bond energies within a molecule. The exact bond enthalpy of a particular chemical bond depends upon the molecular environment in which. Chemical processes are labeled as exothermic or endothermic based on whether they give off or absorb energy, respectively. The following tables list experimental bond dissociation enthalpies of common bonds at 298 k. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. Web atoms are held together by. Bond energies and bond lengths. Web many of the bond energies listed here were taken from the following sources: Energy is required to break bonds. To define and used average bond energies. Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break one. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. Web the average bond energy is therefore +1662/4 kj, which is +415.5 kj per mole of bonds. In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of. Mean bond enthalpies are sometimes referred to as bond enthalpy terms. Typical units are kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol) or kilojoules per mole (kj/mol). Web atoms are held together by a certain amount of energy called bond energy. Web the table shows some representative examples of some of the more common bonds. Bond energies are also called bond enthalpies, and in. Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break one. The exact bond enthalpy of a particular chemical bond depends upon the molecular environment in which the bond exists. Knowing the energies of bonds present in products and substrates, we can estimate the enthalpy of the chemical reaction: Web atoms are held together by a certain amount of energy. That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean (or average) bond enthalpies, although it might not actually say so. Web the bond energy is a measure of the amount of energy needed to break apart one mole of covalently bonded gases. Web quantifying the energy represented by the bonds in different molecules is an important part of understanding the overall energy implications of a reaction. Web a bond’s strength describes how strongly each atom is joined to another atom, and therefore how much energy is required to break the bond between the two atoms. Bond energies and bond lengths. Web from this graph, we can determine the equilibrium bond length (the internuclear distance at the potential energy minimum) and the bond energy (the energy required to separate the two atoms). Web the energy of chemical bonding is given most often in kilojoules per mole : R.t.sanderson, polar covalence , 1983 r.t.sanderson, chemical bonds and bond energy , 1976 Web properties of atoms, radicals, and bonds 4.41 table 4.11 bond dissociation energies the bond dissociation energy (enthalpy change) for a bond a 9b which is broken through the reaction ab : Knowing the energies of bonds present in products and substrates, we can estimate the enthalpy of the chemical reaction: Energy is released when chemical bonds are formed because atoms become more stable. The si units used to describe bond energy is kilojoules per mole of bonds (kj/mol). We can calculate a more general bond energy by finding the average of the bond energies of a specific bond in different molecules to. Web many of the bond energies listed here were taken from the following sources: Bond length and bond energy. This distance is the bond length between the atoms.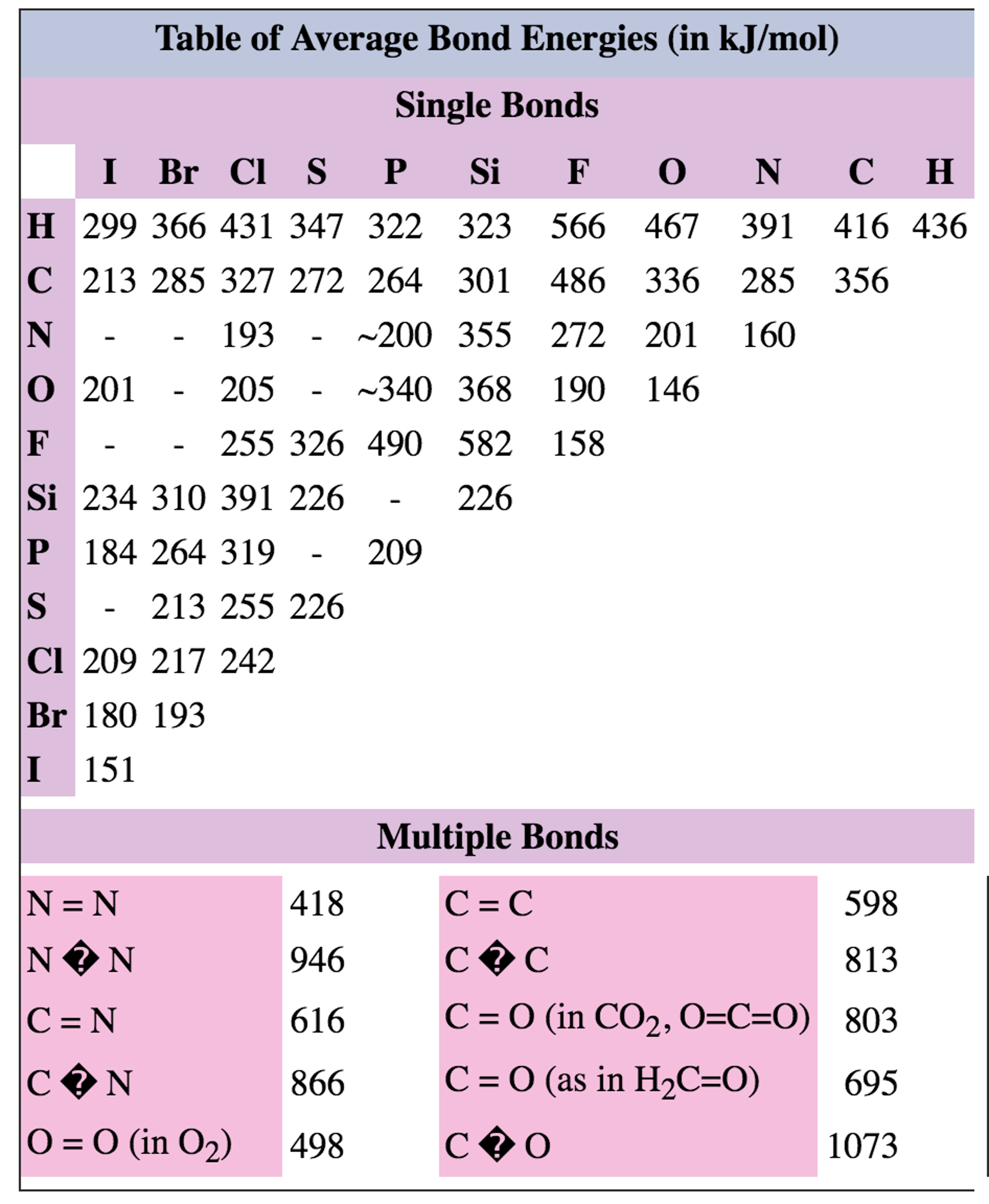
Bond Energies Chart
[Solved] Using the appropriate bond energies, calculate the heat of
Bond Energy Profile Chart
Solved Bond TABLE 10.3 Average Bond Energies Bond Energy
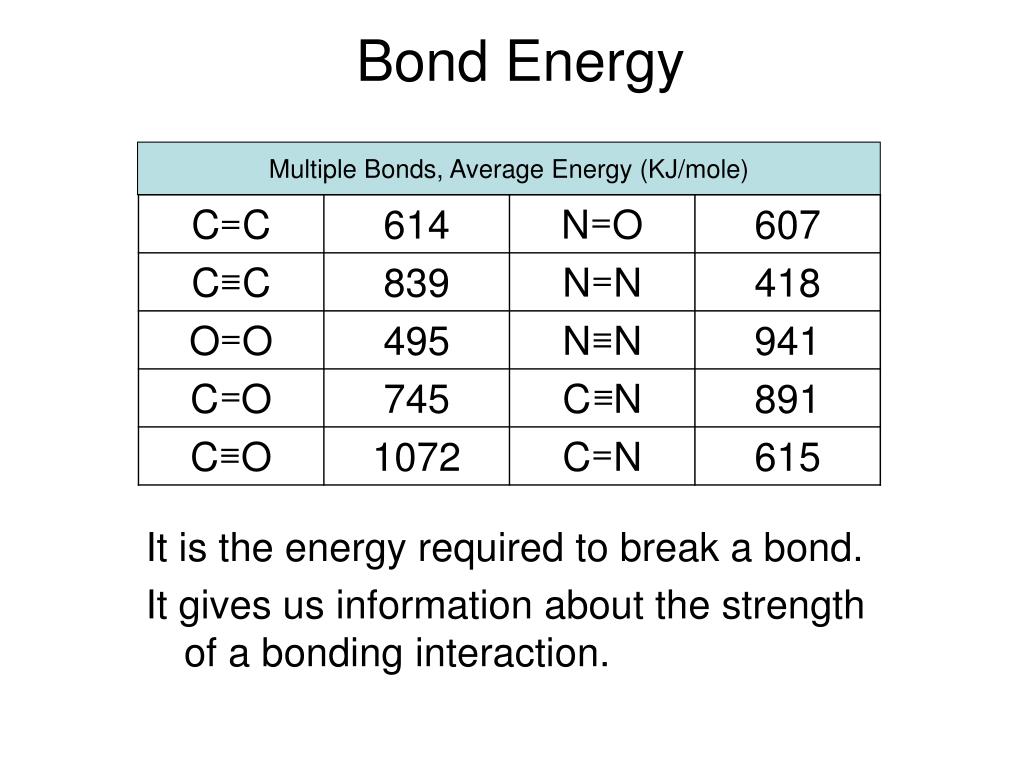
PPT Covalent Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2110028
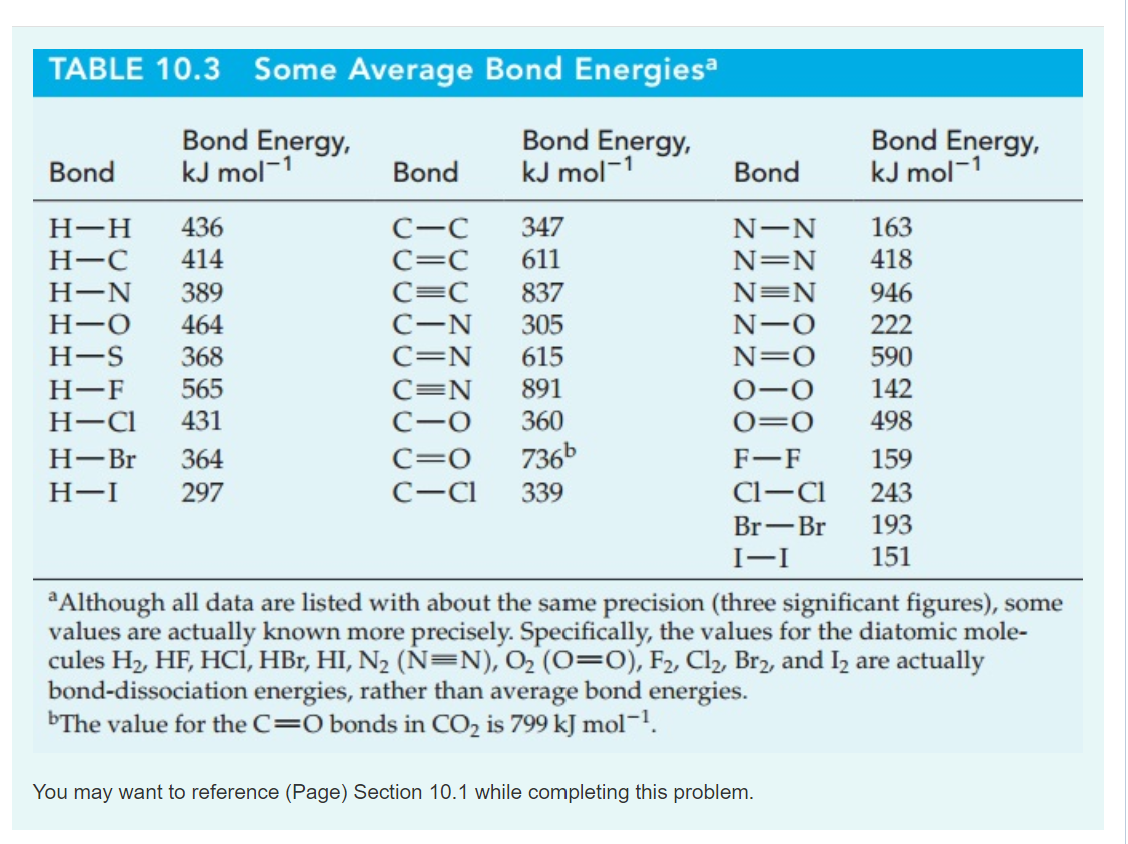
Table Of Bond Energies Pathways To Chemistry vrogue.co
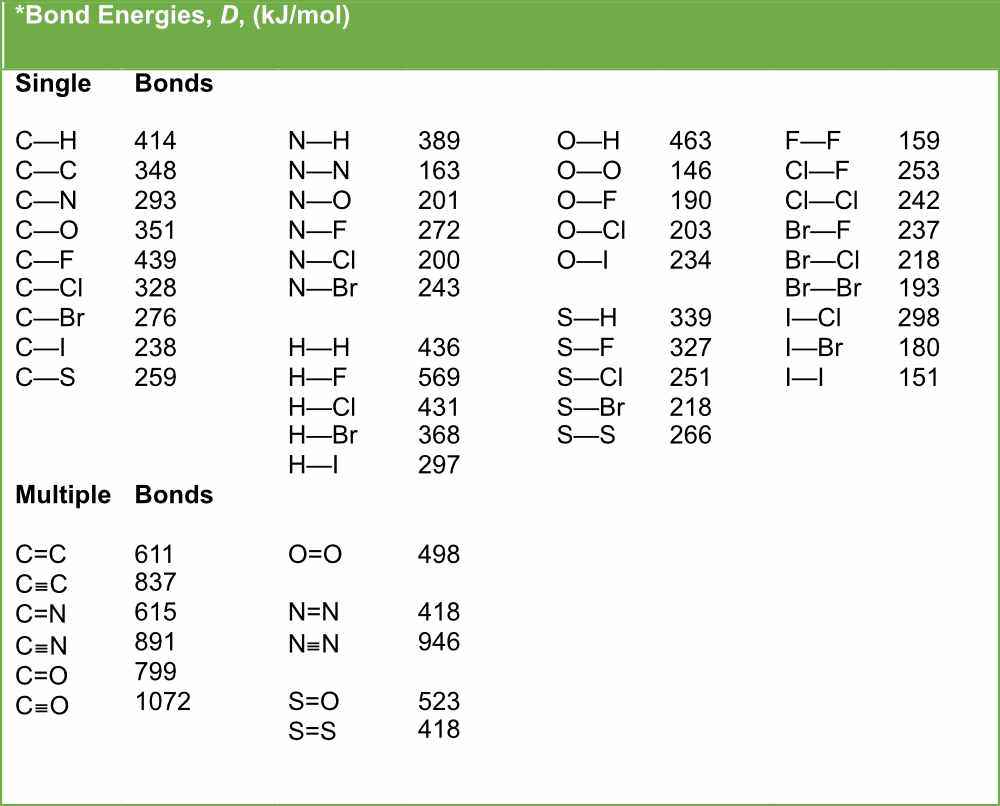
Table of Bond Energies Pathways to Chemistry

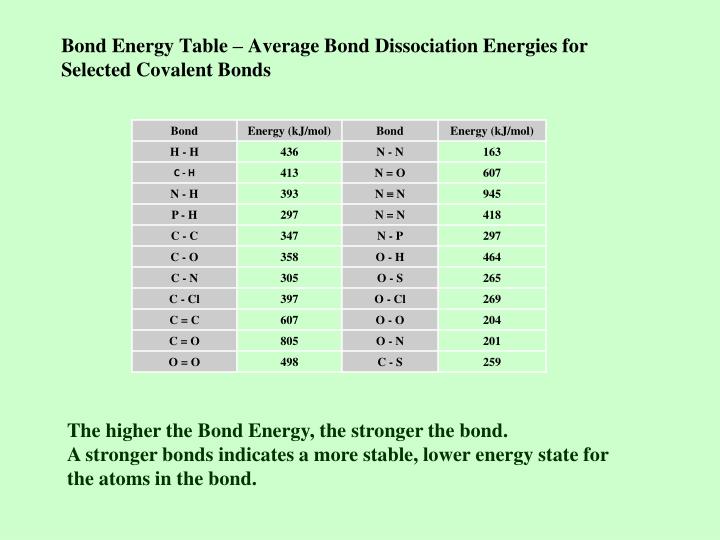
Average Bond Energies Chart

Bond Energy and Strength
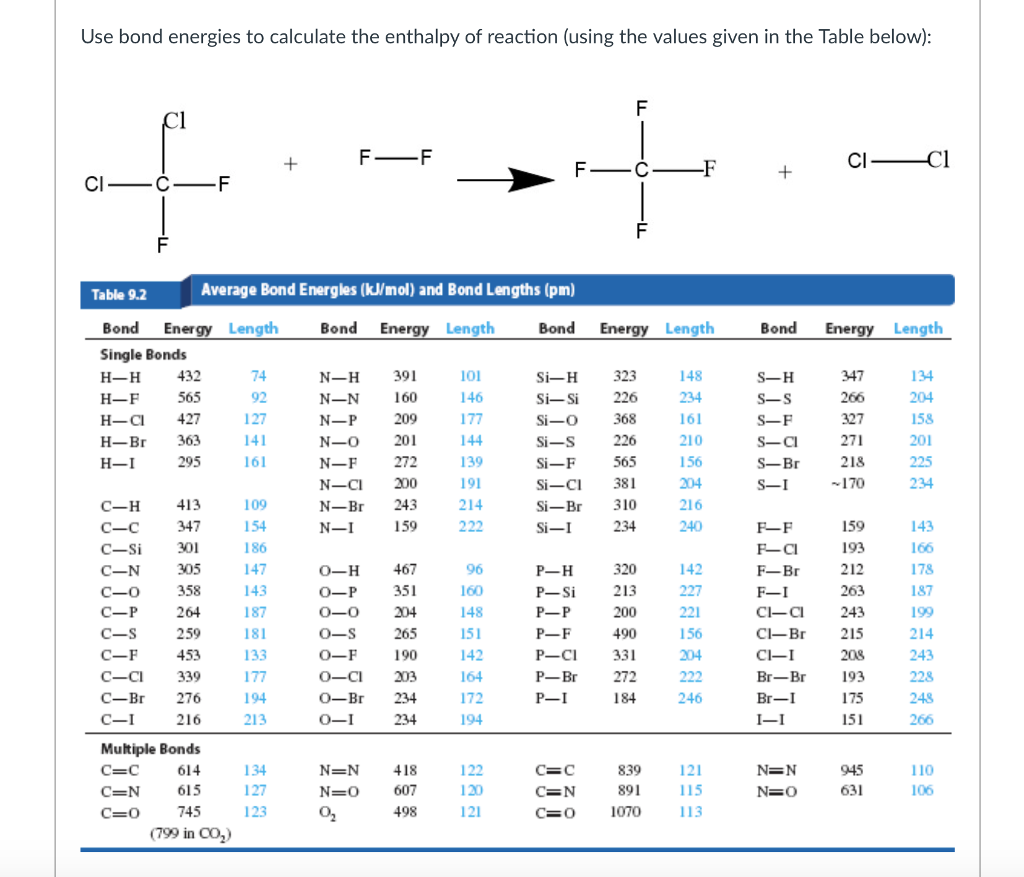
Bond Energies Chart
You Can Calculate The Energy Change In A Reaction Using Average Bond Energies.
Energy Is Required To Break Bonds.
Chemical Processes Are Labeled As Exothermic Or Endothermic Based On Whether They Give Off Or Absorb Energy, Respectively.
In Proposing His Theory That Octets Can Be Completed By Two Atoms Sharing Electron Pairs, Lewis Provided Scientists With The First Description Of Covalent Bonding.
Related Post: