Bioavailability Food Chart
Bioavailability Food Chart - Get more folate by chopping or mincing your dark, leafy greens. Vitamins like a, c, k, d, b12, and e. Flavonoids, carotenoids) can vary widely in the extent they are absorbed and utilized. Web the bioavailability of polyphenols is also reviewed, with particular focus on intestinal absorption and the influence of chemical structure (eg, glycosylation, esterification, and polymerization), food matrix, and excretion back into the intestinal lumen. Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient bioavailability from complex foods in humans, highlighting synergistic and antagonistic processes among food components for two different food groups, i.e., dairy, and vegetables and fruits. Determining if enhanced bioavailability is clinically relevant. Web oral bioavailability investigated by in vitro studies provides the food and drug manufacturers with information to formulate delivery systems more efficiently and to determine the dosage of biocomponents for increase the health benefits and avoid or reduce the risk of toxicity. For dairy, bioavailability of vitamins a, b2, b12 and k, calcium. Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in. To fully digest our food, we must: What sources does your product reference for its data? On the other hand, micronutrients, i.e. Flavonoids, carotenoids) can vary widely in the extent they are absorbed and utilized. (plus bioavailable sources of essential nutrients) knowing that a food is high in protein, calcium, or magnesium can be misleading. This is defined as bioaccessibility. Minerals like potassium, magnesium, zinc, iron, and calcium. What is the difference between natural nutrients and synthetic nutrients? Web try these seven tips to maximize bioavailability before you make a mad dash to the supplement aisle. This is defined as bioaccessibility. The digestive organs of interest are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Web foods to be studied include commercially available plant products selected to provide a range of composition in terms of protein, polysaccharide, mineral and phytochemicals. Vitamins and minerals, and bioactive phytochemicals (e.g. How do you account for the bioavailability of nutrients in real foods? We’ll use vitamin a as a case study to illustrate how bioavailability works, and why it’s. We’ll use vitamin a as a case study to illustrate how bioavailability works, and why it’s relevant to all humans. Protein is found both in animal and plant foods, but their bioavailability is different. On the other hand, micronutrients, i.e. Web why does bioavailability matter in the context of nutrition from real foods? What sources does your product reference for. Protein is found both in animal and plant foods, but their bioavailability is different. Web the bioavailability of particular nutrients in foods depends on several factors: The digestive organs of interest are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. What is the difference between natural nutrients and synthetic nutrients? Web high bioavailability means you absorb more nutrients into your system and. Web foods to be studied include commercially available plant products selected to provide a range of composition in terms of protein, polysaccharide, mineral and phytochemicals. For dairy, bioavailability of vitamins a, b2, b12 and k, calcium. The digestive organs of interest are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Minerals like potassium, magnesium, zinc, iron, and calcium. What sources does your. Vitamins like a, c, k, d, b12, and e. On the other hand, micronutrients, i.e. How do i use your products? For dairy, bioavailability of vitamins a, b2, b12 and k, calcium. Science → what is bioavailability? You should also consider how much of each nutrient is absorbed. How do i use your products? How exactly does this work? Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient bioavailability from complex foods in humans, highlighting synergistic and antagonistic processes among food components for two different food groups, i.e., dairy, and vegetables and fruits. Web. How do i use your products? Web oral bioavailability investigated by in vitro studies provides the food and drug manufacturers with information to formulate delivery systems more efficiently and to determine the dosage of biocomponents for increase the health benefits and avoid or reduce the risk of toxicity. Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient. Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in. Flavonoids, carotenoids) can vary widely in the extent they are absorbed and utilized. What is the difference between natural nutrients and synthetic nutrients? The digestive organs of interest are the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient bioavailability from. For dairy, bioavailability of vitamins a, b2, b12 and k, calcium. To fully digest our food, we must: Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient bioavailability from complex foods in humans, highlighting synergistic and antagonistic processes among food components for two different food groups, i.e., dairy, and vegetables and fruits. Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in. Web high bioavailability means you absorb more nutrients into your system and waste less. Web [ * ] the beneficial nutrients in question can include: Determining if enhanced bioavailability is clinically relevant. Get more folate by chopping or mincing your dark, leafy greens. Conversely, low bioavailability means you absorb fewer nutrients and waste more. Web oral bioavailability investigated by in vitro studies provides the food and drug manufacturers with information to formulate delivery systems more efficiently and to determine the dosage of biocomponents for increase the health benefits and avoid or reduce the risk of toxicity. Vitamins and minerals, and bioactive phytochemicals (e.g. We’ll use vitamin a as a case study to illustrate how bioavailability works, and why it’s relevant to all humans. Web this review provides a narrative overview of recent insights into nutrient bioavailability from complex foods in humans, highlighting synergistic and antagonistic processes among food. Web why does bioavailability matter in the context of nutrition from real foods? Web this review discusses different protein sources and their role in human nutrition, focusing on their structure, digestibility, and bioavailability. Web the bioavailability of particular nutrients in foods depends on several factors:
Nutrient Bioavailability (W2002 20082013)

Bioavailability chart for nutrients, including those crucial to hoof

What is a Protein’s Biological Value and Why is it Important? Fooducate
PPT Maternal Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Foods filled with protein High protein recipes, High protein foods

Understanding bioavailability is so important when we talk about plant

Nutrients are everything We Love Cycling magazine

Bioavailability and Nutrition Guides Big Dog Pet Foods
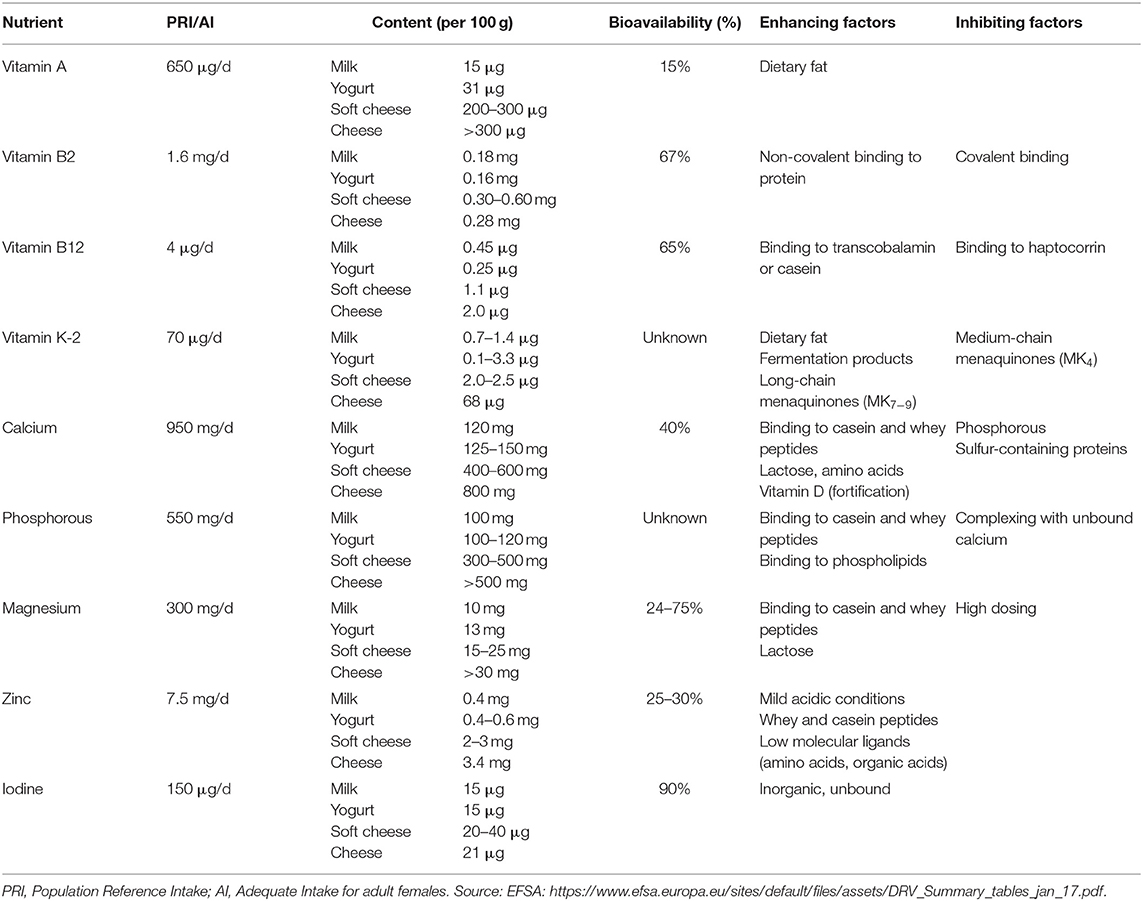
Frontiers Bioavailability of Micronutrients From NutrientDense Whole

The Bioavailability of Nutrients in Animal Foods Only Way to Address
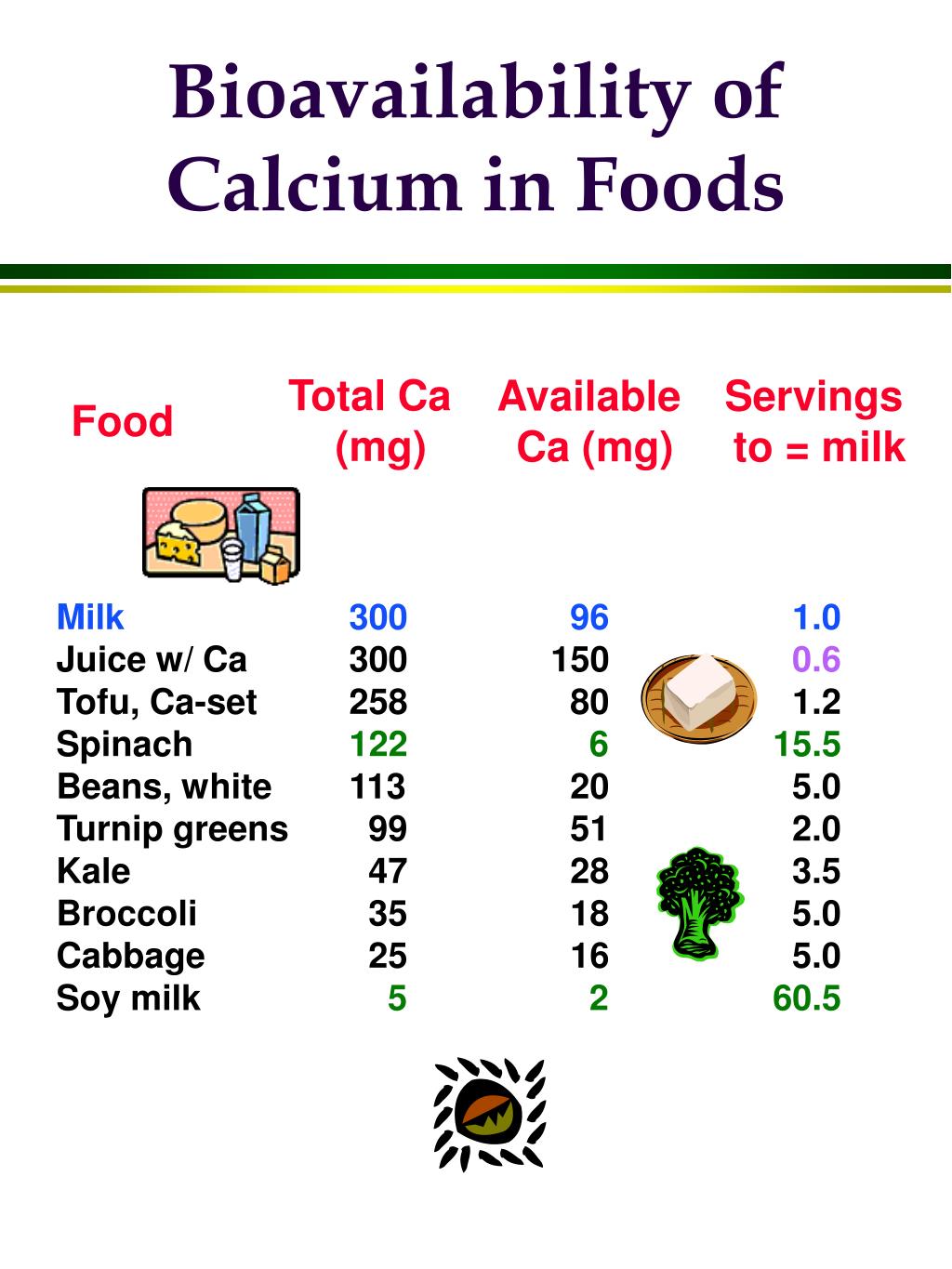
This Table Gives The Serving Size, Calcium Content Of That Food, And Percent Absorbed.
The Calcium Content Is Multiplied By The Absorption Percentage To Calculate The Estimated Calcium Absorbed.
Each Product Will Be Studied In A Variety Of Processed Forms.
You Should Also Consider How Much Of Each Nutrient Is Absorbed.
Related Post: