Biogeochemical Cycles Comparison Chart
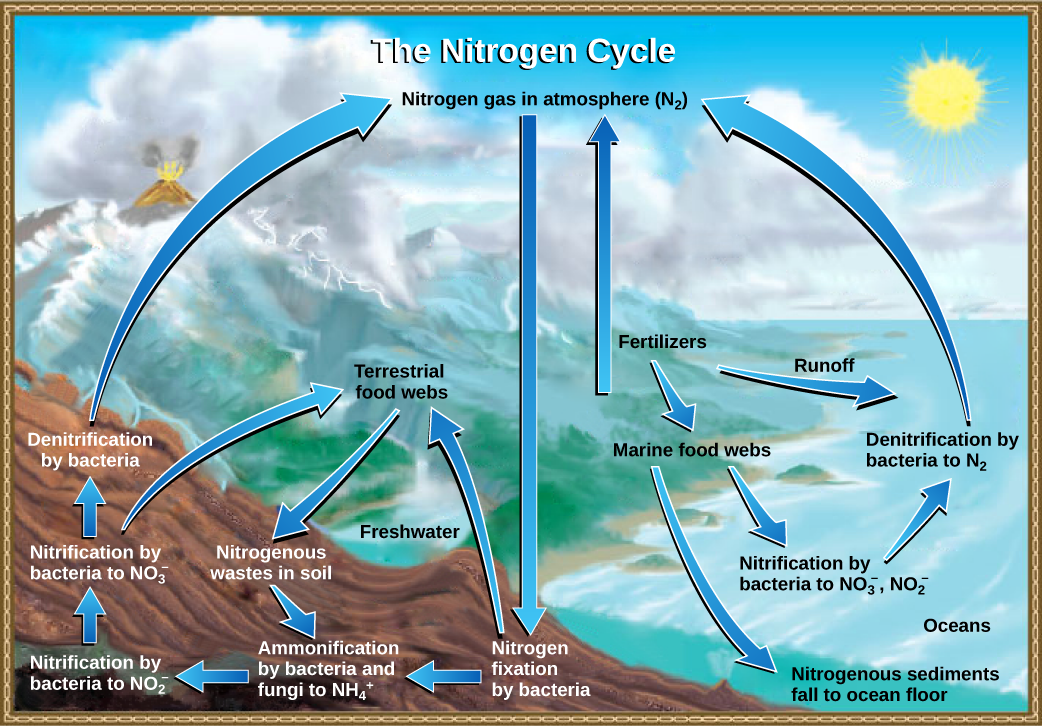
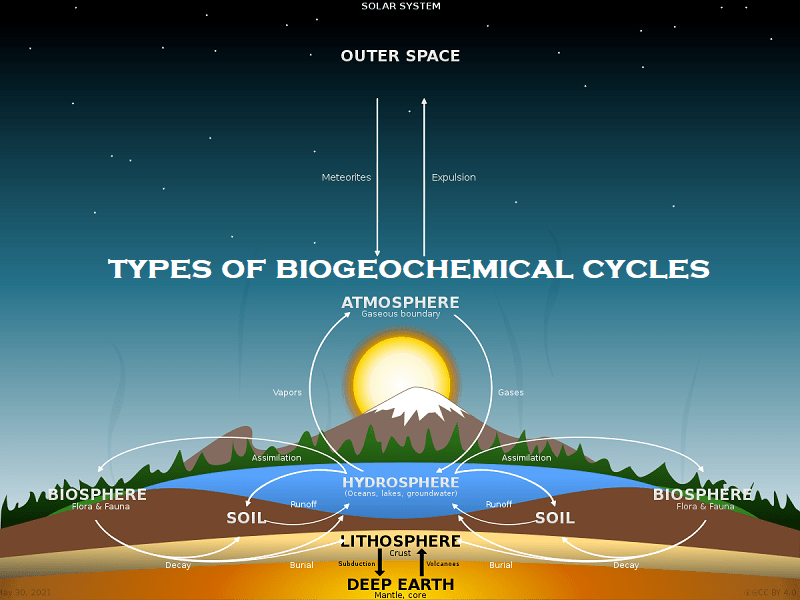
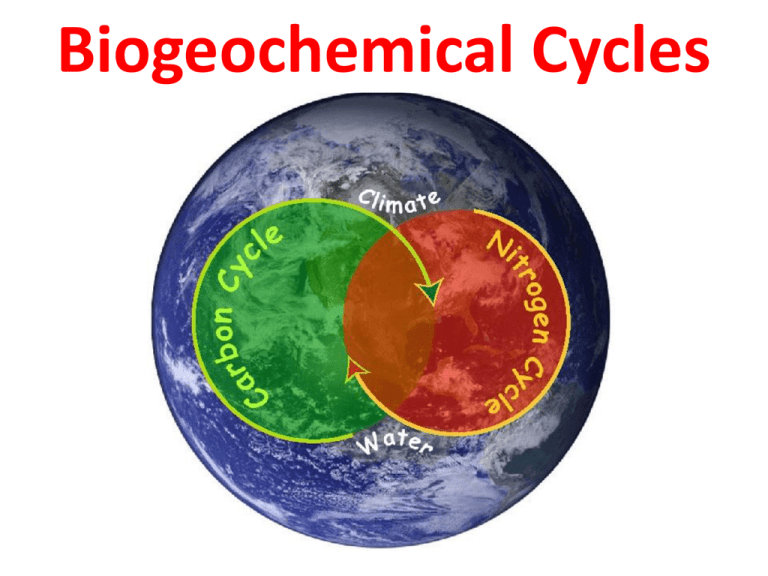
Biogeochemical Cycles Comparison Chart - Web biogeochemical cycles are basically divided into two types: Web biogeochemical cycles can be classed as gaseous, in which the reservoir is the air or the oceans (via evaporation ), and sedimentary, in which the reservoir is earth’s crust. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. Web discuss the biogeochemical cycles of water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur; Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture. Web major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is an essential element in the bodies of living organisms. Lesson 4 introduces the concept of biogeochemical cycles, emphasizing the mechanisms by which elements move through earth’s systems. Define and give an example of bioremediation It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. Web the biogeochemical cycles of four elements—carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur—are discussed below. The cycle moves nutrients, pathogens, and sediments in and out of the ecosystem. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture. Web the ways in which an element—or compound such as. Carbon is an essential element in the bodies of living organisms. These cycles circulate these molecules through ecosystems and the entire biosphere. Web define and describe the importance of microorganisms in the biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur; Microbial communities play integral and unique roles in. Web biogeochemical cycles are nature's way of recycling essential elements for life, like. In each cycle, the chemical element or molecule is transformed and cycled by living organisms and through various geological forms and reservoirs, including the atmosphere, the soil and the oceans. Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as n 2. The water cycle involves changes in the state of water and also the physical movement of water between the different tropic levels.. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment is called a biogeochemical cycle. Define and give an example of bioremediation Sphere/form of nutrient/location /time frame. From the water cycle to the carbon cycle, these processes ensure the constant reuse of matter, while. Web biogeochemical cycles can be classed as gaseous, in which the reservoir is the air or the oceans (via evaporation ), and sedimentary, in which the reservoir is earth’s crust. From the water cycle to the carbon cycle, these processes ensure the constant reuse of matter, while energy flows through the ecosystem. The cycling of these elements is interconnected with. Web the biogeochemical cycles of four elements—carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur—are discussed below. Web biogeochemical cycles are nature's way of recycling essential elements for life, like water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Web among all, the most common biogeochemical cycles are briefly described below. Web biogeochemical cycles can be classed as gaseous, in which the reservoir is the air or the. The cycle moves nutrients, pathogens, and sediments in and out of the ecosystem. In each cycle, the chemical element or molecule is transformed and cycled by living organisms and through various geological forms and reservoirs, including the atmosphere, the soil and the oceans. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of. Explain how human activities have impacted these cycles and the resulting potential consequences for earth Web major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. The most common of these are the carbon and nitrogen cycles. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert n 2. Sphere/form of nutrient/location /time frame. Gaseous cycles include those of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and water; The water cycle involves changes in the state of water and also the physical movement of water between the different tropic levels. Web biogeochemical cycles‐ comparison chart. Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as n 2. Learn how carbon moves through earth's ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon. Web major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Web biogeochemical cycles can be classed as gaseous, in which the reservoir is the air or the oceans (via evaporation ), and sedimentary, in which the reservoir is earth’s crust. Groundwater is found underground between soil particles and in cracks of rocks. Microbial communities play. It is also economically important to modern humans, in the form of fossil fuels. Web biogeochemical cycles‐ comparison chart. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their environment is called a biogeochemical cycle. Web among all, the most common biogeochemical cycles are briefly described below. Aquifers are groundwater reservoirs often tapped by wells. Carbon is an essential element in the bodies of living organisms. Web it is how water goes through the plants and gets into animals and humans. Web biogeochemical cycles are basically divided into two types: Sphere/form of nutrient/location /time frame. Web the physical and biogeochemical controls of greenhouse gases (ghgs) is a central motivation for this chapter, which identifies biogeochemical feedbacks that have led or could lead to a future acceleration, slowdown or abrupt transitions in the rate of ghg accumulation in the atmosphere, and therefore of climate change. Web major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Web because geology and chemistry have major roles in the study of this process, the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment is called a biogeochemical cycle. Web discuss the biogeochemical cycles of water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur; In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert n 2. Gaseous cycles include those of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and water; Tiny atoms of carbon and nitrogen are able to move around the planet through these cycles.
Biogeochemical cycles
46.3 Biogeochemical Cycles Biology LibreTexts
Biogeochemical Cycle Template Inspiration mind map template Biggerplate
Which Biogeochemical Cycle Does Not Involve the Atmosphere
Biogeochemical Cycles

Biogeochemical cycle and its Types The Science Notes
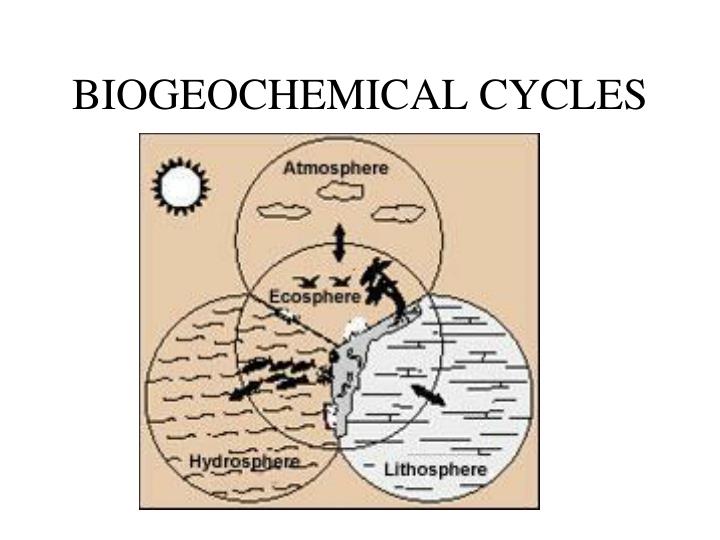
Biogeochemical Cycles Chart
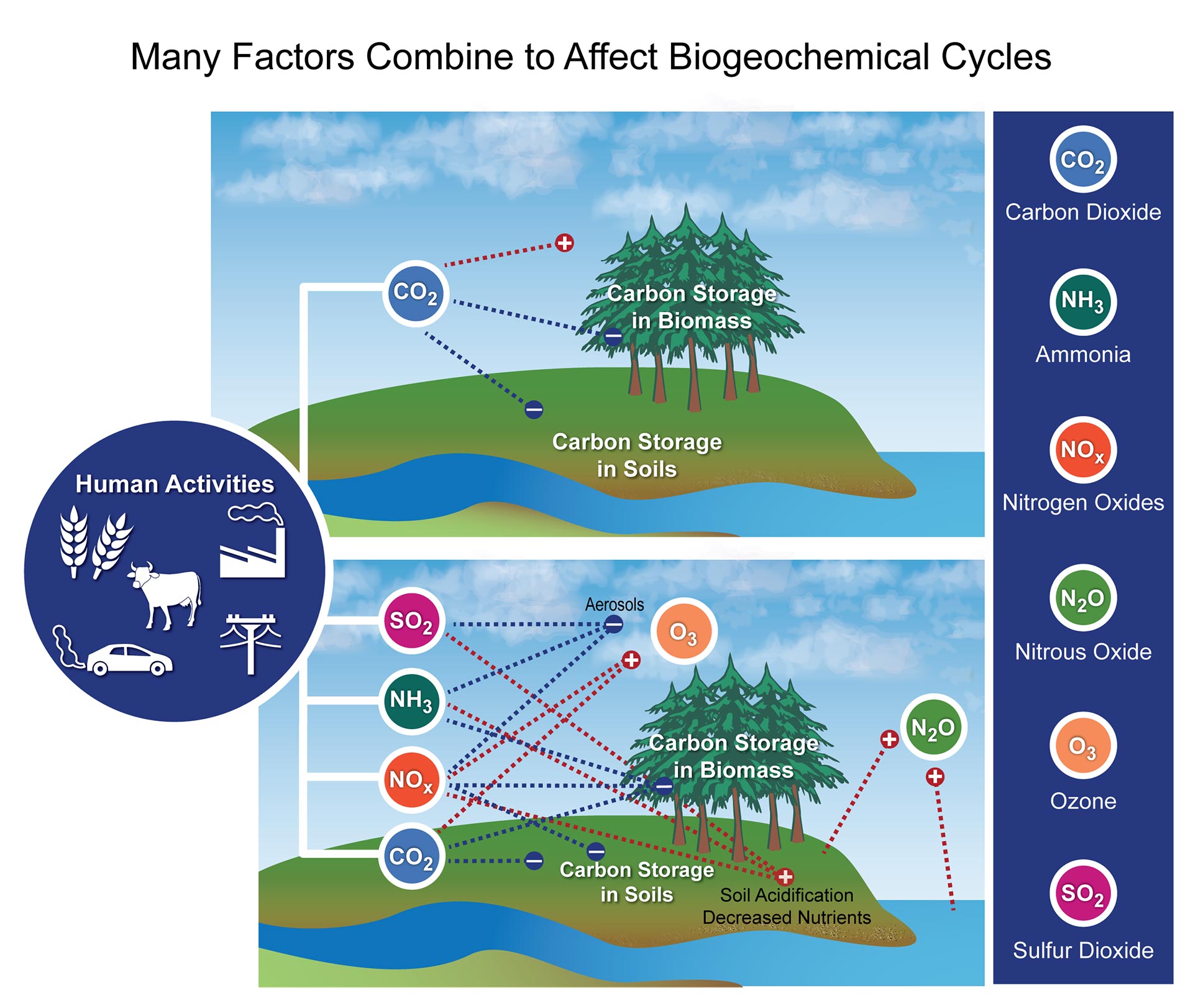
Biogeochemical Cycles National Climate Assessment
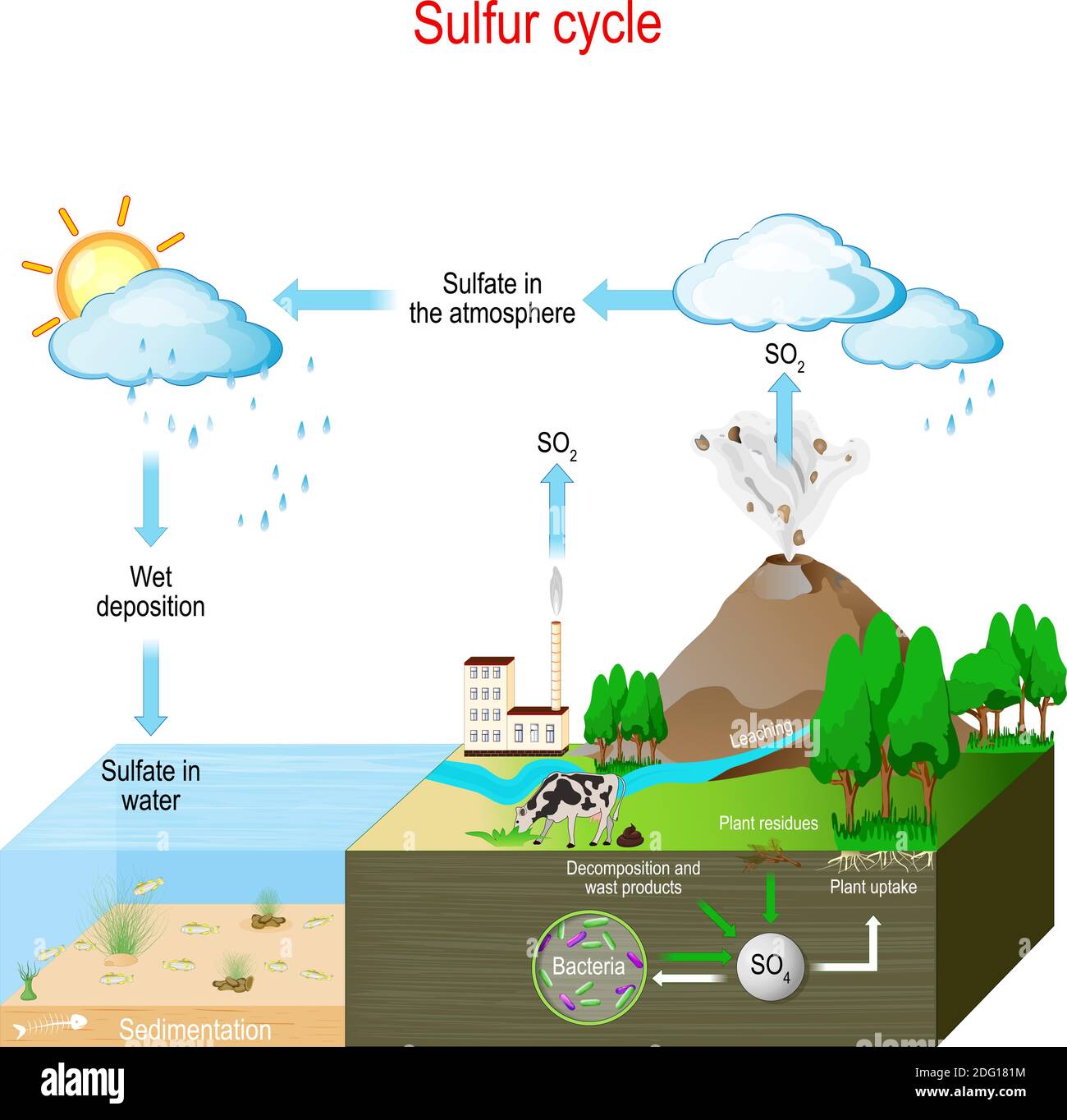
Sulfur cycle. biogeochemical cycle. education chart. vector

(PDF) Biogeochemical Cycles Comparison Chart Blank DOKUMEN.TIPS
These Cycles Circulate These Molecules Through Ecosystems And The Entire Biosphere.
The Cycling Of These Elements Is Interconnected With The Water Cycle.
Web The Recycling Of Inorganic Matter Between Living Organisms And Their Environment Is Called A Biogeochemical Cycle.
Web Biogeochemical Cycles Are Nature's Way Of Recycling Essential Elements For Life, Like Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, And Phosphorus.
Related Post: