Atomic Radius Periodic Table Chart
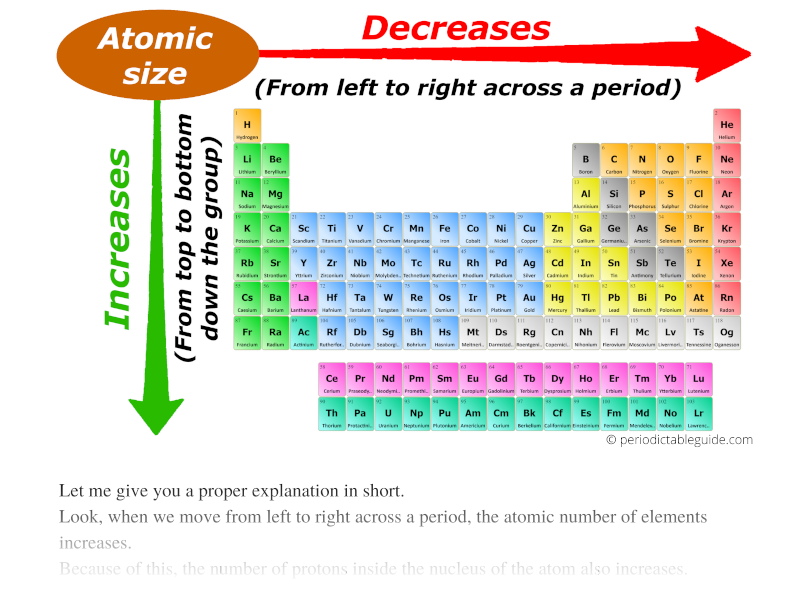
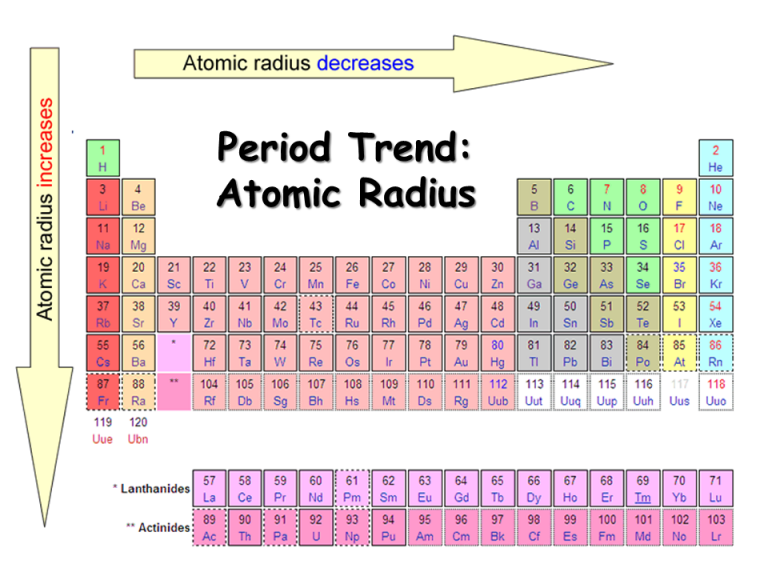
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Chart - Web when you move right across a period, you’re adding more protons and electrons, but you stay at the same number of shells, rather than forcing electrons into higher shells, allowing the magnetic attraction between the protons and electrons to keep the radius of the atom smaller. This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. Web atomic radius trends on periodic table (video) | khan academy. For instance, the radii generally decrease rightward along each period (row) of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. And increase down each group (column). The atomic radius is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost orbit of an atom. Atomic radii (empirical) atomic radii (absolute) atomic radii (density cutoff) covalent radii revisited (2008 values) covalent radii (molecular single bond) Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm)). Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. Practice problems on atomic radius trends. And increase down each group (column). Web atomic radius is determined as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to. Web atomic radius is determined as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together. For instance, the radii generally decrease rightward along each period (row) of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and. Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to. Web the trend on a graph. This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. Atomic radii (empirical) atomic radii (absolute) atomic radii (density cutoff) covalent radii revisited (2008 values) covalent radii (molecular single bond) The above atomic radii of. The above atomic radii of the elements are the van der waals radius and they are in picometers (pm). Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure \(\pageindex{4}\)). Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in. The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. For isolated neutral atoms, the atomic nucleus ranges from 30 picometers (trillionths of a meter) and 300 pm. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Web the latest release of the periodic table (dated 4 may 2022) includes the most recent abridged standard atomic weight values released by the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights ( ciaaw ), compiled as part of the 2021 table of standard atomic weights 2021. Web interactive periodic table showing. Web in the periodic table, atomic radii decrease from left to right across a row and increase from top to bottom down a column. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Web major periodic trends include: Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius. Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. And increase down each group (column). Smallest and largest atomic radius. This is a periodic table with atomic radius values mentioned on it. Web the trend on a graph. This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. Web the periodic table contains nist’s latest critically evaluated data for atomic properties of the elements. For instance, the radii generally decrease rightward along each period (row) of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases; Web the trend on a graph. Atomic radii can be. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right. Ionic radii are also available. Web atomic radius is the distance from the atom’s nucleus to the outermost electron orbital, and a lot of trends in the periodic table rely on this property due to its relationship to other atomic properties such as nuclear charge. The values are in picometres (pm). Periodic trends, arising from the arrangement of the periodic table, provide chemists with an invaluable tool to. Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. And increase down each group (column). The following table shows atomic radii computed from theoretical models, as published by enrico clementi and others in 1967. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web the trend on a graph. Web this table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and vertically across the periodic table. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure \(\pageindex{4}\)). The above atomic radii of the elements are the van der waals radius and they are in picometers (pm). Web when you move right across a period, you’re adding more protons and electrons, but you stay at the same number of shells, rather than forcing electrons into higher shells, allowing the magnetic attraction between the protons and electrons to keep the radius of the atom smaller. Want to join the conversation? The atomic radius is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost orbit of an atom. Covalent radius can be calculated by measuring the distance between the two nucleus of two atoms in covalent compound.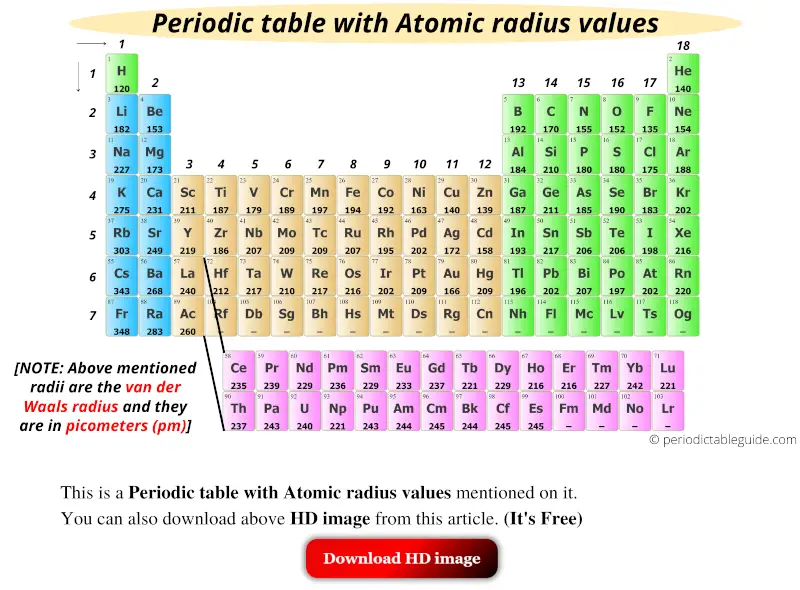
Get the Periodic table with Atomic radius values (Img+Chart)
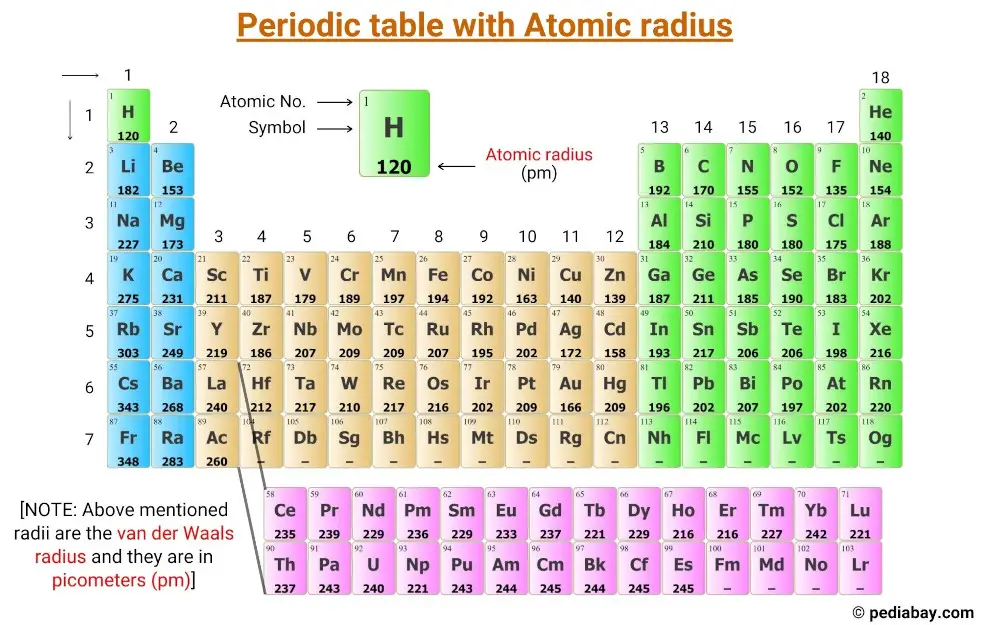
Atomic Radius of Elements (With Periodic table Chart) Pediabay
Atomic radius chart mindsstorm
Atomic Radius NEETLab

Atomic Radius of Elements The Periodic Table

Atomic Radius of Elements
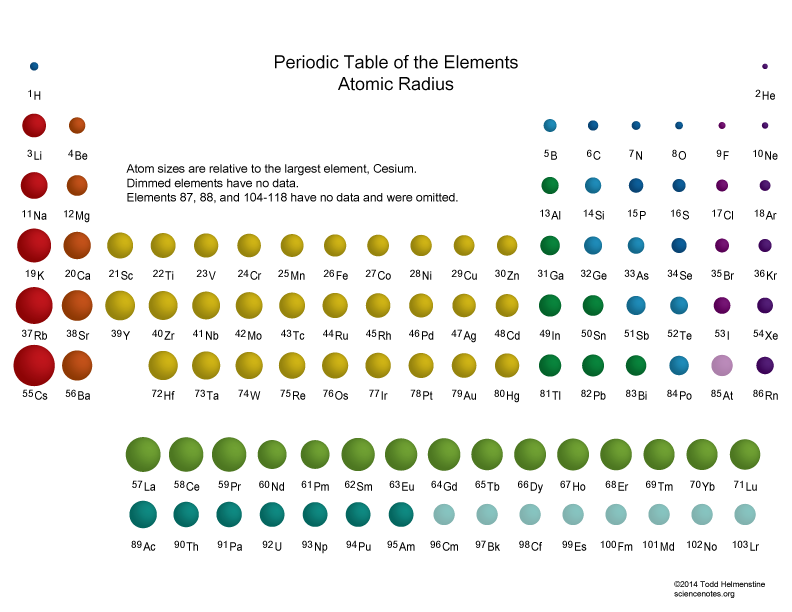
Atomic Radius Trends of the Periodic Table
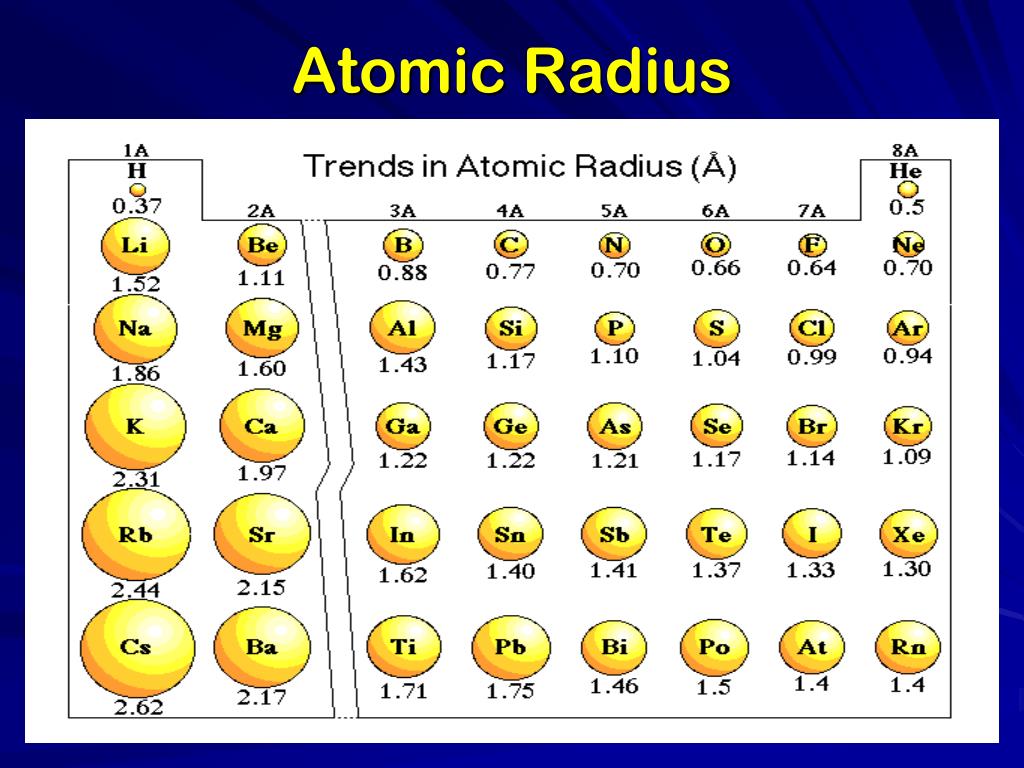
PPT Periodic Table PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2617702
.png)
CK12Foundation
/accurate-illustration-of-the-periodic-table-82020791-57cc76f23df78c71b66efbd7.jpg)
Atomic Radius Table Pdf Elcho Table
Visualize Trends, 3D Orbitals, Isotopes, And Mix Compounds.
Web Major Periodic Trends Include:
Ionic Radii Are Also Available.
Francium Has The Largest Atomic Size On The Periodic Table, And Helium Has The Smallest Atomic Size.
Related Post: